introduction to community, population, public, and global health
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
population health
focuses on analyzing and improving health outcomes within a defined population
- ex. people with diabetes or a specific geographical region
public health
focuses on implementing policies and programs to protect and promote health of an entire population
often through large-scale interventions like vaccination or health education
community health
focuses on identifying and addressing health issues in a specific community
takes into account social and environmental factors
global health
focuses on health issues that transcend national boundaries and affect people worldwide
aims to address broader health and development that affects many populations
population health example
healthcare system that analyzes diabetes rates among their diabetic patient population to develop management programs
public health example
statewide campaign to increase awareness about the importance of flu vaccinations
community health example
a local health clinic working community leaders to address high rates of obesity among children in a specific neighborhood
global health example
the WHO focusing on a global health issue such as COVID-19
public health nurses vs community health nurses
public health nurses
- addresses policy development and reform to address health from a global perspective
community health nurses
- works directly with the community to address health-related needs
parse's view on community
community is a process that lives with each individual
it is not defined by certain numbers of persons
ecological model
can be used for population health as a guide to examine the determinants of health for a population, and for targeting interventions to multiple factors that affect health
ex. traits, family relationships, home environment, etc
health belief model
predicts or explains health behaviors
preventative health focuses
emphasizes change at the individual level
the transtheoretical model (TTM) or states of change (SOC)
describes how people change their behavior
provides strategies to help them to do so
TTM /SOC stages
precontemplation - not seeing a need for change
contemplation - seeing a need for change, but being blocked by barriers
preparation - creating a plan to change
action - implementing the plan
maintenance - implementing and maintaining the plan
termination - the health behavior is ingrained without thoughts of reverting to previous behavior
I PREPARE
helps nurses focus on the environmental factors when assessing the comunity
I PREPARE stands for...
I - investigate potential exposures
P - preset work
R - residence
E - environmental concerns
P - past work
A - activities
R - referrals and resources
E - educate
social cognitive theory
explains a person's interaction with their surroundings regarding their health
theory or reasoned action and planned behavior
discusses how intention can drive implementation of change
systems thinking
studies how individuals or units interact with other organizations or systems
upstream thinking
focuses on interventions that promote health or prevent illness
goal is to prevent problems from happening in the first place
Penters health promotion model (HPM)
focuses on positive health behaviors
individualized approach, focuses on self-efficacy
focuses on perceived benefits, barriers, self-efficacy, and interpersonal influences and situational influences
Nightingale's environmental theory
focuses on relationship between and individual's environment and health
looks at health on a continuum
emphasizes preventative care
Milo's framework for prevention
examines factors that influence a community's health and how to improve it through public policy
works with community like a partner in the health team
