Chapter 5: the Integumentary System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/88
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
1
New cards
Functions of the skin (PTSDE)
1. Protection
2. Temperature regulation
3. Sensation
4. Vitamin D production
5. Excretion
2. Temperature regulation
3. Sensation
4. Vitamin D production
5. Excretion
2
New cards
Which of these is NOT a primary function of the integumentary system?
A. protection.
B. sensation.
C. absorption.
D. temperature regulation.
A. protection.
B. sensation.
C. absorption.
D. temperature regulation.
C. absorption.
3
New cards
Is the hypodermis part of the skin?
No, it's loose connective tissue that connects skin to underlying structures.
4
New cards
3 characteristics of epidermis
1. Avascular (nourished by diffusion from capillaries in papillary layer)
2. Cells are arranged into layers (strata)
3. Basement membrane separates it from the dermis
2. Cells are arranged into layers (strata)
3. Basement membrane separates it from the dermis
5
New cards
Keratinocytes
The most abundant epidermal cells that produce keratin for strength
6
New cards
T or F: There are the same number of melanocytes in all people.
true
7
New cards
Langerhans' cells
part of the immune system
8
New cards
Merkel's cells
detect light touch and superficial pressure
9
New cards
Desquamate
when cells of deeper layers undergo mitosis, move towards the surface, then slough off
10
New cards
Keratinization
when cells move outward through layers, fill with keratin, die, then form a hardened superficial layer
11
New cards
Epidermal strata (Come Let's Get Sun Burnt)
Stratum, corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale
12
New cards
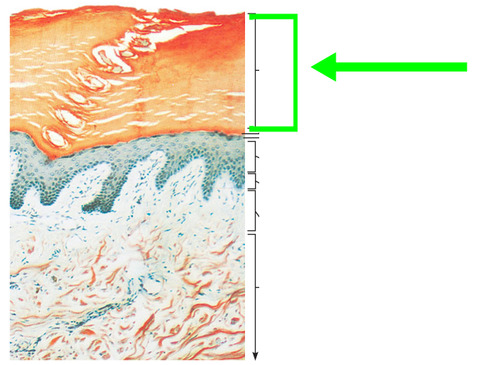
Stratum corneum
most superficial layer that contains cornified cells
13
New cards
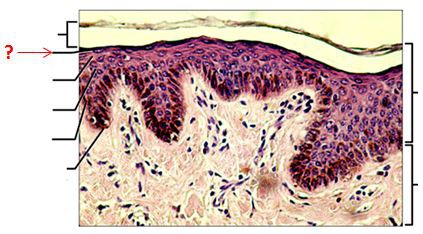
Stratum lucidum
thin clear zone located in the palms and soles only
14
New cards
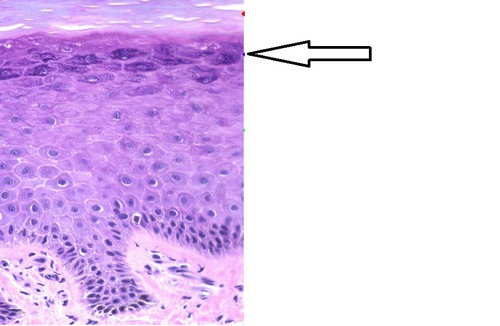
stratum granulosum
contains keratohyalin granules, and in the superficial layers the nucleus and other organelles degenerate, and the cell dies
15
New cards
Stratum spinosum
there is limited cell division in this layer, and it contains desmosomes, lamellar bodies, and additional keratin fibers
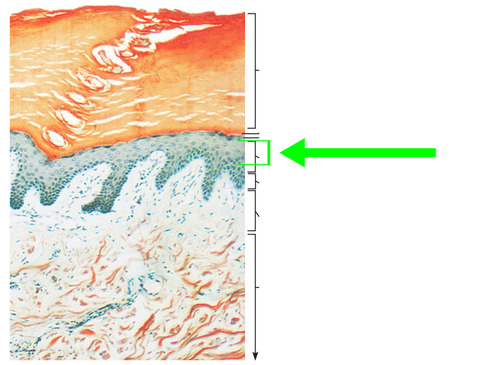
16
New cards
Stratum basale
this is the deepest portion of the epidermis and is high in mitotic activity
17
New cards
How thick is your skin?
1/2mm to 5mm (epidermis+dermis)
18
New cards
What is the main difference between thick skin and thin skin?
Thin skin lacks the stratum lucidum, while thick skin has all 5 epithelial strata.
19
New cards
Where is thick skin located?
Areas subject to pressure or friction (like palms, fingertips, and soles)
20
New cards
When is a callus called a corn?
when it's over a bony prominence
21
New cards
What is a callus?
an increase in the number of layers of stratum corneum
22
New cards
What are the three things that give skin its color?
1. Pigments
2. Blood circulation
3. Thickness of stratum corneum
2. Blood circulation
3. Thickness of stratum corneum
23
New cards
Melanin
protects against UV light, comes from AA tyrosine, and can be brown, black, yellow, or red
24
New cards
Melanocytes
processes that extend between keratinocytes and determine skin color (melanin produced by these is transferred to keratinocytes)
25
New cards
What is the production of melanocytes determined by?
genetics, hormones, and exposure to light
26
New cards
Carotene
a yellow pigment from vegetables that accumulates in the stratum corneum, adipose cells (dermis), and hypodermis
27
New cards
Cyanosis
a bluish discoloration of the skin resulting from a decrease in blood oxygen content
28
New cards
What all does the dermis contain?
connective tissue with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages, some adipocytes and blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, smooth muscles, glands, and lymphatic vessels
29
New cards
Sensory functions of the dermis
pain, itch, tickle, temperature, touch, pressure, two-point discrimination
30
New cards
Papillary layer of dermis
1/5 of the overall layer & contains areolar/loose connective tissue with lots of elastic fibers, dermal papillae, capillary beds, Meissner's receptors to sense touch, and free nerve endings to sense pain
31
New cards
Which layer of the dermis is responsible for fingerprints?
Papillary layer
32
New cards
Reticular layer of dermis
4/5 of the overall layer & contains dense irregular connective tissue and collagen/elastic fibers
33
New cards
Cleavage (tension) lines
formed by the elastin and collagen fibers that are oriented in the same direction in the reticular layer
34
New cards
Striae
stretch marks
35
New cards
If desquamation of the epidermis takes place, why doesn't a tattoo fade?
The macrophages in the reticular layer hold the pigment where it is so it doesn't spread to the rest of the body.
36
New cards
Hypodermis
the deepest layer beneath the skin that consists of loose connective tissue (collagen and elastic fibers)
37
New cards
3 types of cells in the hypodermis
1. Fibroblasts
2. Adipose cells (most)
3. Macrophages
2. Adipose cells (most)
3. Macrophages
38
New cards
What are 2 other names for the hypodermis?
subcutaneous tissue or superficial fascia
39
New cards
How much of the body's fat does the hypodermis contain?
about 1/2
40
New cards
What are the 3 functions of the hypodermis?
1. Energy source
2. Insulation
3. Padding
2. Insulation
3. Padding
41
New cards
Where is hair not found?
