Florida Civic Literacy Test Questions II
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Advice and Consent Clause
Article 11, section 2, clause 2- states that the President should use the advice and consent of the senate to appoint federal judges and sign treaties with foreign countries
Bill of Attainder/ Ex Post Facto Clause
Article 1, section 9, clause 3- Prohibits Congress and states from passing laws that single out individuals for punishment without trial or retroactively criminalize actions
Contracts Clause
Article 1, section 10, clause 1- No state can interfere with the execution of contracts
double jeopardy clause
A clause of the Fifth Amendment that protects persons from being tried twice for the same crime.
Due Process Clause
14th/ 5th amendment clause stating that no state may deprive a person of life, liberty, or property without due process of law
Elastic Clause
Article I, Section 8, of the Constitution, which allows Congress to make all laws that are "necessary and proper" to carry out the powers of the Constitution.
Equal protection clause
14th amendment clause that prohibits states from denying equal protection under the law, and has been used to combat discrimination
Establishment clause
Part of the First Amendment stating that "Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion."
Extradition clause
Part of Article IV section 2, clause 2 of the Constitution that requires states to extradite, or return, criminals to states where they have been convicted or are to stand trial.
Free Exercise Clause
the First Amendment guarantee that citizens may freely engage in the religious activities of their choice
Full Faith and Credit Clause
Section 1 of Article IV of the Constitution that ensures judicial decrees and contracts made in one state will be binding and enforceable in any other state.
Preamble to the Constitution
We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America.
Privleges and Immunities Clause
Article 4 section 2 clause 1- citizens of one state cannot be discriminated in other states
Reserved Power Clause
found in the 10th amendment it gives states powers not delegated to the national government
Search and Seizure Clause
4th amendment Protection against Unreasonable Search and Seizure
Supremacy Clause
Article VI, clause 2 of the Constitution, which makes the Constitution, national laws, and treaties supreme over state laws when the national government is acting within its constitutional limits.
Takings Clause
a clause in the Fifth Amendment that prohibits the government from taking private property for public use "without just compensation"
War Powers Clause
Article 1, section 8, clauses 11-14- Vests in the Congress the exclusive power to declare war
Magna Carta
-1215
-Agreement between King John and Nobles
-Established Rule of Law: everyone including the King must follow the law

Charter of the Virginia Company of London
-1609
-King James of England
-Guaranteed Rights of Englishmen to the Colonists
(Guaranteed overseas settlers the same rights of Englishmen that they would have enjoyed if they had stayed at home)
Virginia Declaration of Rights
-May 1776
-George Mason
-Stated that people have INHERENT RIGHTS
*Served as a MODEL for the BILL OF RIGHTS

The Declaration of Independence
-July 4, 1776
-written by THOMAS JEFFERSON
-Declared Colonies had the right to be FREE and INDEPENDENT from Britain
-Stated GRIEVANCES (complaints) against the King.
-Stated that ALL MEN ARE CREATED EQUAL and have certain UNALIENABLE RIGHTS (rights that can't be taken away)
"life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness"

Articles of Confederation
-1781
-FIRST FORM of GOVERNMENT for the Independent States
-Gave MOST POWER to the STATES making a
WEAK NATIONAL GOVERNMENT
-Only 1 branch-LEGISLATIVE with each state having 1 vote

WEAKNESSES of the Articles of Confederation
*Weak National Government
*National Government could not tax
*Could make laws but No executive branch to enforce laws
These WEAKNESSES led to the writing of the US CONSTITUTION
Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom
-1786
-Thomas Jefferson
-It guaranteed Virginians FREEDOM OF RELIGION and influenced the first amendment
-SEPARATION OF CHURCH AND STATE- the state could not have an official religion

Constitutional Convention
The meeting of state delegates in 1787 in Philadelphia called to revise the Articles of Confederation and give more power to the central government.
It instead designed a new plan of government, the US Constitution.

