Non-Mendelian Genetics: Imprinting, Mitochondrial Genetics and Dynamic Mutations
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Reading •Imprinting: Ch. 20.1 • Dynamic mutations (unstable trinucleotide repeats): Ch. 7 p.211-212, 213, 216 (box). • Mitochondrial Genetics: Ch. 17.1, 17.3, 17.5 Questions • Ch 20: 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, 6 • Ch. 7: 22, 23 • Ch. 17: 23, 24, 25, 26, 28, 29
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
Are maternal and paternal chromosomes functionally equivalent?
Not always (not most of the time). Paternal and maternal copies must be distinguishable
2
New cards
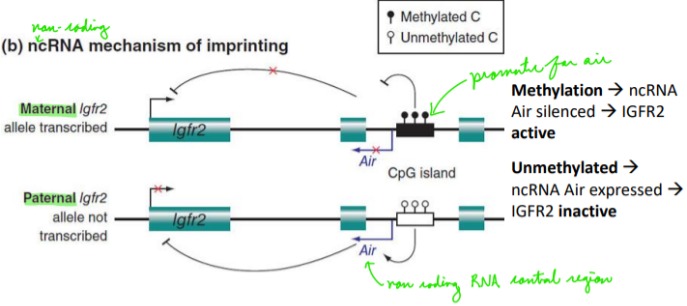
Describe: Genomic Imprinting
A genetic “mark” is placed upon a gene, chromosomal region or whole chromosome that indicates from which parent (male or female) it originated.
\
Sex-specific methylation of CpG islands in imprinting control regions (ICRs) near imprinted genes turn imprinted genes either **off or on**
\
Sex-specific methylation of CpG islands in imprinting control regions (ICRs) near imprinted genes turn imprinted genes either **off or on**
3
New cards
Does the methylation of promoters silence or enhance genes?
ALWAYS silences genes
4
New cards
Describe imprinted genes in somatic cells
Imprints are stable and unchanged in somatic cells (you can tell between maternal and paternal copies)
5
New cards
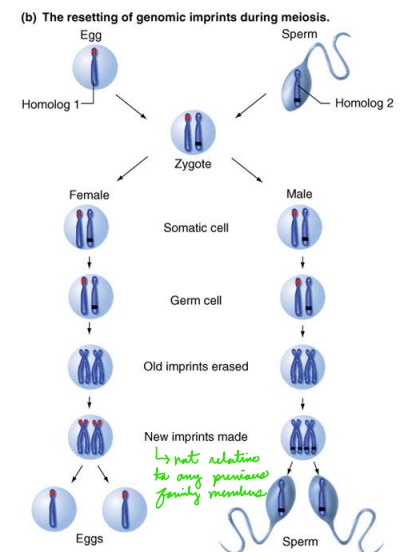
Describe imprinted genes in sex cells (gametes)
Imprints are erased at the time of gametogenesis. The imprint may be reapplied or reversed depending upon the gender of the person.
6
New cards
Does imprinting alter DNA sequence?
Imprinting does not alter the DNA sequence; it is an epigenetic (outside-the-genes, but heritable) alteration of the DNA or chromatin that affects the activity of certain genes
7
New cards
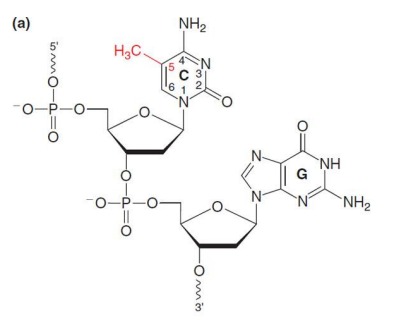
Describe: DNA Methylation
*Does not apply to invertebrates and unicellular eukaryotes*
\
Addition of a methyl group by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) to carbon 5-cytosine in the context of a CpG dinucleotide
\
CpG islands near promoters control gene expression:
Unmethylated, chromatin is open
Methylated, chromatin is closed
\
Addition of a methyl group by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) to carbon 5-cytosine in the context of a CpG dinucleotide
\
CpG islands near promoters control gene expression:
Unmethylated, chromatin is open
Methylated, chromatin is closed
8
New cards
How does uniparental disomy affect imprinting?
If genes are imprinted on one set of parental chromosomes, and homozygosity of this silencing/activation can result in disease, uniparental disomy can lead to the inheritance of doubly imprinted genes resulting in disease.
9
New cards
How many copies of the mitochondrial genome is contained in each mitochondrion?
2-10
10
New cards
How is mitochondrial DNA inherited?
Matrilineal (maternal)
11
New cards
Why don’t males pass on mitochondria?
Mitochondria in sperm is
ubiquitinated upon entering an ovum.
ubiquitinated upon entering an ovum.
12
New cards
Describe: The Mitochondrial genome
Circular dsDNA containing 37 genes.
13 polypeptide subunits for O/P complexes
22 tRNA genes
2 rRNA genes (for translation)
\
Extremely compact, does not contain any introns.
Mitochondria have their own translational apparatus.
13 polypeptide subunits for O/P complexes
22 tRNA genes
2 rRNA genes (for translation)
\
Extremely compact, does not contain any introns.
Mitochondria have their own translational apparatus.
13
New cards
What codes for mitochondrial proteins?
