IBDP Microeconomics
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What is microeconomics
the study of how households and firms make decisions and how they interact in markets
What is the law of demand?
There is an inverse relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded
What does an increase in demand mean?
Means a greater quantity demanded at each and every possible price
shift to right in demand curve
What moves the whole demand curve?
Shift factors
What are the shift factors?
Income
Price of substitutes
Tastes and preference (affected by ads)
Price of complements
Size of the market
What are inelastic/staple goods?
Changes in income do not affect how much you buy (stuff you already buy)
Normal goods: What are luxury goods?
A category of normal goods where demand increases significantly more than proportionally as income rises
e.g super cars
What are inferior goods?
If income goes up you buy less
e.g two minute noodles
What is a demand curve?
a curve that shows the quantity of a good or service with which an individual is willing and able to buy at different prices. Ceteris paribus
What is competition in Microeconomics?
Occurs when there are many buyers and sellers acting independently, so that no one has ability to influence the price at which a product is sold
What is the relationship between market power and control?
higher market power = greater control over price
What is the relationship between market competition, market power and control?
Greater degree of competition between sellers, smaller their market power = weaker control over price
What is Market power?
Refers to the control that seller may have over the price of the product it sells
What us a normal good?
Goods for which the demand rises when income rises, and falls when income falls.
e.g fruits and other necessities
What are non-price determinants of demand?
Variables other than price that can influence demand. Variables assumed to be unchanging by the use of ceteris paribus assumption
What are complementary goods?
goods that tend to be used together
For any two complementary goods X and Y a fall in price of X leads to a rightward shift in the demand for Y, and an increase in the price of X leads to a leftward shift in the demand for Y
Price of X and the demand for Y change in opposite directions
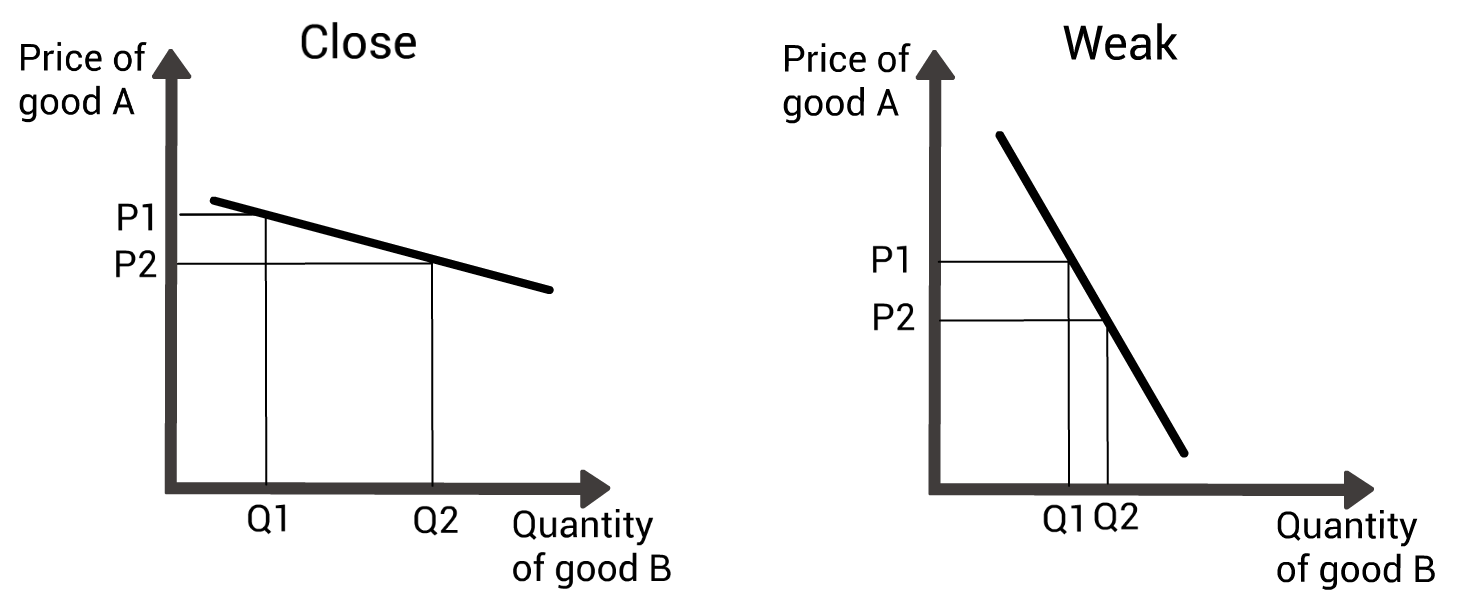
Cross price elasticity of demand - complements: what are close complements?
