Biological Membranes
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
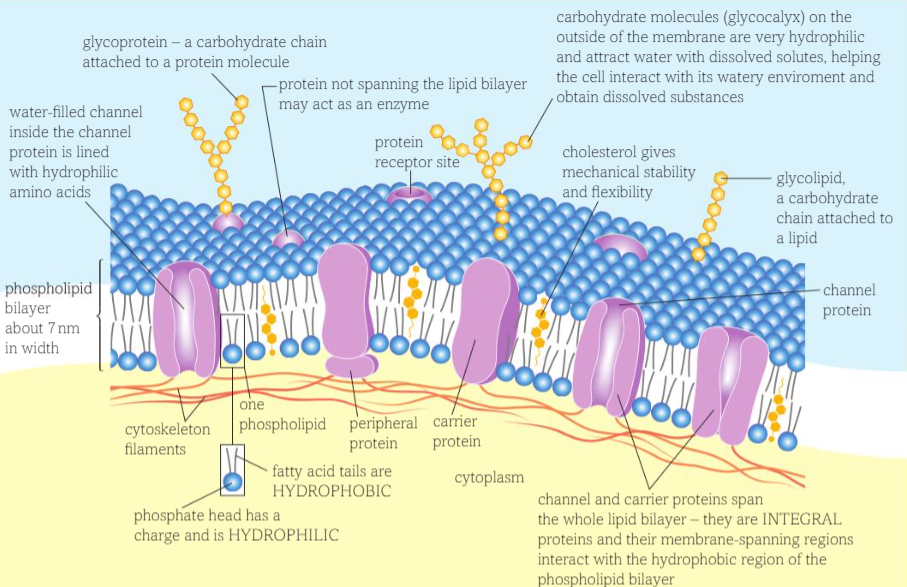
Cell membranes
All cell membranes are composed of a phospholipid bilayer
Partially permeable and the sight of chemical reactions - involved in cell communication
Control the exchange of materials
Seperate the internal and external environments
Substances can cross membranes by diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis and active transport
Fluid mosaic model
The mixture of movement of phospholipids, proteins, glycolipids, glycoprotein the membrane is composed of
Very fluid - phospholipid molecules can move
Mosaic - proteins scattered vary in shape and size
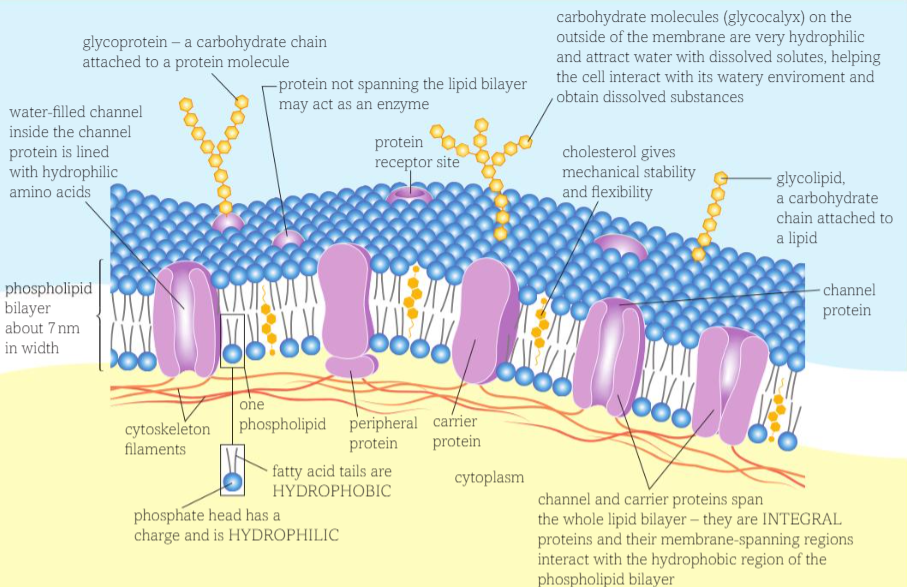
