iGCSE Edexcel Chemistry Metallic Bonding & Electrolysis
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
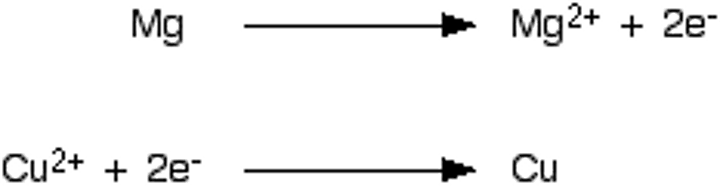
half equation
the part of an overall reaction that represents, separately, either an oxidation or a reduction
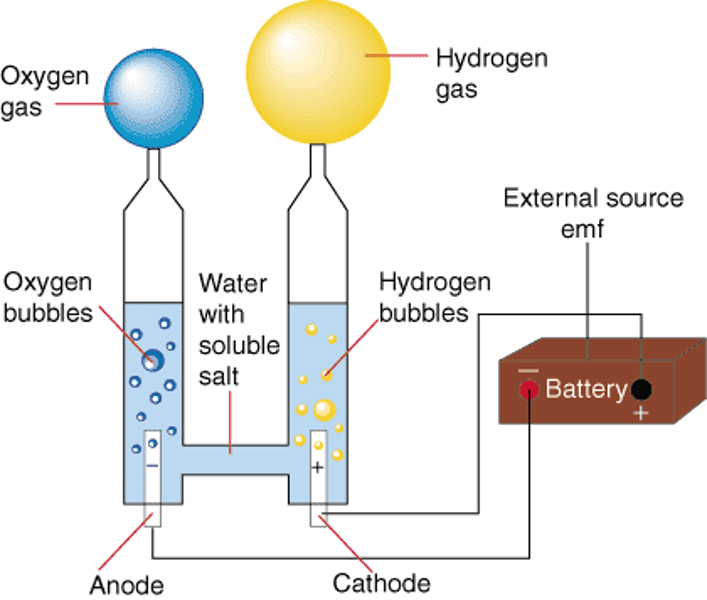
anode
positive electrode, where oxidation occurs
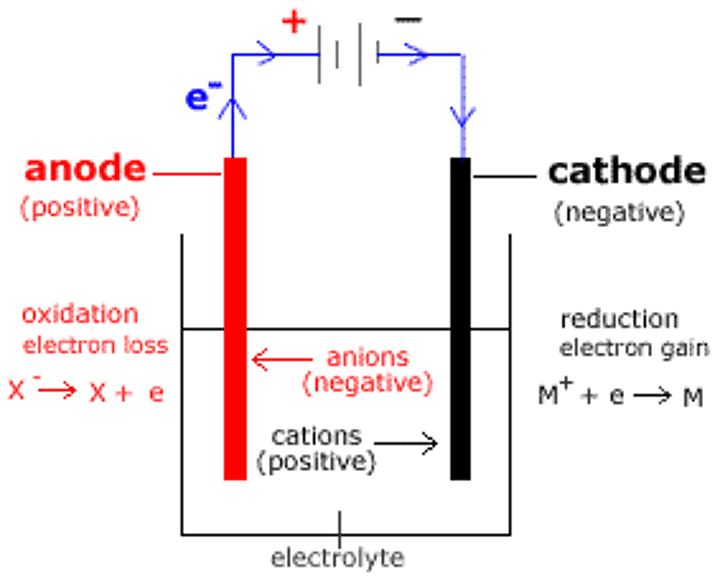
cathode
negative electrode, where reduction occurs
electrode
electrical conductor
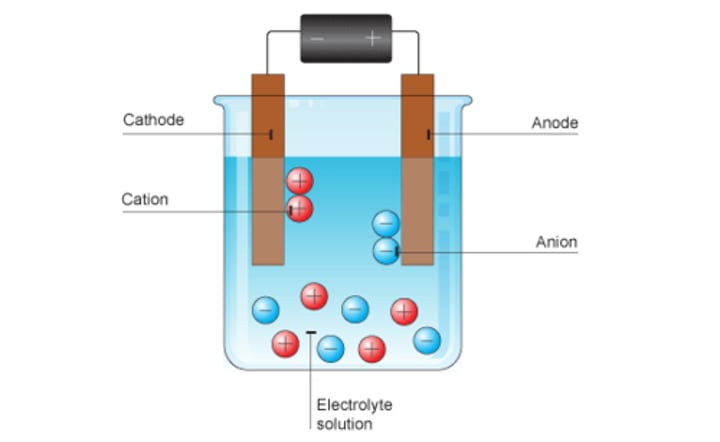