A small fall in price of X cause a large rise in demand of Y
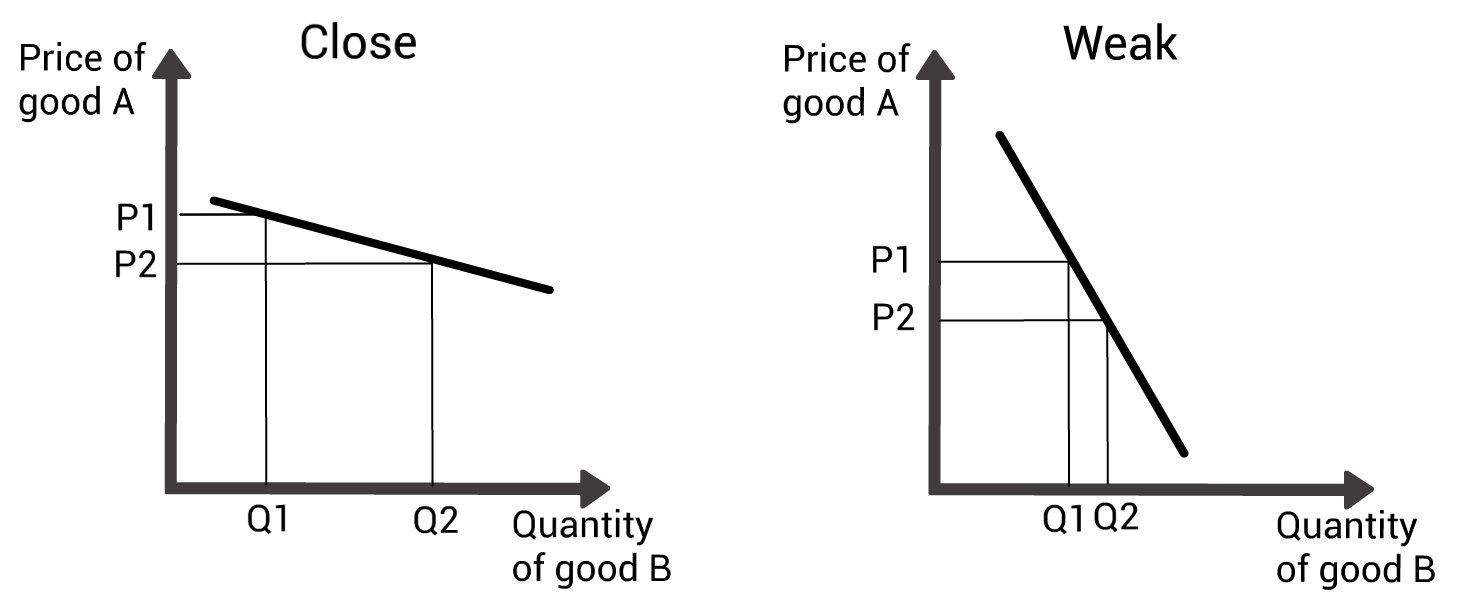
Cross price elasticity of demand - complements: what are weak complements?
A large drop in price of X causes only small rise in demand for Y
What is Mr Kennedy's America china europe saying
America innovates, China replicates, Europe regulates
because in 1990
EU 26.5% of worlds economy
US 26% of worlds economy
IN 2025
EU 16.1% of worlds economy
US 26% of world economy
Rest of worlds economy shot up whilst europe regulates and slows a bit
What is the demand curve also called?
marginal benefit curve
What is the measure of satisfaction?
Utils
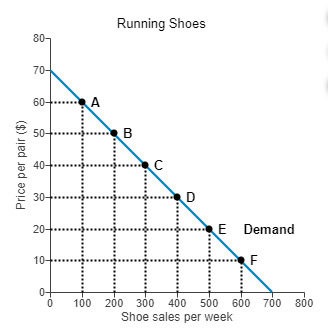
What happens when going from points A to points C in the graph? And also what happens when going from points C to A?
A->C real income has increased because price going down means their income can buy more
C->A real income has decreased they can now buy less with the same income
What is needed for income to be meaningful?
