Global History Regents Review- Questions
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

83 Terms
Who were the leaders of the Scientific Revolution?
Galileo
Copernicus
Isaac Newton

What were the ideas of the leaders of the Scientific Revolution and what did they challenge?
they used reasoning and logic and they conducted or made experiments. they all challenged the church and argued to use reason and logic, not to rely on god!

What was the impact of the Age of Exploration?
new ideas, colonization or Europeans taking land from natives

What was the result of the European colonization of South America?
Encomienda system-we teach you Christianity and you work for us, it became very abusive.
Spanish culture in Latin America.
Christianity.
Disease killing Natives-Caused Atlantic Slave Trade

What was Japan's Tokugawa Shogunate political system?
Emperor-figure head, kind of pretend ruler.
Shogun-had the real power, made all of the decisions.
Isolationist-do not want to work with outsiders, foreigners or strangers are barbaric- like animals

What were Enlightenment's Locke's major ideas?
People had natural rights to life, liberty or freedom and property.
Consent or permission of the governed. People had the right to say "yes, we want this ruler."
People could elect or vote and overthrow, get rid of, their leader

What is Montesquieu known for?
He created the 3 branches of government, separation of powers
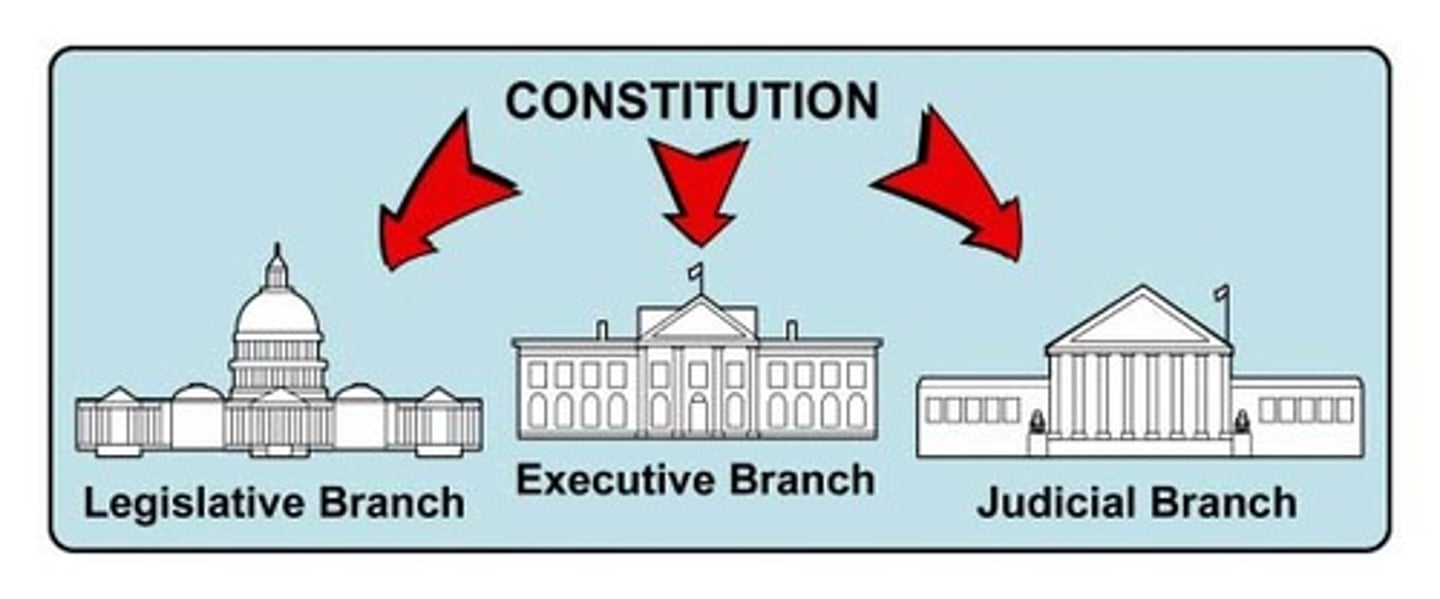
Who were Enlightened Despots?
Absolute Monarchs, rulers who had total power who used some of the Enlightenment ideas. They gave people more rights.
One of the causes of the French Revolution was taxes. Who had to pay the taxes?
The poor people or 3rd estate had to pay almost all the taxes

