Micro 10 | Gram-Negative Bacteria II
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What type of bacterium is Yersinia enterocolitica?
It is a Gram-negative bacillus, facultative anaerobe, and urease-positive.
What temperature can Yersinia enterocolitica grow at?
It can grow at cold temperatures (4°C)
How is Yersinia enterocolitica diagnosed?
Through culture on MacConkey agar at 4°C and 37°C and biochemical profiling.
What are the major virulence factors of Yersinia enterocolitica?
Yops proteins, which inactivate phagocytic proteins, induce apoptosis, and suppress inflammation.
Capsule (anti-phagocytic)
LPS (toxic)
Invasion factors
How is Yersinia enterocolitica transmitted?
Through contaminated food (milk, pork), pet feces (rabbits, dogs, rodents), and contaminated blood products.
What disease does Yersinia enterocolitica cause?
Enterocolitis, which involves diarrhea with abdominal pain due to bacterial invasion and spread.
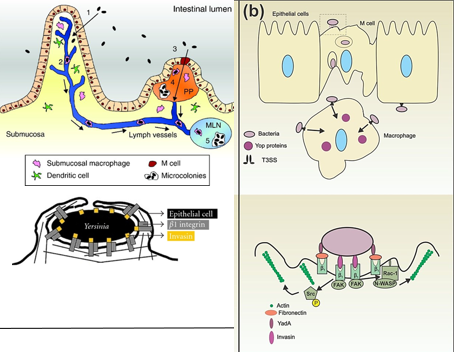
Describe the pathogenesis of Y. entercolitica
The bacteria attach to M cells using adhesins, which cause changes in the cell’s structure with the help of invasin.
They pass through M cells and grow in Peyer’s patches in the intestine.
They inject Yops proteins using T3SS, which stop immune cells from attacking them.
The bacteria trigger IL-8, bringing in immune cells (PMNs) that weaken the epithelial barrier, leading to diarrhea, bacterial spread, and ulcers.
Even after symptoms go away, bacteria can still be spread for 3 months.
What are the major human pathogens in the Vibrio genus?
V. cholerae
V. parahaemolyticus
V. vulnificus
What are the key characteristics of Vibrio bacteria?
They are Gram-negative curved rods, facultative anaerobes, oxidase positive, and motile with polar flagella.
Do Vibrio bacteria need salt to grow?
Most do, but V. cholerae can grow in high salt but doesn’t require it.
V. parahemolyticus and V. vulnificus require it
How is Vibrio diagnosed?
By culturing on TCBS agar and using biochemical tests.
Where can Vibrio cholerae grow?
It can grow in freshwater, brackish water, and salt water.
What does it mean that Vibrio cholerae is "acid-labile"?
It means the bacteria are sensitive to stomach acid and need a high dose to cause infection
How is Vibrio cholerae transmitted?
Through the fecal-oral route, mainly via contaminated water, fish, and shellfish. Typically seen more after natural disasters (floods, earthquakes).
Who is at risk of Vibrio cholerae infection?
People with low stomach acidity, as they need a smaller infectious dose.
People of all ages in endemic areas.
Young children in non-endemic areas.
What is the primary virulence factor of Vibrio cholerae?
Cholera toxin, a classic A/B toxin.

How does cholera toxin work?
The CTA subunit binds to and ADP-ribosylates the Gs protein in the ER, keeping it permanently active.
This leads to increased cAMP production, which causes the secretion of Na⁺, K⁺, and Cl⁻ ions, followed by water secretion.
The result is severe watery diarrhea and electrolyte loss.
Presentation of cholera?
“Rice Water Diarrhea”
Profuse watery diarrhea with mucus ("rice water diarrhea"), vomiting, abdominal cramps, and sometimes low-grade fever.
Who is more susceptible to severe cholera?
People using antacids, proton pump inhibitors, or histamine receptor blockers because these drugs increase stomach pH, allowing the bacteria to survive more easily.
What is Vibrio parahemolyticus?
A bacterium found in marine and coastal waters. It can cause foodborne illness, usually from eating raw or undercooked seafood, leading to diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, and fever.
How is Vibrio parahaemolyticus transmitted?
Through contaminated seafood or skin infections in seafood handlers.

What is vibrio vulnificus?
A bacteria found in warm seawater. It can cause severe foodborne illness from eating raw seafood (like oysters) and life-threatening infections if it enters wounds, sometimes leading to sepsis or necrotizing fasciitis.