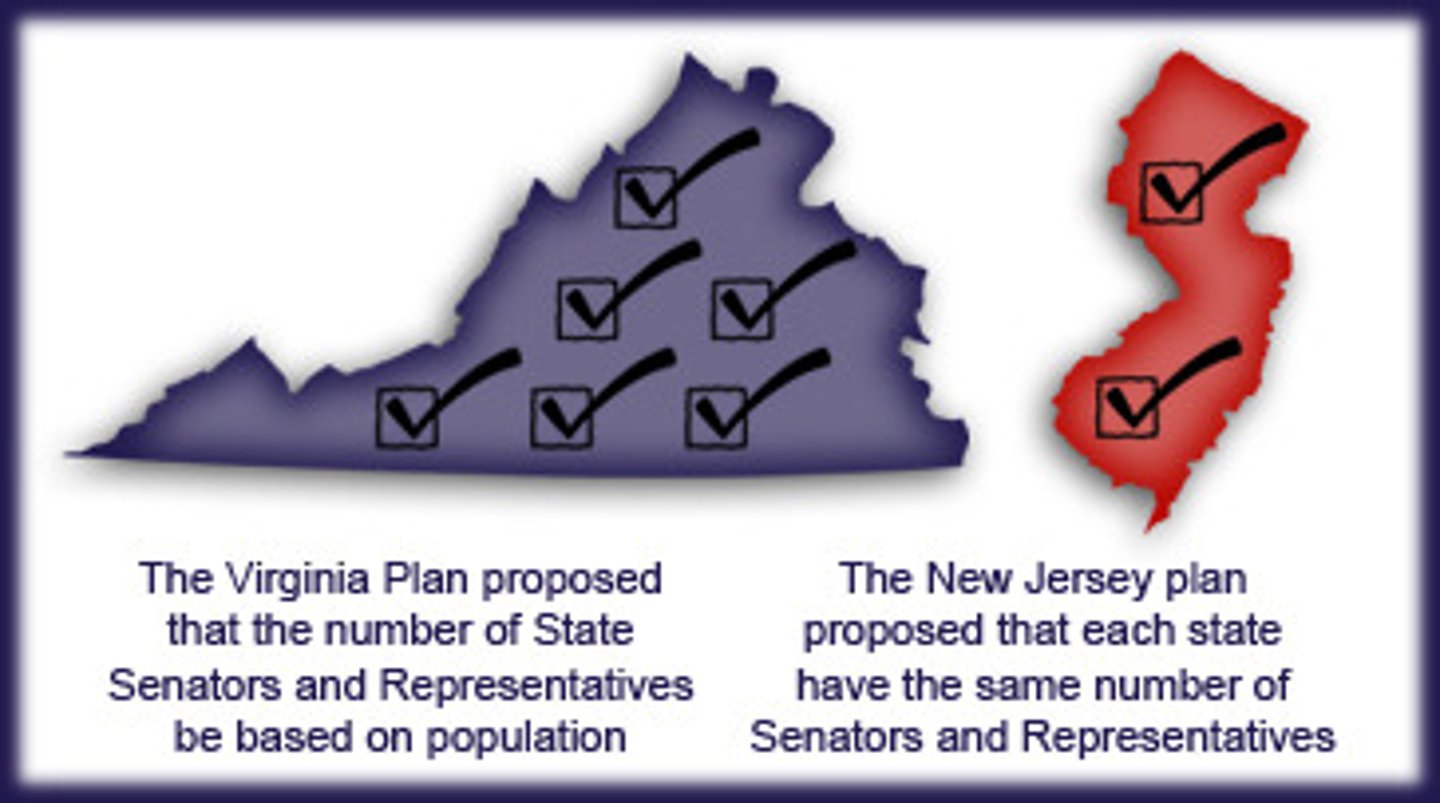
New Jersey Plan
A constitutional proposal that would have given each state one vote in a new congress
Favored SMALL states