Who represented or spoke up for the third estate?
No one, that was one of the causes of the French revolution

How were the people of the 3rd estate treated?
How much land and food did the people of the 3rd estate have ?
They were treated unfairly, they wanted Enlightenment ideas, natural rights.
They had very little food and very little land
What were the key events and effects of the French Revolution?
estates General, Storming of the Bastille, Tennis Court Oath, Declaration of Rights of Man and Woman and Citizen

What was the Reign of Terror?
Beheading of Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette by Robespierre and the Jacobins.
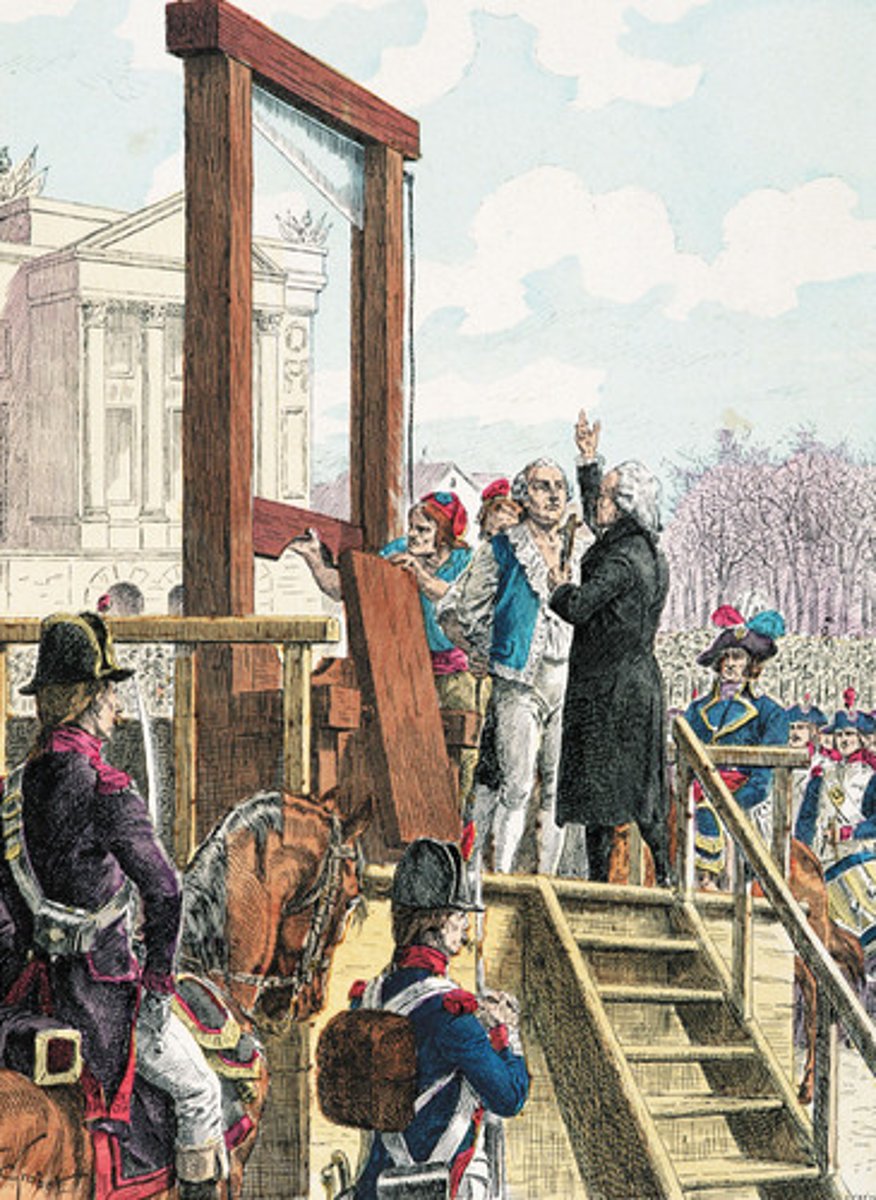

