spinal cord
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
how many cervical vertebrae are there
7
how many vertebrae in the thoracic region?
12
how many vertebrae in the lumbar region?
5
how many vertebrae in the sacral region?
5 (fused)
how many vertebrae in the coccyx?
3-4 (fused)
name all the regions of the vertebral column top to bottom?
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccyx
how many spinal nerves is each vertebrae associated with?
2 (except C1 which is associated w 3)
describe the 3 spinal nerves coming off C1?
1- spinal nerves (contain motor axons only)
2- spinal nerves (motor + sensory axons)
3- spinal nerves (motor + sensory axons )
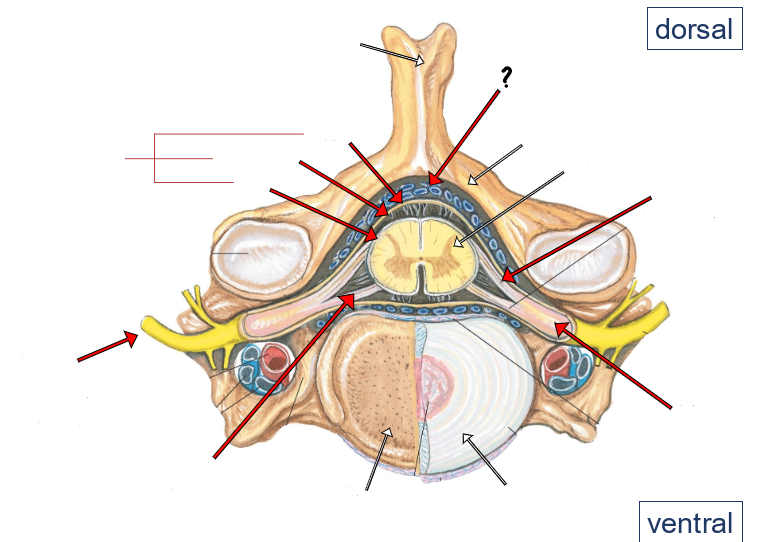
epidural space (containing small veins and fat)
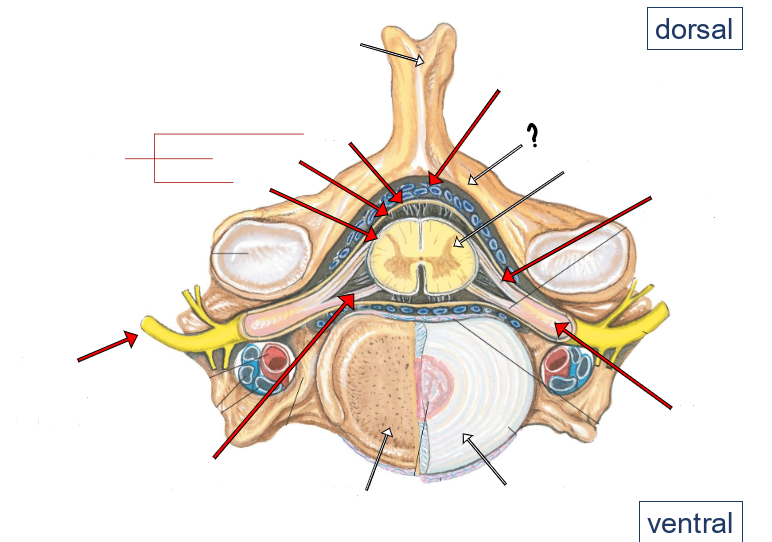
vertebral arch
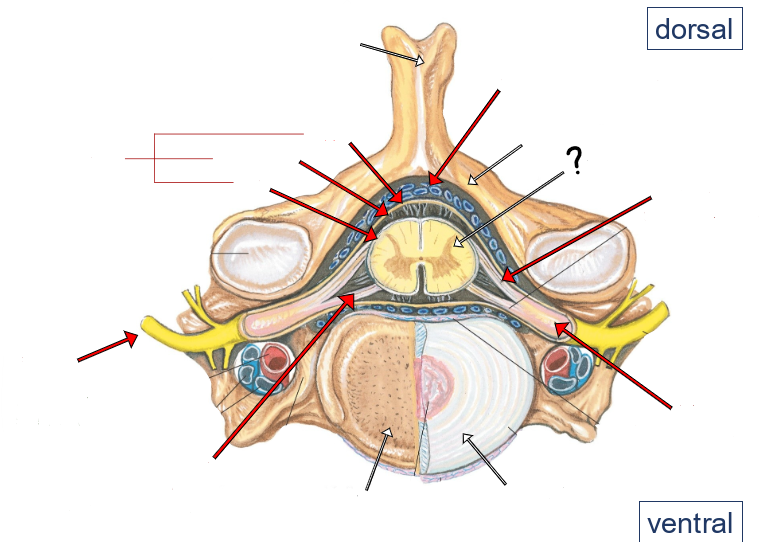
spinal cord
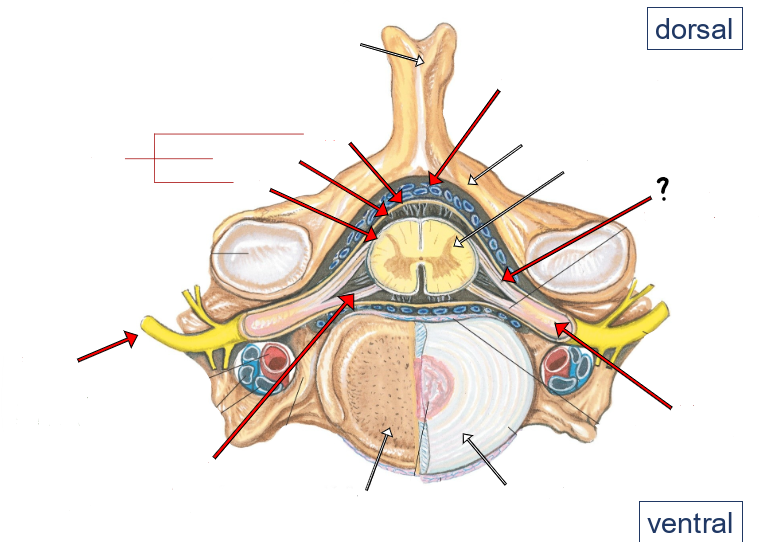
dorsal roots
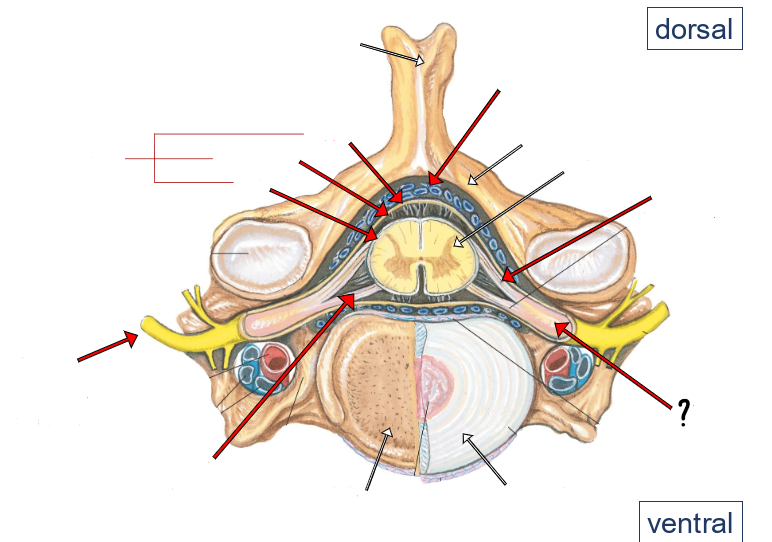
