Ch. 6 Contraction of Skeletal Muscle
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about the contraction of skeletal muscle.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is the sarcolemma?
The cell membrane of a muscle fiber, which includes the plasma membrane and an outer coat of polysaccharide material.
connects muscle tendons to bone
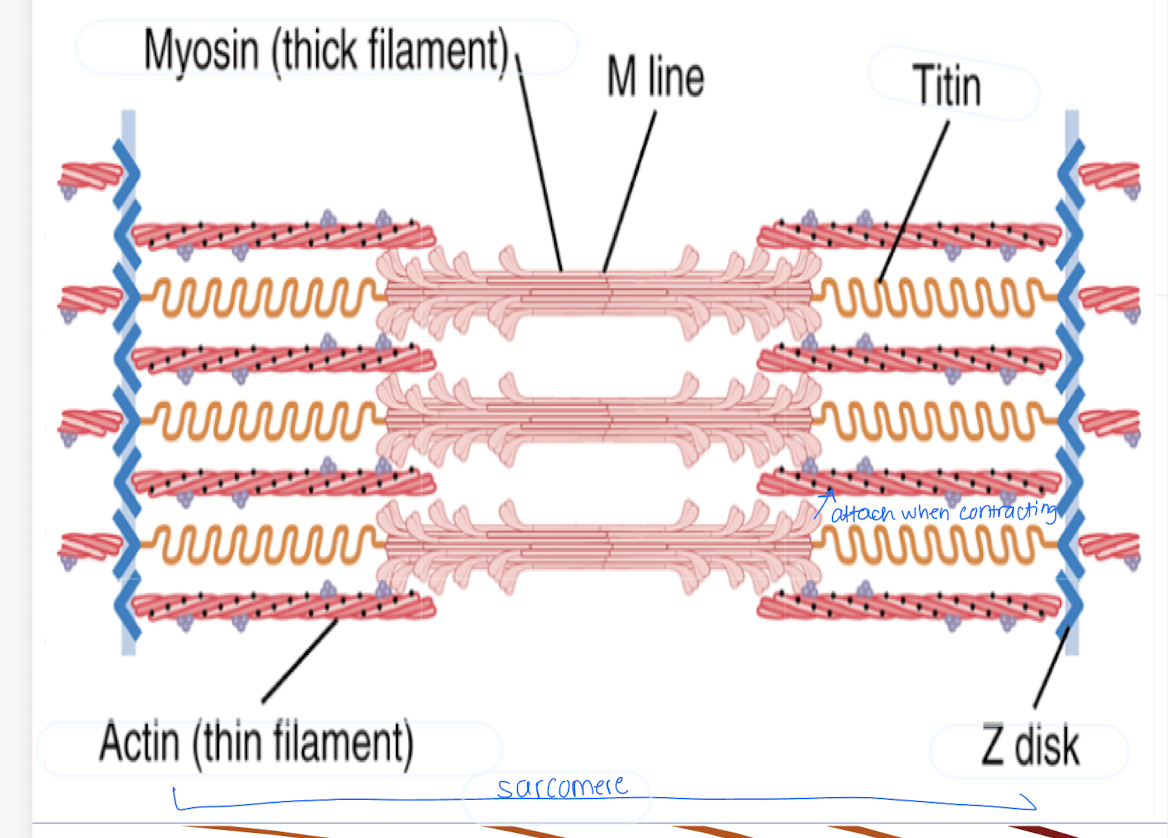
Describe each that we see in the sarcomere
Myofibrils
I bands
A bands
Z disc
Myofibrils - fibers that extend across the entire muscle fiber
I bands - contain only actin filaments
A bands - contain only myosin filaments
Z disc - ends of actin are attached to
what is a sarcomere?
function unit of muscle fiber
What is the role of titin in muscle fibers?
Titin holds the actin and myosin filaments in place, providing structural support.
Contracts Z discs together
What is the role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
Helps control muscular contraction by regulating calcium levels.