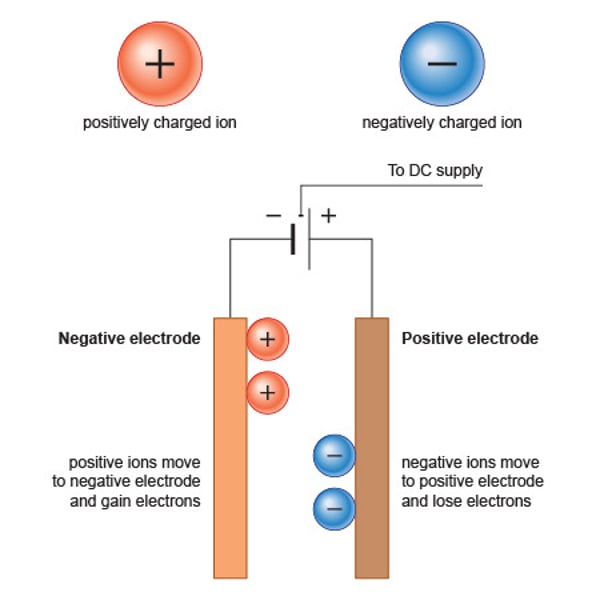
cation
a positively charged ion

anion
a negatively charged ion
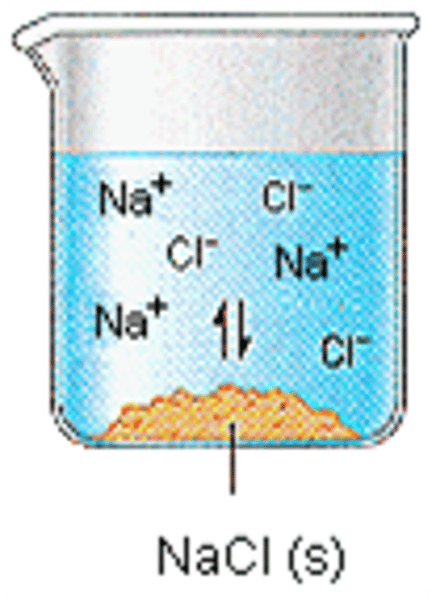
electrolysis
a chemical change caused by passing an electric current through an ionic compound that is either molten or in solution
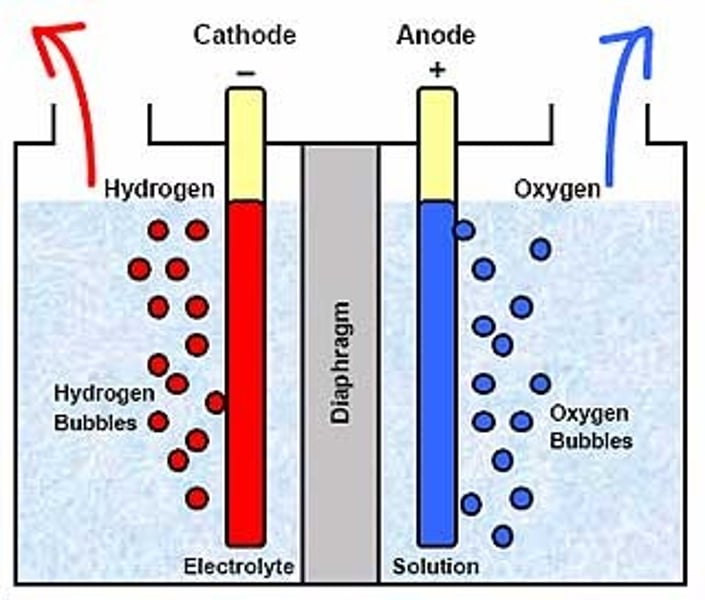
electron flow
anode to cathode
metallic bonding
electrostatic attraction between positive metal ions and delocalised electrons
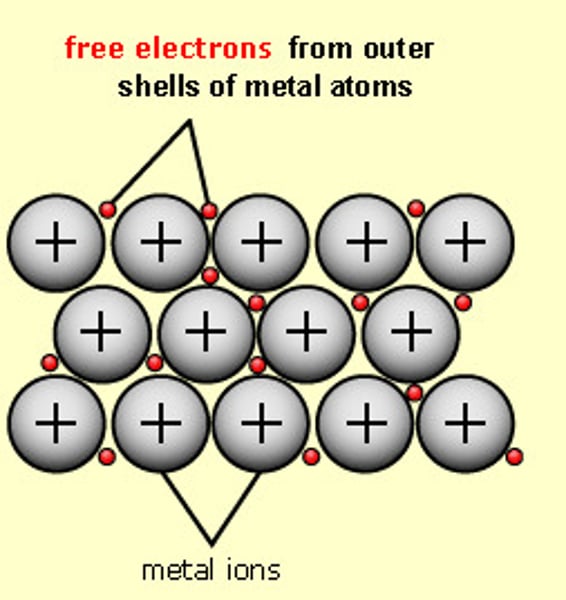
delocalised electrons
outer electrons do not have fixed positions but move freely