dorsal root ganglion
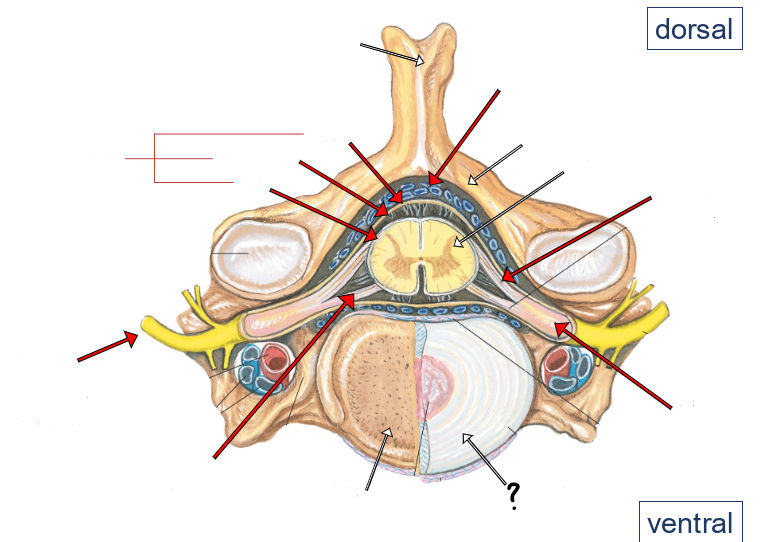
intervertebral disc
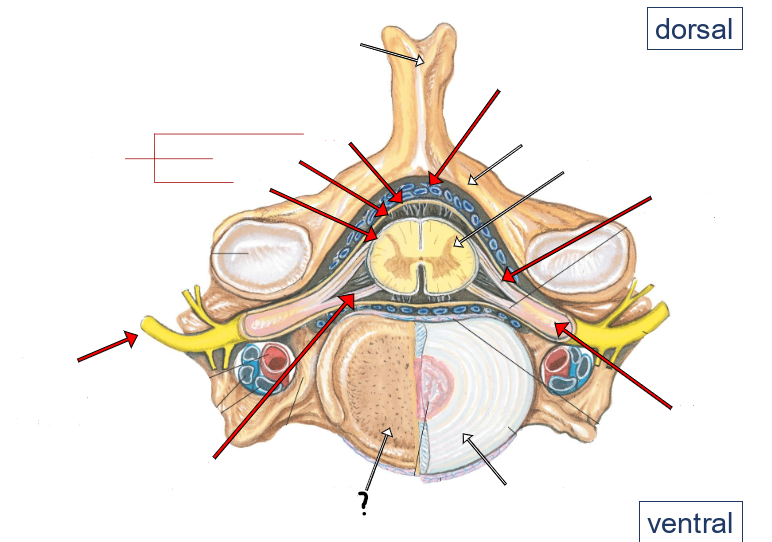
ventral roots
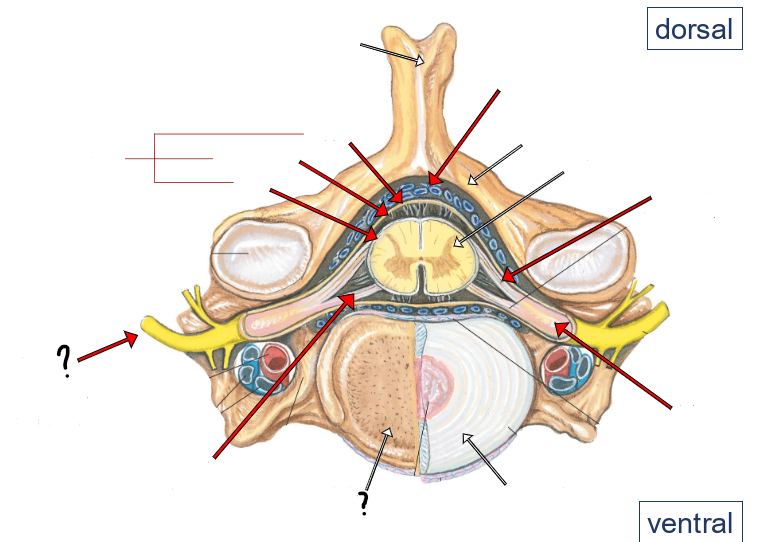
spinal nerve
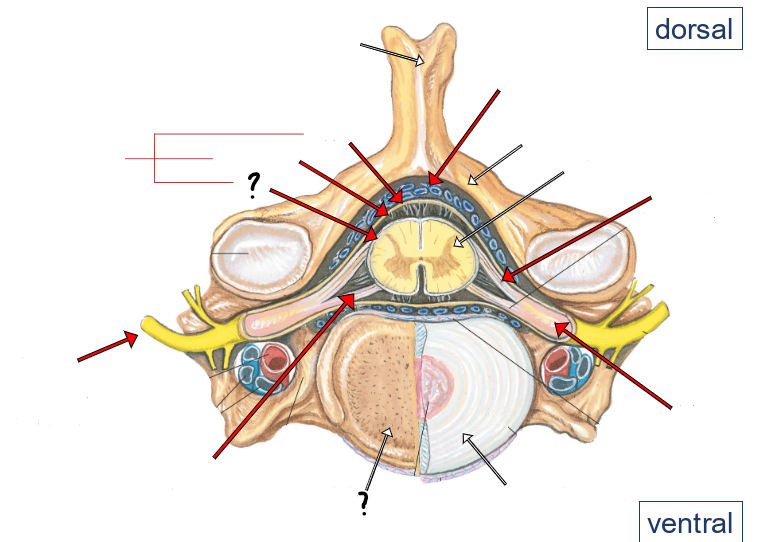
pia
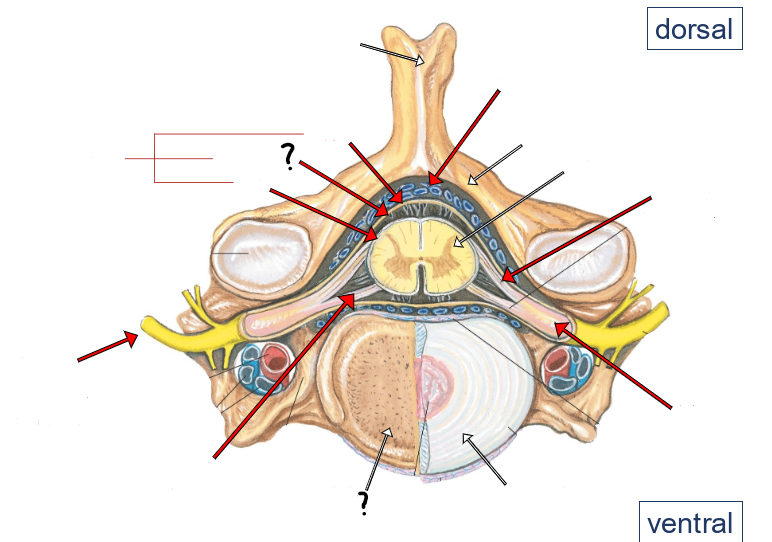
arachnoid
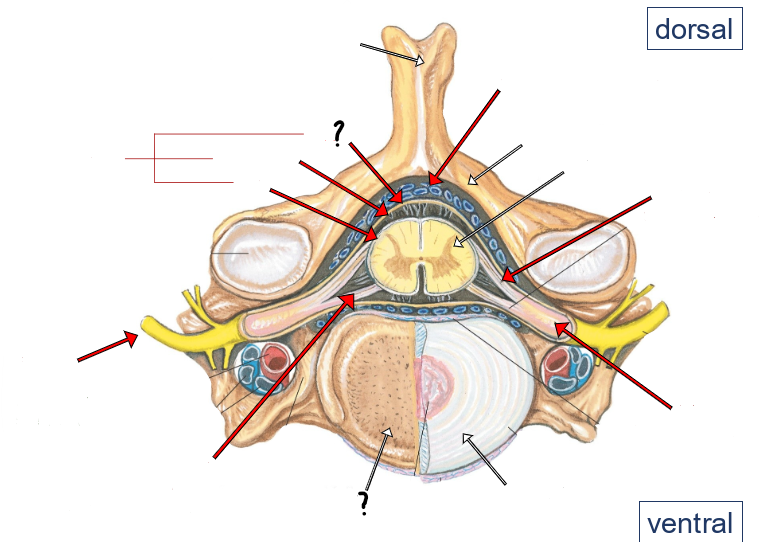
dura
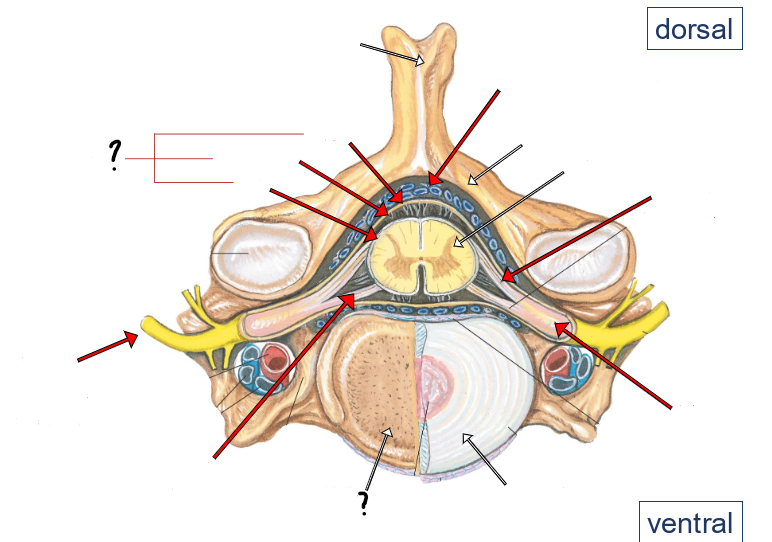
meninges
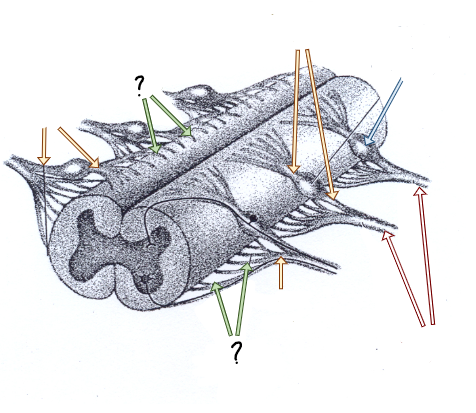
dorsal and ventral rootlets
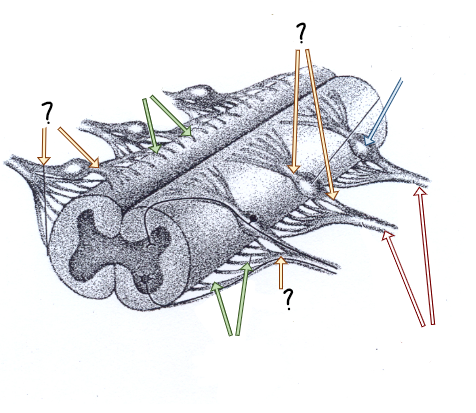
dorsal and ventral roots
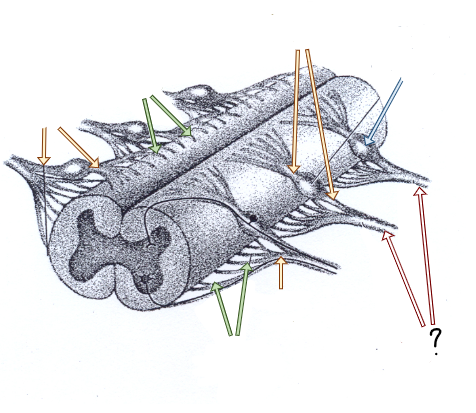
spinal nerves
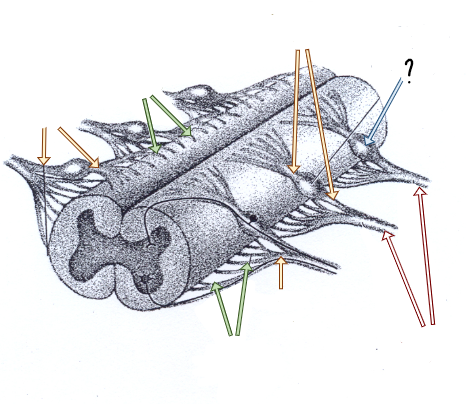
dorsal root ganglia
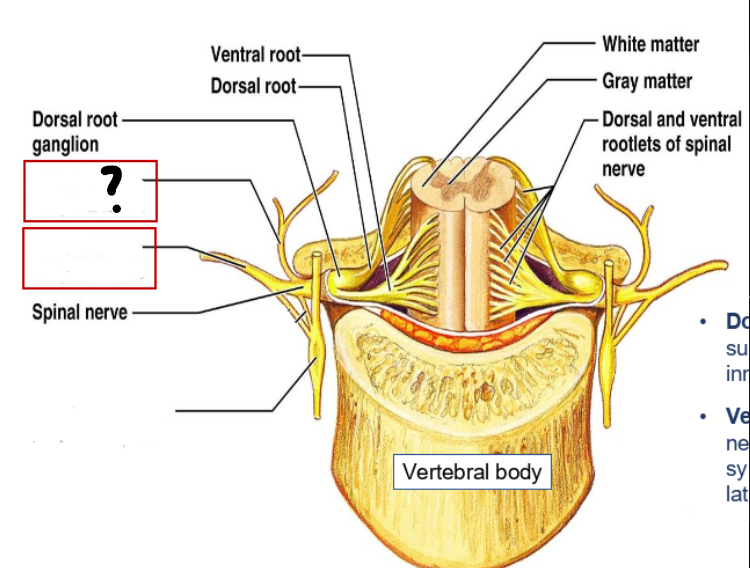
dorsal ramus of spinal nerve
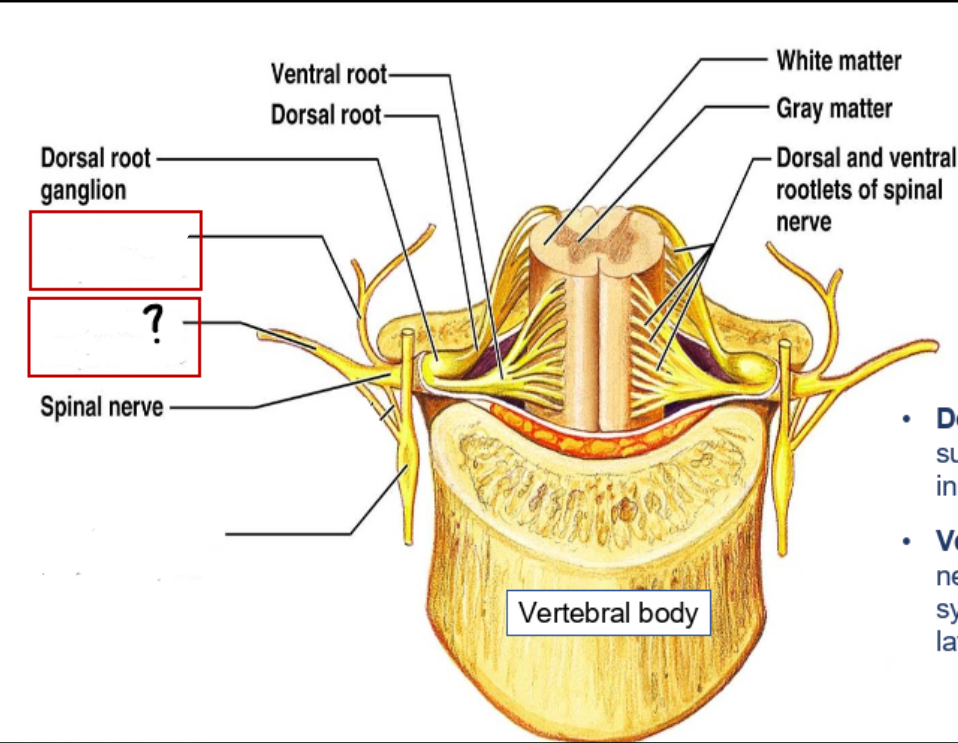
ventral ramus of spinal nerve
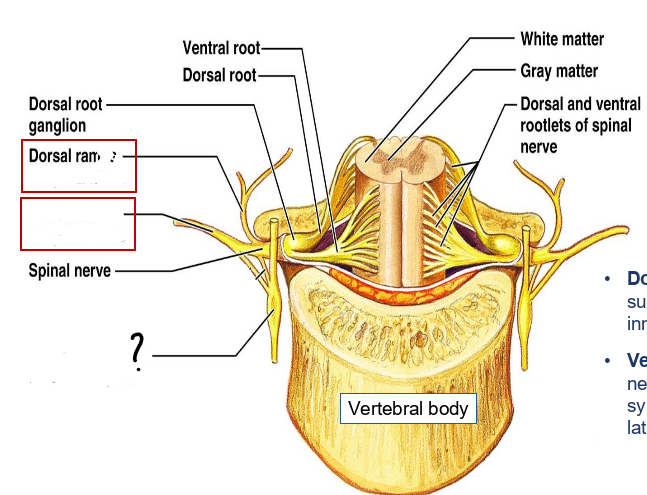
sympathetic trunk (chain) ganglion
what does the dorsal (posterior) ramus of spinal nerve do?
supplies sensory, motor and sympathetic innervation to the back
what does the ventral (anterior) ramus of spinal nerve do?
supplies sensory, motor and sympathetic innervation to the antero-lateral parts of the trunk and the limbs
at what vertebral level does the spinal cord end?
L1/L2
what are the 2 regions of the spinal cord that are enlarged?
cervical enlargement, lumbosacral enlargement
why is there a cervical enlargement in the spinal cord?
origin of brachial plexus (network of nerves supplying arms)
why is there a lumbosacral enlargement in the spinal cord?
origin of lumbar and sacral plexi (nerves supplying lower limbs and pelvis)(enlarged subarachnoid space in lumbar cistern)
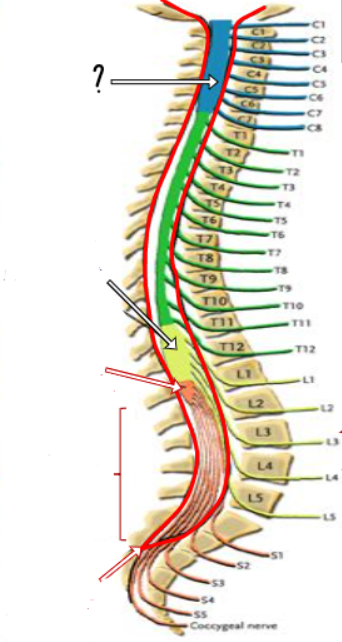
cervical enlargement
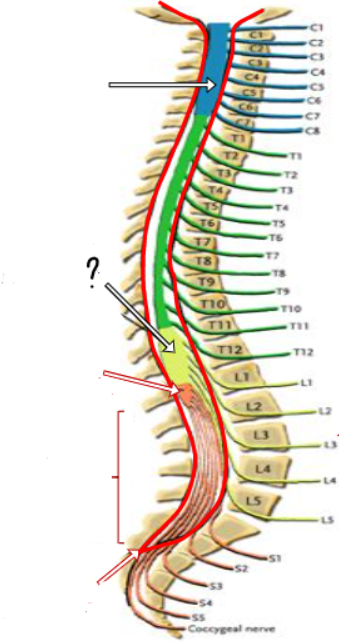
lumbosacral enlargement
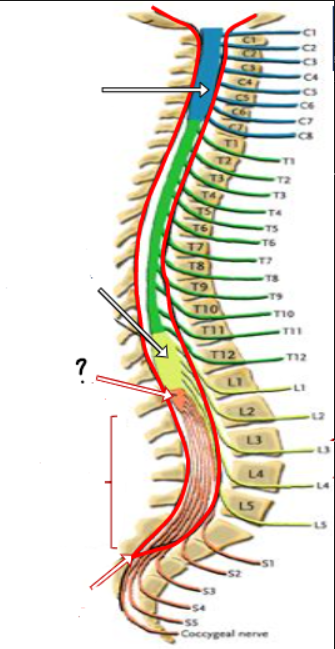
conus medullaris ()
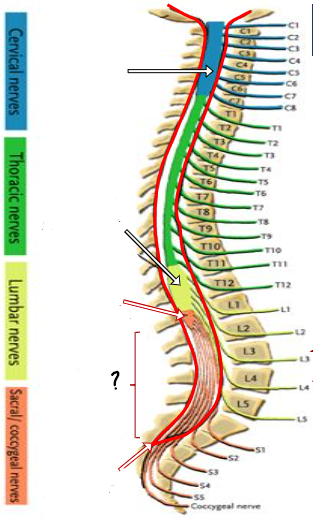
cauda equina
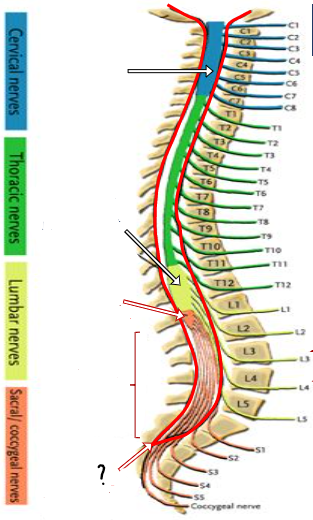
end of dura/ arachnoid
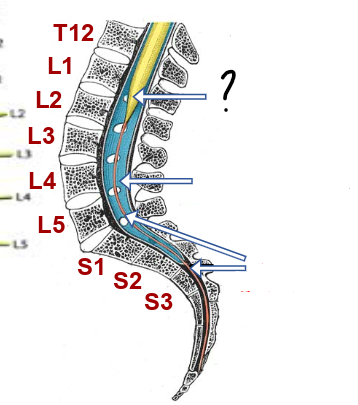
conus medullaris
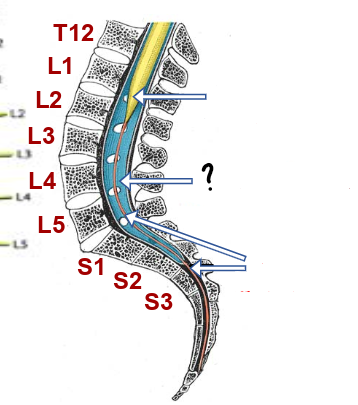
lumbar cistern
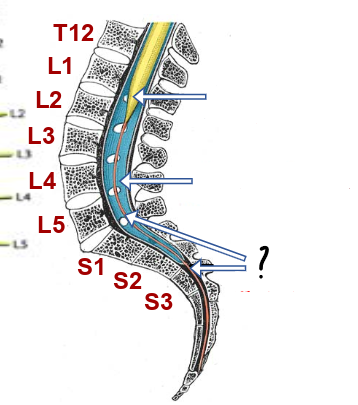
filum terminale
what is the filum terminal made of?
fused pia
why doesn’t the spinal cord move about?
the filum terminal anchors it via attaching to the coccyx
where do the dura and the underlying subarachnoid space merge with the filum terminal?
S2/3
what is the difference between where an epidural and lumbar puncture are injected into?
epidural- outside the dura (since its an injection), lumbar - inside the subarachnoid space, puncture through the dura (since its collection of csf)
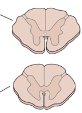
what is the shape of grey matter at cervical levels?
skinny at the top butterfly
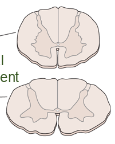
what is the shape of grey matter at thoracic levels?
underweight butterfly
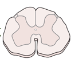
what is the shape of grey matter at lumbar levels?
well-proportioned butterfly
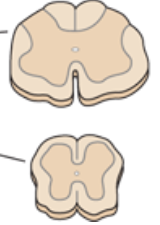
what is the shape of grey matter at sacral levels?
overweight butterfly
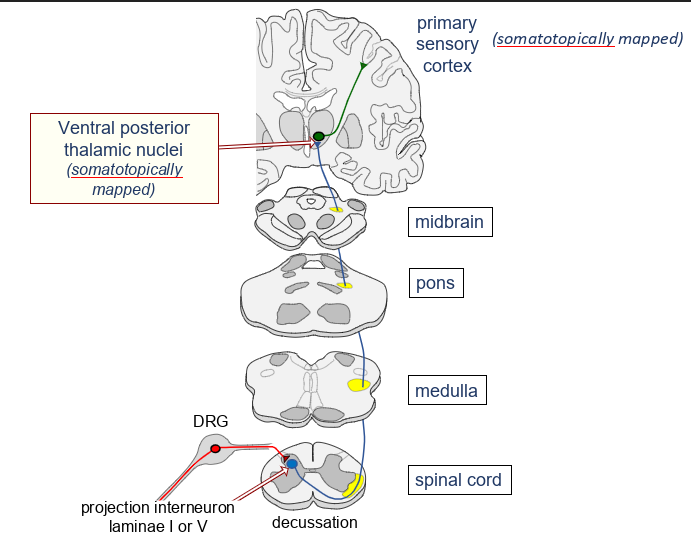
name the major ascending tracts
spinothalamic tract, dorsal column medial lemniscus, spinocerebellar pathway
name the major descending tracts
pyramidal motor pathway, non-pyramidal: reticulospinal tract, vestibulospinal tract
what does the spinothalamic tract do?
pain, temperature, itch and simple touch
what does the dorsal column medial lemniscus tract do?
discriminative touch and conscious proprioception
what does the spinocerebellar tract do?
non-conscious proprioception
what does the pyramidal motor pathway do?
conscious movement- lateral and anterior corticospinal tracts
what does the reticulospinal tract do?
muscle tone, posture, and simple stereotyped movements
what does the vestibulospinal tract do?
coordinating balance and keeping the head balance and the eyes horizontal when moving
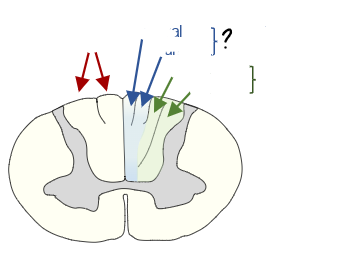
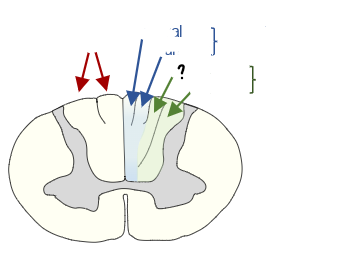
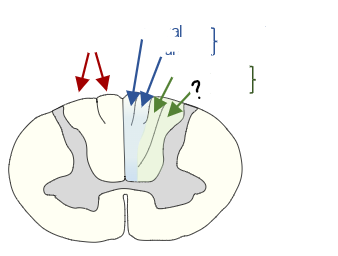
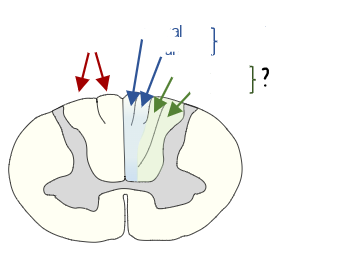
what tract is this
spinothalamic
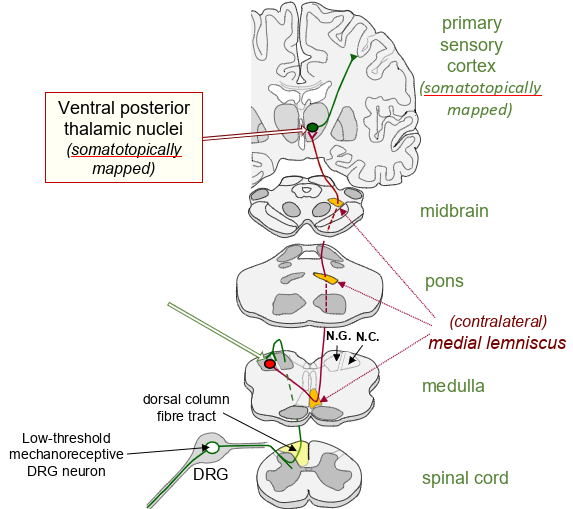
what pathway is this
dorsal column pathway
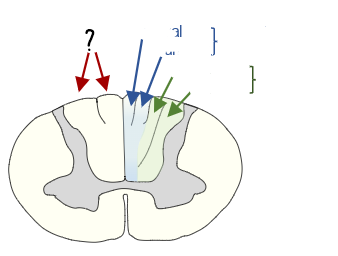
dorsal columns
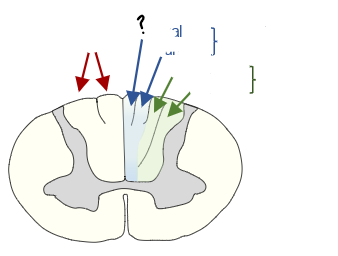
sacral
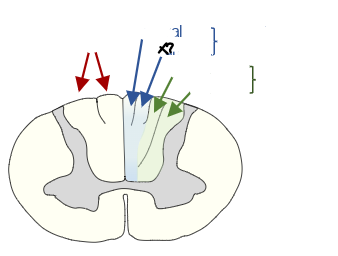
lumbar
gracile fasciculus
thoracic
cervical
cuneate fasciculus
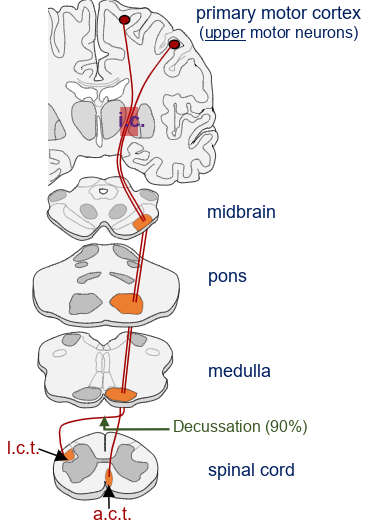
what tract is this
pyramidal motor pathway
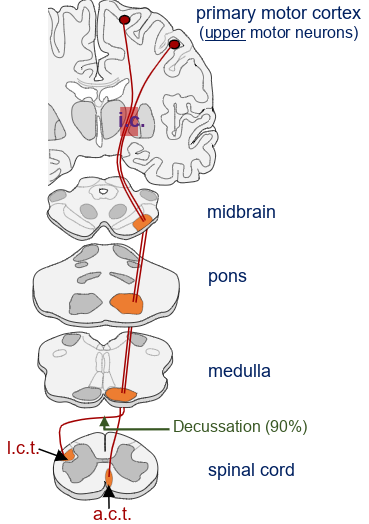
in this picture, what does the i.c. and l.c.t. stand for?
i.c. -internal capsule, l.c.t. - lateral corticospinal tract
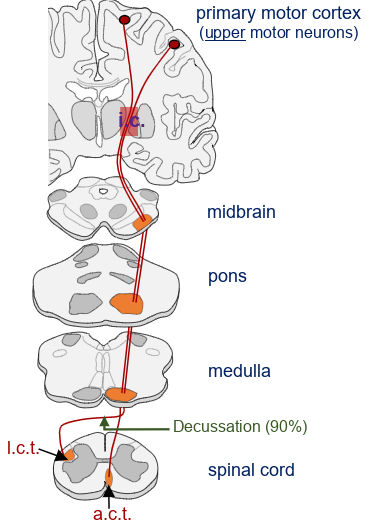
in this picture, what does the 90% stand for?
90% of pyramidal motor axons crossover at the junction of medulla and spinal cord, travel in l.c.t., make synaptic connections to lower motor neurons (innnervating limb muscles)
what path do the remaining 10% pyramidal motor axons take?
decussate at level of lower motor neuron, travel in anterior/ventral corticospinal tract, connect lower motor neurons (innervating trunk/ axial muscles)
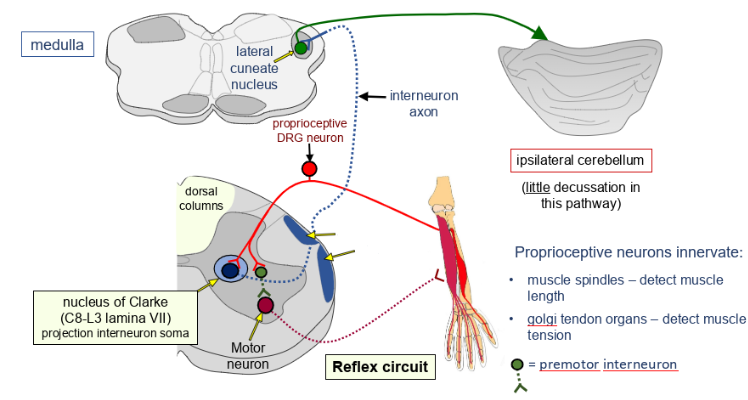
what pathway is this?
spinocerebellar
what do proprioceptive neurons innervate?
muscle spindles- detect muscle length, golgi tendons- detect muscle tension, premotor interneuron
spinal cord grey matter - what do laminae V-VII do?
central terminals of proprioceptive and visceral sensory DRG neurons + associated interneurons
spinal cord grey matter - what does laminae VII do?
soma of sensory projection neurons of spinocerebellar tract (non-conscoius proprioception)
soma of preganglionic sympathetic neurons (T1-L2) and preganglionic parasympathetic neurons (S2-S4)
spinal cord grey matter - what does laminae VIII/ IX do?
soma of lower motor neurons projecting to skeletal muscle
what are the T1 spinal nerves associated with?
hands and fingers
what are the T2-5 spinal nerves associated with?
chest muscles
what are the T6-8 spinal nerves associated with?
chest + abdominal muscles
what are the T9-12 spinal nerves associated with?
abdominal muscles
what are the C1/2 spinal nerves associated with?
movement of the head/ neck
what are the C3 spinal nerves associated with?
diaphragm (breathing)
what are the C4 spinal nerves associated with?
diaphragm (breathing), shoulder shrug
what are the C5 spinal nerves associated with?
deltoid (lift arm sideways), biceps
what are the C6 spinal nerves associated with?
wrist extensors (lifts wrists back)
what are the C7 spinal nerves associated with?
triceps (straightens elbow)
what are the C8 spinal nerves associated with?
hands and fingers
what are the L1/2 spinal nerves associated with?
hip muscles
what are the L3 spinal nerves associated with?
knee extension muscles (straightens knee)
what are the L4 spinal nerves associated with?
knee flexion + ankle movement muscles
what are the L5 spinal nerves associated with?
ankle and toe muscles (lifts big toe and foot)
what are the S1 spinal nerves associated with?
leg and toe muscles (points foot)
what are the S2 spinal nerves associated with?
toe muscles + anal and bladder external sphincters
what are the S3-5 spinal nerves associated with?
anal and bladder external sphincters