Lecture 1 - Epidemiology Introduction, History, and Definitions
1/38
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What is associated with the LMU One Health Model?
Prevention, Detection, Response
Human, Animal, Environment
Economics, Culture, Global Context

What is one of the deadliest viruses known to man?
Ebola
Who is the English anesthesiologist who innovated several of the key epidemiologic methods that remain valid and in use today?
John Snow
What did John Snow believe?
That cholera was transmitted by contaminated water and was able to demonstrate this association
During Snow’s time had the connection between microorganisms and disease been ascertained?
No not yet
What is the theory that disease was transmitted by a miasm, or cloud, that clung low on the surface of the earth?
Miasmatic Theory of Disease
Think Malaria for ‘Bad Air’
What was Snow’s natural experiment?
Broad Street, London - major Cholera outbreak in 1849
2 different water companies supplied water from the Thames River
1852 - Lambeth Co. relocated its sources of water to a less polluted portion of the river
1854 - Snow noted during a later outbreak, those served by Lambeth Co had fewer cases than those served by the other
What is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity?
Health
What is the absence of health?
Disease
What is a non-compensated perturbation of one or several functions of the host; a pathological condition occurring in a susceptible host?
Disease
What is “the study of what is upon the people”?
Epidemiology
What Greek term has the meaning “upon, among”?
Epi
What Greek term has the meaning “people, district”?
Demos
What Greek term has the meaning “study, word, discourse”?
Logos
While there are multiple - what is the LMU definition of epidemiology?
The study of the health of populations
What is the standard set of criteria for deciding whether an individual has a particular health condition?
Case Definition
Why is a Case Definition necessary?
Because you won’t always know what is causing the symptoms you are seeing during an outbreak or epidemic
What does a Case Definition define?
Who is included (as a numerator) in an outbreak investigation
A Case Definition defines a case in terms of what?
Person, Place and Time
What is a Case Definition developed with?
Criteria specific to the investigation
What are the characteristics of a Case Definition?
Sensitive
Specific
Influence by # of cases
Why are consistent Case Definitions important?
Can skew results
What is the occurrence of more cases of disease than expected in a given area or among a specific group of people over a particular period of time?
Epidemic or Outbreak
T or F: An outbreak may occur in a restricted geographical area or may extend over several countries.
True
An Epidemic or Outbreak can also be a single case of a communicable disease long absent from a population…esp. one of high mortality. What is an example of this?
Botulism, Rabies, etc.
What is an epidemic that becomes very widespread and affects a whole region, a continent, or the world due to a susceptible population?
Pandemic
By definition - what is a true pandemic associated with?
High Morbidity and Significant Mortality
What is the Attack Rate Formula?
AR = (# new cases in pop. at risk / # people in pop. at risk) x 100
Example of Attack Rate:
3 health care providers contract Ebola virus during a response
There were 100 responding health care providers
What is the attack rate?
Attack rate = 3/100 —> .03 or 3%
What is the mortality rate from all causes of death for a population during a specified time period?
Crude Mortality Rate
What is the denominator for the Crude Mortality Rate?
The total population at the mid-point of the time period
What is the proportion of animals/persons with a particular condition who die from that condition?
Case Fatality Rate
What is the numerator for the Case Fatality Rate?
The # of deaths among those cases
What is the denominator for the Case Fatality Rate?
The # of incident cases
What is the # of deaths from a specified cause per person/animal - years at risk?
Cause-Specific Death Rate
What is the numerator for Cause-Specific Death Rate typically restricted to?
Resident deaths in a specific geographic area (country, state, county, etc.)
How is the Cause-Specific Death Rate typically expressed?
As X deaths per 10^n population
What is the Iceberg Dilemma of Disease (in order)?
Confirmed Linked
Confirmed Cases
Sick Cultured
Sick seen by Health Care
Sick unseen in Health System
Subclinical
Exposed
At Risk Population
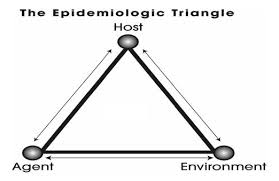
What is the Epidemiologic Triad?
Host, Agent, Environment