The nuclear and mitochondrial genome
\
Nuclear genes show biparental expression (except those imprinted)
Mitochondrial genes are maternally expressed (No paternal contribution)
\
Nuclear genes show biparental expression (except those imprinted)
Mitochondrial genes are maternally expressed (No paternal contribution)
14
New cards
Define: Homoplasmic
Cells containing 100% of 1 type of mtDNA are homoplasmic (could be all wild type or all mutant)
15
New cards
Define: Heteroplasmic
Cells containing >1 type of mtDNA are heteroplasmic
16
New cards
Why is the mutation rate in the mitochondrial genome higher than the nuclear genome?
Oxidative damage from oxidative phosphorylation to produce energy (cellular respiration)
17
New cards
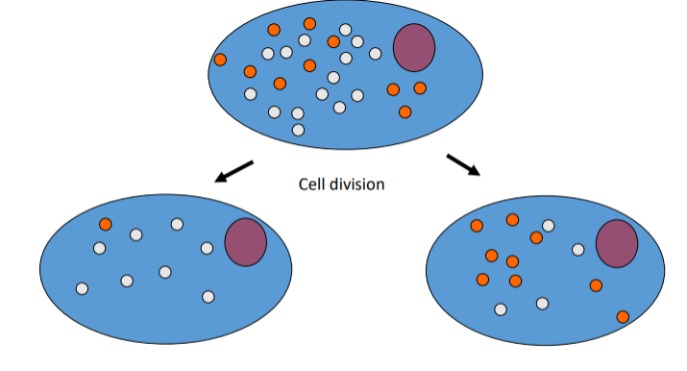
Describe the process of mitochondrial division
No spindles are involved in the cytoplasm, so division is completely random and dependent on where different kinds of mitochondria are at the time of replication.
\
This results in differing degrees of heteroplasmy in offspring.
\
This results in differing degrees of heteroplasmy in offspring.
18
New cards
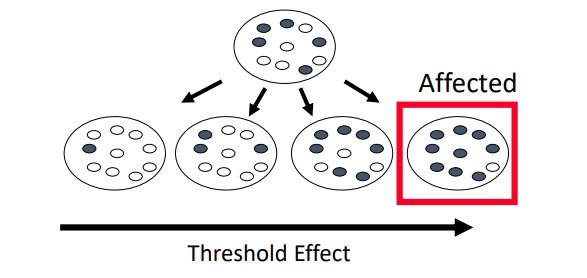
Describe: The treshhold effect
At a certain level of heteroplasmy (proportion of mutant mitochondria), a cell is unable to produce sufficient energy and the cell will die
At a certain level of heteroplasmy in a tissue, the tissue will no longer function normally, which will manifest a phenotype
\
(enough mutant mitochondria must be present for disease)
At a certain level of heteroplasmy in a tissue, the tissue will no longer function normally, which will manifest a phenotype
\
(enough mutant mitochondria must be present for disease)
19
New cards
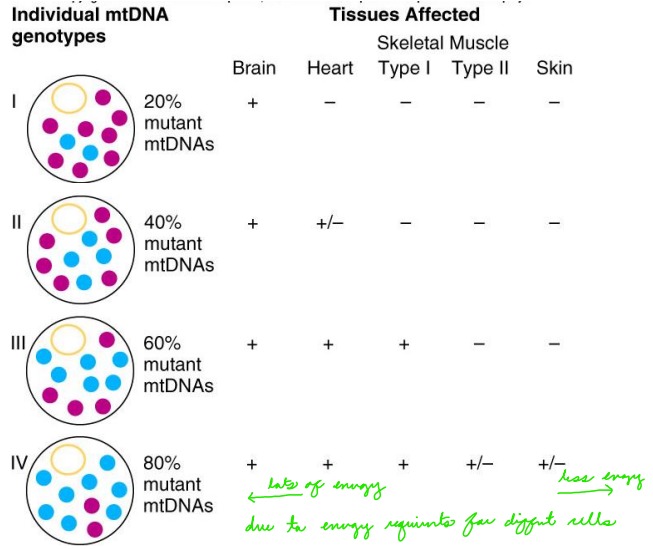
Why are some tissues, like the brain and heart, more affected by mutant mitochondria than others?
These tissues require more energy = mitochondria are more necessary/involved in the cell.
20
New cards
Describe: Dynamic Mutations
Expansion of a simple sequence repeat in coding region or non-coding region
\
Could result in loss or gain of function mutations.
\
Dynamic mutations are inherently more mutagenic than unique sequences
\
Could result in loss or gain of function mutations.
\
Dynamic mutations are inherently more mutagenic than unique sequences
21
New cards
Why are dynamic mutations so mutagenic?
Normal repeats are stable, but pre-mutation and pathogenic repeats have increased probability of expansion due to misalignment (slip strand) and non-homologous recombination.
22
New cards
Define: Anticipation
Earlier age at onset through successive generations of a pedigree is known as genetic anticipation.
The size of the expansion correlates with age of onset; the larger the expansion, the earlier the age of onset.
The size of the expansion correlates with age of onset; the larger the expansion, the earlier the age of onset.
23
New cards
What is the effect of methylated insulators?
Methylation of insulators prevents binding of CTCF proteins (no loops form), which can bring together enhancers and genes into the same chromatin loop.