malleable
capable of being shaped or bent
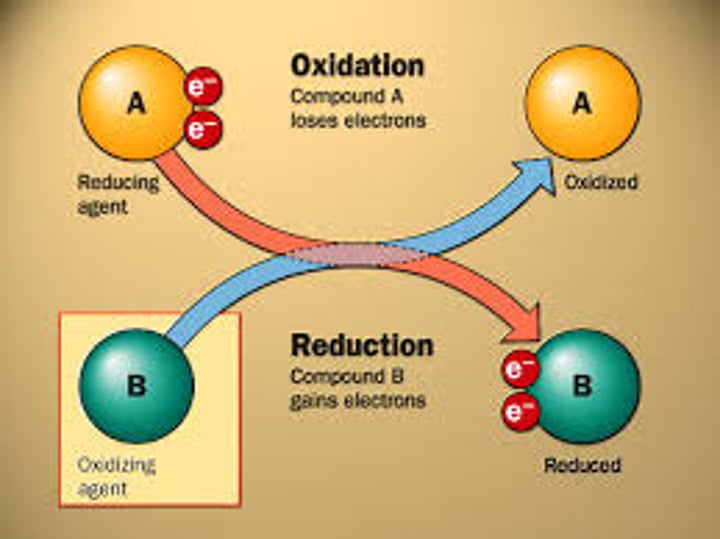
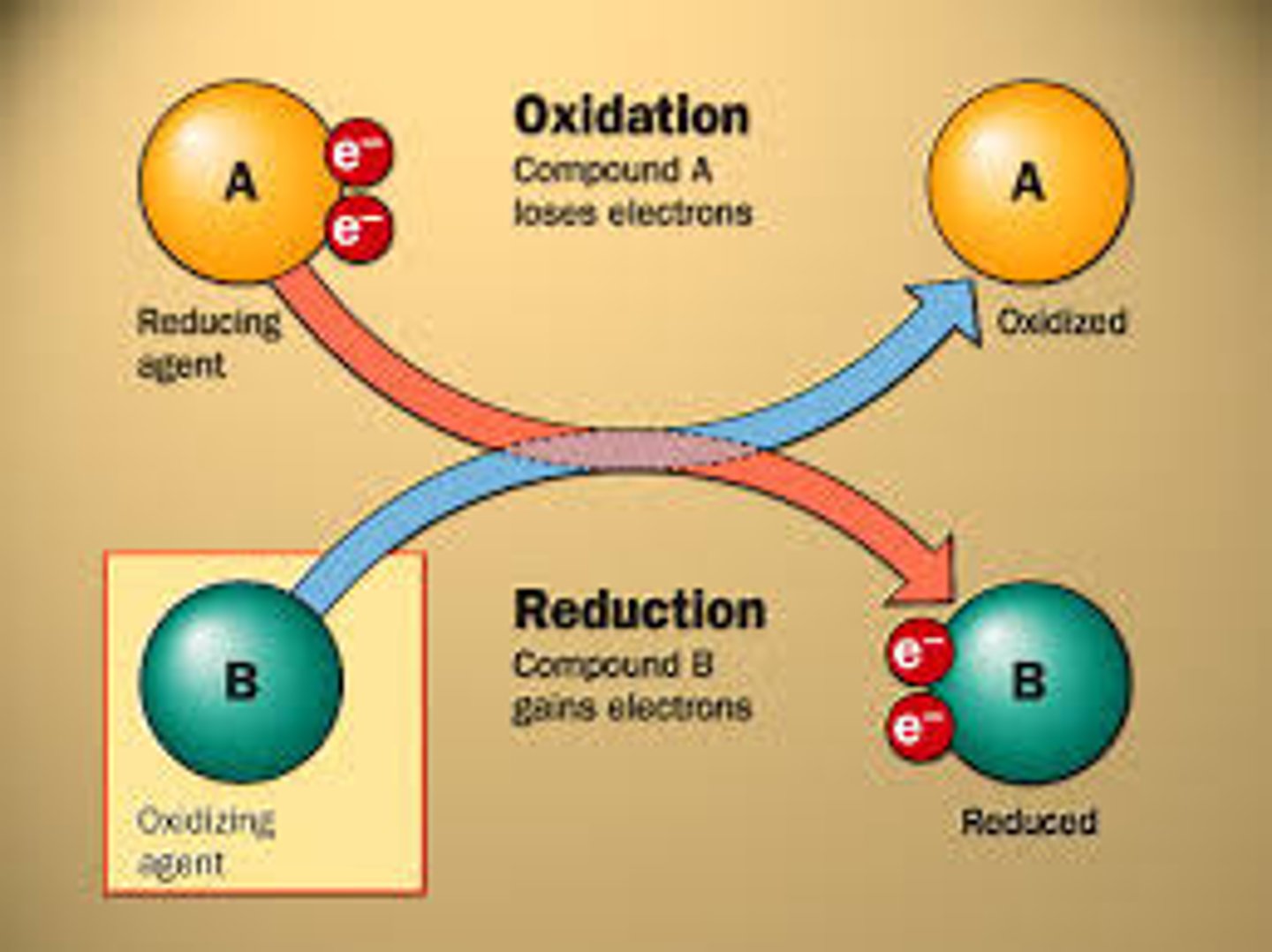
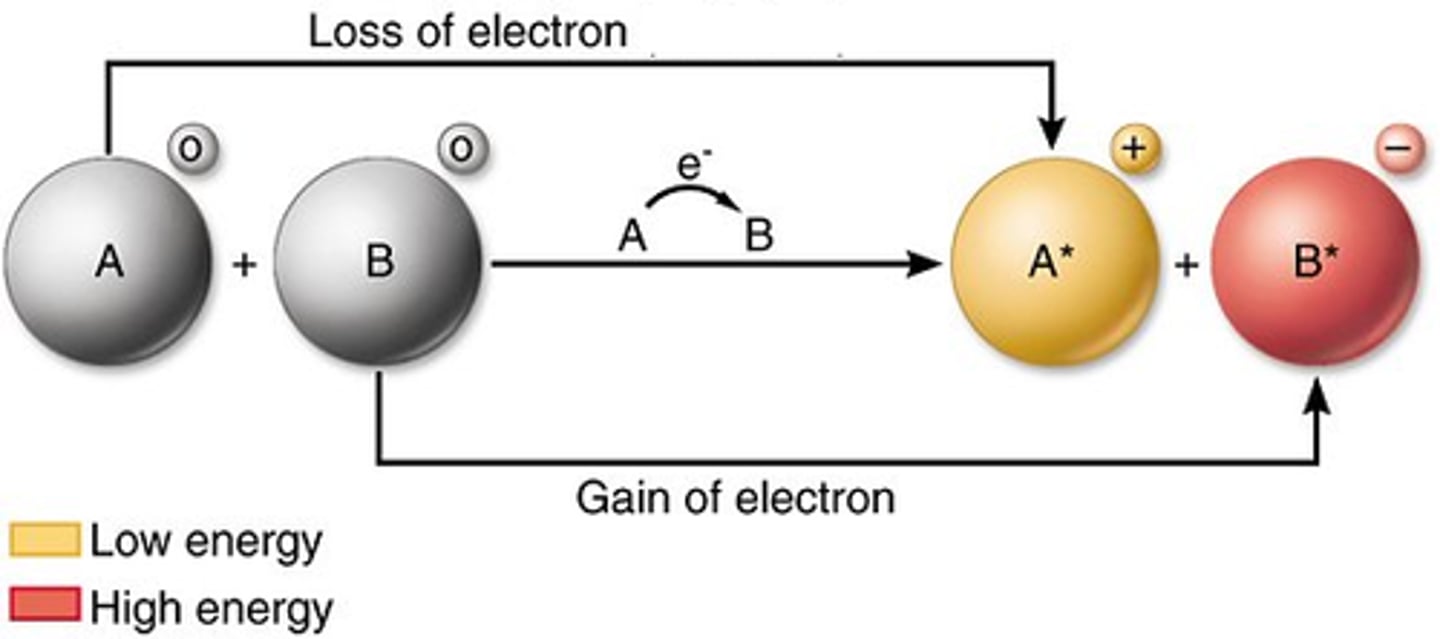
oxidation
loss of electrons
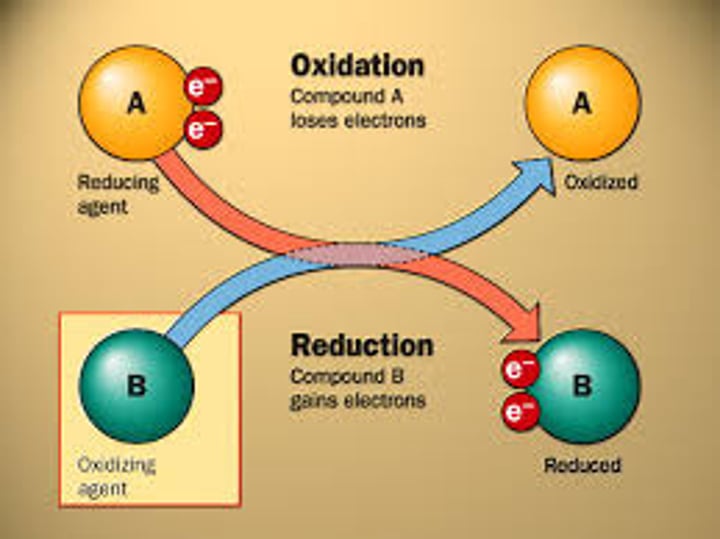
reduction
gain of electrons
electrostatic attraction
the attraction between positive and negative charges
electrolyte
a substance that breaks up into ions when it is dissolved in water
PANIC
positive anode negative is cathode
OIL RIG
oxidation is loss, reduction is gain