palms, soles, lips, portions of external genitalia, and distal fingers/toes
42
New cards
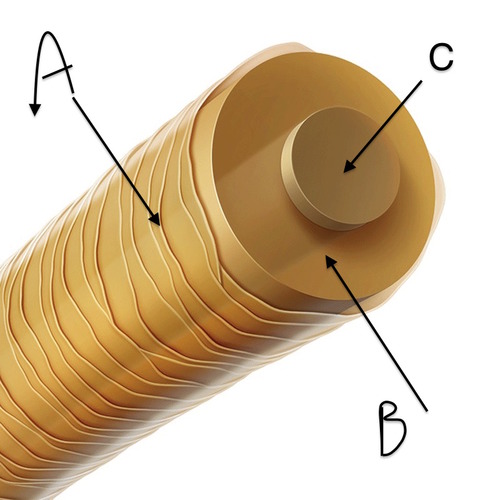
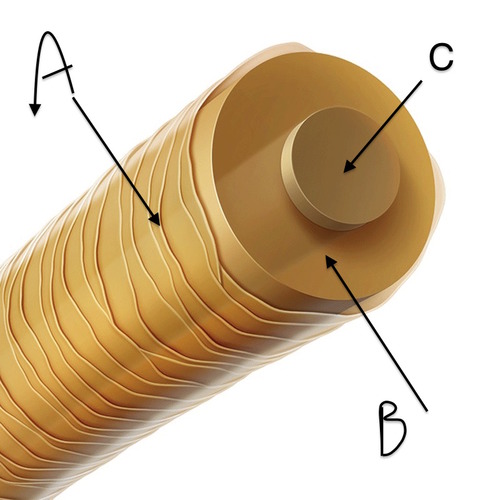
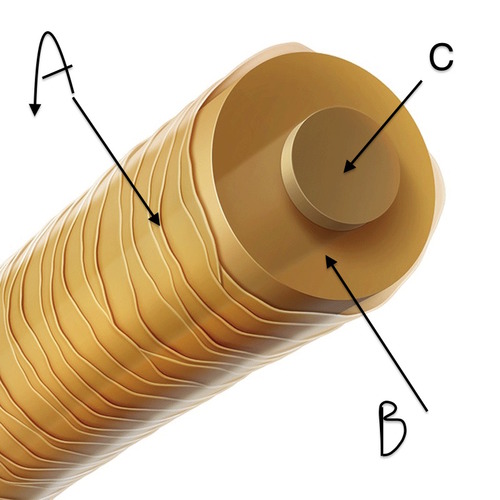
What are the 3 layers of hair?
medulla, cortex, cuticle
43
New cards
Medulla
the central core of a hair (C)
44
New cards
Cortex
the bulk of a hair (B)
45
New cards
Cuticle
the hair surface (A)
46
New cards
Dermal root sheath
part of dermis that surrounds the epithelial root sheath
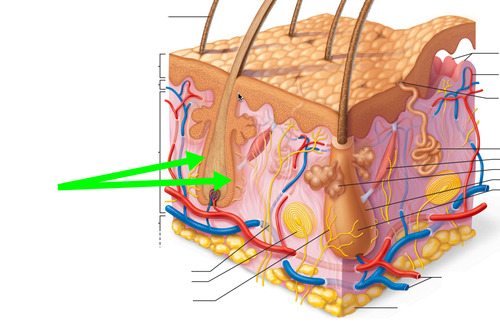
47
New cards
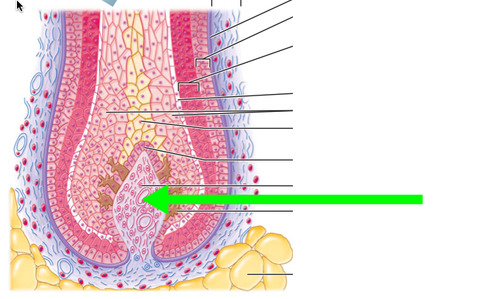
Matrix of hair bulb
source of hair
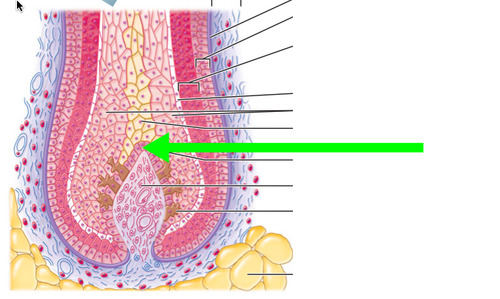
48
New cards
External epithelial root sheath
This is the stratum basale and remains after injury to supply a source of new epidermis.
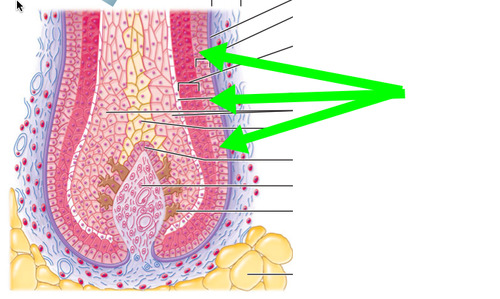
49
New cards
Internal epithelial root sheath
This is the white bulb you see when hairs are pulled out
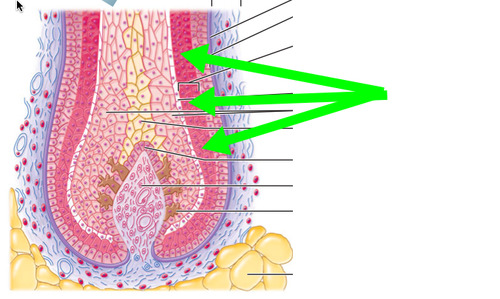
50
New cards
Hair papilla
part of the dermis that projects into the hair bulb and supplies blood
51
New cards
Growth stage of hair growth
matrix adds cells at base of hair root and hair elongates at an average rate of 0.3mm/day
52
New cards
Rest stage of hair growth
follicle shortens and holds hair in place until the hair falls out of the follicle
53
New cards
Arrector pili
a smooth muscle attached to hair follicles that causes "goose bumps" to appear on the skin and the hair to "stand on end" when contracted
54
New cards
The outermost layer of the hair shaft is the
A. cortex.
B. medulla.
C. cuticle.
D. corn
A. cortex.
B. medulla.
C. cuticle.
D. corn
C. cuticle.
55
New cards
Hair is formed from epithelial cells in the
A. matrix.
B. dermal root sheath.
C. hypodermis.
D. cuticle.
A. matrix.
B. dermal root sheath.
C. hypodermis.
D. cuticle.
A. matrix.
56
New cards
What does the sebaceous gland do?
secretes sebum that prevents drying and may inhibit bacteria
57
New cards
What type of secretion do sweat glands display?
merocrine/eccrine usually (especially on palms and soles), but apocrine in the axillae and genitalia areas
58
New cards
Merocrine (eccrine) secretion
open directly onto surface, and produce isotonic fluid (water + NaCl)
59
New cards
Apocrine secretion
open into hair follicles (like sebaceous glands) and produce odorless organic compounds - bacteria make it smell
60
New cards
Ceruminous glands
modified merocrine sweat glands in external auditory meatus that produce earwax (sebaceous and ceruminous secretions)
61
New cards
What does earwax do?
prevents dirt and insects (along with hair) from getting in your ear and it keeps eardrum supple
62
New cards
Mammary glands
modified apocrine sweat glands
63
New cards
Which of these parts of the body have the most merocrine sweat glands?
A. margin of the lips.
B. soles of the feet.
C. forearm.
D. back of the neck.
A. margin of the lips.
B. soles of the feet.
C. forearm.
D. back of the neck.
B. soles of the feet.
64
New cards
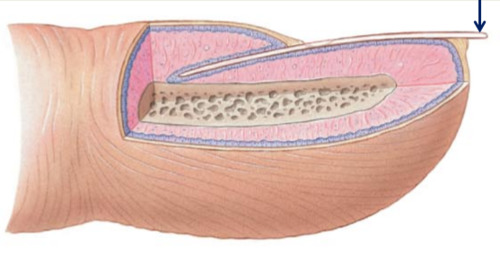
free edge of nail
65
New cards
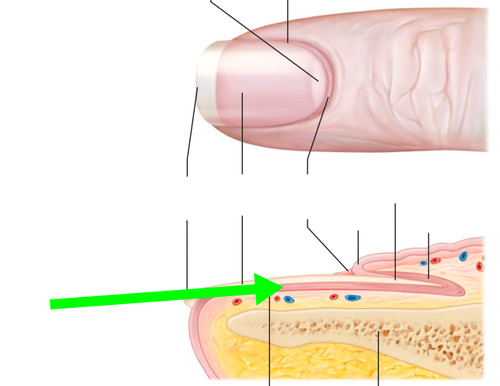
nail body
66
New cards
eponychium of nail
67
New cards
nail root
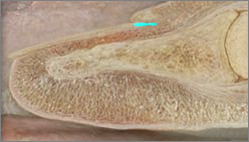
68
New cards
nail matrix
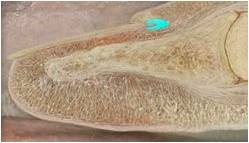
69
New cards
What is the nail body made of?