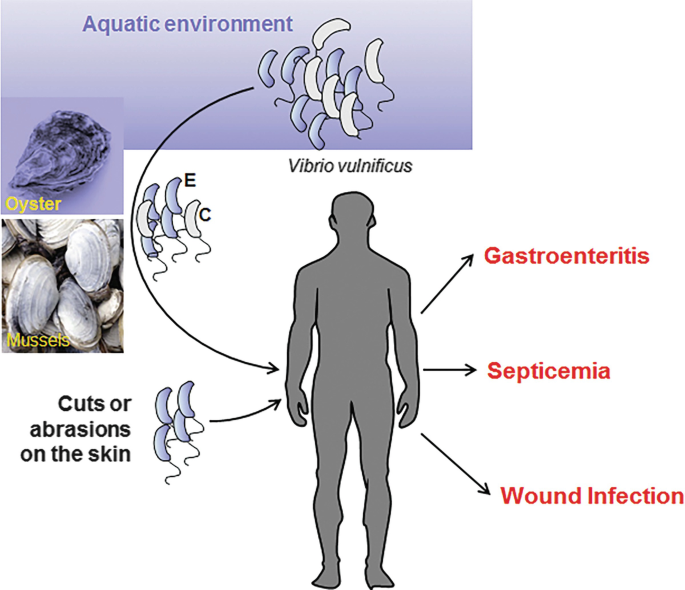
How is Vibrio vulnificus transmitted?
Through contaminated seafood (especially shellfish) and skin wounds exposed to infected seafood or saltwater.

Who is at higher risk of Vibrio vulnificus infection?
Seafood handlers (e.g., oyster shuckers).
Wading fishermen.
People who keep saltwater or reef aquariums.
How severe is a Vibrio vulnificus infection?
It is a life-threatening infection and requires immediate treatment.
What are the main virulence factors of Vibrio vulnificus?
Vibriolysin, which destroys tissue and causes necrosis.
Acidic polysaccharide capsule, which helps the bacteria evade the immune system.
How does V. vulnificus cause severe infections?
It produces vibriolysin, leading to tissue destruction, hemorrhage, and necrosis.
How can Vibrio species be identified on TCBS agar?
V. cholerae ferments sucrose → turns agar yellow (due to pH drop).
V. parahaemolyticus and V. vulnificus do not ferment sucrose → agar stays green.
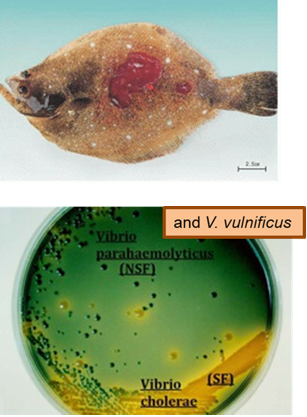
What are the two main disease forms caused by Vibrio vulnificus?
Wound Infection – Leads to secondary skin lesions and tissue necrosis.
Primary Septicemia – A food-borne infection that spreads through the blood, causing fever, vomiting, and diarrhea.
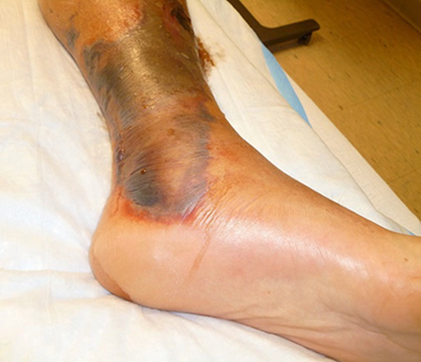
What virulence factor is responsible for necrosis (primary disease) in Vibrio vulnificus infections?
Vibriolysin, which destroys tissue and leads to progressive necrosis.
How does Vibrio vulnificus cause septicemia?
The bacteria inactivate stomach acid, invade the bloodstream, and spread using cytolytic enzymes like vibriolysin.
What is Campylobacter jejuni?
A bacteria that causes food poisoning, mainly from undercooked poultry, unpasteurized milk, or contaminated water. It leads to diarrhea, fever, cramps, and sometimes more severe complications like Guillain-Barré syndrome.
What shape is Campylobacter jejuni?
It is a thin-curved rod, often appearing comma-, S-, or seagull-shaped.
What are the key characteristics of Campylobacter jejuni?
Gram-negative curved rod
Microaerophilic
Oxidase positive
Motile with a single polar flagellum
Grows at 42°C
How is Campylobacter jejuni diagnosed?
By culturing on MacConkey agar at 37°C and 42°C and biochemical tests.
What are the main virulence factors of Campylobacter jejuni?
Adhesion (helps bacteria stick to host cells)
Invasion (allows bacteria to enter cells)
Cytotoxins and enterotoxins (damage cells and cause symptoms)
LPS (helps bacteria evade the immune system)
How is Campylobacter jejuni transmitted?
Through contaminated poultry, unpasteurized milk, and water. It is zoonotic and rarely spreads person-to-person.
What are the symptoms of Campylobacter jejuni infection?
Bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps, vomiting, and fever.
What serious complication can follow a Campylobacter jejuni infection?
It is a common precursor to Guillain-Barré Syndrome, a neurological disorder that causes muscle weakness and paralysis.
What mnemonic helps to remember at which temperature Campylobacter jejuni grows best at?
