Diagnosis of Lung Pathogens Causing Pneumonia
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
S. Pneumoniae Identification
Conventional methods: morphological appearance (diplococci, gram positive)
Molecular detection (PCR)
Antigen test detecting C polysaccharide cell wall antigen
Conventional Methods
appearance
gram stain
α-hemolysis of blood agar
Quellung positivity
Catalase negativity
Optochin susceptibility
Bile solubility
get sample from
Mainly Sputum
blood agar culture
alpha hemolytic colonies
microscope
gram positive
diplococci
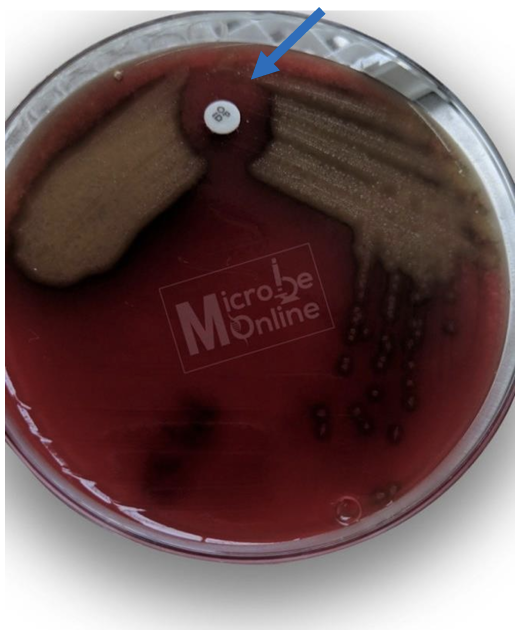
Optochin susceptibility test sensitive
-Most of S. Pneumoniae are sensitive to the chemical optochin (ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) hwile other a-hemolytic streptococcal species are resistant.
-Zone of inhibition is 14 mm or greater in diameter with 6 mm disk
amidase enzyme
Bile or bile salts activate amidase enzyme present in S. Pneumoniae resulting in organism lysis.
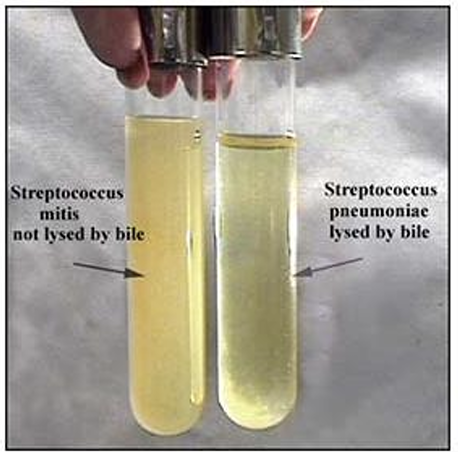
Bile solubility test
Streptococcus pneumoniae is bile soluble (lysed) whereas all other alpha-hemolytic streptococci are bile resistant.
The bile (2% sodium deoxycholate) solubility test distinguishes Streptococcus pneumoniae from all other alpha-hemolytic streptococci

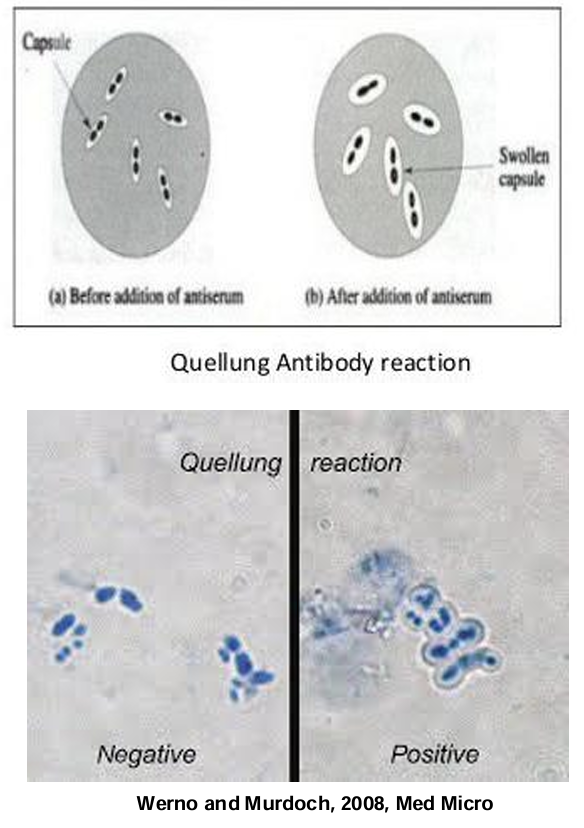
Quellung (swelling) reaction / Capsular swelling reaction
-Add specific antiserum (anti-capsular antibodies)
-If S. pneumoniae is present pneumococcal capsule will bind AB causing a microprecipitin reaction on the surface of the Streptococcus pneumoniae (swollen capsule).
—> also can occur in klebsiella pneumoniae
Sequential Scheme for Streptococcus pneumoniae Diagnosis
Collect Clinical Sample
Gram Stain Examination
Culture on Blood Agar (hemolysis)
Optochin Sensitivity Test + Bile Solubility Test (if optochin less than 14mm)
Antigen (quelling reaction= Gold standard) & Molecular Testing (PCR for pneumolysin/capsular genes)

