DEFINITIVE IMPRESSIONS
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
what are other terms for definitive impression
secondary impression
working impression
outline the magnitude of alveolar resorption
the magnitude of alveolar resorption is approx. x4 greater in the mandible than the maxilla
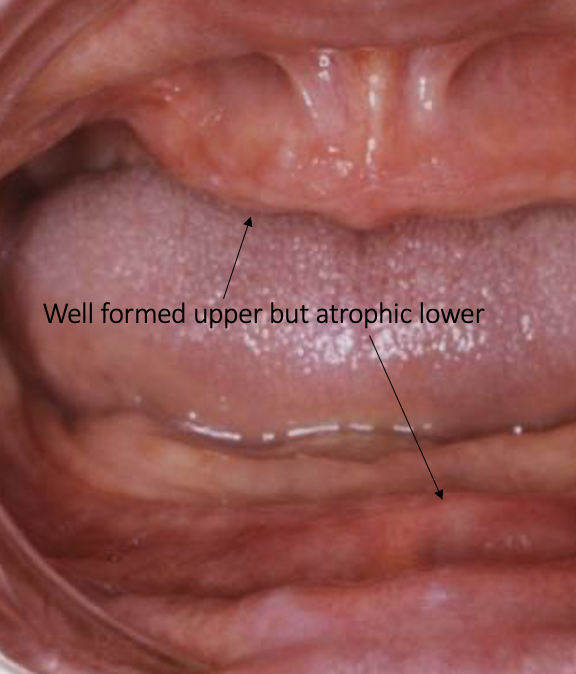
outline the site and pattern of mandibular resorption
the residual ridge becomes more:
lingually placed anteriorly compared to the natural dentition because the labial bony plate is weaker
buccally placed posteriorly compared to the natural dentition because the lingual palate is weaker
» in at the front and out at the back
what is the relevance of mandibular resorption to the position of the denture
because the residual ridge becomes more lingually placed anteriorly, the lower anteriors must be set on or slightly ahead of the residual ridge
because the residual ridge becomes more buccally placed posteriorly, the 6 must be set on or just inside the residual ridge
—
the canines and premolars must be set directly over the residual ridge
the 7 must be set on or just outside of the residual ridge
outline the site and pattern of maxillary resorption
the residual ridge is more palatal in all regions than the position of the natural dentition
what is the relevance of maxillary resorption to the position of the denture
all the maxillary teeth can be set slightly labially/ buccally rather than directly over the residual ridge
describe the trend of bone resorption
rate of bone resorption is rapid when the teeth are first taken out
rate of resorption slows after 12 months
what factors influence the rate of resorption
