Chapter 27
1/41
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
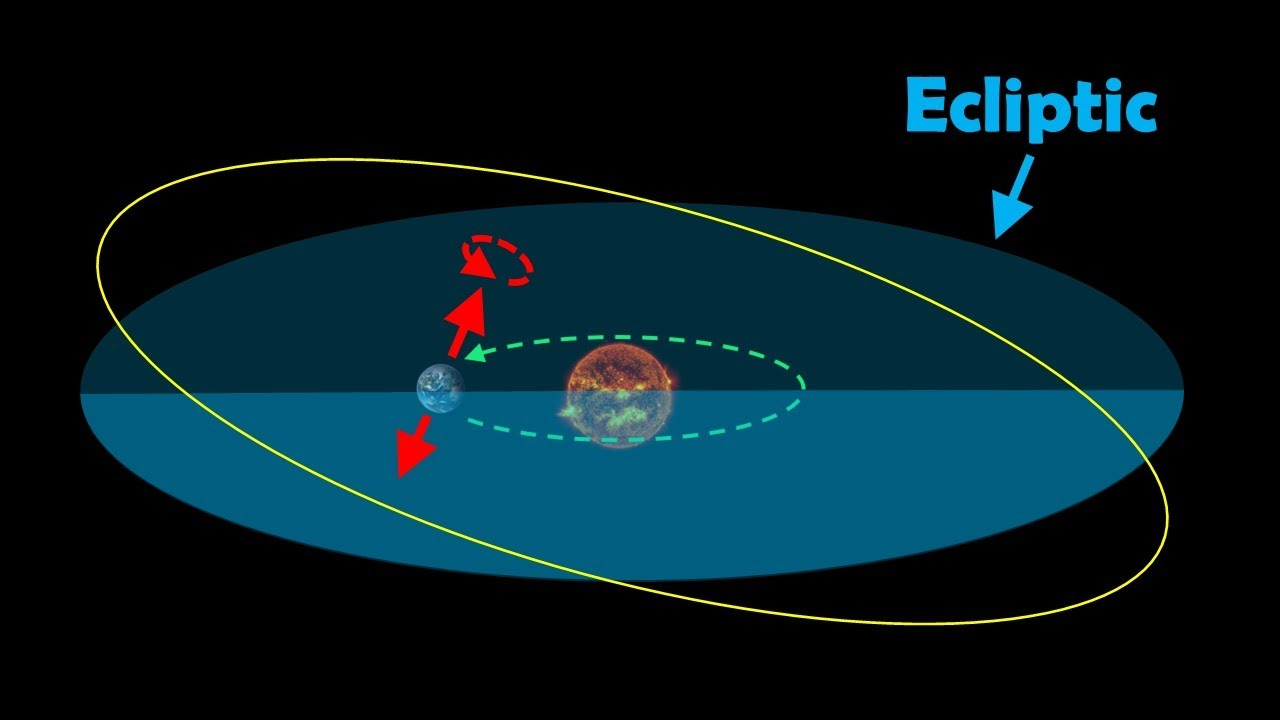
The ecliptic
is the plane of Earth’s orbit
The Sun tends to bloat outward from nuclear fusion, and contract due to
gravity
In what region of the Sun is solar energy generated?
the inner core
With daytime temperatures that can reach 430°C, why is nighttime on Mercury so cold?
very little atmosphere, so heat is lost to space
The Large Magellanic Cloud is
a) an irregular galaxy colliding with the Milky Way galaxy.
b) an unusually bright planetary nebula.
c) a bright nebula within our galaxy.
d) the farthest known object visible to the naked eye in a clear nighttime sky.
a
Describe Mar’s amtosphere what what effect it has?
thin, cold

Describe a quasar in 3 words
energetic, disant, puzzling
Where is our solar system?
Milky way, spiral
The most common galaxy shape is
elliptical
In a museum collection you can likely see a
meteorite not meteoroid
a group of stars named by old astronomers, existed for centuries.
constelation
Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, and Cassiopeia are part of the 88 ___ in the night sky.

