Chapter 9 - Patterns of Inheritance
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What is heredity?
it is the transmission of traits from on generation to the next.
When did genetics begin?
Genetics (the scientific study of heredity) began with Gregor Mendel’s experiments.
What did Mendel cross?
Mendel crossed pea plants and trace traits from generation to generation.
What did Mendel hypothesize?
He hypothesized that there are alternative versions of genes (alleles), the units that determine heritable traits.
What did Mendel develop?
Mendel developed four hypotheses, described below using modern terminology
What is Mendel’s first hypothesis?
There are alternative versions of genes (called alleles) that account for variations in inherited characters.
What is Mendel’s second hypothesis?
For each character, an organism inherits two alleles of a gene, one from each parent.
What is homozygous?
An organism that has two identical alleles for a gene
What is heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a gene
What is Mendel’s third hypothesis?
If the two alleles of an inherited pair differ, then one determines the organism’s appearance and is called the dominant alleles and other has no noticeable effect of the organism’s appearance and is called the recessive allele
What is Mendel’s fourth hypothesis?
A sperm or egg carriers only one allele for each inherited character because allele pairs separate (segregate) from each other during the production of gametes. This statement is called the law of segregation.
What does Mendel’s hypotheses explain?
It also explains the 3:1 ratio observed in the F2 generation
What do the F1 hybrids all have?
They all have a Pp genotype
What does the punnett square show?
It shows the four possible combinations of alleles that could occur when these gametes combine
What does every diploid cell have?
It has pairs of homologous chromosomes
What do the chromosomes in a homologous pair carry?
They carry alleles of the same genes at the same locations
What is monohybrid cross?
A cross between two individuals that are heterozygous for one character.
What is a dihybrid cross?
a mating of parental varieties that differ in two characters
What does Mendel’s law of independent assortment state?
It states that the alleles of a pair segregate independently of other allele pairs during gamete formation.
What can the offspring of a testcross reveal?
The offspring of a testcross, a mating between an individual of an unknown genotype and a homozygous recessive individual, can reveal the unknown genotype
What is the rule of multiplication?
calculating the probability of two independent evens both occurring
What is the rule of addition?
calculating the probability of an even that can occur alternative ways.
What follows Mendel’s Laws?
The inheritance of many human traits.
What do family pedigrees determine?
They can help determine individual genotypes
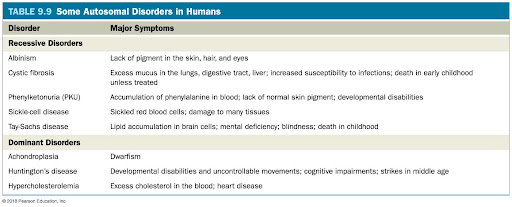
What are the genetic disorders listed in Table 9.9 known for?
They are known to be inherited as dominant or recessive traits controlled by a single gene
How are most people who have recessive disorders born?
They are born to normal parents who are both heterozygous — That is, parents who are carriers of the recessive allele for the disorder but are phenotypical normal
What carrier screening, fetal testing, fetal imaging, and newborn screening provide?
It can provide information for reproductive decisions but may create ethical dilemmas
What are Mendel’s laws valid for?
They are valid for all sexually reproducing species, but genotype often does not dictate phenotype in the simple way Mendel’s laws describe.
What did Mendel’s pea crosses always look like?
They always looked like one of the two parental varieties, a situation called complete dominance
What is incomplete dominance?
For some characters, the appearance of hybrids falls between the phenotypes of the two parental varieties.
What controls the ABO blood group?
The ABO blood group phenotype in humans is controlled by three alleles that produce a total of four phenotypes.
Which alleles are codominant?
The IA and IB alleles are codominant: Both alleles are expressed in heterozygous individuals (IAIB), who have type AB blood.
When does pleiotropy occur?
It occurs when one gene influences multiple characters
What is a human example of pleiotropy?
Sickle-cell disease
This disease affects the type of hemoglobin produced and the shape of red blood cells and causes anemia and organ damage
Sickle-cell and nonsickle alleles are codominant.
Carriers of sickle-cell disease have increased resistance to malaria.
What are the many character results from polygenic inheritance?
Many characters result from a polygenic inheritance, in which a single phenotypic character results from the addictive effects of two or more genes a single phenotypic character
What is an example of polygenic inheritance?
Human skin color
How are many traits affected?
In varying degrees, by both genetic and environmental factors.
What does the chromosomes theory of inheritance state?
It states that genes occupy specific loci (positions) on chromosomes and chromosomes undergo segregation and independent assortment during meiosis.
What does Mendel’s laws correlate with
It correlates with chromosomes separation in meiosis
What did Bateson and Punnett study?
They studied plants that did not show a 9:3:3:1 ratio in the F2 generation. What they found was an example of linked genes which, are located close together on the same chromosomes and tend to be inherited together.
What does crossing over between homologous chromosomes produce?
it produces new combinations of alleles in gametes.
Linked genes can what?
They can be separated by crossing over, forming recombinant gametes.
What is recombination frequency?
The percentage of recombinant offspring among the total
How can recombination frequencies be used?
They can be used to map the relative positions of genes on chromosomes.
What is a genetic map?
an order list of the genetic loci along a chromosomes
What is a linkage map?
such a genetic map based on recombinant frequencies
In mammals, what are the male and female sex chromosomes?
A male has XY sex chromosomes, and a female has XX
What is a sex-linked gene?
A gene located on either sex chromosomes
What do X chromosomes carry?
They carry many X-linked genes that control traits unrelated to sex
What illustrates an X-linked recessive trait?
the inheritance of white eye color in the fruit fly
Most X-linked human disorder are due to what?
Recessive alleles and therefore are seen mostly in males.
What happens to a male who receives a single X-linked recessive allele from his mother?
They will have the disorder
What does a female must receive?
They must receive the allele from both parents to be affected
What can Y chromosomes provide?
They can provide data about recent human evolutionary history because they are passed on intact from father to son.