Income is only meaningful when you know what you can buy
What is the substitution effect?
If the price of one good increases, demand for a similar (substitute) good increases
What is an example of the substitution effect?
BMW prices increase mercedes demand increases meaning a rightward shift in mercedes demand curve
Why do we talk about the LAW of demand?
TO understand the relationship between price and the quantity of goods demanded. The law is true and corresponds to real-life
What is meant by a change in quantity demanded vs change in demand?
Change in quantity demanded = movement along a fixed demand curved caused by a change in price of good or service
Change in demand = shift of the entire demand curve either left or right caused by changes in non-price factors e.g income, tastes or the price of related goods
What is the income effect?
a change in quantity demanded caused by a change in consumer income
Explain why the demand curve is also called the marginal benefit curve?
Demand curve shows the max price a consumer is willing to pay for each additional unit of a good, as you consume more units, the law of diminishing marginal utility applies, each extra unit gives you less added satisfaction, so the demand curve slopes downward because marginal benefit falls as quantity increase
If price were zero it eventually gets to a point where it creates a cost e.g health problems
What relationship exists between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded of that good or service cetirus paribus?
An inverse relationship ceteris paribus
What are examples of pairs of substitues?
-Mercedes and BMW
-Nike and Adidas
-Coke and pepsi
What are examples of pairs of complements?
Laptop and charger
Twix and coke
Ink and printer
Why do economists employ the ceteris paribus principle when we look at demand curves?
Allows for one factor, price to be concentrated on and not others
What are competitive markets?
Lots of buyers and sellers (main characteristic)
What is meant by the 'short run' in microeconomics?
In the short run, at least one factor of production is fixed
What is meant by the 'long run' in microeconomics?
In the long run, all factors of production are variable
Why is the school for example in the short run?
Because
Land ( Hard to vary/fixed)
Labour (easy to vary)
capital (easy to vary)
Enterprise (easy to vary)
Because land is fixed the school is in the short run
What is the definition of supply (supply curve)?
Supply is the quantity of a good or service which producers are willing and able to bring to market at different prices, ceteris paribus
What are the shift factors of supply?
Costs of production e.g raw materials/labour
Supply shock e.g supply chains/harvests/geopolitical
Taxes
Number of suppliers
Competitive and joint supply
Where is a shortage on the supply and demand curve?
The point where demand exceeds supply (Base of graph triangle shape)
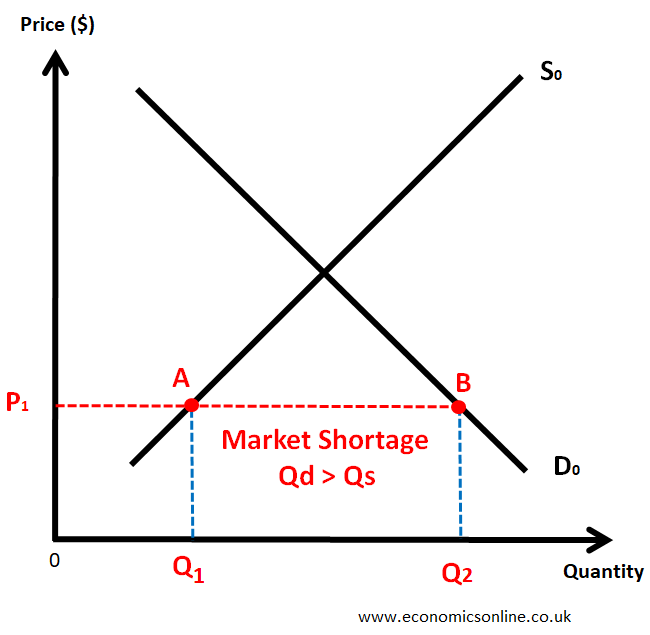
Where is a surplus supply on the supply and demand curve?
The point where supply exceeds demand (upside down triangle above the shortage triangle)
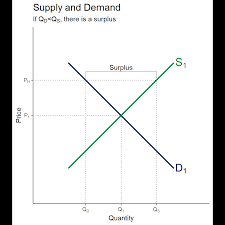
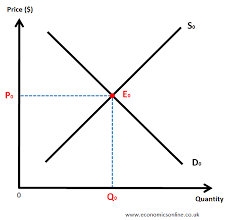
What is the point where supply meets demand called?
equilibrium
What is utility?
The satisfaction that consumers gain from consuming something
What is total utility?
