testing and iq
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
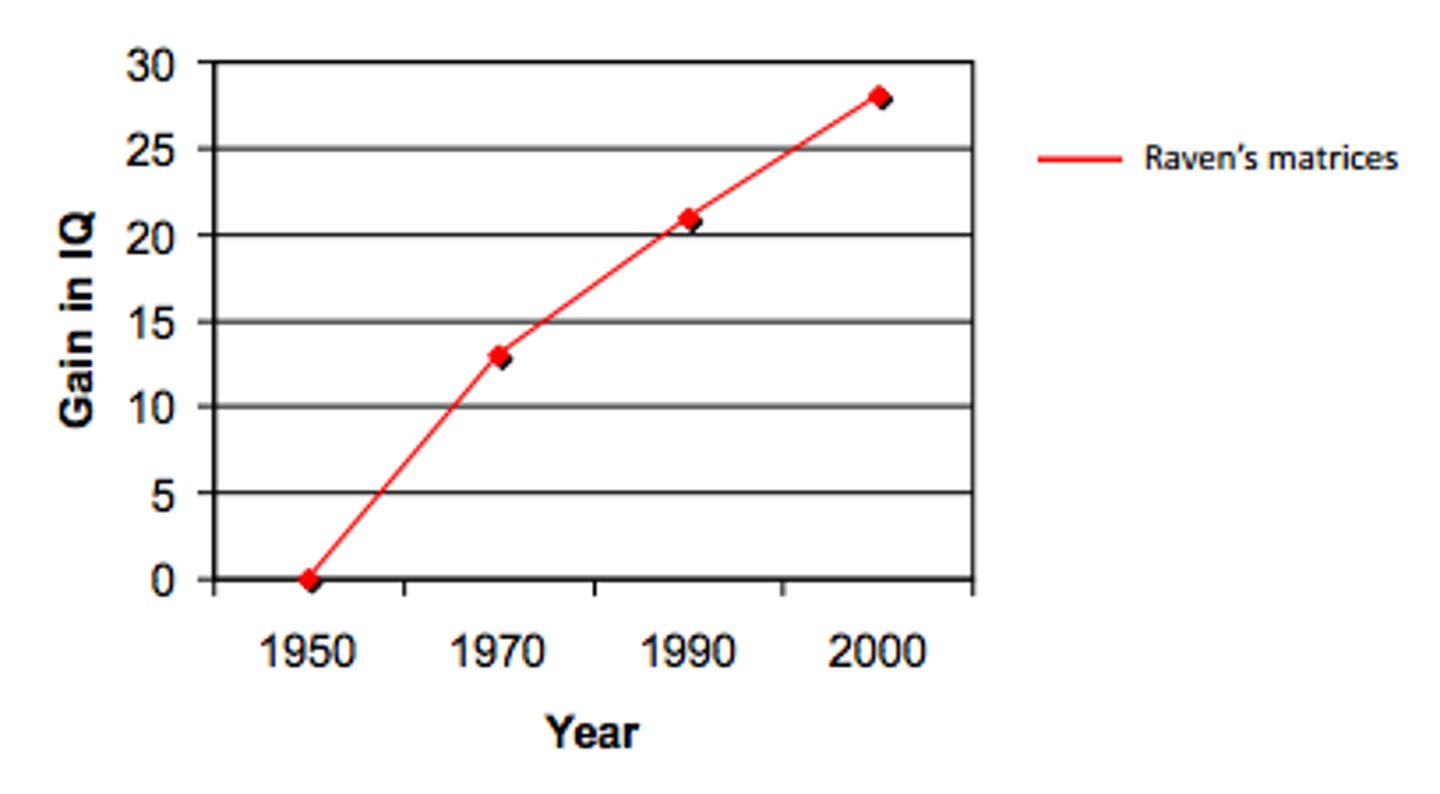
flynn effect
The higher IQ scores today
norms must be re-calculated every so often. Compared to the 1930s, people score much higher today. In the 30s, the average would only be 76 using today's scale.
intelligence test
a method for assessing an individual's mental aptitudes and comparing them with those of others, using numerical scores
intelligence
mental quality consisting of the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations

general intelligence (g)
a general intelligence factor that, according to Spearman and others, underlies specific mental abilities and is therefore measured by every task on an intelligence test

factor analysis
a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items on a test; used to identify different dimensions of performance that underline a person's total score
savant syndrome
a condition in which a person otherwise limited in mental ability has an exceptional specific skill, such as in computation or drawing

emotional intelligence
the ability to perceive, understand, mange, and use emotions
mental stage
a measure of intelligence test performance devised by Binet; the chronological age that most typically corresponds to a given level of performance