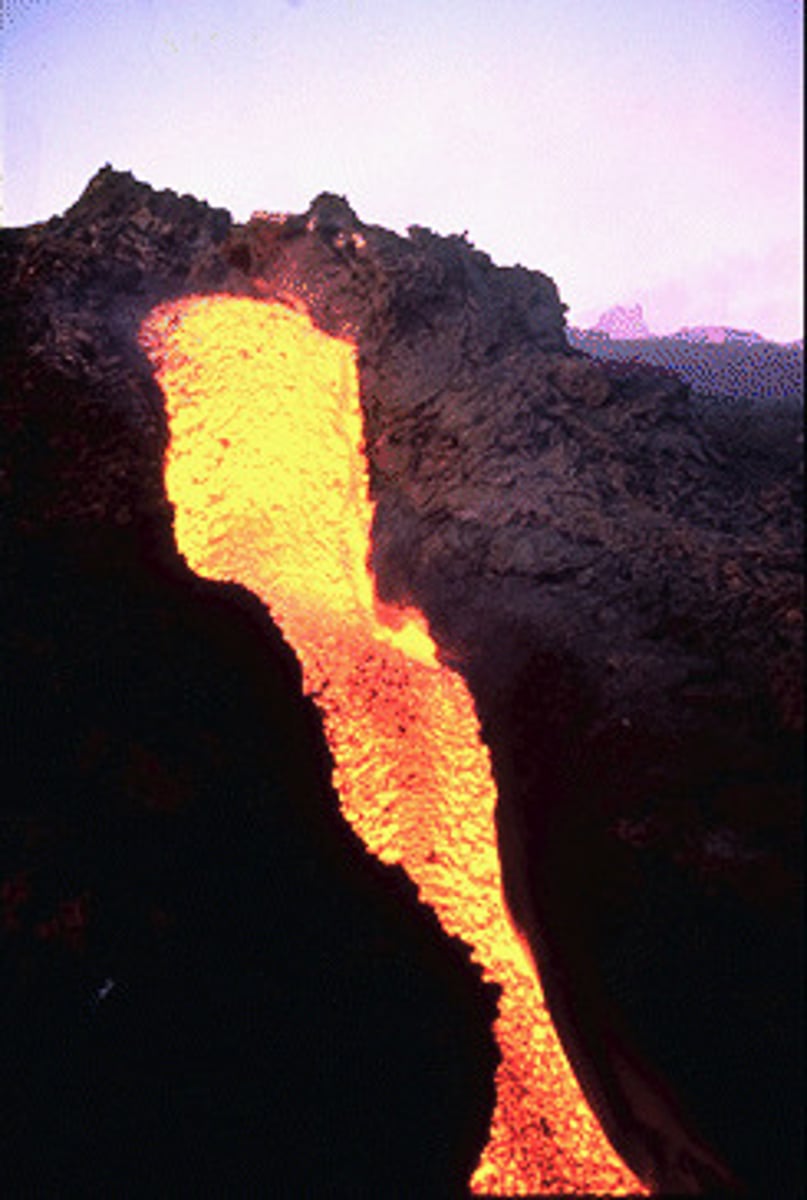
molten
melted

aqueous
dissolved in water
inert
inactive

ions in water
H⁺ and OH⁻

halide
a compound formed with a halogen
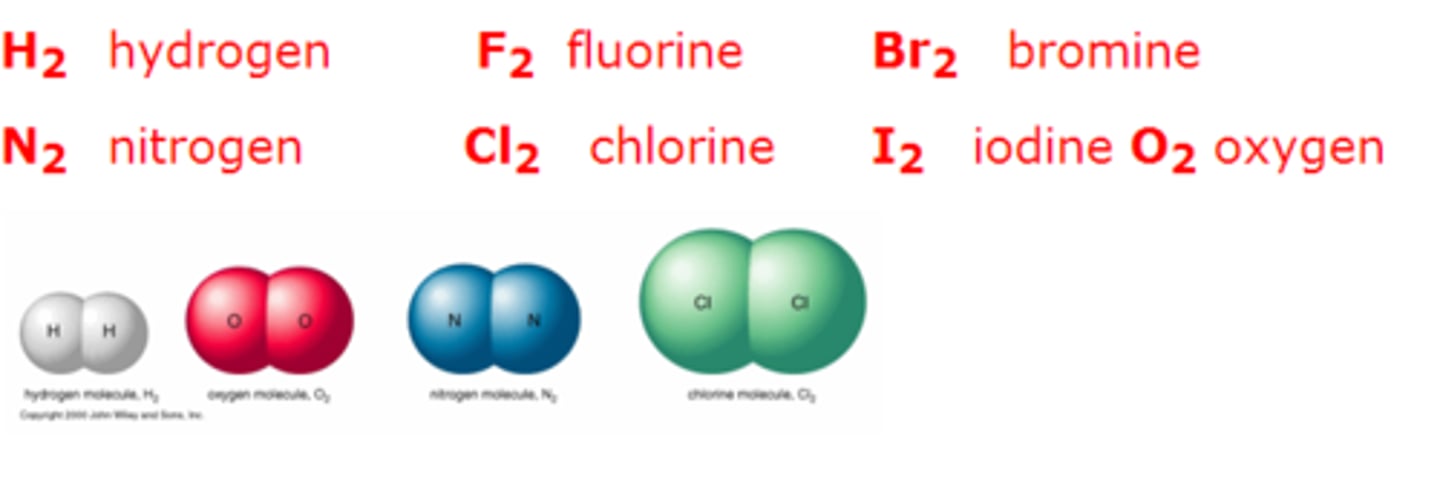
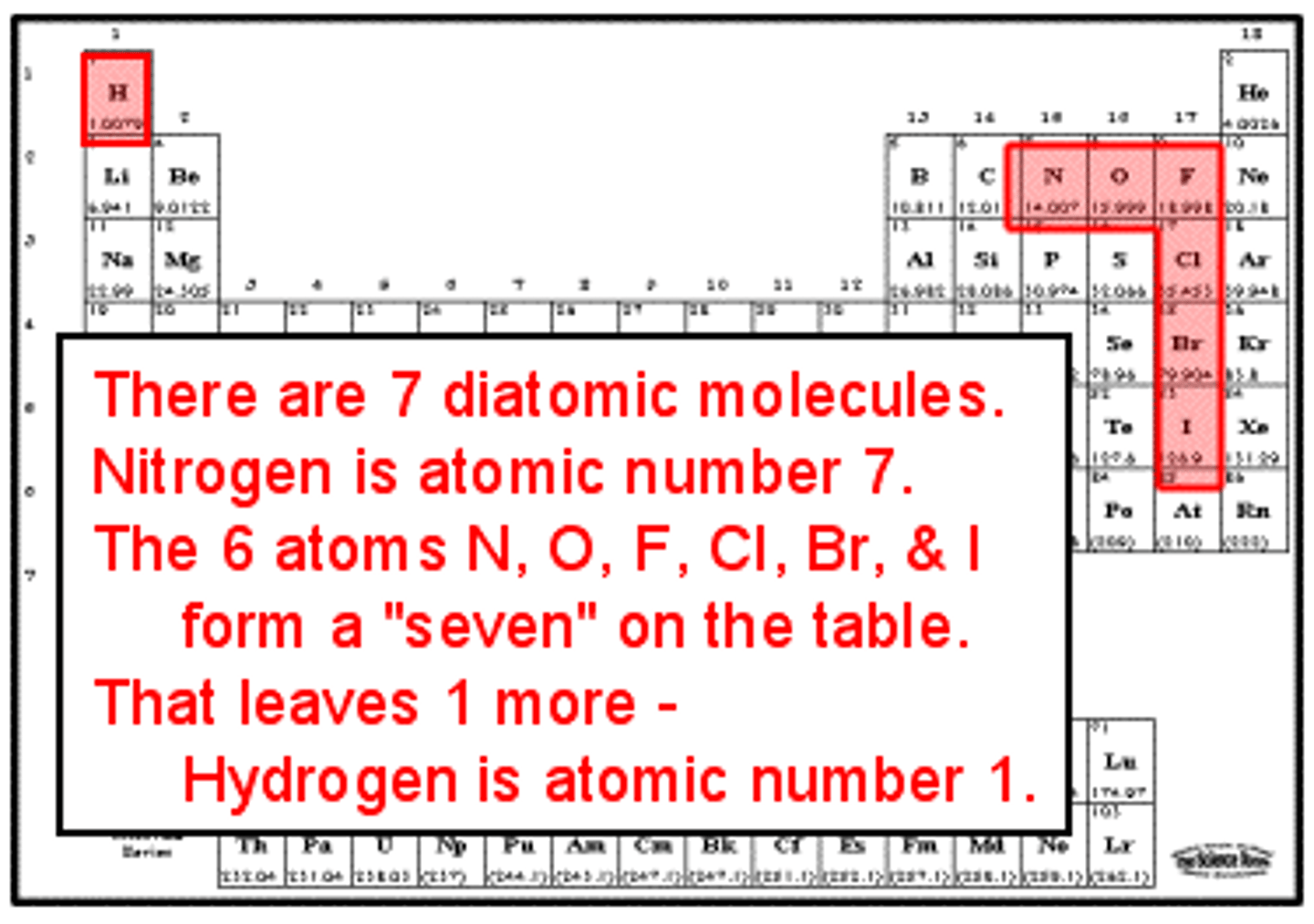
never have fear of ice cold beer
nitrogen, hydrogen, fluorine, oxygen, iodine, chlorine, bromine
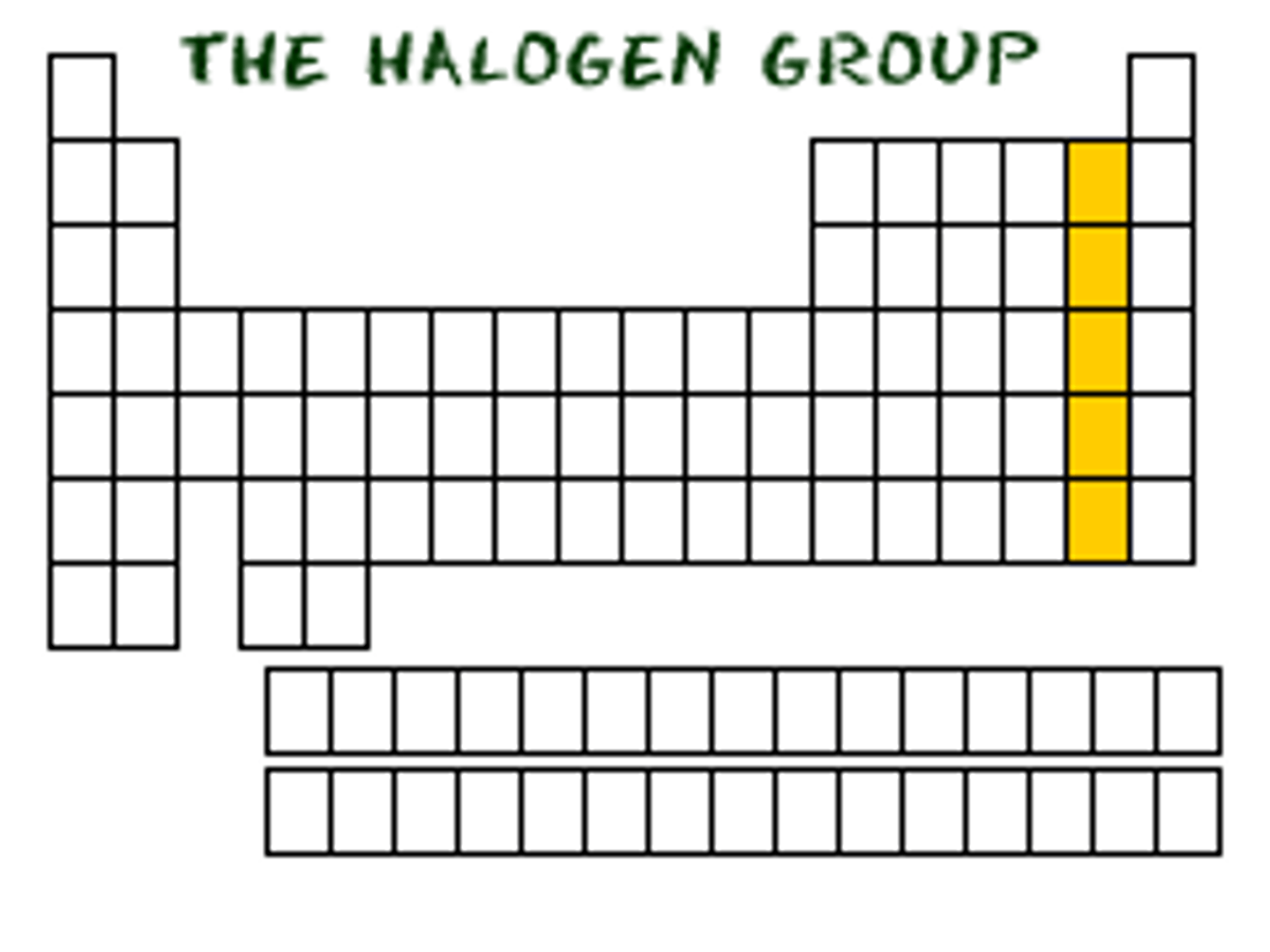
halogen
group 7 elememts
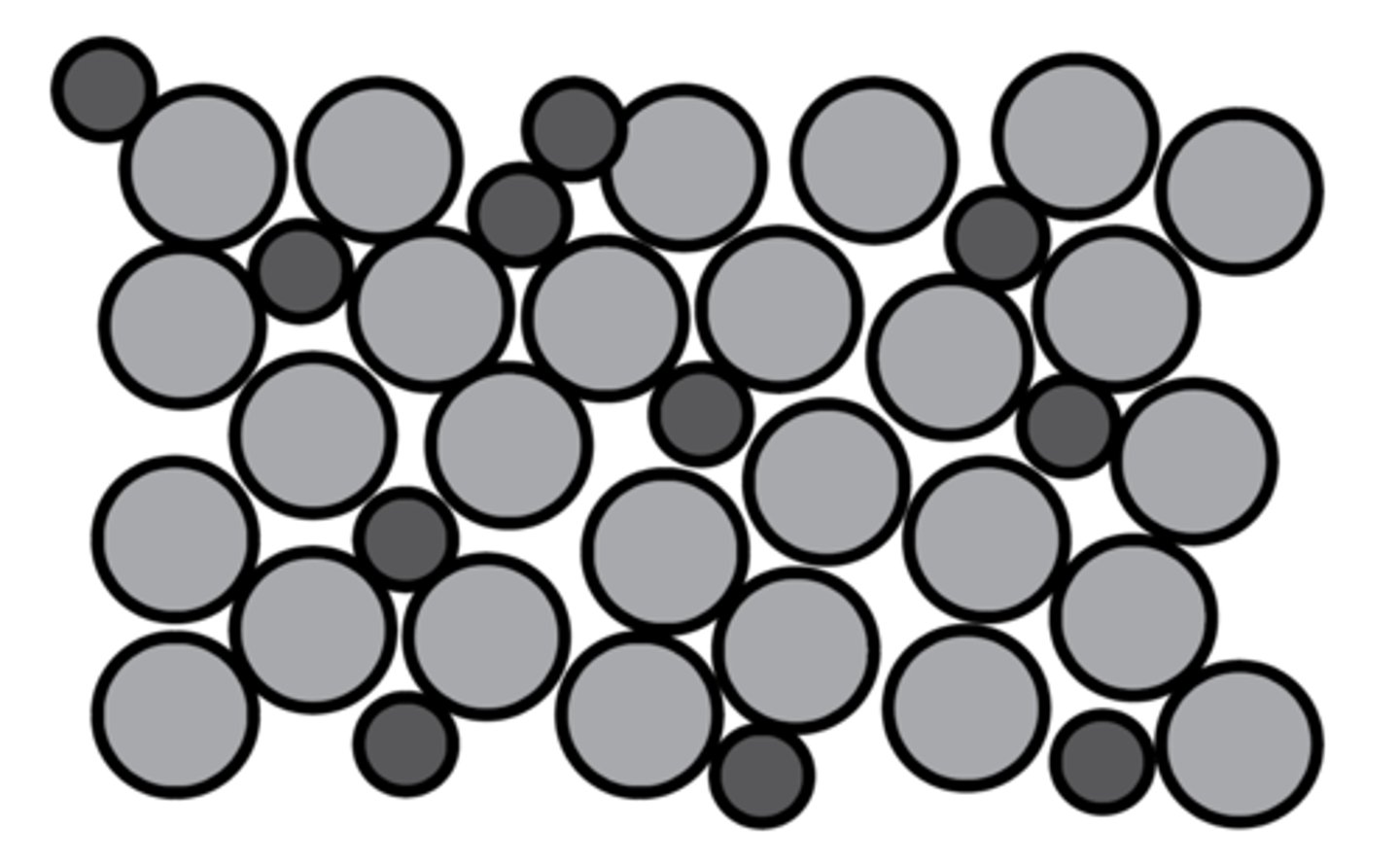
alloy
a mixture of two or more metals
why are alloys harder than pure metals?