focuses on primary prevention
considers broader determinants of health
recognizes the role of personal choice
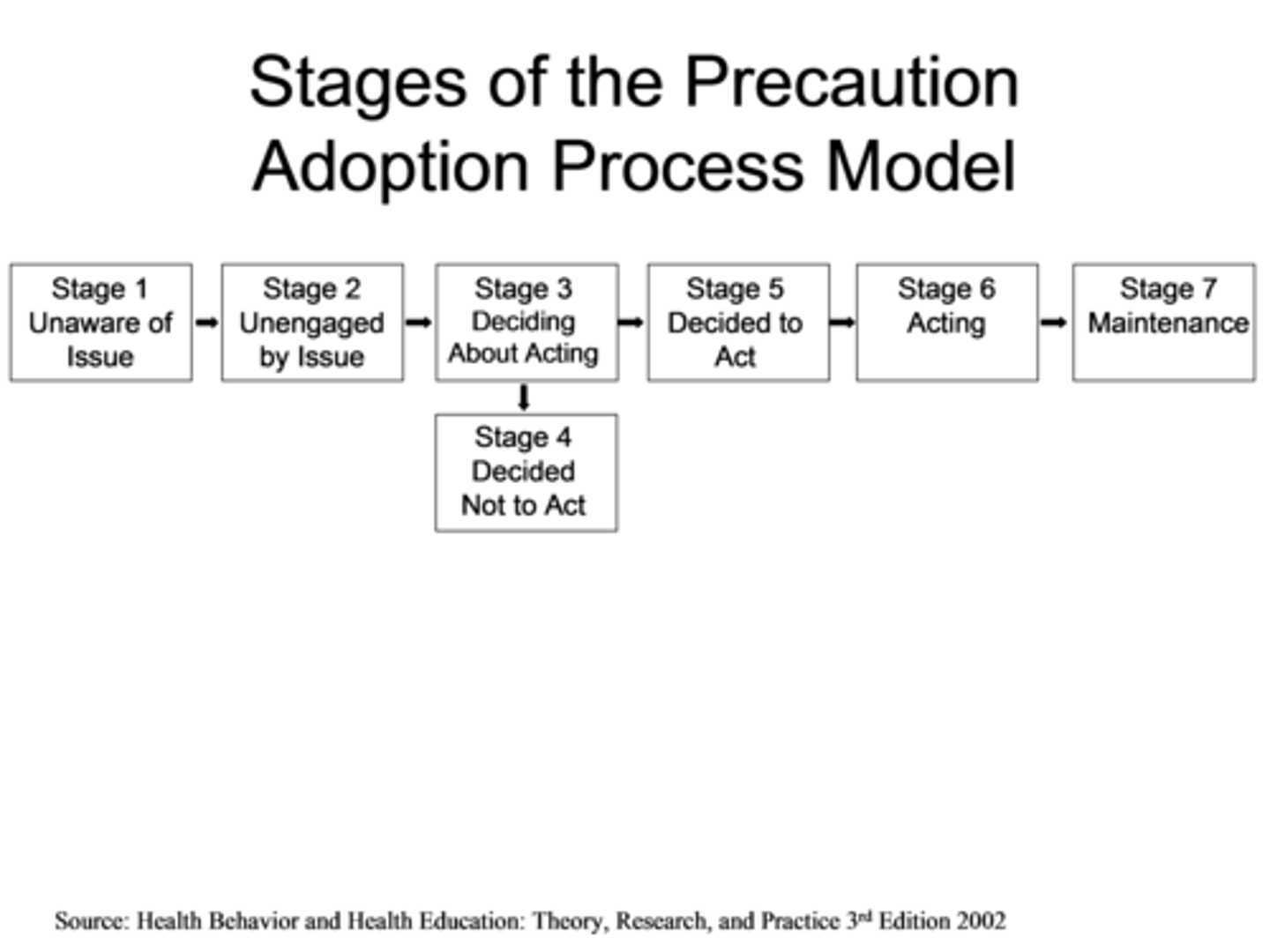
precaution adoption process model
describes the stages people go through when deciding to take action to prevent harm such as illness or injury
ethical principles of public health
beneficence
nonmaleficence
justice
autonomy
veracity
informed consent
confidenciality
health care technology
telehealth
EHR
surveillance systems
OMAHA system - promotes the practice and documentation to explain client care needs
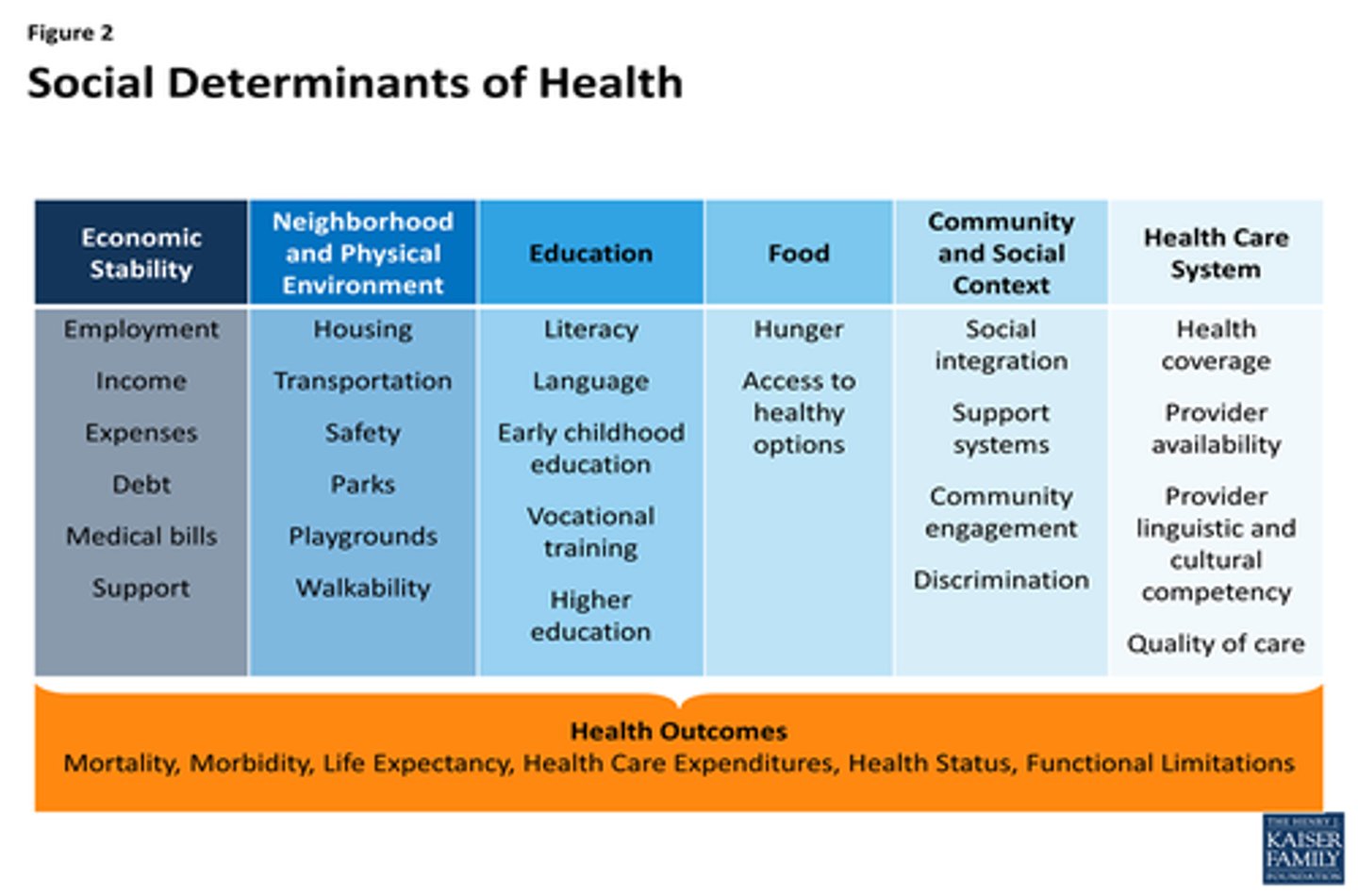
social determinants of health
economic stability
neighborhood and physical environment
education
food
community and social context
health care systems
health promotion
activities that enhance resources directed at improving well being
health prevention
focuses on avoiding disease and the effects of the diesase
levels of prevention
primordial prevention
primary prevention
secondary prevention
tertiary prevention primary prevention
primordial prevention
targets social and economic policies effecting health
primary prevention
targets risk factors leading to injury/disease
ex. safety belt laws, vaccination
secondary prevention
prevents injury/disease once exposure to risk factors occurs, but still in early "pre-clinical" stage
ex. screening tests, physical exams, BP checks
tertiary prevention
rehabilitating persons with injury/disease to reduce complications after injury
ex. someone learning how to walk again after stroke
core public health function
assessment
assurance
policy development
community and public health nursing specialties
public health nurse
epidemiology
community nurse
school nurse
nurse midwife
nurse educator
case management
occupational health nurse
nurse practitioner
forensic and correctional nursing
hospice nursing
home health nursing
faith-community nursing