What does the model help explain
Passive and active movement between cells and their surroundings
Cell-to-cell interactions
Cell signalling
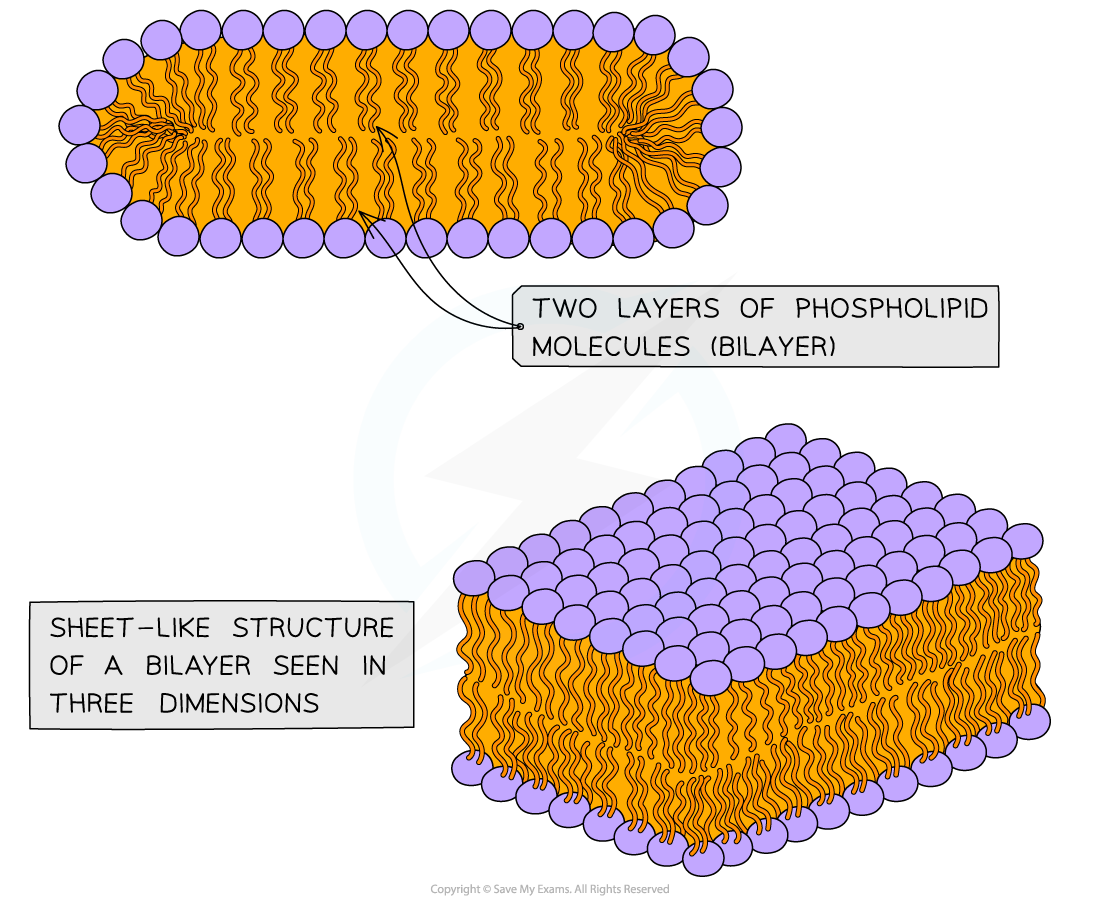
Phospholipid role in model
Align as a bilayer ensuring sugars, amino acids and proteins cannot leak out (due to hydrophobic heads and hydrophilic tails)
Stops unwanted molecules getting in
Composed of two sheet - like layers
About 7nm width
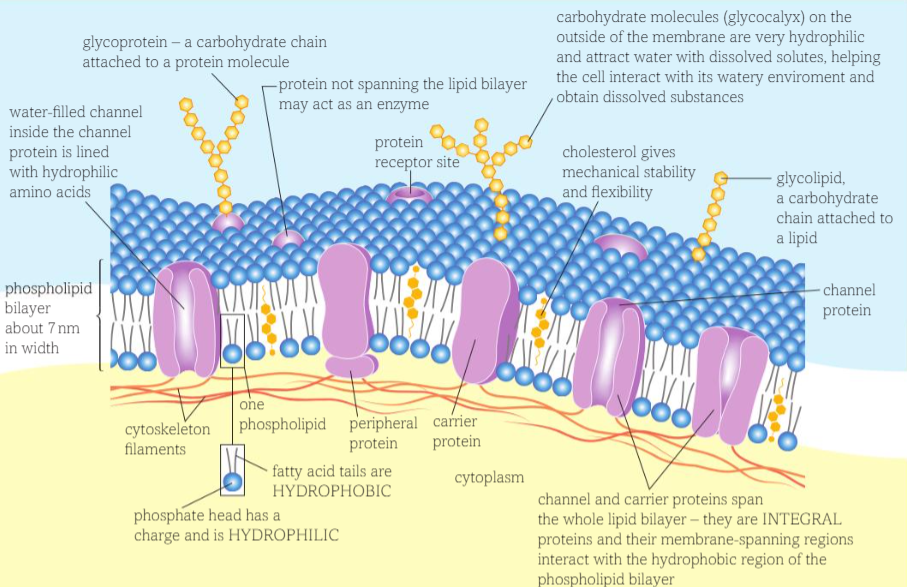
Cholesterol role in model
restricts lateral movement of other molecules in the membrane.
Cholesterol molecules bind to the hydrophobic tails of phospholipids, stabilising them and causing phospholipids to pack more closely together.