the different sized atoms of the metal, make it difficult for the layers to slide over each other
ductile
can be drawn into wires
rules for aqueous solutions
1. lower reactivity metals are discharged instead of H+ ions
2. halide ions are discharged instead of OH-
3. H+ ions are discharged instead of higher reactivity metals
4. OH- ions is discharged instead of sulfate, nitrate, carbonate, hydroxde
hydrogen ion
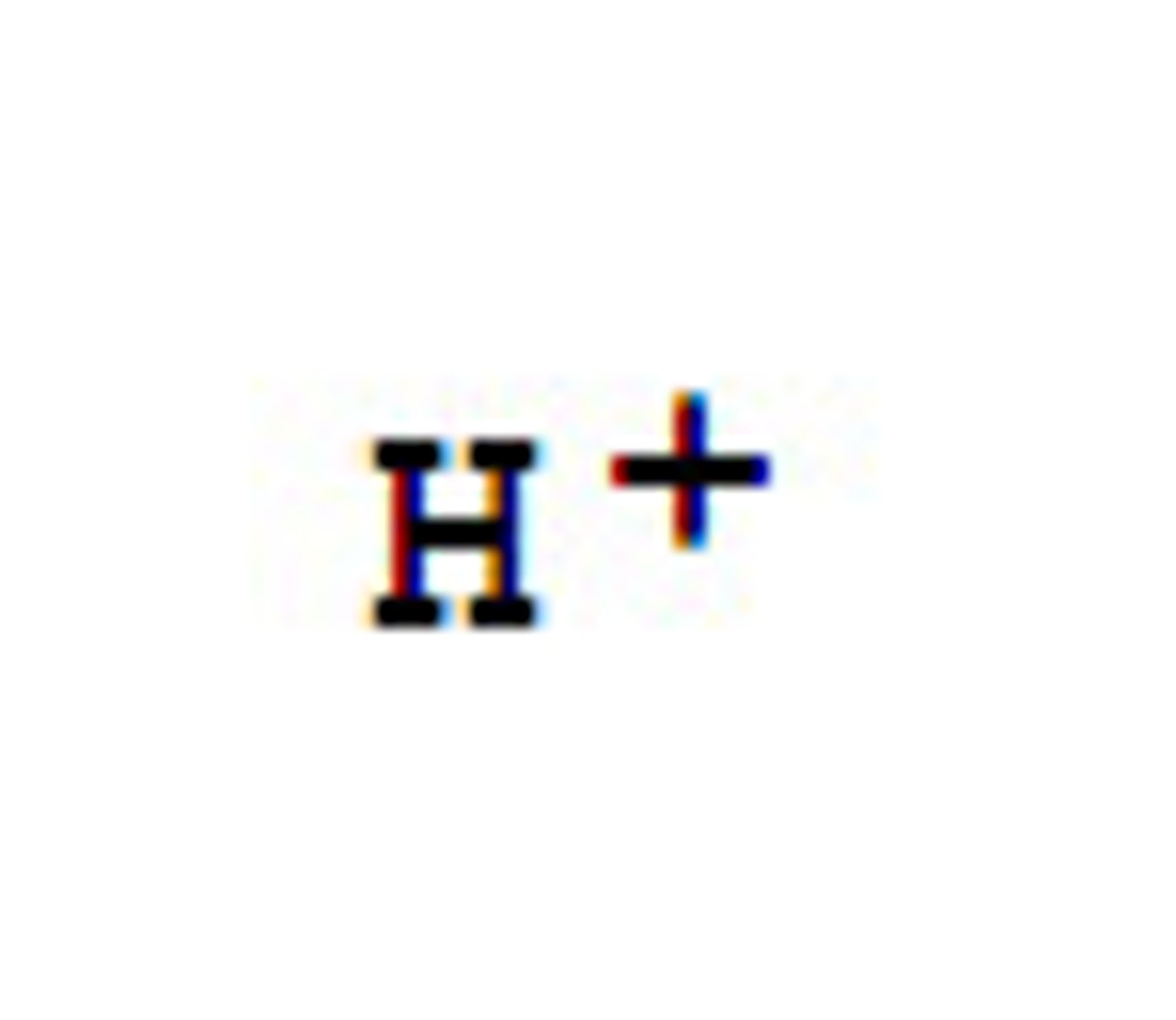
hydroxide ion
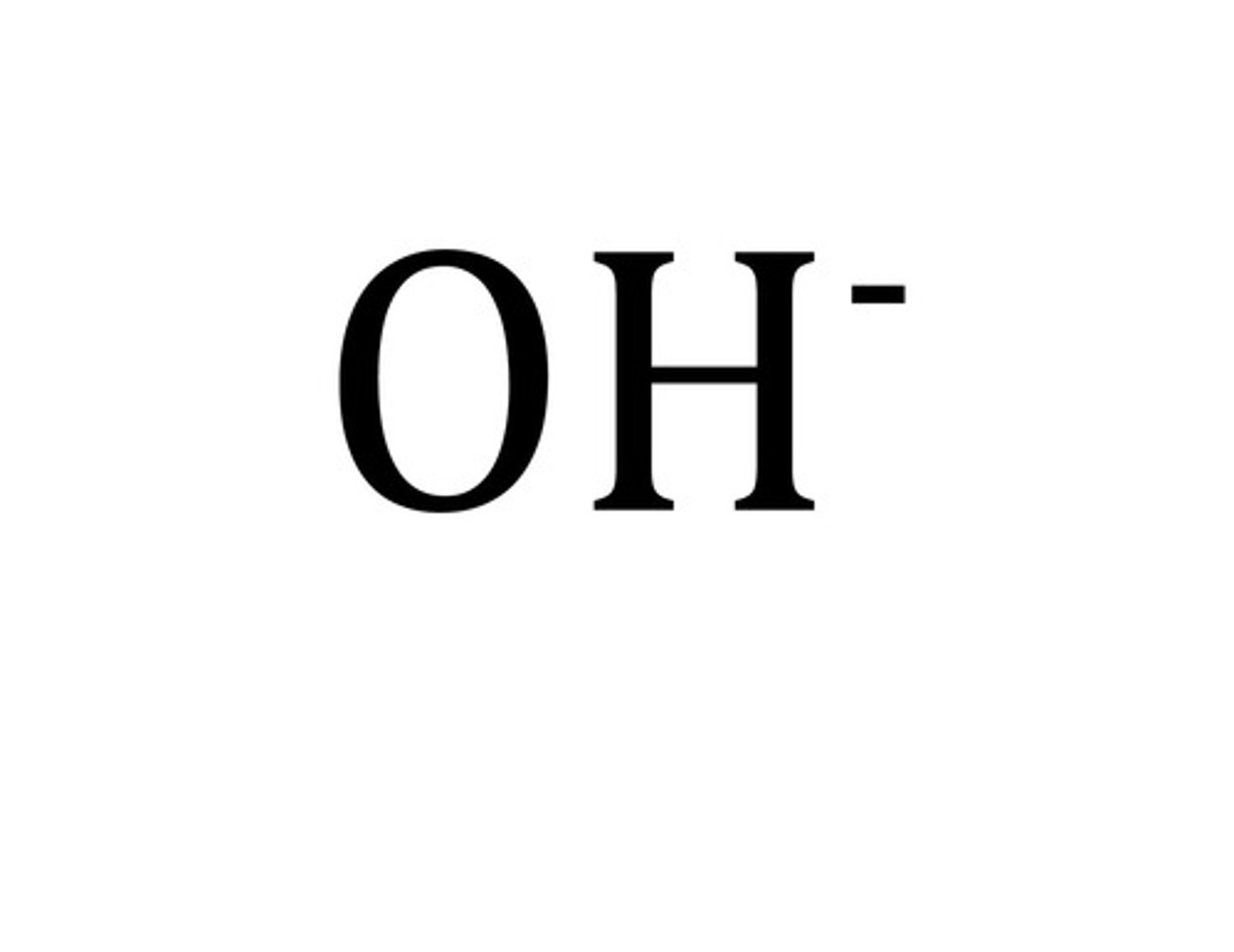