systemic factors: osteoporosis increases rate of resorption
local factors: retained roots and biocompatible implants preserve alveolar bone
denture induced: limited evidence that denture wearing contributes to resorption
what are immediate dentures
temporary prosthetics custom made to be fitted right after teeth have been extracted
this provides an immediate replacement
what issues can arise due to having dentures
denture insecurity
occlusal problems
pain and pain caused by irregular resorption
appearance
what occlusal problems can denture patients encounter
if the patient has a cross bite or a class III malocclusion (underbite) the placement of denture teeth will be influenced by the skeletal classification of the patient
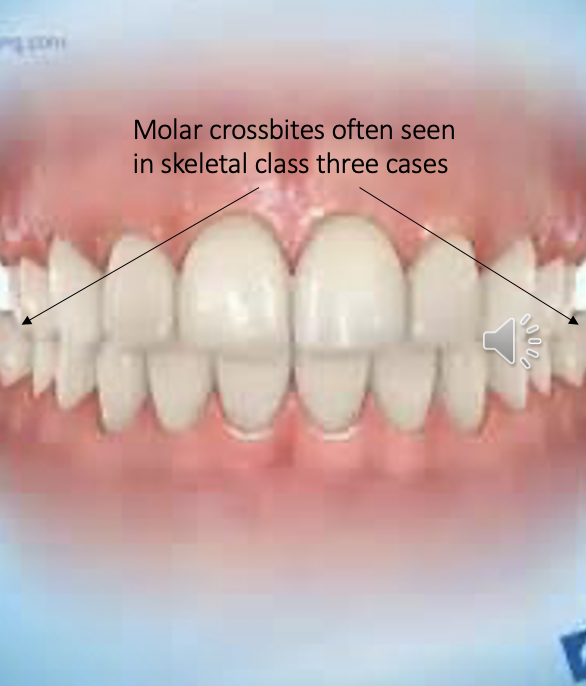
what is a molar crossbite
when the buccal cusps of the upper molars sit inside of the buccal cusps of the lower molars
how do issues of pain come about in denture patients
as the mandibular ridge resorbs, the mental foramina becomes closer to the surface, making it more likely to be affected by compression of the overlying mucosa by the denture
this can lead to numbness and paresthesia
irregular resorption of the ridges can also cause pain when the denture is compressed against sharp bony spicules
how do aesthetic issues come about with dentures
the lack of support of the soft tissues lead to a loss in face height overtime which can age the patient significantly
this sagging can contribute to angular cheilitis (fungal infection in oral commissures)
what are requirements of taking a working impression of a ridge without undercuts
a ridge without undercuts or minimal undercuts
rigid impression material in a close fitting special tray