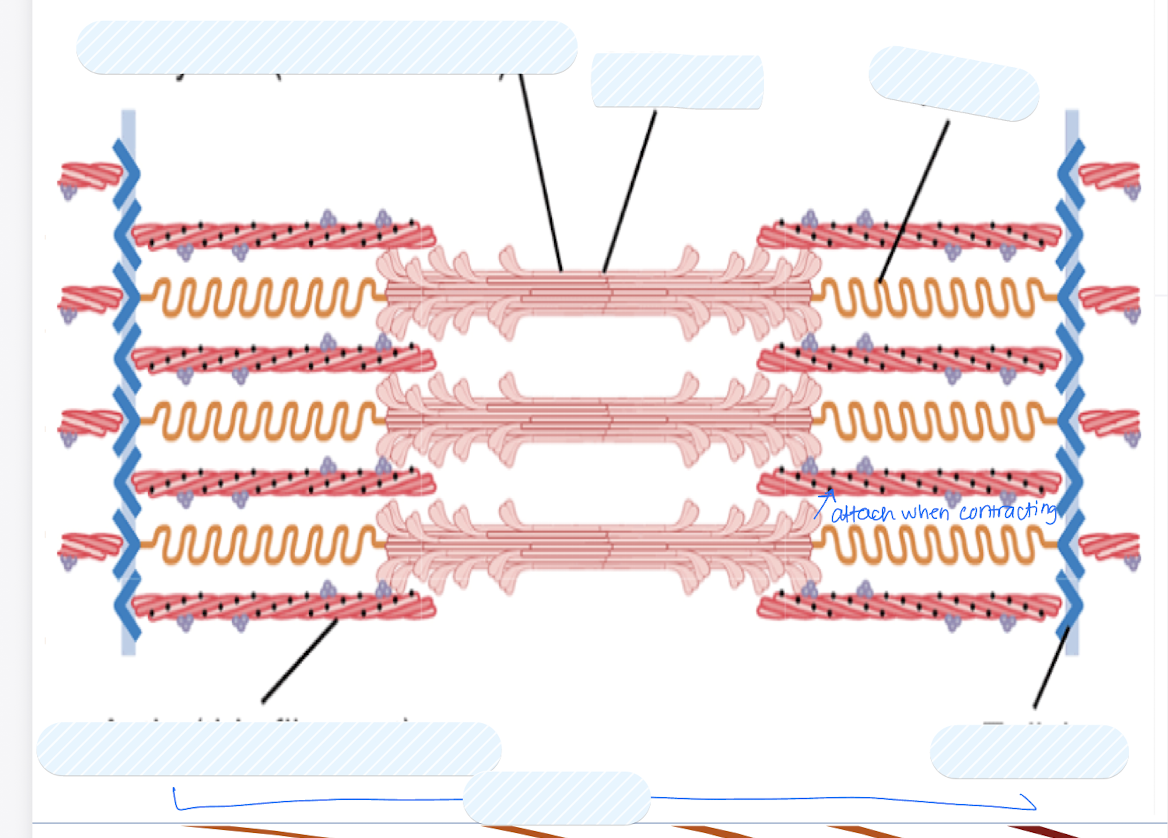
Label each part in the diagram
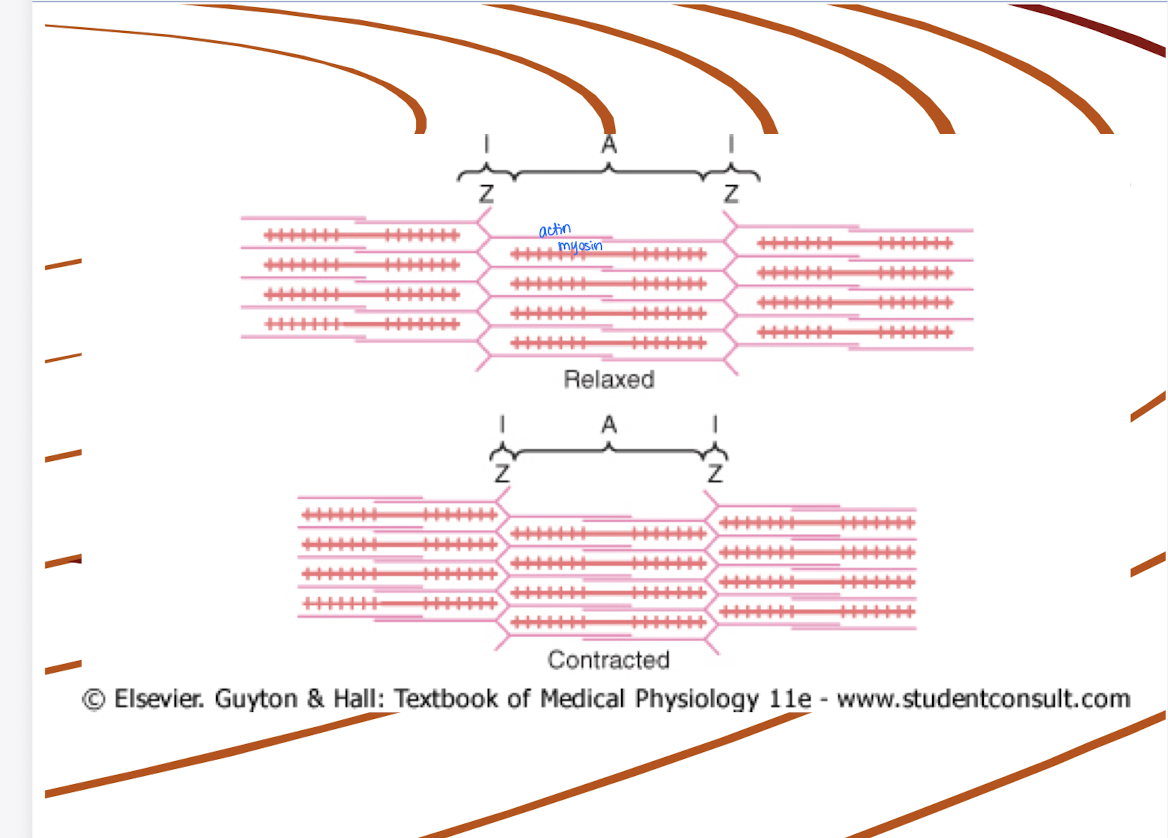
Describe the sliding filament theory.
Actin filaments slide past myosin filaments, causing the Z discs to be pulled closer together and the sarcomere to shorten.
What are the components of a myosin molecule?
6 polypeptide chains (2 heavy, 4 light)
heavy chain forms double helix creating the head
the light chain is part of the myosin head as well - important for control during contraction
At the cross bridge (off the body are the arms and heads of the myosin molecule) of myosin molecule, what are the 2 flexible points or hinges?
Where the arm leaves the body
Where head attaches to arm
What is the function of the ATPase enzyme in the myosin head?
It is responsible for providing the energy for muscle contraction by hydrolyzing ATP.
Released energy causes the myosin head to change confirmation and pull the actin filament during power stroke
What are the three protein components of actin filaments?
Actin
tropomyosin - during the resting state, covers the active sites on the actin strands; When exposed, myosin binds to active site on actin and power stroke occurs
troponin - has three loosley bound protein subunits (form a complex that sits on actin)
Troponin I - bound to actin (anchor)
Troponin T (bound to tropomyosin)
Troponin C - bines to calcium (released from SR)
What role does tropomyosin play in muscle contraction?
In the resting state, tropomyosin covers the active sites on the actin strands, preventing contraction.
Describe the three types of troponin
troponin - has three loosley bound protein subunits (form a complex that sits on actin)
Troponin I - bound to actin (anchor)
Troponin T (bound to tropomyosin)
Troponin C - bines to calcium (released from SR)
Why are calcium ions important for muscle contraction?
Calcium ions bind to troponin C, causing a conformational change that uncovers the active sites on the actin strand, allowing the power stroke to occur.
As each cross bridge operates independently, what do we see?
allows fluid movement for muscle contraction - otherwise muscle flexion would be static like
What happens during the power stroke in muscle contraction?