Stanford Binet
the widely used American revision (by Terman at Stanford University) of Binet's original intelligence test

intelligence quotient (IQ)
defined as the ratio of mental age to chronological age multiplied by 100. On contemporary intelligence tests, the average performance for a given age is assigned to a score of 100.

achievement tests
tests designed to asses what a person has learned

aptitude tests
tests designed to predict a person's future performance;

Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
the most widely used intelligence test; contains verbal and performance (nonverbal) subtests
standardization
defining meaningful scores by comparison with the performance of a pretested group
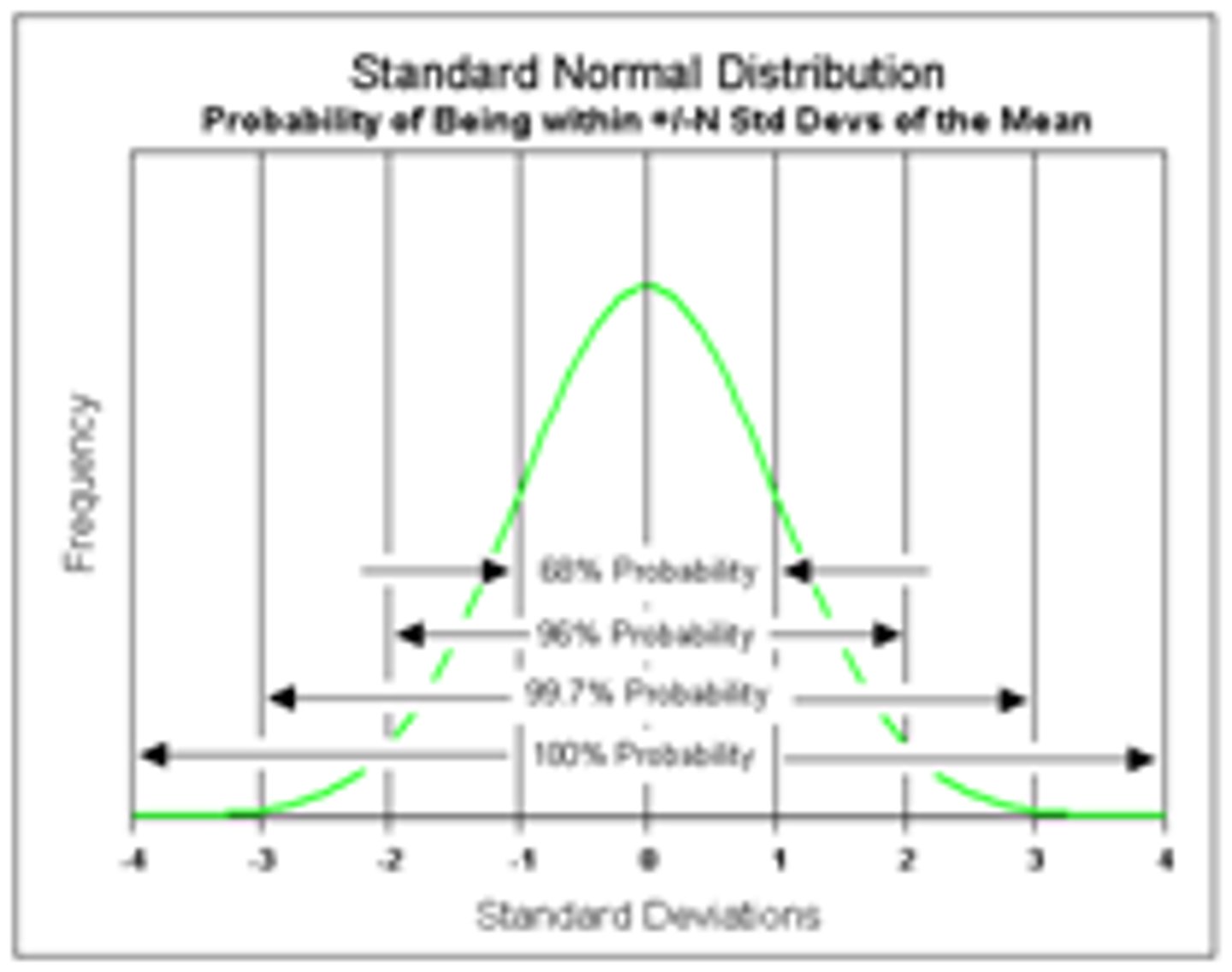
normal curve
a symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many types of data; most scores fall toward the mean 85-115 avg: below 70 diability
reliability
the extent to which a test yields consistent results, as assessed by the consistency of scores on two halves of the test, or on retesting