Klebsiella pneumoniae
Gram Negative
Short Plump rods (like h.influenza)
Klebsiella pneumoniae test
Diagnosis (sputum, urine, blood, nasal secretions)
(Lactose fermenting species will grow pink colonies).
Urinary antigen test (detect Ag in urine)
PCR
Serology (Abs in serum)
Catalase test –Positive
Urease test –Positive (phenol red indicator-ammonia-Alkaline)
Triple Sugar Iron Test (TSI)
Acid/acid (yellow but and slant)
No hydrogen sulfide (H2S) production
Production of gas
Urease Test
-The urease test is a biochemical test used to detect the presence of the enzyme urease, which hydrolyzes urea into ammonia (NH₃) and carbon dioxide (CO₂).
-This reaction increases the pH, leading to a color change in the medium.
-klebsiela and H.pylori have urease enzyme
Urease Test principle
• Some bacteria produce the enzyme urease, which breaks down ureainto ammonia and carbon dioxide:
• The release of ammonia increases the pH, making the medium alkaline.
• The phenol red indicator in the medium changes color based on pH:
• pH < 6.8(acidic) → Yellow
• pH > 8.2(alkaline) → Bright Pink/Magenta

cultures for klebsiella
MacConkey
Blood
Nutrient
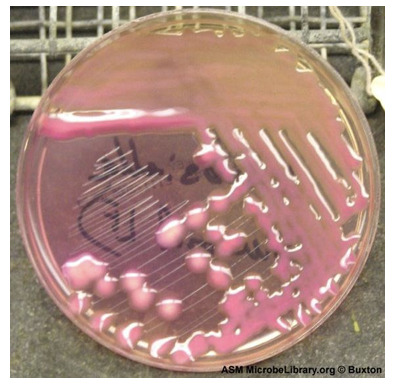
MacConkey agar
Mucoid, pink, round and elevated colonies
Lactose fermenting species will grow pink colonies
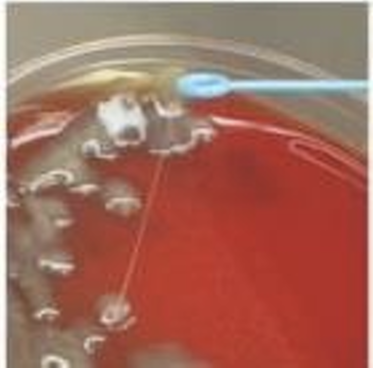
Blood agar
Gummy feature of the colonies due to the capsule, can be checked by string formation with a wire loop.
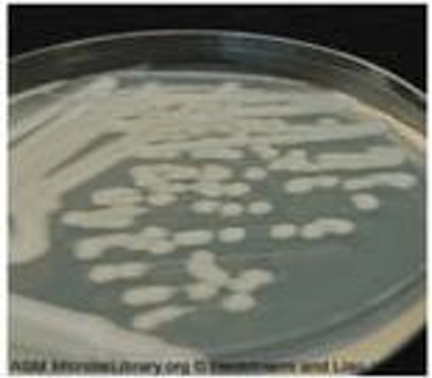
Nutrient agar
Colonies are large, thick, greyish white, mucoid, smooth and opaque.
Sequential Diagnostic Scheme for Klebsiella pneumoniae
1.Sample Collection
1. Sputum, blood, urine, or wound swab (depending on infection site).
2.Microscopy & Staining 1. Gram Staining → Gram-negative, encapsulated bacilli.
2. Capsule Staining (India Ink/Quellung Reaction) → Prominent capsule.
3.Culture on Selective & Differential Media
1. MacConkey Agar → Lactose fermenter (pink colonies).
2. Blood Agar → Mucoid colonies due to capsule.
4.Biochemical Tests
1. Indole Test → Negative.
2. Methyl Red (MR) Test → Negative.
3. Urease Test → Positive.
4. Catalase Test → Positive.
5.Molecular & Serological Tests
1. PCR for Capsular (K) and Lipopolysaccharide (O) Antigens.
Legionella pneumophila (pneumoniea) characteristics
-gram
-oxygen
-capsule
-shape

![<p>Culture on buffered charcoal yeast extract extract ((BCYE] agar) high in iron and cysteine)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6b3bee07-cf03-4efd-8a09-f766b86cddcc.png)
Culture on buffered charcoal yeast extract extract ((BCYE] agar) high in iron and cysteine)
(Gold Standard; but slow)
Small, gray-white colonies in 3-5 days
Legionella pneumophila
Urinary antigen test (detect Ag in urine using ELISA)
Rapid and highly specific, but detects only serogroup 1
PCR
Detects L. pneumophila DNA in sputum or lung tissue
Highly sensitive and rapid
Serology (Abs in serum)
4-fold rise in antibody titers, Retrospective; not useful for acute diagnosis
gram staining
Poor staining, weakly Gram-negative rods