The total satisfaction that consumers get from consuming something
What is marginal utility?
The extra satisfaction that consumers receive from consuming one more unit of a good
What type of relationship exists between the quantity of a good supplied over a particular time period and its price?
Positive relationship
What is market supply?
Total quantities of a good that firms are willing and able to supply in the market at different possible prices and is given by the sum of all individual supplies of that good
What is a perfectly inelastic supply curve?
perfectly inelastic as the quantity supplied is independent of price
What are the two reasons for a vertical supply curve?
1) Fixed quantity of the good supplied because there is no time to produce more of it. e.g tickets in movie theatre
2) Fixed quantity of the good supplied because there is no possibility of ever producing more of it. e.g antiques
What are the non price determinants of supply?
1) Cost of factors of production
2) technology
3) price of related goods: Competitive supply
4) Prices of related goods: joint supply
5) Producer price expectations
6) Taxes
7)Subsidies
8)Number of firms
9) Shocks or sudden unpredictable events
What are subsidies?
a sum of money granted by the government or a public body to assist an industry or business so that the price of a commodity or service may remain low or competitive.
Why can the short run in the school be more expensive?
Paying overtime
Agency workers
Free time is a factor
What is nominal price?
absolute price of a good, unadjusted for inflation
What is real price?
a price that has been corrected for inflation
What is a change in quantity supplied?
movement along the supply curve
What causes a change in quantity demanded?
Change in demand (shift of whole demand curve)
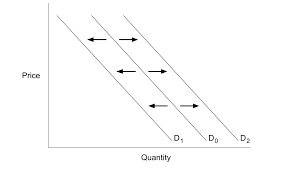
What is a change in supply?
a shift in the supply curve
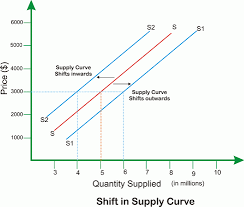
What is a change in supply caused by?
factors other than price
What is OPEC?
organisation of petroleum exporting countries
What is competitive supply?
competitive supply of two or more products refers to production of or or the other by a firm
goods compete for the use of the same resources - producing more of one means producing less of another
What is joint supply?
refer to production of goods that are derrived from a single product, so that it is not possible to produce more of one without producing more of the other
e.g butter and skim milk both produced from whole milk
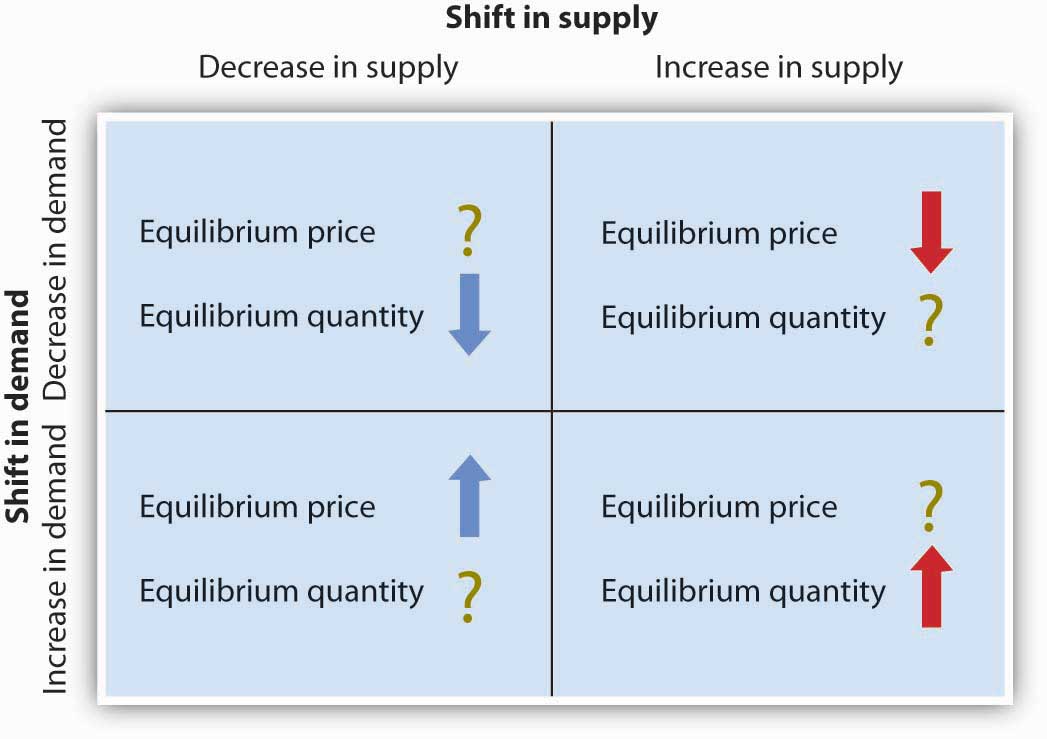
What happens to the equilibrium quantity and price when theres an increase in supply and demand?