Virginia Plan
The proposal at the Constitutional Convention that called for representation of each state in Congress based on that state's population
Favored LARGE states
The Great Compromise
created two houses (bicameral) in Congress; one based on population (Virginia Plan) and the other gave equal representation (New Jersey Plan) to each state.
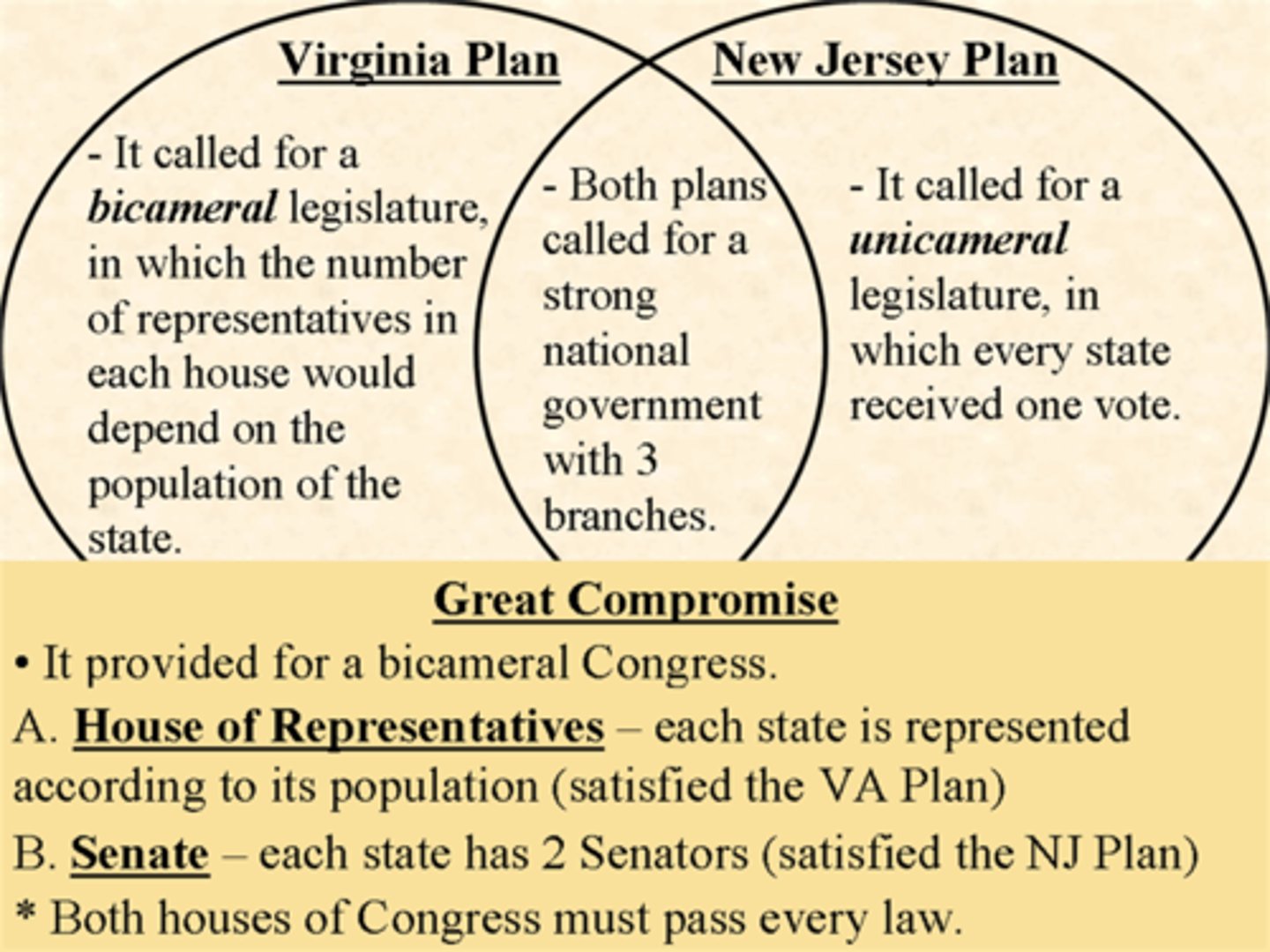
Bicameral
2 houses
HOUSE of REPRESENTATIVES would be based on POPULATION,
the SENATE would have TWO representatives from each state
US Constitution
-1787
-JAMES MADISON "Father of the Constitution"
-Established the Structure of our Government
-Guarantees equality under the law with majority rule and the rights of the minority protected
-The Supreme Law of the Land