what are requirements of taking a working impression of a ridge with large undercuts
a ridge with large undercuts
elastic impression material in a spaced special tray
what is an undercut
undercut: the area between the maximum bulbosity of the ridge and the deepest part of the sulcus beneath it
diagrams of undercuts
outline ZOE
ZOE: zinc oxide eugenol
rigid impression material
usually used with a mucostatic technique in patients with little/ no undercuts
ZOE can become mucocompressive if used in a close fitting special tray
sometimes used with one spacer or two
what are advantages of ZOE
cheap
easy to modify
accurate
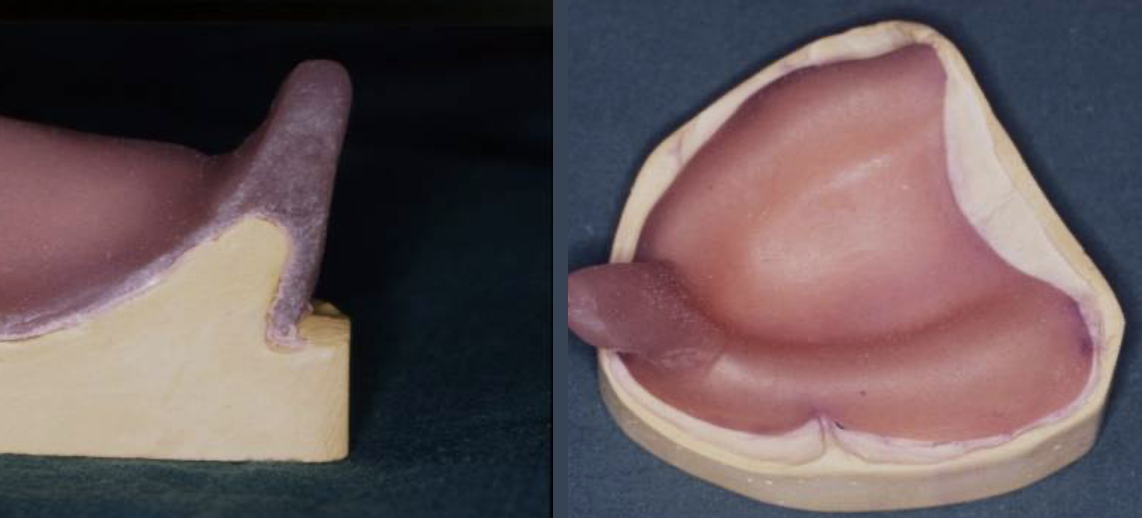
outline a close fitting special tray
close fitting special tray
extends 1-2mm short of where the final denture border should be
used in minor/ moderate undercuts
takes a mucocompressive impression
ZOE used
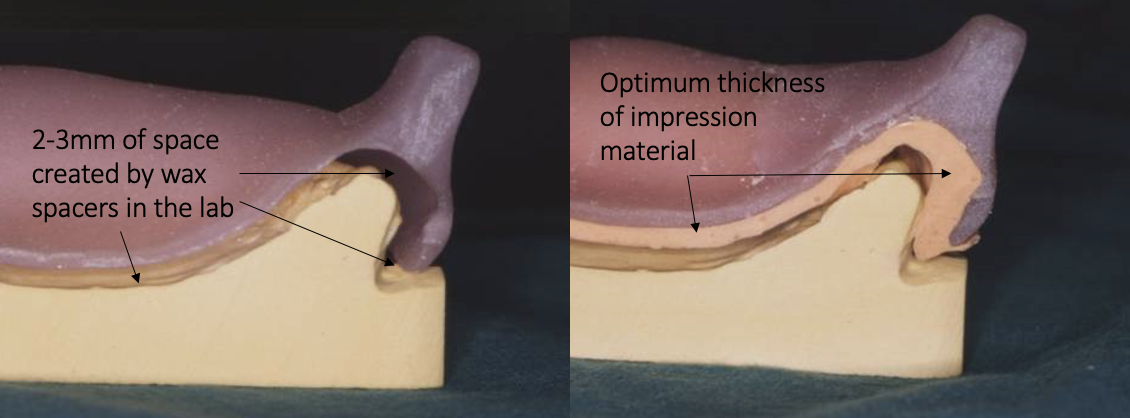
outline a spaced special tray
spaced special tray
extends 2-3mm short of where the final denture should extend to
used in moderate to severe undercuts
takes a mucostatic impression
alginate used (tray should be perforated if alginate is used to ensure mechanical retention)
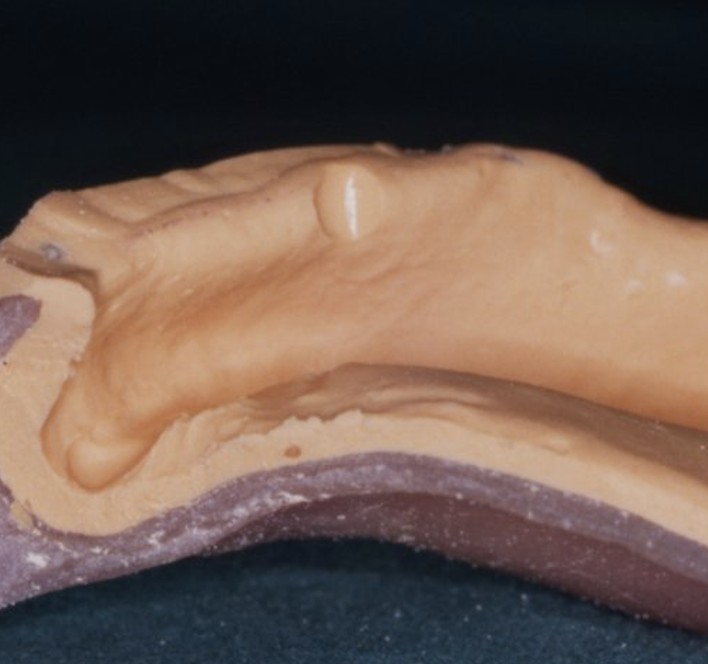
outline tissue stops
all impression materials work at an optimum thickness
tissue stops ensure a uniform thickness of the impression material by preventing the tray from being fully seated against the oral tissues
i.e. stops the tray showing through if excessive pressure is placed
different tissue stop depths for different impression materials

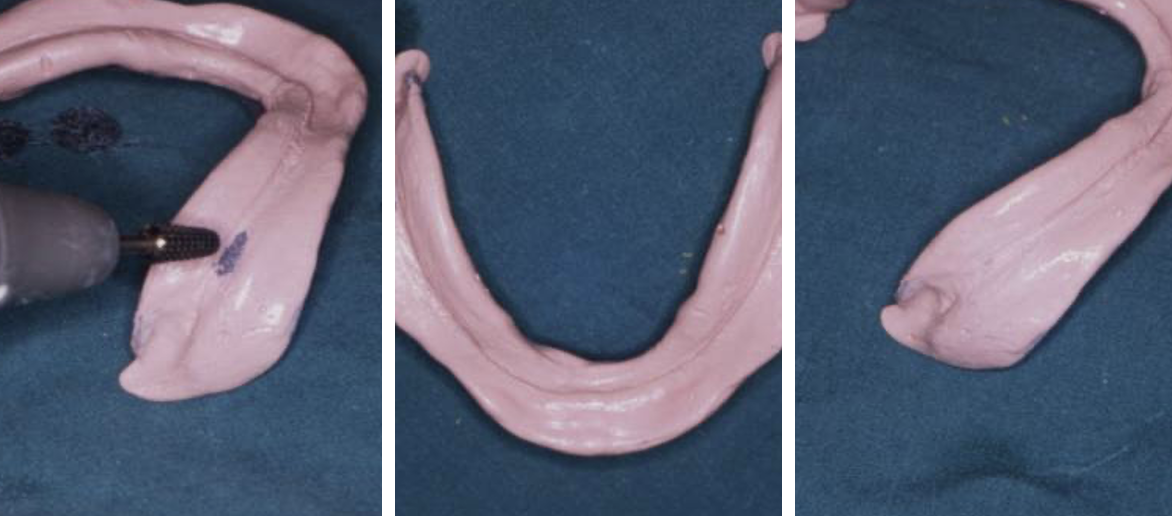
what should be done before taking a secondary impression
check the tray!