Equilibrium Quantity = increase
Equilibrium price = indeterminate
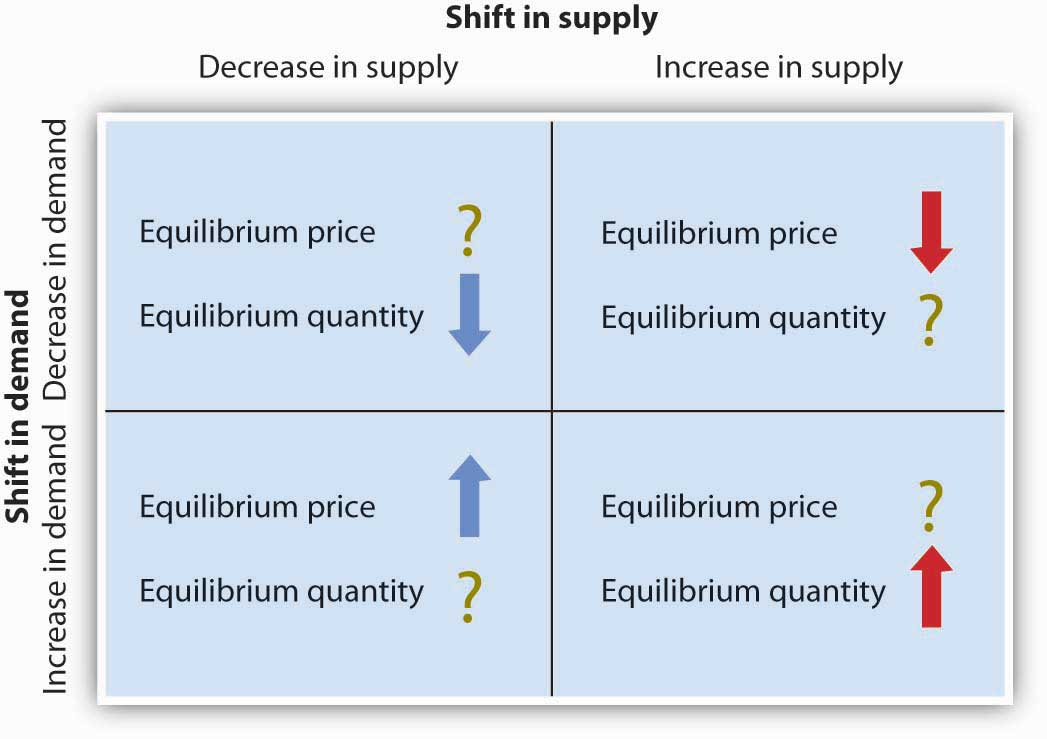
What happens to the equilibrium quantity and price when theres an increase in supply and a decrease in demand?