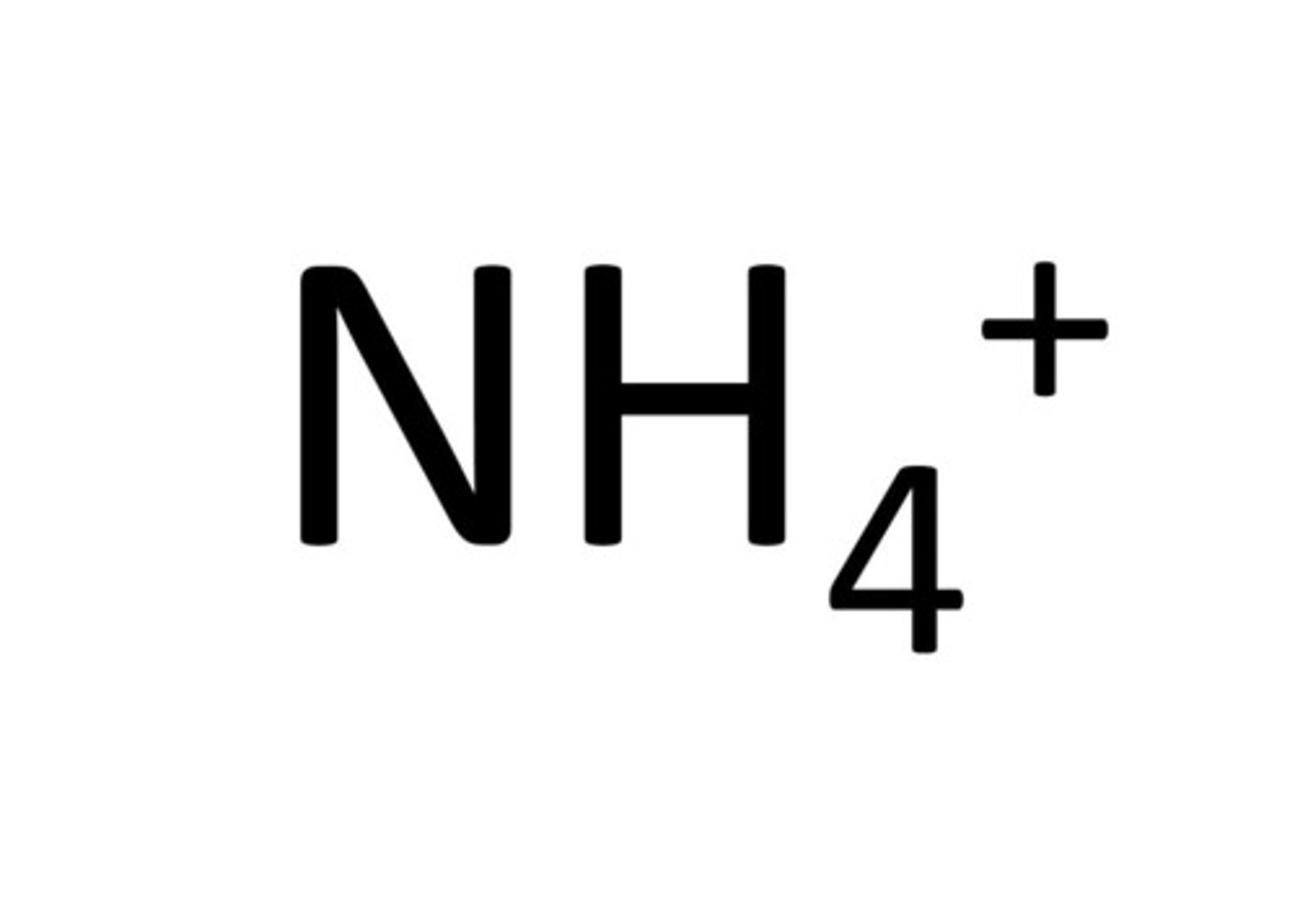
ammonium ion
carbonate ion
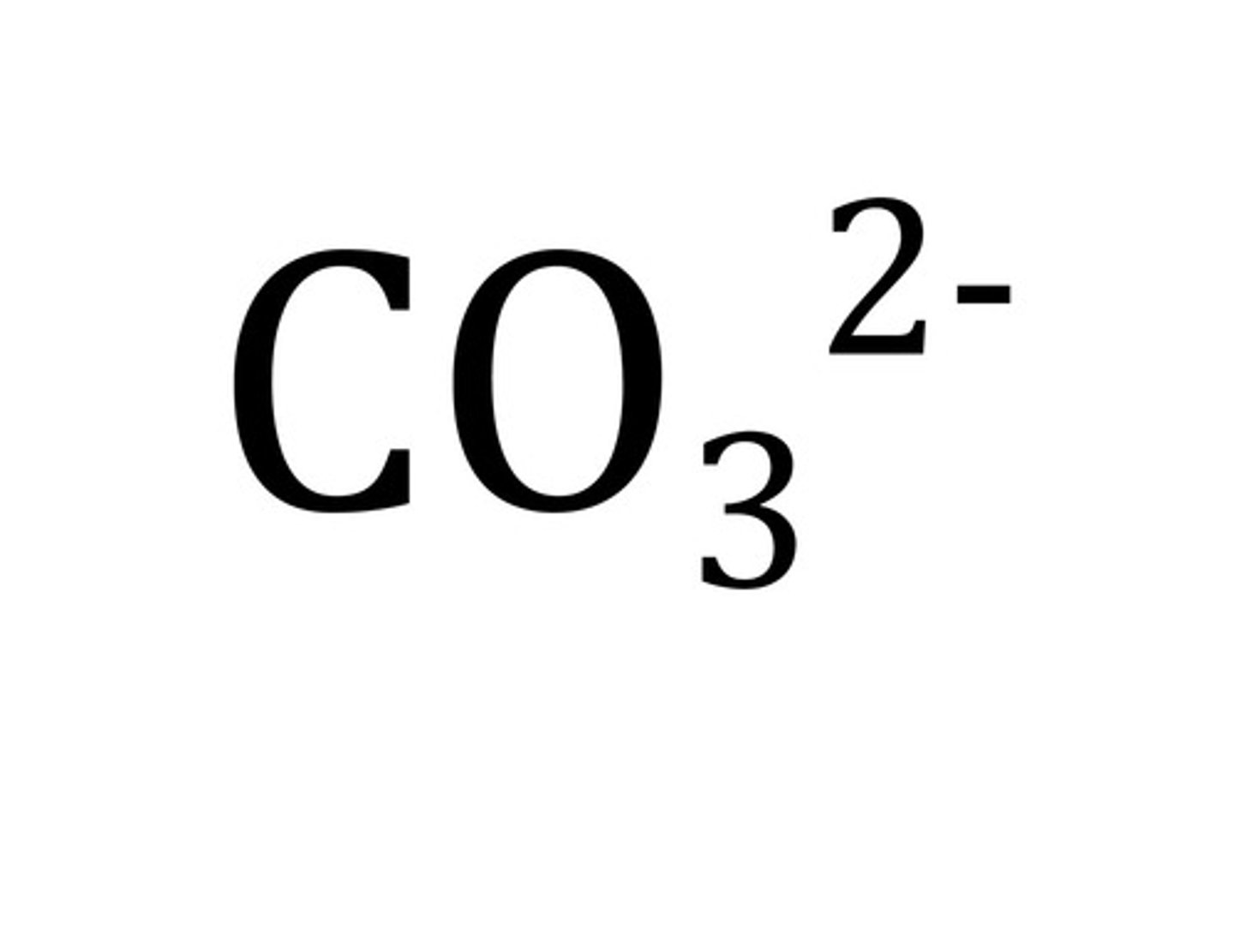
nitrate ion
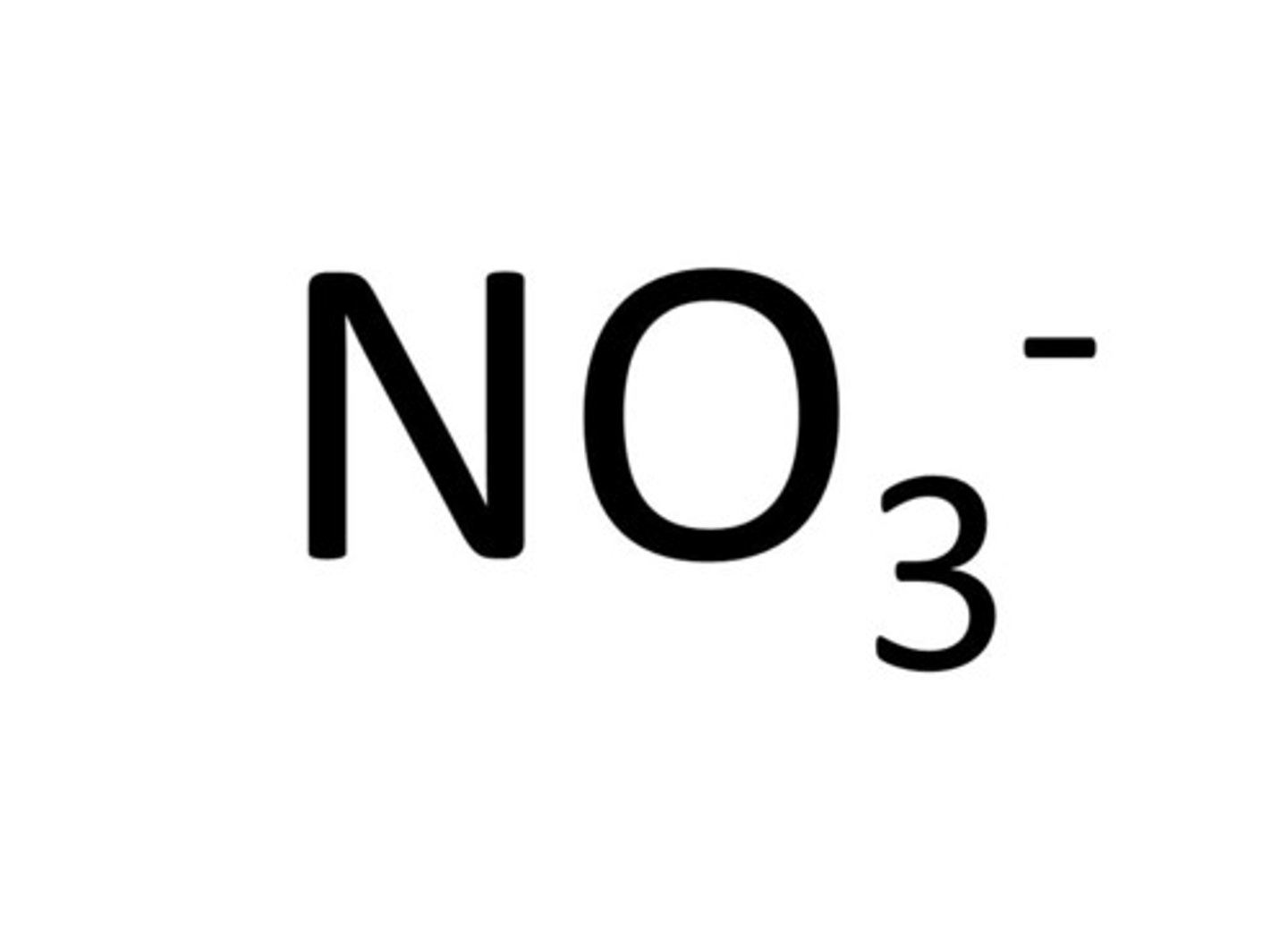
sulfate
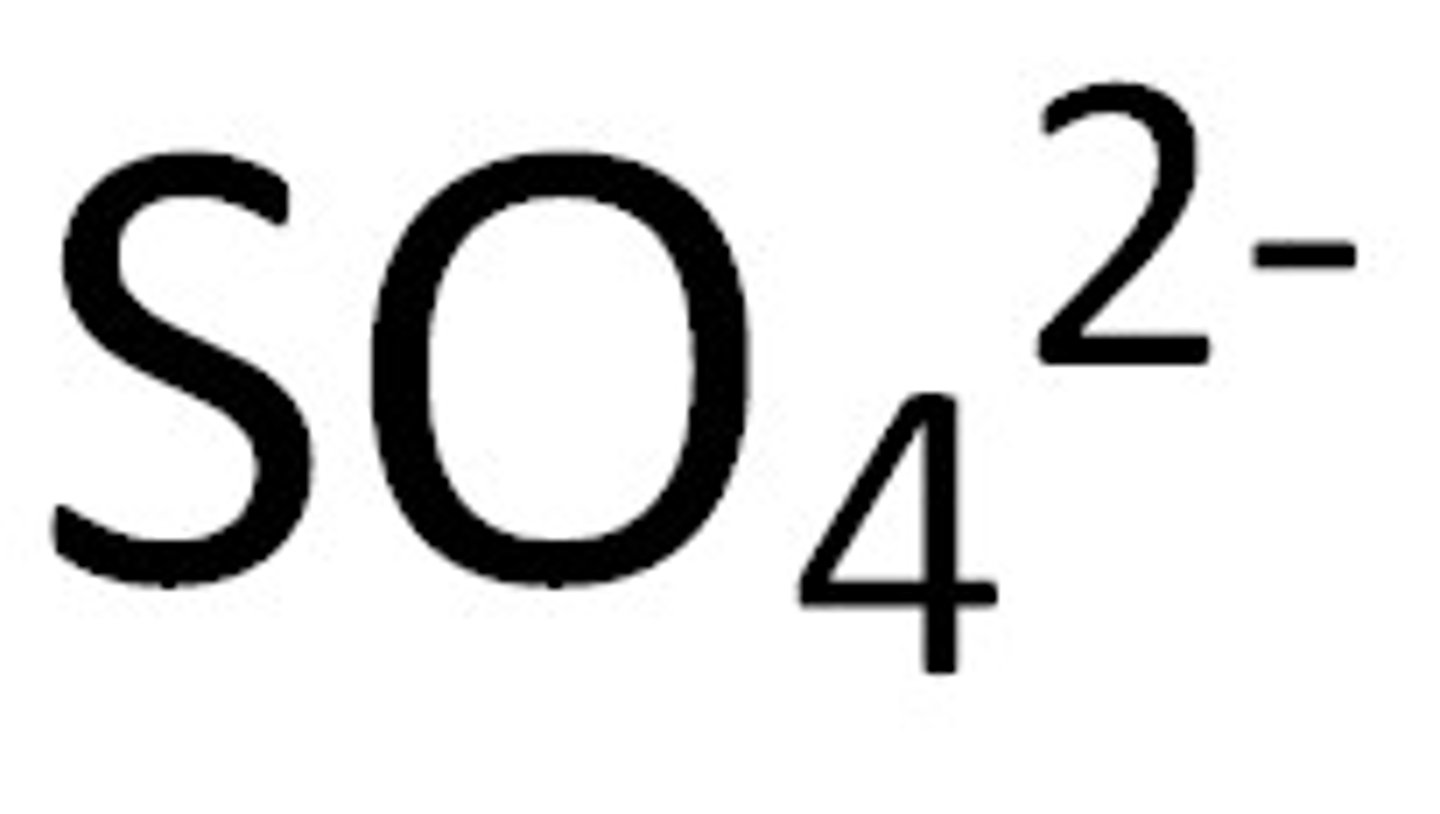
quantitative electrolysis
the amount of substance at an electrode is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity passed
if the litmus paper remains blue or red the solution is ...
neutral
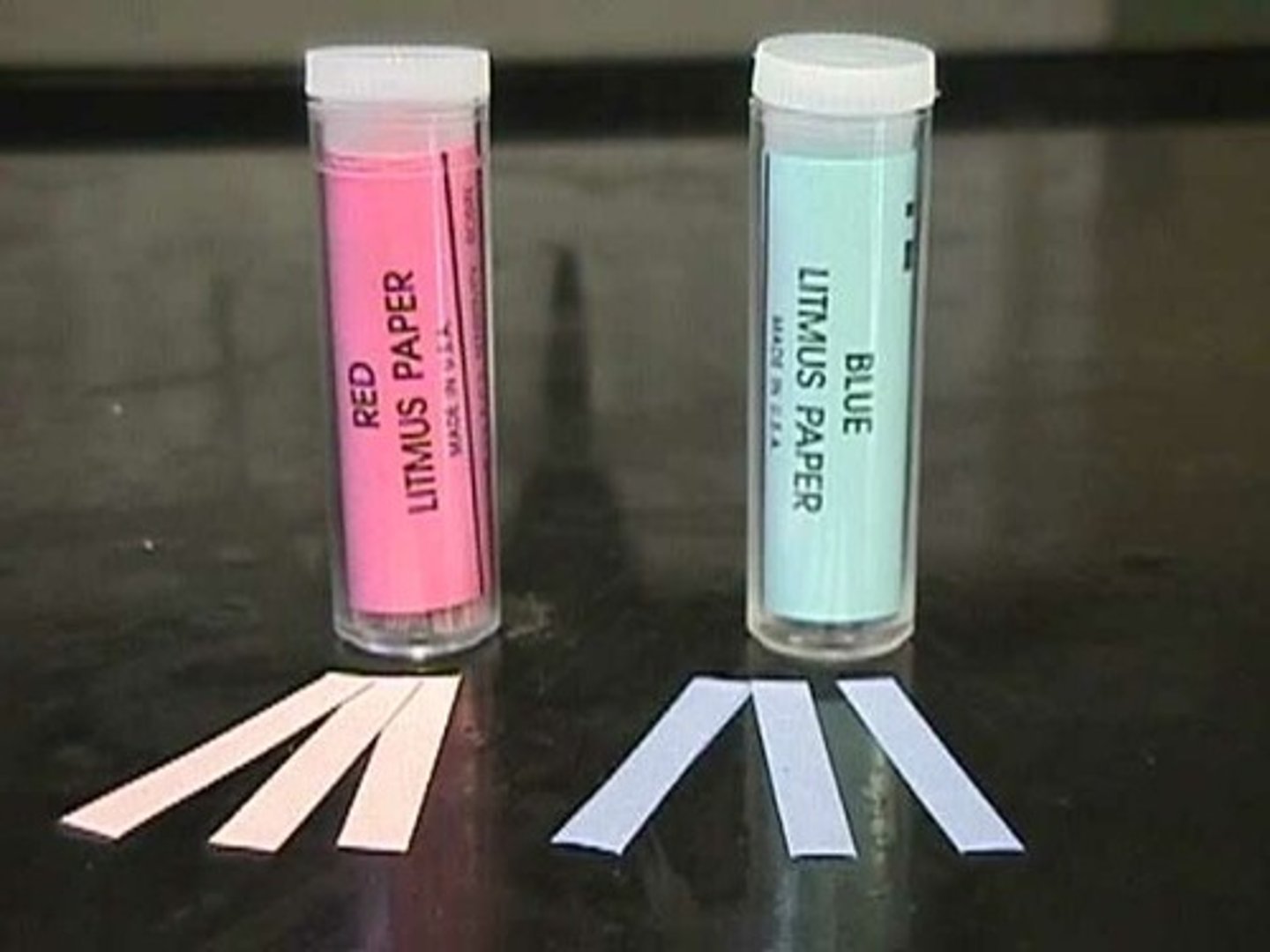

if the red litmus paper remains red and blue litmus turns red the solution is ...