if the tray is overextended what should be done
trim back using a burr so the frenae and junction of fixed and mobile mucosa are not impeded
if a tray is underextended what should be done
add green stick compound or self curing acrylic
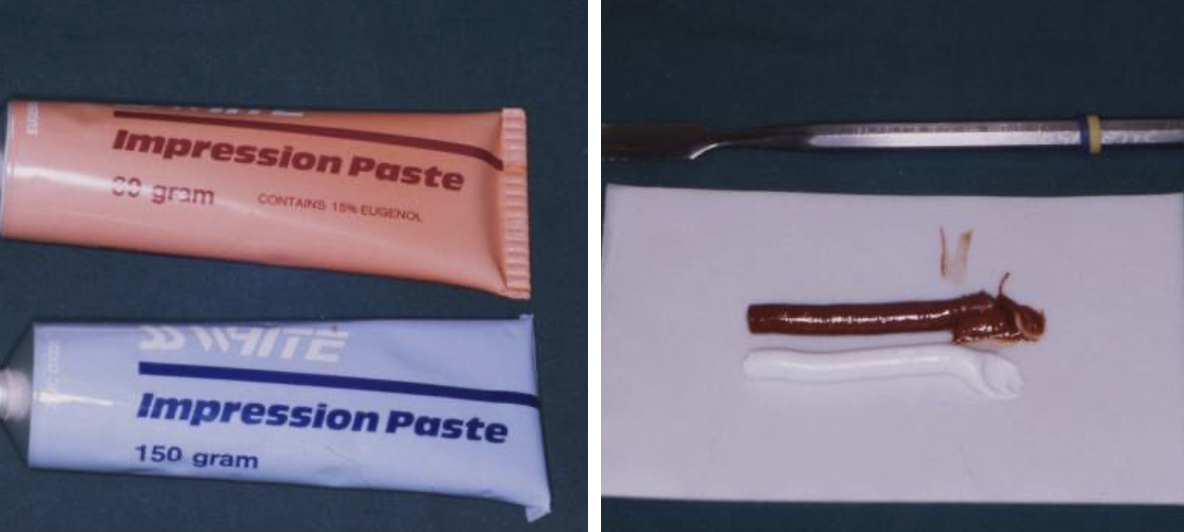
how to obtain Zinc Oxide Eugenol
when mixing, the ratio of the materials MUST be 1:1 otherwise setting times will change

when is ZOE contraindicated
if patients have an elastoplast allergy, do NOT use ZOE
how should patients be informed before a ZOE impression is taken
ZOE has a strong taste and may give a burning sensation - tell the patient it is normal to feel some warmth
the material is also sticky
it sets reasonably quick, after which we will take it out
how should a xerostomic patient be prepared for a ZOE impression
if a patient has xerostomia, they should rinse their mouth beforehand
how should a ZOE impression be taken
ensure border moulding is done well and the patient moves their tongue - wait a little after putting the material in their mouth to ensure it is not too runny before BM
always keep fingers on the tray in premolar region (finger rests can be incorporated into the special tray)
how can a ZOE impression be adjusted if the tray penetrates through
can add some more ZOE onto the tray and take the impression again if there are imperfections
rather than retaking the whole impression
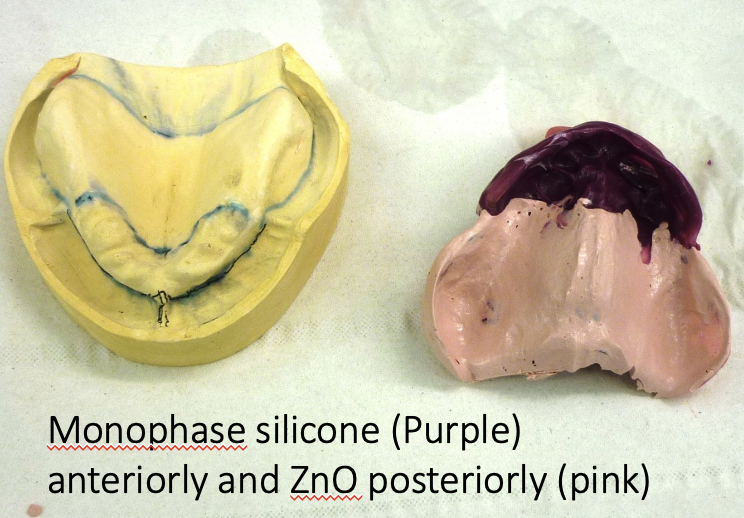
if fibrous ridges are present, how can an impression be taken
use different materials for different areas of the mouth for a selective pressure impression