validity
the extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to
content validity
the extent to which a test samples the behavior that is of interest

predictive validity
the success with which a test predicts the behavior it is designed to predict; it is assessed by computing the correlation between test scores and the criterion behavior

intellectual disability
( formerly referred to as mental retardation) a condition of limited mental ability, indicated by an intelligence score of 70 or below and difficulty in adapting to the demands of life; varies from mild to profound

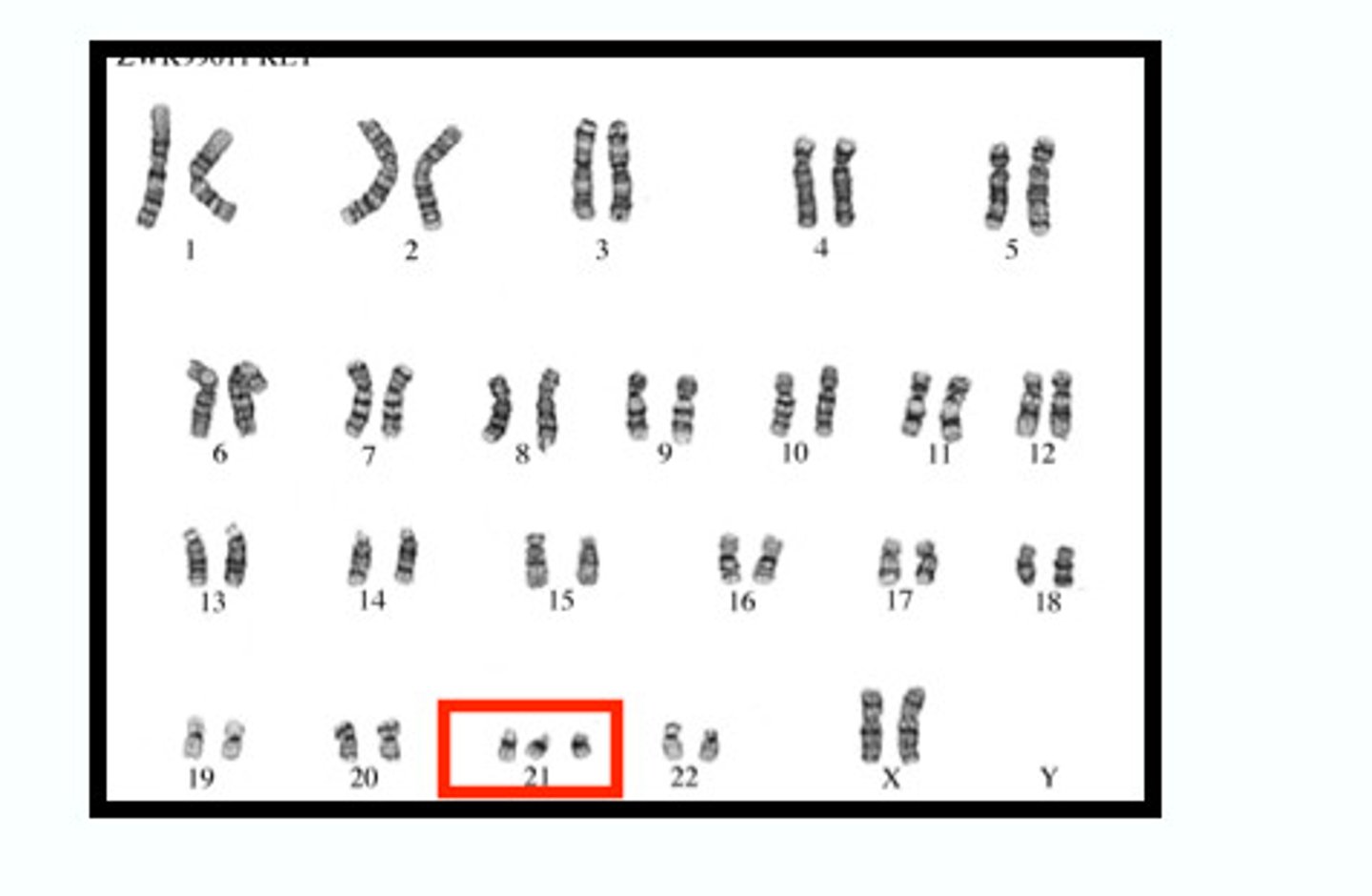
Down syndrome
a condition of intellectual disability and associated physical disorders cause by an extra copy of chromosome 21
stereotype threat
a self-confirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype

reification
Viewing an abstract, immaterial concept as if it were a concrete thing (ex. IQ)
David Wechsler
Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children and Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale two main categories, verbal and performance, and is broken into 11 subtests.
It gives an overall intelligence score
It also gives separate scores for verbal comprehension, perceptual organization, working memory, and processing speed.
These sub-scores can help identify strengths and problem areas.
Charles Spearmen
- Intelligence can be expressed by a single factor
-Believed that there was a general intelligence (g)
- g factor underlies all specific factors
Evidence: people who score high in one specific area also score high in others
Howard Gardener's Multiple inteligences (8)
Linguistic
Logical-mathematical
Musical
Spatial
Bodily-kinesthetic
Intrapersonal (self)
Interpersonal (others)
Naturalist
Robert Stenberg's Inteligences
Proposed the Triarchic Theory of Intelligence
Analytical intelligence (academic problem-solving)
These tests set up a specific problem with a single answer.
These tests predict school success well and vocational success fairly well.
Creative intelligence
These tests measure how a person responds to a novel situation and how they create fresh ideas.
Practical intelligence
These skills are used for everyday life, so the skills-set is rather wide open. The skills could include writing, speaking, interacting, motivating, etc.
Criticism of emotional inteligence
overextending the definition: doesn't mean anything
Math and Spacial Information located in
lower parietal lobe
Neural Plascitity
the ability of the brain to form and reorganize synaptic connections, especially in response to learning or experience or following injury.
Brain size and intelligence
Brain size and intelligence correlate at +0.33. This is a slightly positive correlation, meaning, to a small degree, larger brains mean smarter people
perceptual information and speed of processing
speed with which a person processes info also hints at intelligence. Speed and a score on an intelligence test correlate at about +0.30 to +0.50
binet and simon
(French) developed a test to predict how well a student would do in school in order to identify kids with special needs

Lewis Terman
revised the french version for California in Stanford (Stanford binet) and believed that a number could be given to intelligence (IQ)

eugenics
the idea that only smart and strong people should be encouraged (allowed) to reproduce. The idea was to stamp out the poorer human traits and continue the strong ones.
GRE (graduate record examination)
exam is a broad assessment of your critical thinking, analytical writing, verbal reasoning, and quantitative reasoning skills — all skills developed over the course of many years (required for grad school)--
tracking "gifted children"
controversial- if one child is "gifted", then the others are therefore "not gifted." Does this create a self-fulfilling prophecy for one group to do well and one poorly?
Isolating the "gifted" could also insulate them socially and hurt people-skills
intelligence; twin and adoption
identical twins separated do have a closer IQ than siblings
heritability
the amount of group variation in intelligence that can be attributed to genetics
gender differences in ability
Spelling - Females spell better.
Verbal ability - Females are by far better than males.
Nonverbal ability - Females are better at locating things and remembering pictures.
Sensation - Females are more sensitive to touch, taste and smell.
Emotion-detecting ability - Females are better at recognizing emotions of others.
Math and spatial ability - The results are mixed.

race and ethnic differences
IQ Asian, White, Hispanic, Black
As to nature, there is no proof that one race is more or less intelligent than another.
As to nurture, undoubtedly the environment affects one's education and results on IQ tests. The question is, how much?
Often, blacks and Hispanics grow up in less well-off circumstances.
In Asian-American cultures, parents often push their children hard to do well in school.