acidic
if red litmus paper turns blue and blue litmus paper remains blue the solution is ...
alkaline
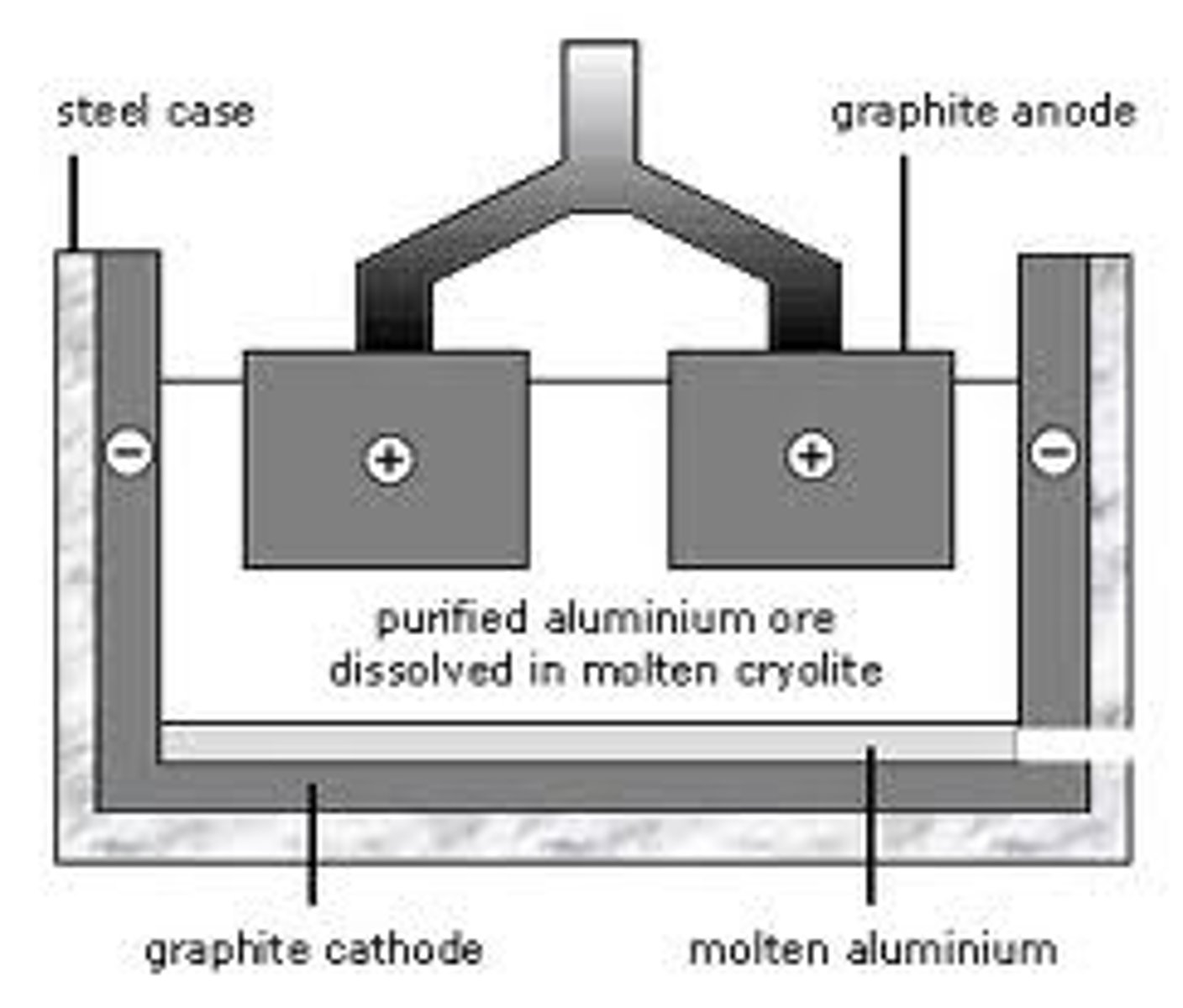
what are electrodes made of?
graphite
acidic
pH less than 7
neutral
pH of 7
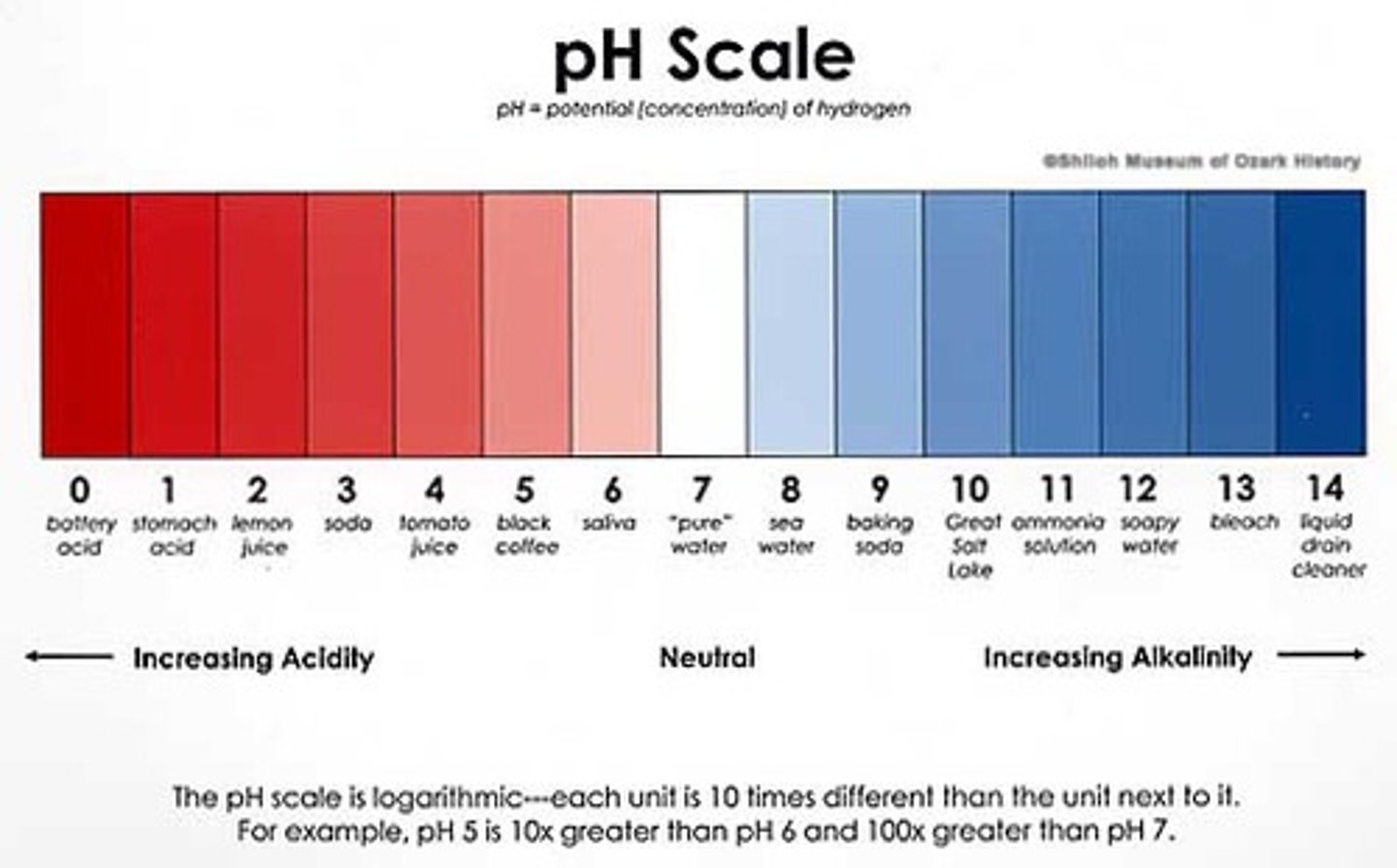
alkaline
having a pH greater than 7
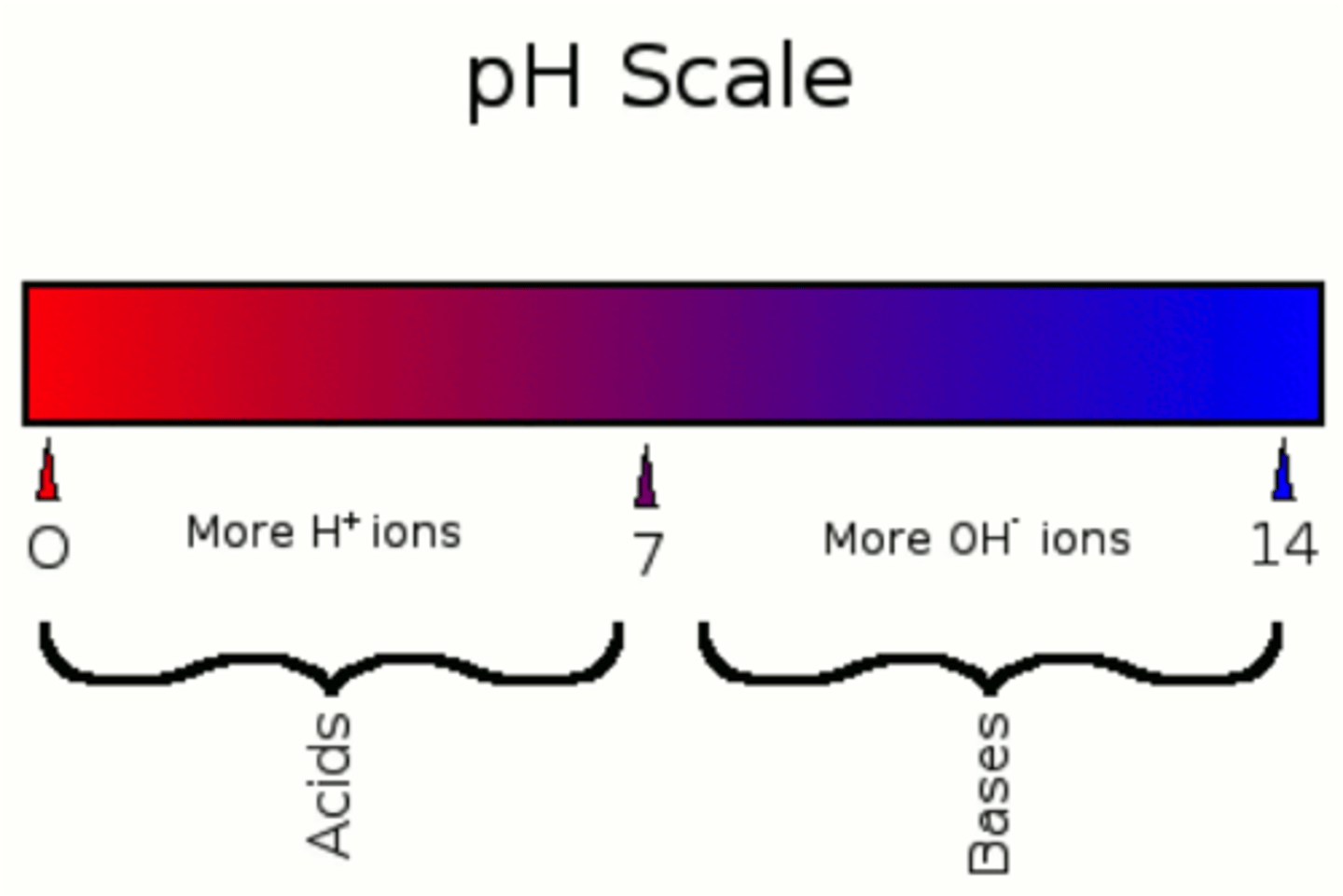
why can't covalent compounds conduct electricity?