outline flabby/ fibrous ridges
a ridge that becomes displaceable due to fibrous tissue deposition
most frequently seen in upper anterior region
can occur when natural teeth oppose an edentulous ridge
what issue can flabby/ fibrous ridges cause in relation to dentures
denture instability due to the lack of underlying bone
flabby/ fibrous ridge statistics
found in 1 in 4 upper ridges
found in 1 in 20 lower ridges
how should flabby/ fibrous ridges be recorded during impression taking
record this area with a mucostatic technique
what kind of special tray can be made to accommodate flabby/ fibrous ridges
window box trays
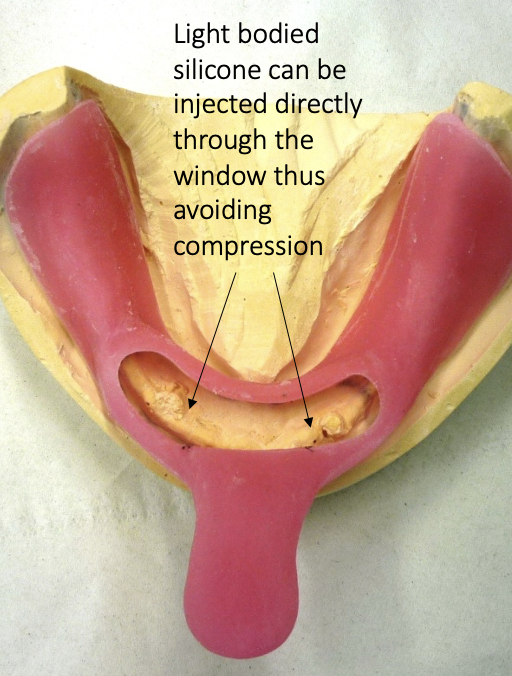
window box tray technique for recording flabby/ fibrous ridges
posterior region recorded in ZnO using a mucocompressive technique
anterior region will be recorded in a mucostatic way with a material such as light bodied silicone
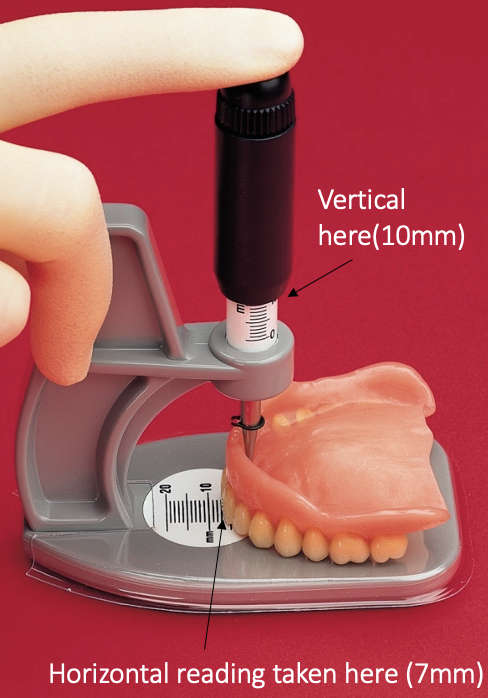
outline the Alma Gauge
Alma Gauge
a measurement tool that gives the lab a vertical and horizontal reading so bite blocks come back at approx. the correct dimensions
can be used if patients have an old set of dentures they like
image of the Alma Gauge
place plunger in indentation where the incisive papilla is
instructions to give to the lab
please make upper and lower registration rims
Alma gauge readings of old upper denture using incisive papilla as fixed point V12 H7
if the patient has no previous dentures, what measurements should be given to the lab
22mm upper
18mm lower
» these measurements are from the deepest point of the labial sulcus, not the incisive papilla