The myosin head binds to the active site on the actin filament (when exposed)
Causing a conformational change (myosin head bends)
Leading to a power stroke, and pulling the actin filament (pulling Z discs together)
The head will release active site once ATP is bound and recocks the head to the original position
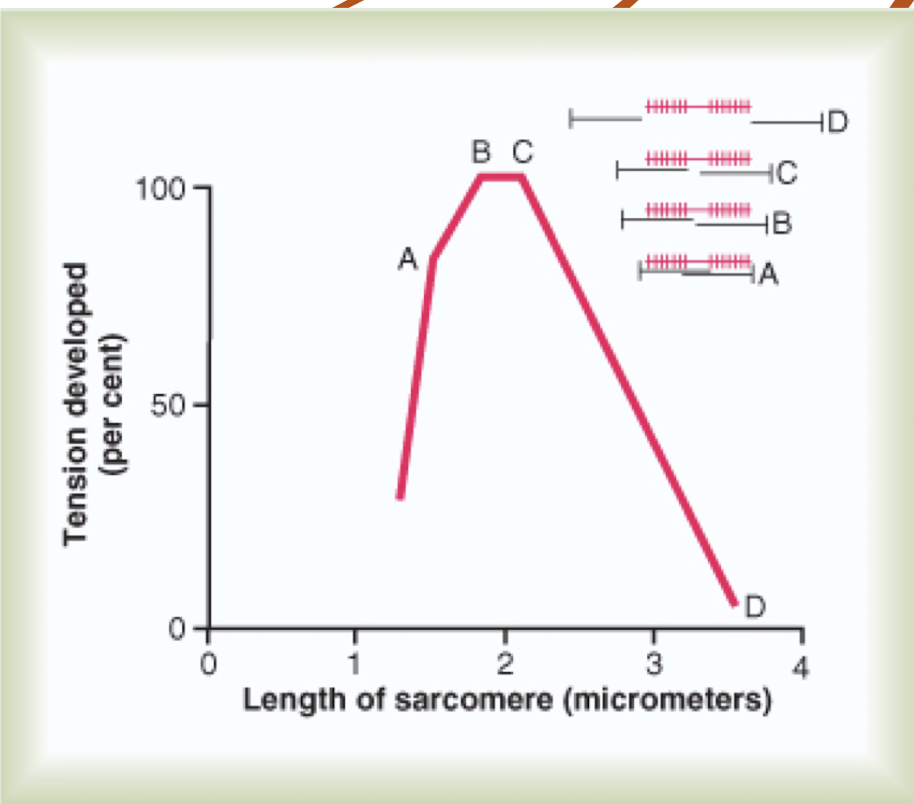
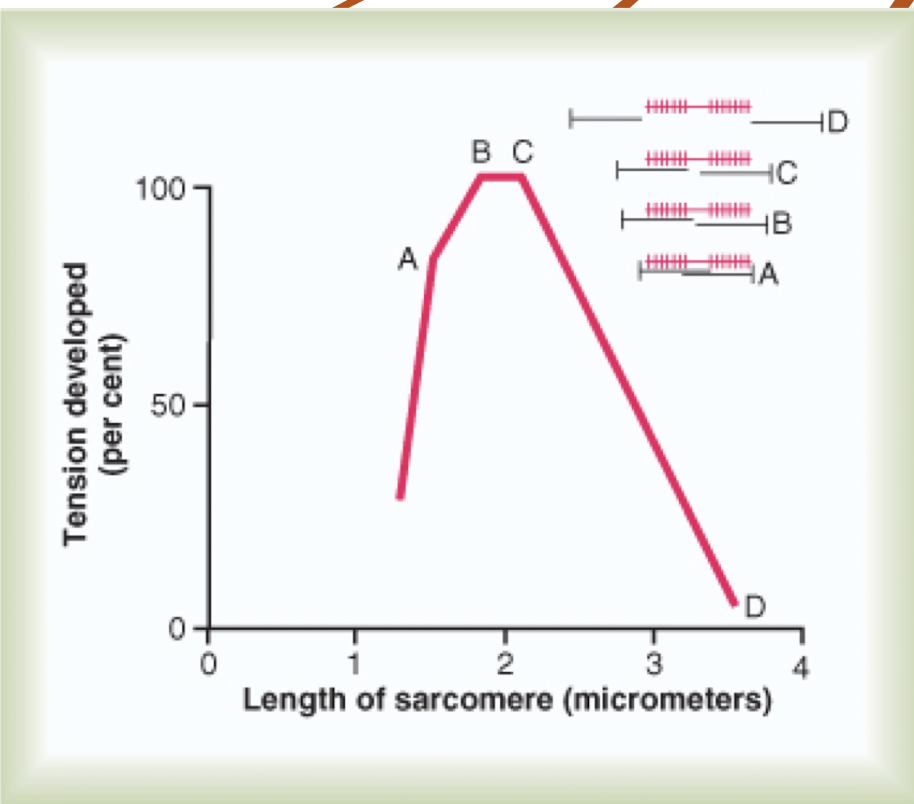
Explain what occurs in tension of contracting muscle
At D there is no overlap with actin and myosin = no muscle contraction and sarcomere is stretched
B/C have optimal overlap creating maximal force (highest tension)
A is when muscle is contracted and overlapping can lead to fatigue due to insufficient cross-bridge cycling.