Cholesterol increases the fluidity of the membrane, stopping it from becoming too rigid at low temperatures (allowing cells to survive at lower temperatures)
Increases mechanical strength and stability so cell does not burst
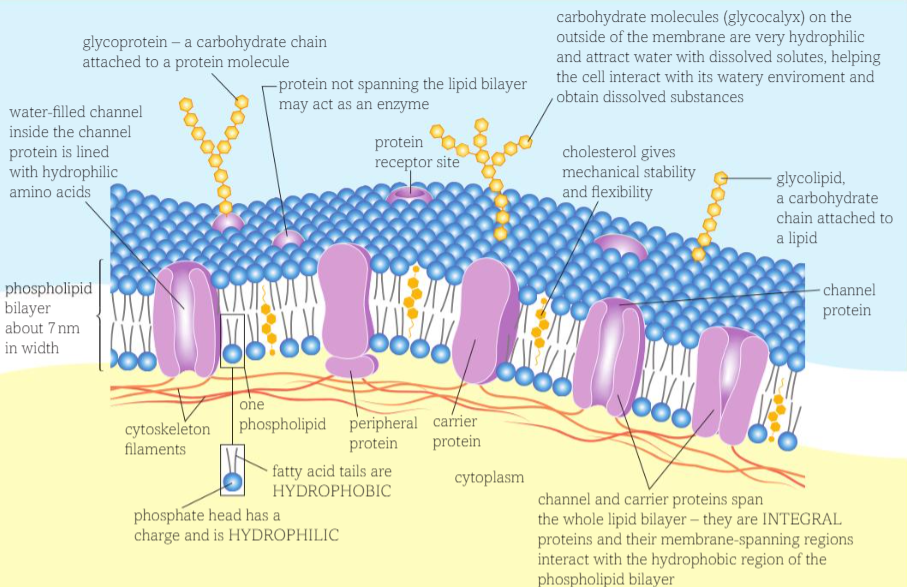
Glycolipids and Glycoproteins role in model?
They contain very hydrophilic carbohydrate chains on the surface of proteins and lipids - attract water with dissolved solutes
They act as receptor molecule for hormone's and drugs
Signalling receptors, endocytosis receptors, cell adhesion receptors (C - H20 H bond)
Act as antigens, for cell recognition of self and non self cells
Hydrogen bonds can form between water molecules and glycoproteins - thus maintaining cell membrane stability
Transport proteins
Channel and carrier proteins - INTEGRAL proteins (completely penetrate layer)
Channel - Create hydrophilic channels with wayer to allow water soluble polar molecules to facilitated diffusion through membrane
Carrier - bind with other ions and large molecules such as glucose and amino acids, change shape to transport them specific shape for particular molecule
Other proteins may be attached to the carrier proteins and function as enzymes, antigens or
receptor sites PERIPHERAL
Membranes in neurons
Neurons have a myelin sheath formed by flattened cells giving several layers of membrane
Membranes in white blood cells
The plasma membranes of white blood cells contain special protein receptors that enable them
to recognise the antigens on foreign cells
Membranes in root hair cells
Root hair cells in plants have many carrier proteins to actively transport nitrate ions from the soil into the cells.
Membrane of mitochondria
The inner membranes of mitochondria are mostly protein
Inner membranes contain many protein - electron carriers and hydrogen ion channels associated with ATP synthase enzymes.
Factors affecting membrane structure and permeability
High temp increases kinetic energy of phospholipids - increase fluidity - larger gaps - more permeable easier for particles to cross
High temp can denature channel and carrier proteins - wider - more molecules can move across membrane
Solvents - dissolve lipids - this damage increase fluidity and permeability
Simple diffusion
Net movement of high conc to low conc until equilibrium
Must be lipids soluble and small - through bilayer until no gradient
Facillitated diffusion
Move through embedded and carrier proteins and channel proteins as too big or not lipid soluble
Movement of ions and and polar molecules
Isotonic
Same water potential in solution and in cell - no net movement of water
Hypotonic
Positive WP in solution - more water in solution than solute - water moves from solution to cell causing it swell and sometimes burst
Hypertonic
Water potential is more negative in solution than cell so moves out of cell making it - shrivelled, animal cells (cremated) plant cells (plasmlysed)
Why does adding solute make water molecules less free
Adding solute lowers the water potential as solute molecules associate with some of the water molecules.
The more solute the more negative the Water potential
water always moves from a less negative to more negative water potential, meaning it has to move less
Active transport
Requires ATP - energy and carrier proteins
Selective process - only certain molecules are complementary
ATP binds to protein and is hydrolysed to ADP and Pi - causing protein to change shape and open up to molecule on other side
Pi molecule is then released and protein reverts
Faster than diffusion
Where does active transport take place?
Absorption of amino acids from the gut
Absorption of mineral ions by the plant root
Excretion of urea and hydrogen ions by the kidney
Loading of sucrose from the leaf into the phloem of plants
Exchange of sodium out and potassium ions in nerve cells
Similarities and differences between of carrier proteins in active and passive movement
Similarities
In active and passive movement carrier
Proteins and integrated inside the cell.
Both selective
Change shape to allow passage of substances
Carries large molecules and charged ions
Differences
Passive goes down diffusion gradient,
No energy or ATP used
Active Active transport
Against concentration gradient
Requires energy from ATP
Endocytosis
Bulk movement of materials into a cell by active means
Membrane folds around material outside ---> formation of a sac- like vesicle containing external material
Brings external material into cell
Requires ATP and the cytoskeleton
Exoctyisis
Bulk movement of materials into a cell by active means
Vesicle moves through cytoplasm to membrane
Fuses with membrane
releases internal contents outside cell
Requires ATP and the cytoskeleton
Phagocytosis
Transport of solid
Pinocytosis
transport of liquid