APWHIST Unit 0: Concepts and Vocabulary
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The context and years before 1200 (the start of APWORLD course)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Periodization
process of dividing the past into easily understandable sections, grouping years based on similarity.
Civilization
a group of people living and working together for a common goal.
Logograms
symbols representing entire words or concepts.
Define: Bureaucracy and its pros and cons:
a system used to manage tasks using complex, structured, hierarchies. (pros: specialized labor, chain of command, formal procedures, rules, efficiency. cons: rigid, slow, and impersonal)
Describe: the First Industrial Revolution in a simple formula
Science revolution + capitalism
Describe: the Second Industrial Revolution in one phrase
technology advancement
Describe: the French and Indian War and its effects
9 year war fighting over N.A territory resulted in British raising taxes in the Colony and eventual political revolution.
What advancements came out of the Pre-Columbian Era?
advanced calendar, mathematical system, domesticated animals, sedentary villages, urban civilization.
What does it mean to be civil?
acting in the societies best interests and staying in line with what is culturally “acceptable.”
What era marked the last of the great land-based empires?
Gunpowder Empire Era
In what era did the empires: Mauryan/Gupta, Han China, Rome, Greece rule greatly?
Classical Antiquity
What civilizations were active during the Pre-Columbian Era?
Pueblo, Missiissippian, Mayan, Aztecs, Incas, Moche.
Around what time did the Polynesian Migration happen?
1500 BCE
Which came first, the Classical Antiquity or Middle Ages?
Classical Antiquity
What empires ruled during the Gunpowder Empire Ages?
Ottoman, Mughal, Safavid, Russia, China.
Explain what era Rome ruled in, how Rome fell, and the significance / what era it ushered in:
Rome ruled during the Classical Antiquity era and fell due to devolution and Germanic tribes overturning it. This was significant because it ushered in the Dark Ages for the destroyed European continent.
How long are we given to write LEQ?
40 mins
What years are considered the Modern Era?
1492-Present
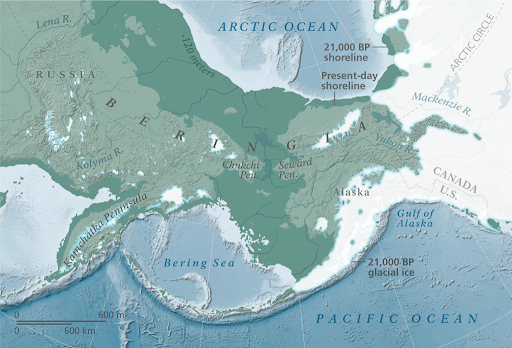
Bering Land Bridge
idea of a bridge connecting Asia to North America
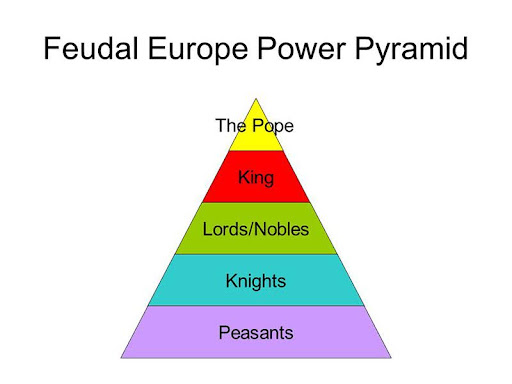
Draw: the ranking of hierarchy in Feudalism Europe during the Middle Ages.
Describe: communism to a child -
Describe: capitalism to a child -
What years did the Pre-Columbian era last?
Describe: Pueblos
.
Describe: Mississippian
.
Describe: Mayan
.
Describe: Aztecs
.
Describe: Intecs
.
Describe: Moche
.
Describe: LEQ
.
How did civilizations grow their power in the Pre-Columbian era? Provide example and effects
How did empires grow their power in the Classical Antiquity era? Provide examples and effects
Explain what era Russia ruled in, how Russia fell, and why this is important:
The Crusades
religious wars between Roman Christianity and Muslim Islam to claim and defend land
Silk Road
trade of people, spices, knowledge, material, and religion across Europe and Asia.
rigid social hierarchy
difficult upward movement (ex. Latin American Castas i.e. Ecuador)
egalitarian social hierarchy
easy upward movement (ex. Nomadism)
old world slavery
focused on paying debt (i.e. indentured servants/prisoners of war) by working the land of master
new world slavery
became racialized, stealing people to work fields, care for babies, all for making a profit
Buddhism
“why do people suffer? Becauxe of self-seeking pleasure” opposed past Hindu; 8-fold path to enlightenment and being a good person
BCE/BC
before common era / before christ
CE/AD
common era / (Anno Domini) “year of our Lord”
How did religion unify a population?
Gave a central view on life and specific rules to follow and legitimized rule
What role did empires play in history?
political and economical security for their people; Based on conquement and controlling people group/land
Is there correlation between countries who were along the Silk Road and historical-present-day success?
Yes, Regions that engaged with the Silk Road benefited from increased trade, the growth of vibrant commercial centers, and the spread of diverse ideas and practices, leaving a lasting cultural and economic legacy still visible today.
Confucius
live in harmony with one another; first response to Warring States Period; no deity but education, benevolence, obedience
What things were traded along the Silk Road?
spirituality by world-religion missionaries and merchants along route, technological/agricultural innovation, etc.
Mauryan and Gupta under centralized rule, robust administration, and policies promoting peace and tolerance