Principles in the US Constitution
Majority Rule, Minority Rights, Equality Under the Law
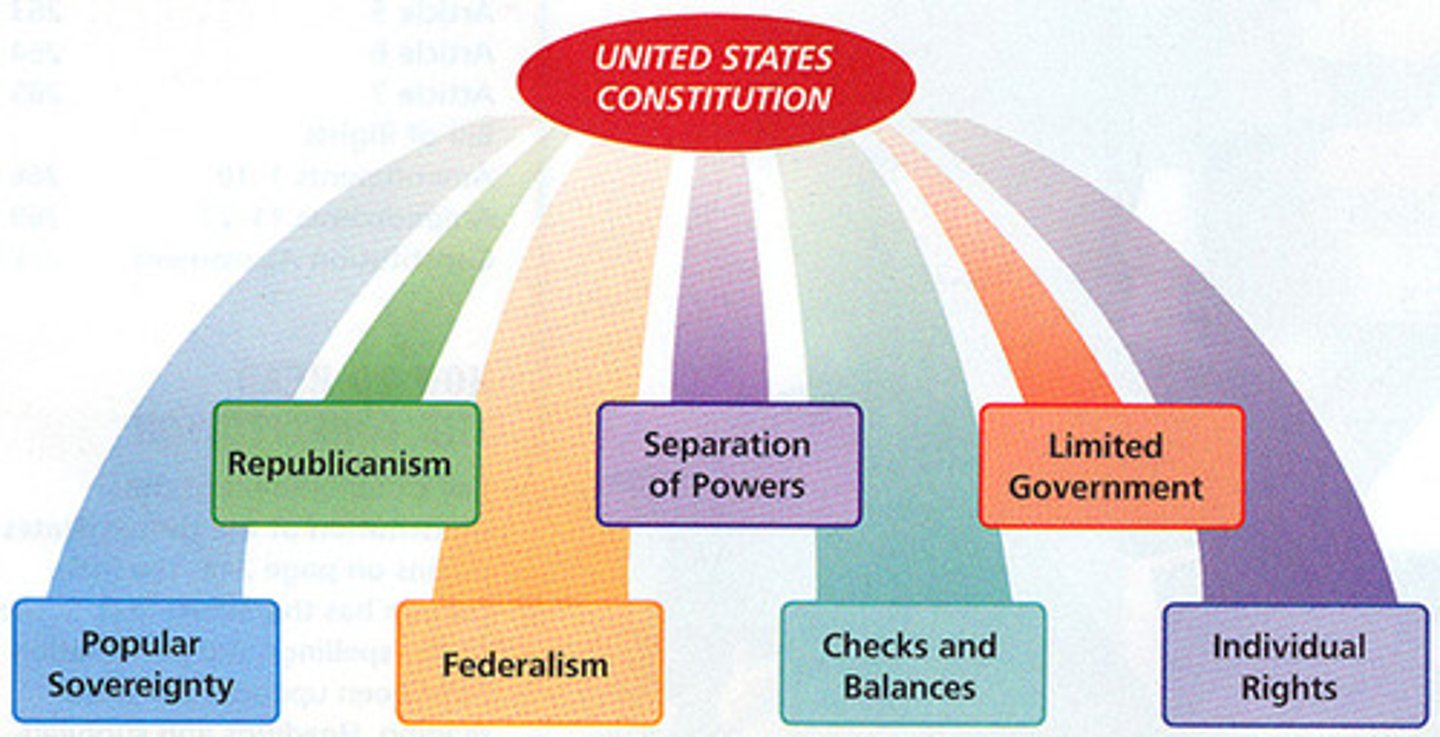
Constitution
a written PLAN of GOVERNMENT
Ratification of the Constitution
required 9 of the 13 states approval
By promising to add a Bill of Rights, it won the necessary 9 states and eventually was ratified by all 13 in 1790

Federalists
SUPPORTERS of RATIFICATION of the CONSTITUTION and of a strong central government.

Anti-Federalists
They opposed the ratification of the Constitution because it gave more power to the federal government and less to the states, and because it did not ensure individual rights. The Anti-federalists were instrumental in obtaining passage of the BILL of RIGHTS as a prerequisite to ratification of the Constitution in several states.