constellations
Is the Big Dipper a constellation?
No, it is apart of the Ursa Major
The pairs of stars at the end of its bowl point to ___, the North star. (Tail or Ursa Minor)
Polaris
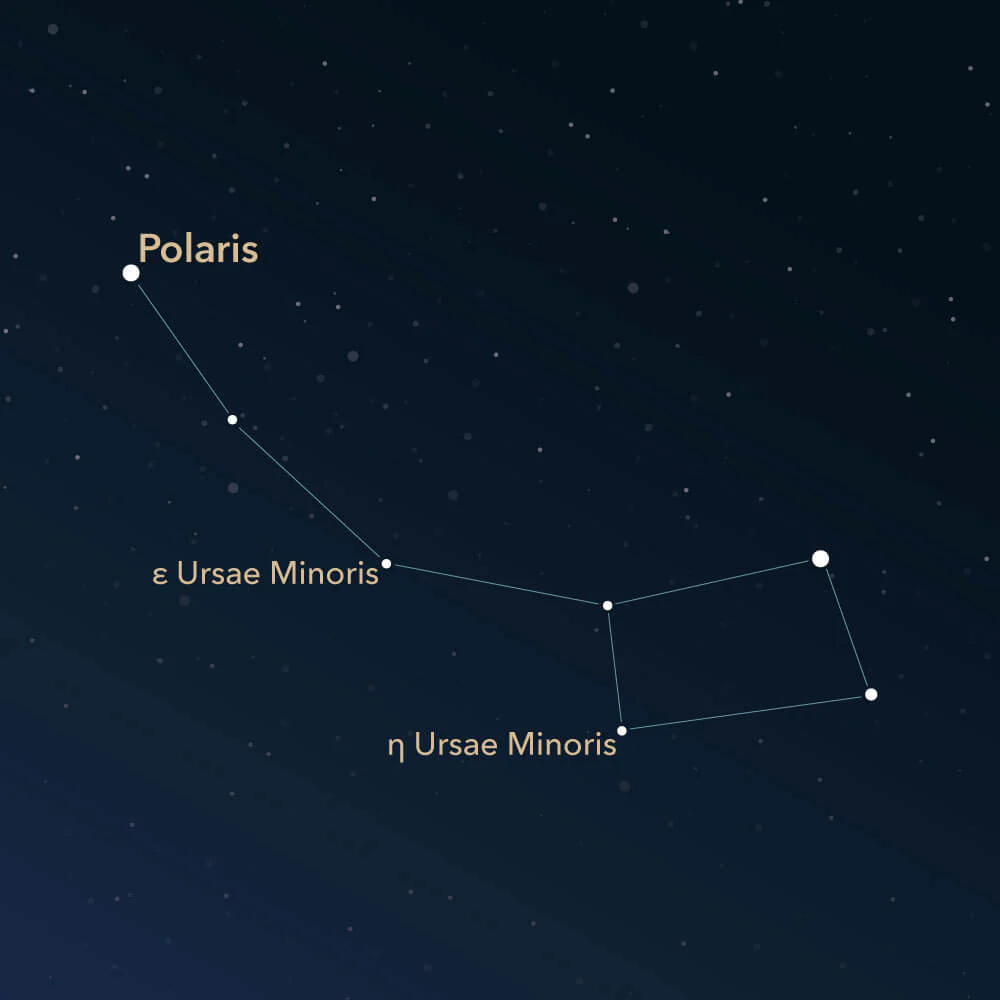
Constellations are all very different ____ from Earth.
distances
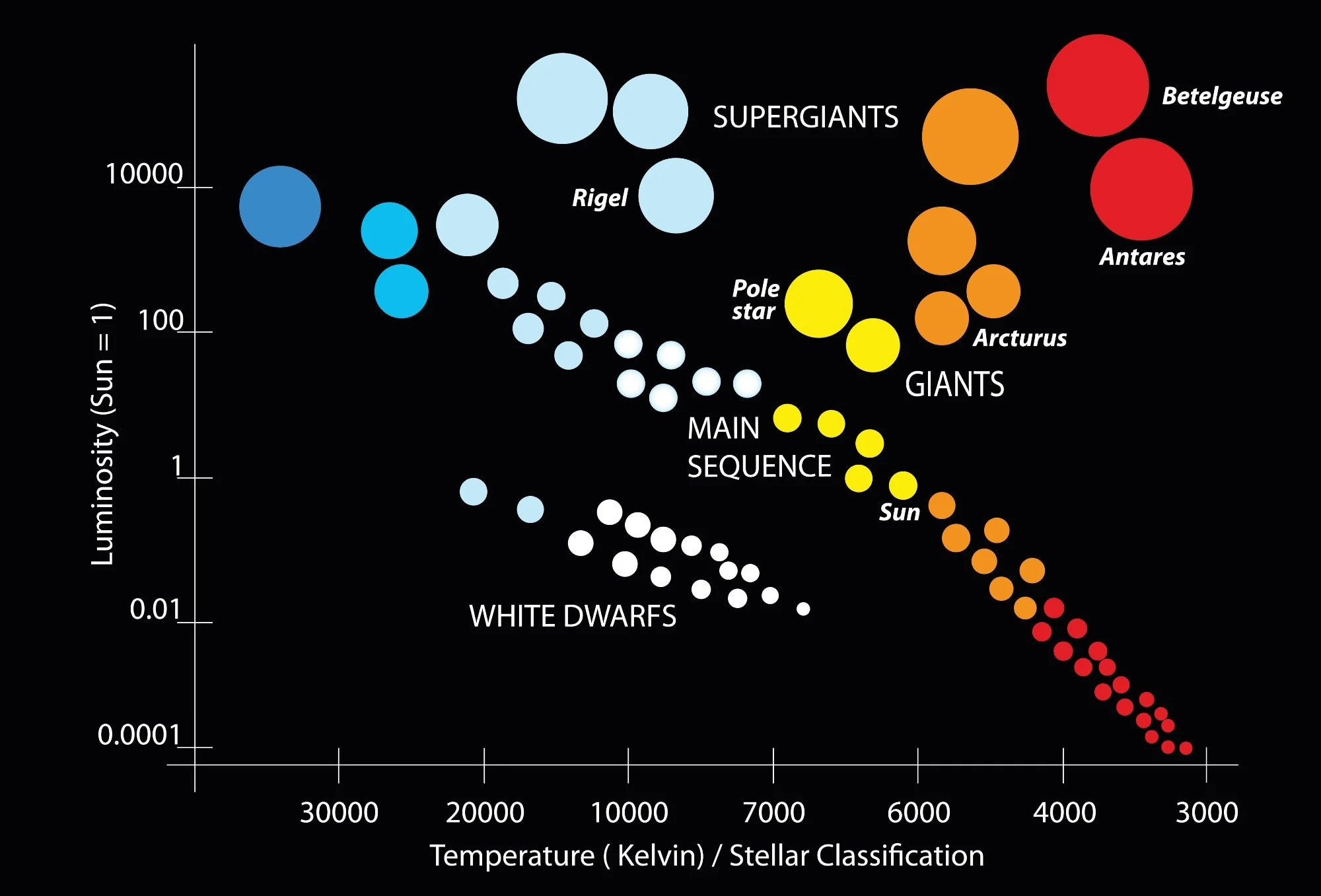
What is the hottest star according to color?
Blue
A blue star is 2x. hotter than a ___ star.
red
Give an example of the hottest blue star
Sirrus
Give an example of the coolest red star
Beetlejuice
T/F - The sun is hot, which is why it emits a yellow hue.
F, due to scattering of light
All stars begin as a
nebula

