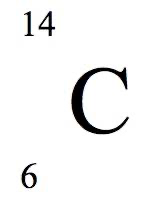Isotopes and Ions
Atoms- the base unit of any element, smallest piece of an element that still has the qualities of the element
Electrons- negatively charged particle that orbits the nucleus of an atom
Protons- positively charged particle located in the nucleus of an atom
Ions- charged atoms
Cations- positively charged atoms/ions
- lost electrons (more protons than electrons meaning more positive charges)
Anions- negatively charged atoms/ions
- gained electrons (more electrons than protons meaning more negative charges)
Atoms can lose/gain electrons only in chemical reactions when it steals an electron from/an electron is stolen by another atom/ion
Neutrons- have a neutral charge and make up the nucleus with the protons
- all elements have neutrons except hydrogen since it only has one proton
- elements can vary in amounts of protons
- amount of neutrons effects the atoms atomic mass
Mass number: the amount of protons + neutrons in an atom
Isotopes: atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
- each has different atomic mass depending on the amount of neutrons
- does not affect how the element chemically reacts
Atomic mass: how much stuff in the atom measured in amu
- weighted average of the atomic mass of each isotope of that element
To find average atomic mass:
- relative atomic mass of 1 isotope x percent abundance = weighted score
do this for each isotope, then add the weighted scores to get the atomic mass
Example:
| Isotope | Mass (mass number if don’t have actual mass) | Percent Abundance | Weighted Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon - 12 | 12 | 98.89 | 11.87 |
| Carbon - 13 | 13 | 1.11 | 0.14 |
| Carbon - 14 | 14 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Atomic Mass of Carbon: | 12.01 |
How to write isotopes:
element name - mass number
Element symbol:
- mass number
- atomic number
- element symbol
Carbon- 14 symbol: