Lecture 21 - Cell communication and cell signaling I
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Cells can act as both ___ cells and ____ cells
target; signaling
______ ______ is the process whereby one type of signal is converted into another
signal transduction
Describe signal transduction
receptor on a target cell receives an extracellular signal and the produces intracellular signal molecule that alter cell behavior
____ ______ encompasses the mechanic of signal reception and transduction
cell signaling
5 types of cell signaling
endocrine
paracrine
autocrine
neuronal
contact-dependent
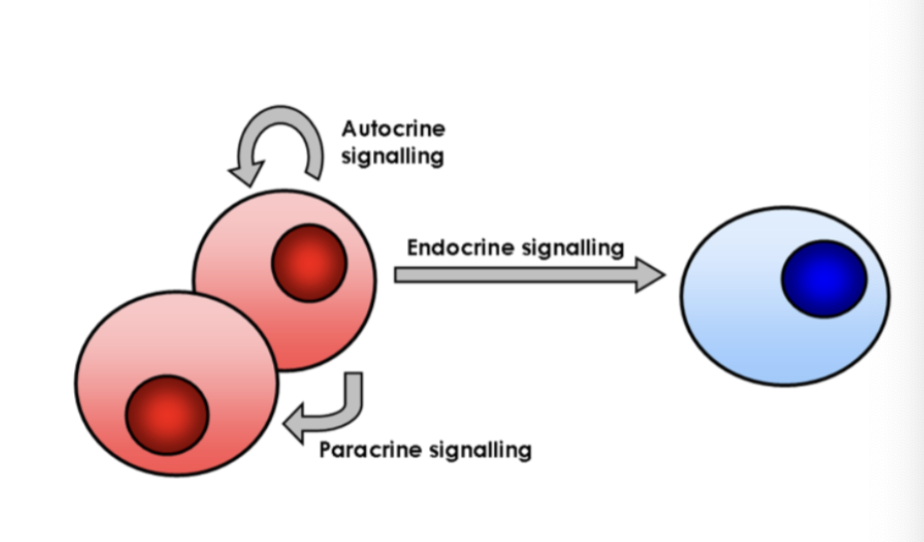
Endocrine signaling
signaling cell:
signaling molecule:
communication distance:
communication mode:
endocrine cell, hormones, long, public broadcast to whole body
Paracrine signaling
signaling cell:
signaling molecule:
communication distance:
communication mode:
many cell types, cytokines & interferons, local, semi-public
Example of paracrine signaling
regulate inflammation at the site of infection
promote cell proliferation at a wound site
Define autocrine signaling
a specialized form of endocrine signaling in which cells respond to signaling molecules they secrete themselves
Autocrine signaling
signaling cell:
signaling molecule:
communication distance:
communication mode:
many cell types, cytokines & interferons, local, semi-public
examples of autocrine
cancer cells promote their own survival and proliferation
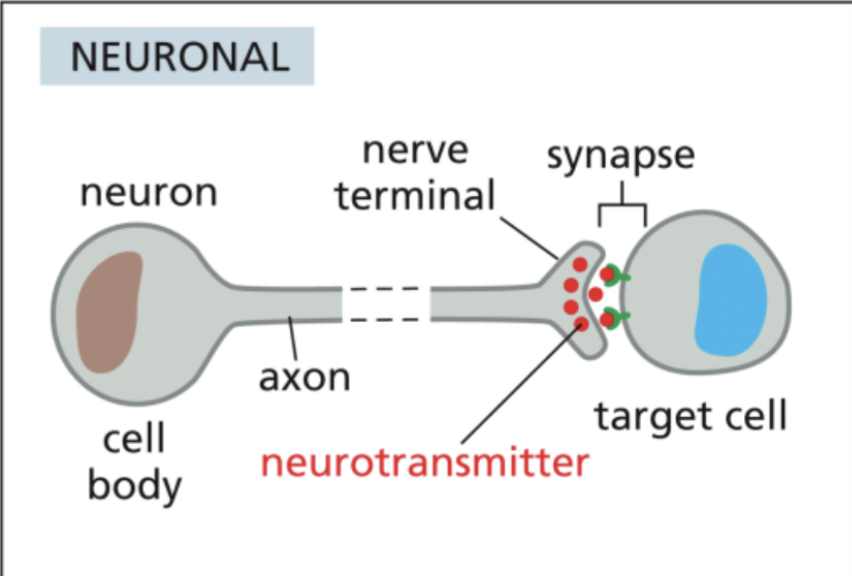
Neuronal signaling
signaling cell:
signaling molecule:
communication distance:
communication mode:
nerve cell, neurotransmitter, long, private
In contact-dependent signaling, signals are transmitted through _____ _____ _____ between neighboring cells
direct physical contact
Contact-depending signaling
signaling cell:
signaling molecule:
communication distance:
communication mode:
several (epithelial and mesenchymal), several, very short, private
Example of contact-dependent signaling
during embryonic development, adjacent cells are initially similar then become specialized
Two types of signaling receptors
large and/or hydrophillic
small and/or hydrophobic
How do large/hydrophillic molecules signal to other cells
bind and rely on surface receptors to relay their message
How do small/hydrophobic molecules signal to other cells
bind to intracellular receptors
(T or F) the same signal molecule can induce different responses in different target cells
True
How does the cell limit the type of of signals that can affect it
By producing only a limited set of receptors
Is it possible for the same receptor to induce a different intracellular signaling response?
Yes
Examples of cell signals that are typically fast
changes in cell movement, secretion, or metabolism
Examples of cell signals that are typically slow
cell differentiation and increased cell growth or division
Cell-surface receptors relay extracellular signals via ____ _____ ______
intracellular signaling pathways
5 functions of the intracellular signaling pathways
relay
amplify
integrate
distribute
modulate
What does it mean to integrate an extracellular signal
detect from more that one signaling pathway and integrate them before passing it on
What does modulation mean in an intracellular pathway
the activity of upstream signaling molecules provides feedback
Some intracellular signaling proteins act as molecular ______
switches
What can turn molecular switches on or off
addition or removal of phosphate groups
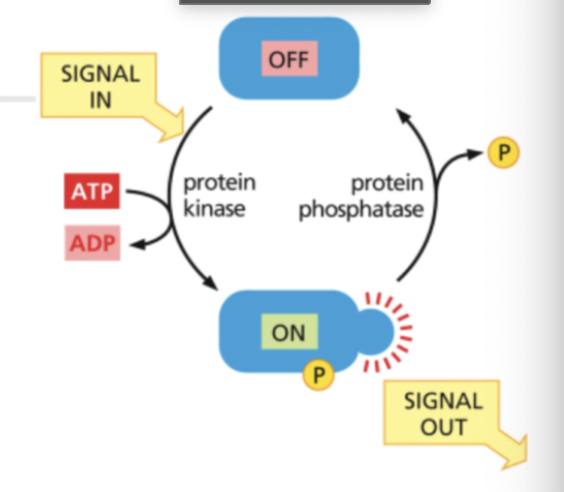
Kinases ____ phosphate groups while phosphates _____ them
add; remove
Class 1 molecular switch proteins
protein phosphorylation
Class 1 switch protein is ___ by protein kinase and ______ by protein phosphatase
activated; deactivated
Class 2 switch protein
GTP-binging proteins
Class 2 molecular switch proteins are _____ upon binding to GTP and ____ by the exchange of GTP for GDP
activate; deactivates
2 types of G-proteins
large heteromeric G-proteins
small monomeric G-proteins
Subunits of large, heteromeric proteins
alpha, beta, gamma
Another name for small, monomeric G-proteins
Ras proteins
3 main classes of cell-surface receptors
ion-channel-coupled receptors
G-protein-coupled receptors
enzyme-coupled receptors
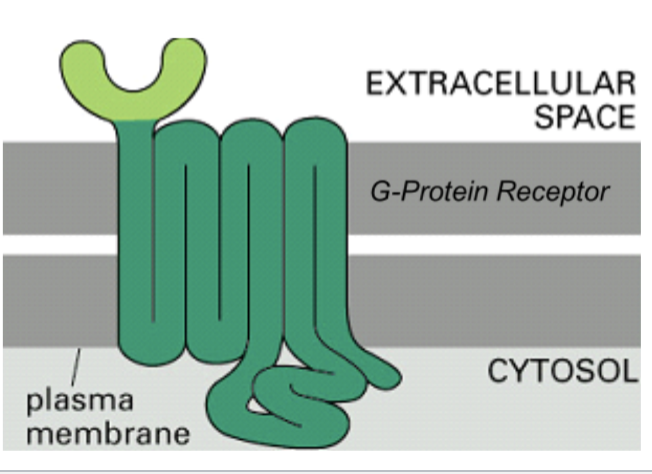
G-coupled protein receptor structure
seven alpha-helix domain
cytosolic G protein binding loop - specific for a particular G protein
G protein structure
Heterotrimeric G-proteins with subunits being a,B, and y
G proteins are a type of _____ _____ whose on or off states depends on whether the G protein is bound to GTP or GDP
molecular switch
Did you watch video for G proteins
Yes
_____ _____ binds receptor triggering a conformational change, thus starting the activation process of the G-protein
signal molecule
How is G-protein activated
alpha subunit releases GDP and binds to GTP → activates G-protein
When an activated a subunit interacts with its target protein → it activates that target protein and activates that protein for as long as the two …
remain in contact
How does the alpha subunit inactivate G protein
a subunit hydrolyzes its bound GTP to GDP
(T or F) the GPCR pathway must be tightly regulated
True
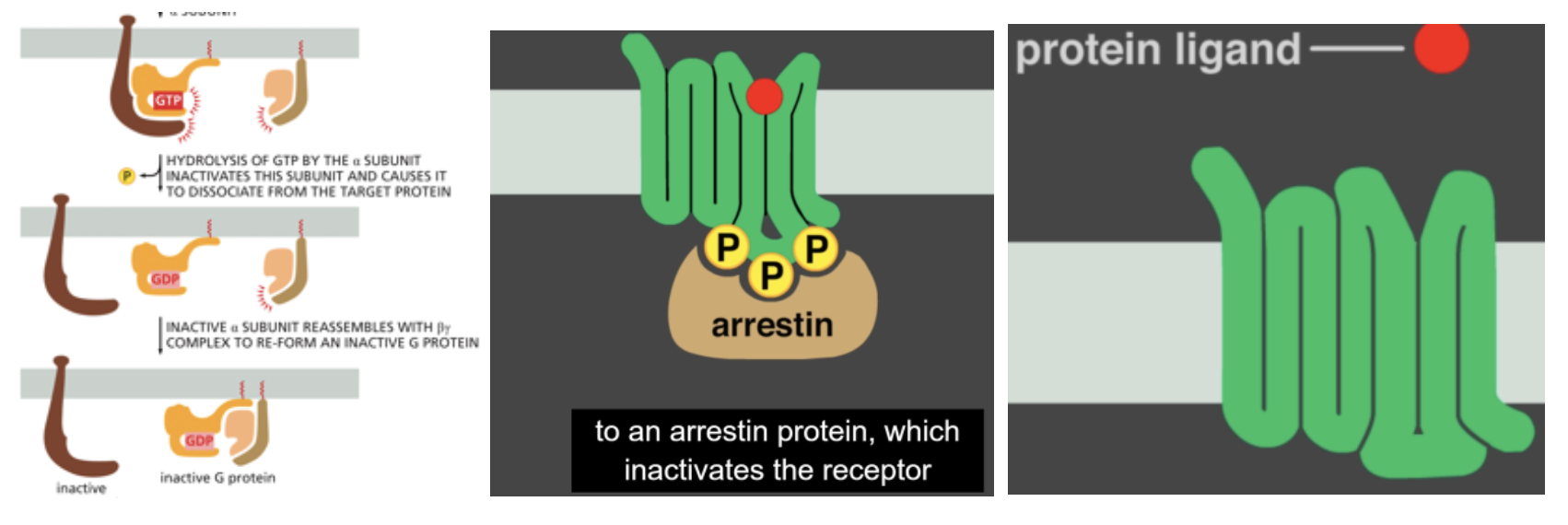
3 mechanisms that allows GPCR pathway to be shut down
GTP on a subunit is hydrolyzed to GDP
arrestin binds to phosphorylated GCPR
primary signal (ligand of the GPCR) is removed