culture and content validity
The races are genetically different.
The races are socially different in their upbringing.
The tests themselves are biased for/against certain races.
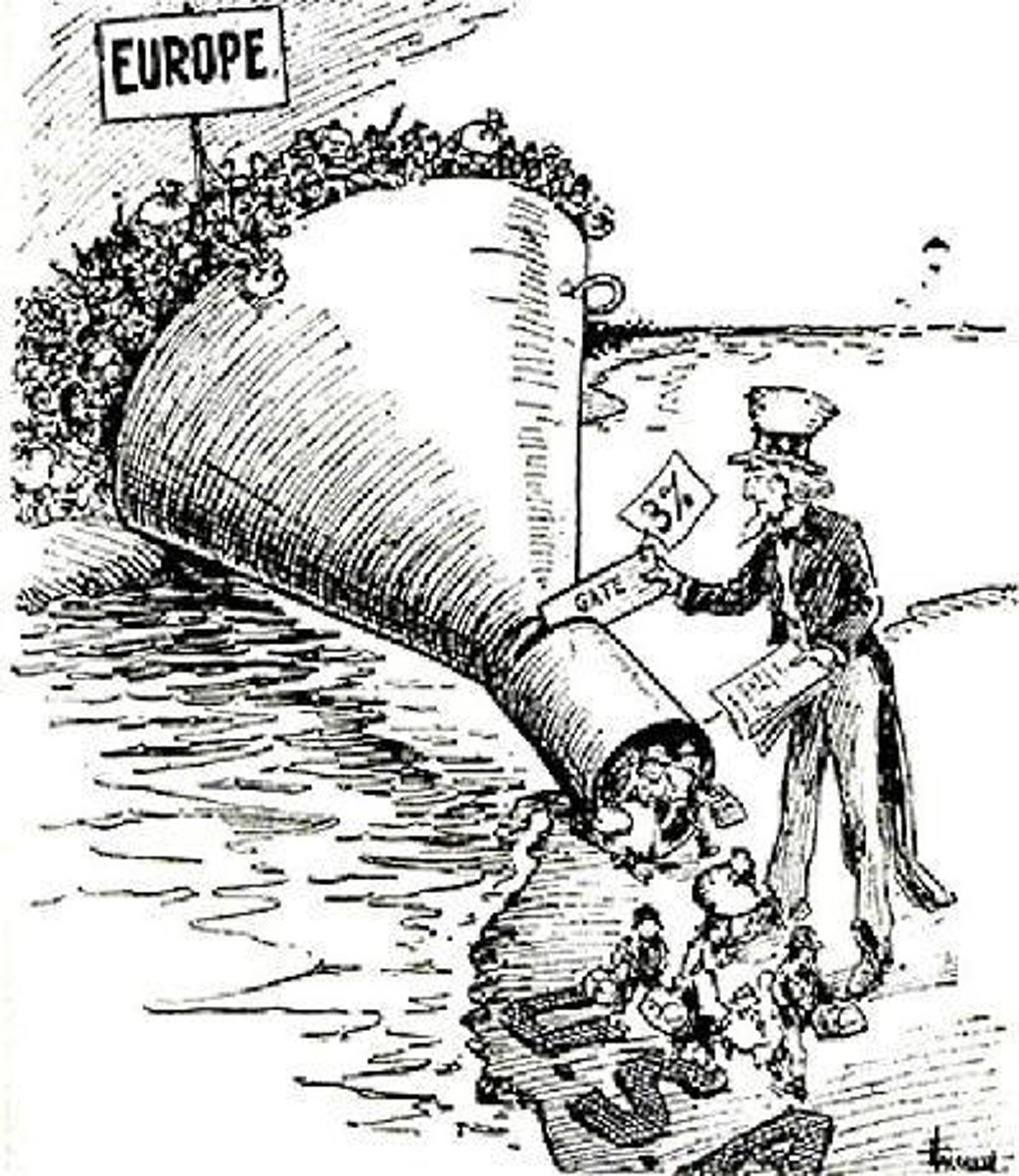
immigration act of 1924
In the 1920s, immigrants were given IQ tests. They often did poorer than Anglos (people of German/English descent). This helped fuel discrimination and laws to limit non-Anglo immigrants. But it had more to do with the culture the tests were written in