CAMPylobacter likes HOT CAMP fires
Indicates that Campylobacter jejuni grows best at higher temperatures (42°C), which is similar to the body temperature of birds, one of its main reservoirs.
Campylobacter jejuni is thermophilic (heat-loving) and grows optimally at 42°C, unlike many other enteric bacteria that prefer 37°C.

Most common cause of Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
C. jejuni
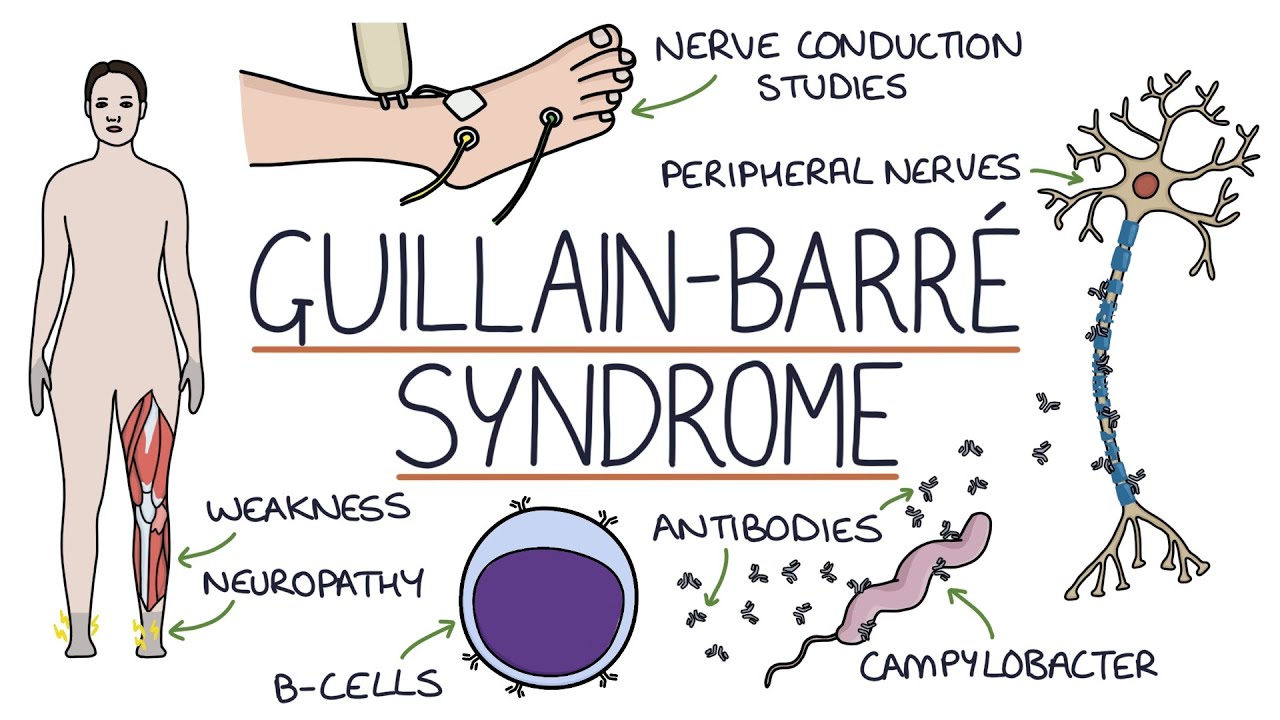
What is molecular mimicry, and how does it relate to C. jejuni?
Molecular mimicry occurs when Campylobacter jejuni's antigens resemble components of human nerve cells, causing the immune system to mistakenly attack nerves, leading to Guillain-Barré Syndrome
How does Helicobacter pylori survive in the stomach?
It produces urease, which creates ammonia (NH₃) to neutralize stomach acid, making the environment more hospitable for survival.
What makes some people more susceptible to H. pylori infection?
Since H. pylori is acid-labile, people with low stomach acid (due to medications or conditions reducing acid production) are more vulnerable to infection.
Virulence factors of H. pylori
Flagella – Help the bacteria burrow into the stomach lining.
Mucinase – Breaks down the mucosal layer, making it easier for bacteria to reach stomach cells.
Urease – Produces ammonia (NH₃), which raises stomach pH and helps the bacteria survive.
Presentation of H. pylori?
Stomach and duodenal ulcers
Acute gastritis (persistent or recurring pain in upper abdomen with no structural evidence for disease)
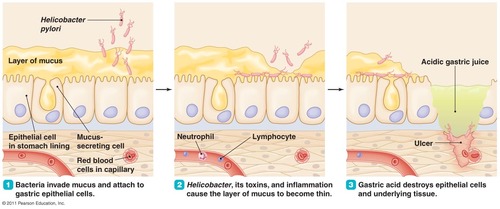
How to diagnose H. pylori?
Stool antigen (stool Ag) test – Detects bacterial proteins in stool.
Radio-labeled urea breath test – Identifies urease activity from H. pylori.