because there are no ions present to carry the charge
redox
reduction and oxidation
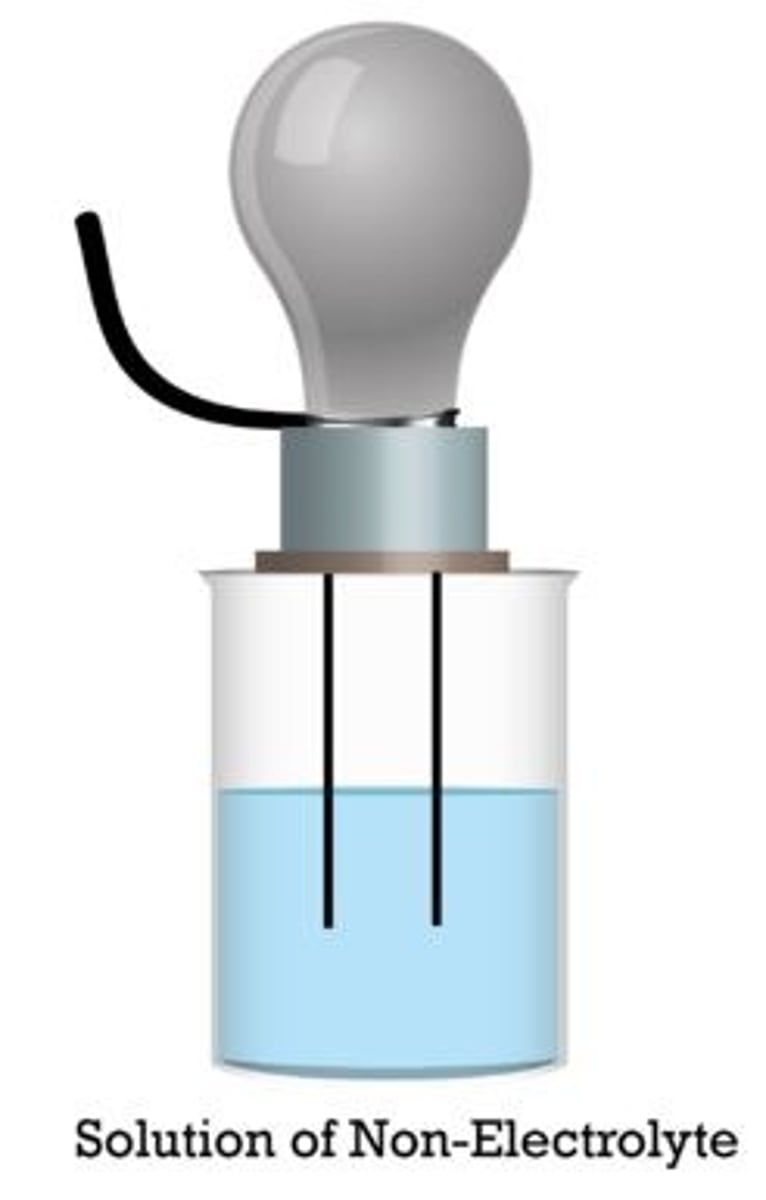
nonelectrolyte
has no freely moving ions when dissolved
OH- forms
oxygen
reactant
chemical substance that is present at the start of a chemical reaction
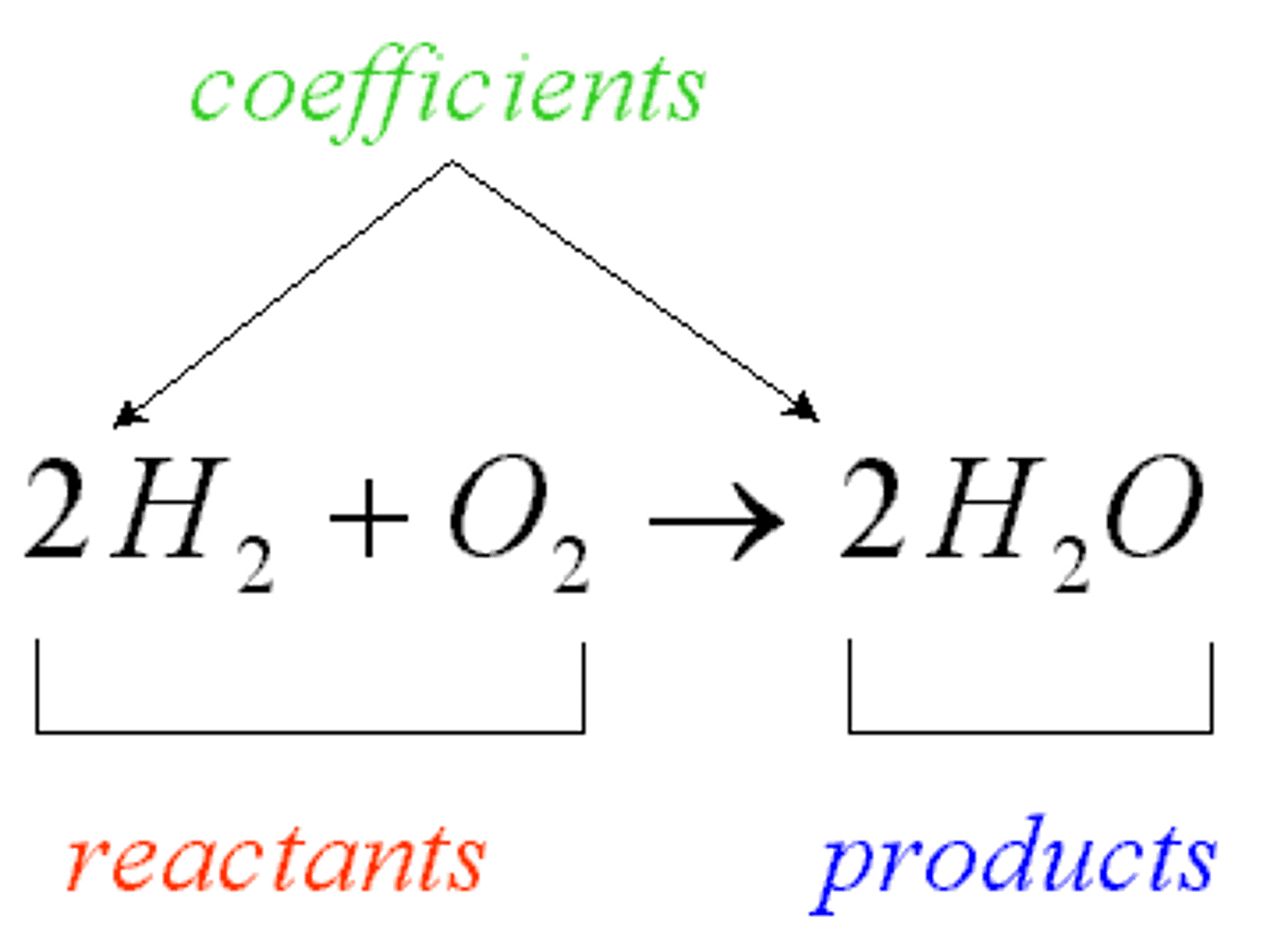
products
ending materials in a chemical reaction.