T/F: As we stretch our muscles, they become more optimal for performance
False - less optimal because they are so stretched out which reduces the ability to generate force effectively. Instead, muscles perform best with moderate stretching. Site B/C
What are the energy needs of muscle to be able to contract?
mechanical work
calcium pumps - calcium comes from SR and to get back to Sarcoplasmic reticulum needs pumps
Na/K pump
List the sources of energy for muscle contraction
ATP-PC (immediate)
Glycogen (short-term)
uses carbs
anaerobic (high intensity, short duration)
Oxidation (long-term)
uses fats
aerobic (low intensity, long duration)
Why is it argued that humans are not efficient machines?
Input energy (food) converts less than 25% efficiency with remainder given off as heat
Half is used to create ATP
45% is converted for work
Describe the 4 contraction types
Isometric - force with no change in length of muscle (push on solid wall)
Isotonic - same tension (ex: you can lift max weight in a bicep curl at its weakest “hinge” point”
Concentric - Shortening muscle fiber (bicep curl)
Eccentric - elongation of muscle fiber (extend bicep curl using triceps)
Name the two traditional categories of muscle fibers.
Slow twitch (Type I)
smaller fiber size and recruited first because they are closer to reach threshold
High number of mitochondria so they are able to resist fatigue (marathon runners)
High myoglobin content (muscle is red in color) - shuttle oxygen well
Fast Twitch (Type II)
Why would slow twitch fibers be found most commonly in marathon runners?
Marathon runners will need constant oxygen pushed towards their muscles = high myoglobin content
High capillary density - good oxygen supply
Many mitochondria = resist fatigue
Low force production = they are unable to sprint because they can’t produce enough force
Define a motor unit.
A single motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates.
What is the All or None Law in the context of motor units?
When a neuron reaches threshold, it generates an action potential which is conducted the length of the axon without any voltage change and all fibers innervated by that motor unit contract.
T/F: When the nerve fires, all muscle fibers it innervates contract together
true - all thigh muscles are used to squat
What is Force Summation?
What are the two ways force summation occurs?
Adding together of individual twitch contractions to increase intensity of contraction
Multiple Fiber Summation (increase # of Muscle Units contracting simultaneously) - 1 fiber vs 10 fibers
smaller motor neurons in the spinal cord are recruited first or easily excited
Frequency Summation (increase frequency of contraction)
What is tetanization?
How does the process occur?
Tetanization is a sustained muscle contraction and occurs by frequency summation
As frequency increases, a new contraction occurs before the preceding one is over and the contraction is added partially to the first.
When the frequency reaches a critical level, contractions fuse together leading to tetanization - enough calcium ions remain in sarcoplasm not allowing relaxation between action potentials
What is the staircase effect (Treppe)?
When a muscle contracts after a long period of rest, the initial contractions are weak but progressively get stronger.
Occurs due to increase in calcium ions with each successive action potential and failure of Sacroplasmic reticulum to recapture immediately
What contributes to skeletal muscle tone?
A low rate of nerve impulses from the spinal cord, controlled by signals from the brain and muscle spindles.
impulses are controlled by signals from the brain (CNS) and muscle spindles (PNS)
Describe Muscle Fatigue.
Inability to maintain work output or intensity
ex: Runner is will begin his work out 5 mph, but they are unable to keep running at the pace so they must decrease their intensity. They will keep running but at a slower pace
Differentiate Hypertrophy, Atrophy & Hyperplasia
Hypertrophy - increase in number of actin and myosin filaments causing enlargement of fiber
Atrophy - loss of contractile protein due to little to no use
Hyperplasia - increase in actual fiber number (occurs in bird maturation)
If a muscle loses _______ atrophy begins ________
a. blood supply; immediately
b. blood supply; 72 hours
c. nerve supply; immediately
d. nerve supply; 72 hours
c. nerve supply; immediately
What is contracture?
Form of muscle degeneration; Fibrous tissue continues to shorten
it is okay when 1 fiber undergoes contracture but not an entire muscle group because it restricts movement and can lead to loss of function.
example: rigor mortis - due to loss of ATP and energy is required for myosin head to detach from actin
What is rigor mortis?
State of contracture due to loss of ATP, which is required for myosin head to detach from actin.