Nebula
large cloud of gas and dust in space
To transfer from nebula to a prostar, the core temperature reaches 10 million K, which is hot enough to begin ______ of ___ and ____.
thermonuclear fusion
hydrogen
helium

The primary energy source for the sun is
thermonuclear fusion
If thermonuclear fusion emits so much energy, why don’t stars explode?
Hydrostatic Equilibrium
What outward force keeps stars stable?
thermal pressure
What inward force keeps stars stable?
gravity pulls it inwards to try to collapse it
White dwarfs are high or low mass stars?
low
What am I describing?
Cools for eons until too cold to emit light
“Dead stars”, that continue to slowly shrink
White dwarf
White Dwarfs are part of a binary, so it pulls matter from its bud <3, which can lead to what?
nuclear blast, nova

Shorter life span
Hydrogen fusion fuel burns at a FASTER rate
High temperature and pressure
High mass stars
Longer life span
Hydrogen fusion fuel burns slowly…
Lower temperature and pressure
Low mass star
A red giant is much heavier than a red dwarfs, which has the shorter life span?
red giant
T/F - Supernovas can be repeated, while novas cannot.
F, supernova = final
nova = bud helps sustain life
When massive stars collapse (explosion)
supernova

Black Holes and Neutron stars are a result of an explosion of
supernovas
When a supergiant collapses into itself due to the inability to generate heavier elements together through fusion
black hole
Spherical, no bulge, M87
Elliptical
Barred, spiral bulge, Milky Way
Spiral
Local clusters are apart of _____
superclusters
The brightest thing in the universe is
a) Sun
b) Neutron Star
c) Eclipses
d) Quasars
d
When a quasar is 1.55 billion light years away, what does that mean?
we see that as they were 1.55 billion years ago