Bill of Rights
-1791
FIRST 10 AMENDMENTS added to the Constitution
*PROTECTED citizens from abuses of power by the national government
-Guarantees Equality under the Law

What document was written by George Mason and served as a model for the first 10 Amendments to the US Constitution?
Virginia Declaration of Rights
What document guaranteed the colonists the same rights of Englishmen?
Charter of the Virginia Company of London
The "right to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness" is found in what document?
Declaration of Indepencence
What are the unalienable rights listed in the Declaration of Independence?
Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Happiness
Weakness of which document led to the writing of the US Constitution?
Articles of Confederation
What document by Thomas Jefferson influenced the First Amendment's freedom of religion?
Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom
Who is the "Father of the US Constitution"?
James Madison
Which document stated the colonists' grievances against King George?
Declaration Of Independence
Which document guarantees rights to Americans and protects them from government abuses?
Bill of Rights
Which document is the "Supreme Law of the Land"
US Constitution
The New Jersey Plan and Virginia Plan differed mainly over
what?
State representation in the legislative branch
The first 10 amendments to the US Constitution is known as
Bill of Rights
Which document created the first form of government for the US?
Articles of Confederation
Which document stated why the colonists wanted to break away from Great Britain?
Declaration of Independence
Who wrote the Declaration of Independence?
Thomas Jefferson
Each state had one vote in the lawmaking house under
Articles of Confederation
This document guaranteed freedom of religion to Virginians
Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom
Under which document was the government unable to charge taxes or enforce laws?
Articles of Confederation
A written plan of government
Constitution
What are some of the principles in the Constitution?
Majority Rule, Minority Rights, Equality Under the Law
1st Amendment
Freedom of religion (establishment & free exercise clauses), speech, press, assembly, and petition.

2nd Amendment
Right to bear arms.
A well regulated Militia, being necessary to the security of a free State, the right of the people to keep and bear Arms, shall not be infringed.

3rd Amendment
You do not have to take in and take care of soldiers during peace times into your home. (Prohibits the forced quartering of soldiers during peacetime.)

4th Amendment
No unreasonable searches and seizures
- they have to have a warrant (paper giving permission to enter with exactly what they are looking for)

5th Amendment
(1) No Self-Incrimination, don't have to testify against yourself
(2) No Double Jeopardy (defendant cannot be tried again on the same, or similar charges)
(3) No deprivation of life liberty or property without "due process of law" (fair treatment)
4) Eminent Domain: Government cannot take property without just compensation
5) Right to a Grand Jury

6th Amendment
You have the right to a speedy & public trial. The right to counsel in criminal trials. You get a free lawyer ("public defender"). Right to jury in criminal trials.

7th Amendment
Right to jury in civil trials.

8th Amendment
Court cannot issue excessive bail ($ paid to leave jail between arrest and the trial) and there can be no cruel and unusual punishment (the punishment should fit the crime)
9th Amendment
Unenumerated Rights Amendment. Rights in addition to those stated in the Constitution. . Not everything can be written down. rights retained by the people

10th Amendment
Powers not expressly given to federal government by the Constitution are reserved to states or the people.
"reserved powers amendment"
"states' rights amendment"

11th Amendment
One State cannot be sued by another state
12th Amendment
Determines how the people elect the President and Vice
President every four years using the Electoral College, separation of votes for President and Vice President

13th Amendment
Abolished slavery.

14th Amendment
(1) All persons born in the U.S. are citizens; (2) no person can be deprived of life, liberty or property without DUE PROCESS OF LAW; (3) no state can deprive a person of EQUAL PROTECTION of the laws.
15th Amendment
States cannot deny any person the right to vote because of race.

16th Amendment
Power of Congress to tax income (money from your job)

17th Amendment
Established the direct election of senators (instead of being chosen by state legislatures)
18th Amendment
Prohibition of alcohol (made sale and consumption of alcohol illegal)
19th Amendment
States cannot deny the right to vote based on gender (Women's Suffrage)

20th Amendment
Congress begins on January 30th; President starts on January 20th
"Lame-duck" Amendment

21st Amendment
Repeal of Prohibition

22nd Amendment
Limits the president to two terms (8 years) or 10 years if circumstances arise.

23rd Amendment
Gives Washington DC electoral college votes as if it were a state (DC still has no representation in Congress)

24th Amendment
Abolishes poll taxes

25th Amendment
(1) Succession of VP if president dies or become incapable to do his job.(2) if there is no VP, president must appoint one, and congress must approve

26th Amendment
States cannot deny the right to vote based on age (18+) Lowered from 21

27th Amendment
congressional pay raises are not begun until the next election

Bill Of Rights
The name for the first 10 amendments to the Constituion