stratum corneum
70
New cards
What is the eponychium of the nail?
the corneum superficial to the nail body (the cuticle)
71
New cards
Where is the nail root located?
under the skin
72
New cards
What two things produce the nail body?
the matrix and nail bed
73
New cards
T or F: Nails grow continuously.
true, at a rate of 0.5-1.2mm/day
74
New cards
What makes up the integumentary system?
skin, hair, glands, nails
75
New cards
Which of these qualities must a medication possess to be readily absorbed from a skin patch?
A. lipid soluble.
B. water-soluble.
C. must contain keratin.
D. must be acidic
A. lipid soluble.
B. water-soluble.
C. must contain keratin.
D. must be acidic
A. lipid soluble.
76
New cards
In what layer of the skin does vasodilation/constriction take place?
the papillary layer of the dermis
77
New cards
Sweating usually happens after exercise. What specific glands and in what layer of the skin are they found?
78
New cards
Vitamin D (calcitriol), a hormone, aids in the absorption of what ion?
Calcium (Ca++), by stimulating uptake of Ca++ from intestines
79
New cards
What is calcium used for?
bone growth/repair, clotting, & nerve and muscle function
80
New cards
What are sources of calcitriol (Vitamin D)?
dairy, liver, egg yolks, supplements
81
New cards
First-degree burn
epidermis
82
New cards
Second-degree burn
part of dermis
83
New cards
Third-degree burn
dermis and epidermis are destroyed
84
New cards
Partial thickness burn
includes 1st and 2nd degree burns (epidermis and part of dermis destroyed)
85
New cards
Full thickness burn
3rd degree burn (dermis and epidermis destroyed)
86
New cards
What is the rule of nines?
Adult:
each upper limb = 9%
each lower limb = 18%
trunk = 18%
head and neck = 9%
perineum and genitalia = 1%
Child:
each upper limb = 9%
each lower limb = 17%
trunk = 16%
head and neck = 15%
perineum and genitalia = 1%
each upper limb = 9%
each lower limb = 18%
trunk = 18%
head and neck = 9%
perineum and genitalia = 1%
Child:
each upper limb = 9%
each lower limb = 17%
trunk = 16%
head and neck = 15%
perineum and genitalia = 1%
87
New cards
7 effects of aging
1. Skin is more easily damaged because the epidermis thins and amount of collagen decreases
2. Skin infections will be more likely
3. Wrinkling occurs because of a decrease in elastic fibers
4. Skin becomes drier
5. Blood supply decreases because of a poor ability to regulate temperature
6. Melanocytes decrease (vitiligo) or increase (age spots)
7. Risk of skin cancer increases because sunlight ages skin
2. Skin infections will be more likely
3. Wrinkling occurs because of a decrease in elastic fibers
4. Skin becomes drier
5. Blood supply decreases because of a poor ability to regulate temperature
6. Melanocytes decrease (vitiligo) or increase (age spots)
7. Risk of skin cancer increases because sunlight ages skin
88
New cards
Actinic keratosis
rough scaly patches on the skin on areas that are sun exposed
89
New cards
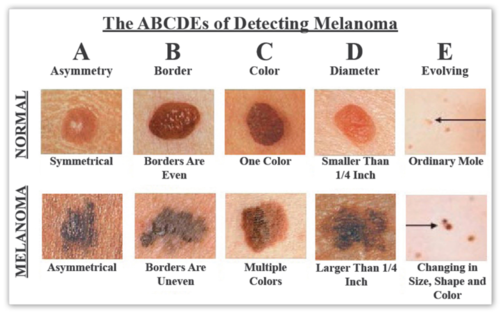
What are the ABCDEs of melanoma?
asymmetry, border, color, diameter, evolving