Equilibrium Quantity = indeterminate
Equilibrium Price = Decrease
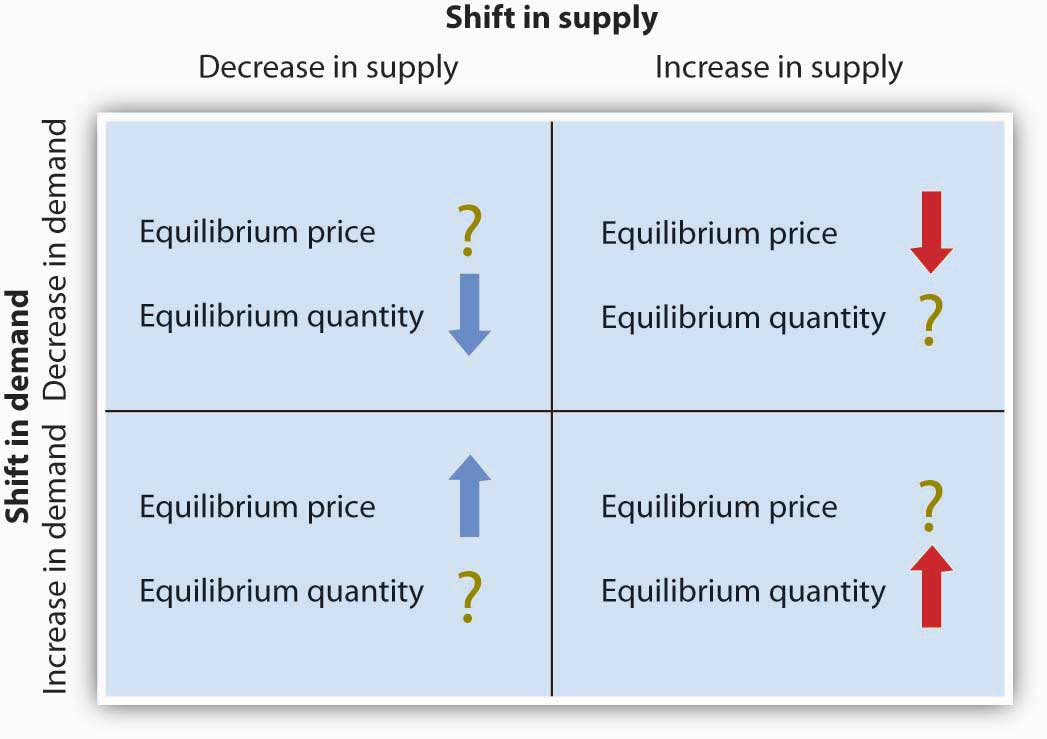
What happens to the equilibrium quantity and price when theres an decrease in supply and demand?
Equilibrium Quantity = Decrease
Equilibrium Price = Indeterminate
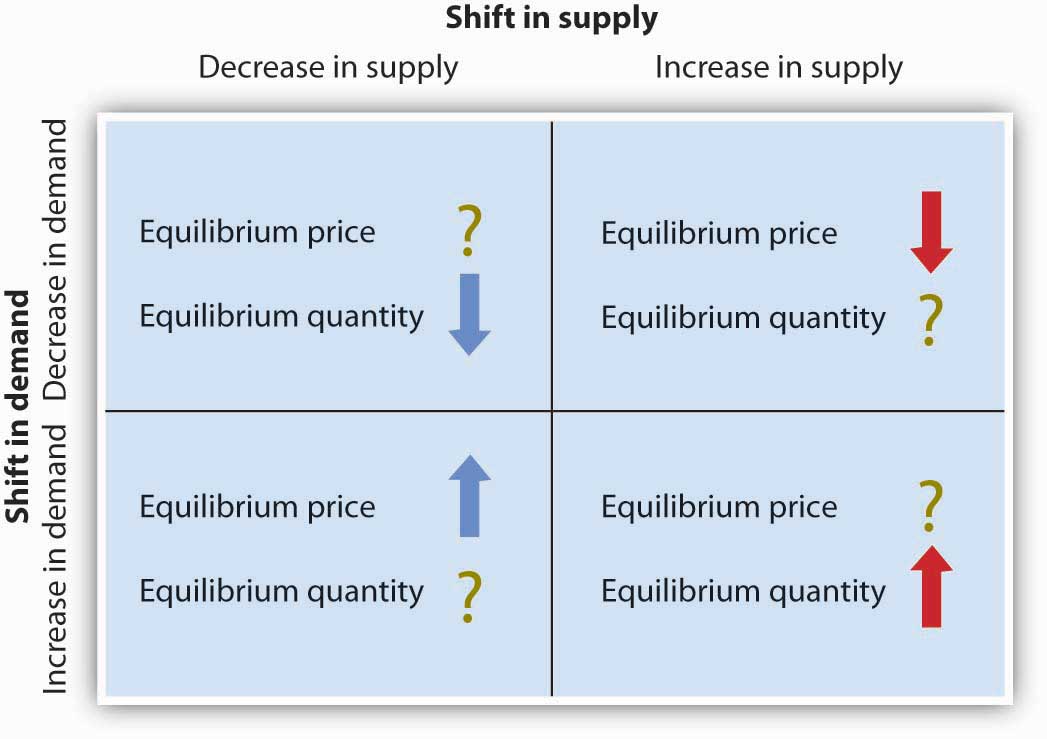
What happens to the equilibrium quantity and price when theres an decrease in supply and an increase in demand?
Equilibrium Quantity = Indeterminate
Equilibrium Price = Increase