What is the guillotine?
a weapon to cut heads off

What were the Napoleon and Napoleonic Codes?
Laws for all citizens, they achieved revolutionary goal of natural rights. Napoleon as Emperor, failed revolutionary goal of electing leader. Taxes for all, achieved revolutionary goal of 3rd estate splitting taxes with 1st and 2nd.

How was Napoleon defeated by Russia during the Napoleonic Wars?
burned all crops, or plants, "scorched earth",
size of Russia which was very big, climate which was freezing winters
What was the goal or purpose of the Congress of Vienna?
To balance the power between countries so that no one country had more power than others. Restore or bring back monarchies, leadership, in power before Napoleonic wars

Who were the important leaders of Latin Independence movements?
Toussaint L'ouverture-Haitian Revolutionary Leader, he fought against France.
Miguel Hidalgo- Mexico.
Simon Bolivar- Argentina-could not unify South America because of the Andes Mountains acting as a barrier
What inspired or caused the leaders of the Latin Independence movements to fight?
The American and French Revolution.
Limited rights, not enough rights.
Enlightenment ideas of Natural Rights, John Locke.
Nationalism- Loyalty, love for country, culture.

How did the Agricultural revolution impact society? Think farming revolution
more food = more people were born, it increased life expectancy, people lived longer and birth more people were born.
Caused the industrial revolution and industrialization-forced to move into cities because workers are no longer needed on farms.

What are the possible impacts of nationalism, which is pride for your country, language, culture?
unites people, so small states want to unite and become one country.
Can cause wars, when large countries have different groups that want independence

Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain?
They had adequate, or enough and even extra food.
Close to water which generated, made, electricity for factories.
natural Harbors, ports for trading
Britain had the money, capital for factories.
Britain had an energy revolution, steam power and coal.

What are Capitalist ideas?
people can make a lot of money, private businesses are great.
Laissez-Faire-no government interference, meaning government gets involved very little.
supply, or how much we make, is based on demand, or how much people want.

What is Adam Smith known for?
He wrote The Wealth of Nations, a capitalist book.

What are communist ideas, opposite of capitalist?
no social classes, everyone is equal.
no private property.
everything belongs to everyone.
proletariat/workers must revolt or fight back to improve society and overthrow capitalist system.

Who created Communism?
Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels.
Wrote The Communist Manifesto, a communist book

What does urbanization refer to?
people moving from the countryside or farms to cities

How did society change during the industrial revolution-when we made things using factories?
people moved to the cities.
transportation improved since we were using trains and steamboats using steam engine.
Middle class started.
Factories started

What were the working conditions during the industrial revolution before unions?
women and children were working for less money than men.
the working conditions were dangerous- there were accidents and deaths.
there were low wages or very little pay and long work hours, 16 hour work days

What changes or reforms did the unions create for problems that were caused by the industrial revolution?
fought for worker's rights to higher wages or pay, shorter work hours and better working conditions

What changed were made after the industrial revolution?
outlawed slavery.
rights to vote or suffrage for all citizens
more schools were set up, public education for all boys and girls

Why did Irish citizens emigrate or leave Ireland during the 1840s and 1850s?
because of the potato famine, they didn't have any food

Why did Europeans imperialize or take over areas of India, China and Africa?
Industrial Revolution.
Use natural Resources to produce or make manufactured goods at home.
New markets to see manufactured goods.
Social Darwinism- survival of the fittest-racism, whites are better than colored.
Christianity-Educated and save savages-people who act like animals.

What were the effect of imperialism-countries taking over others?
European nations controlled others because of their superior/stronger military.

What were the effects of imperialism on India?
British colony.
Sepoy Mutiny-to remove foreign/imperial influence.
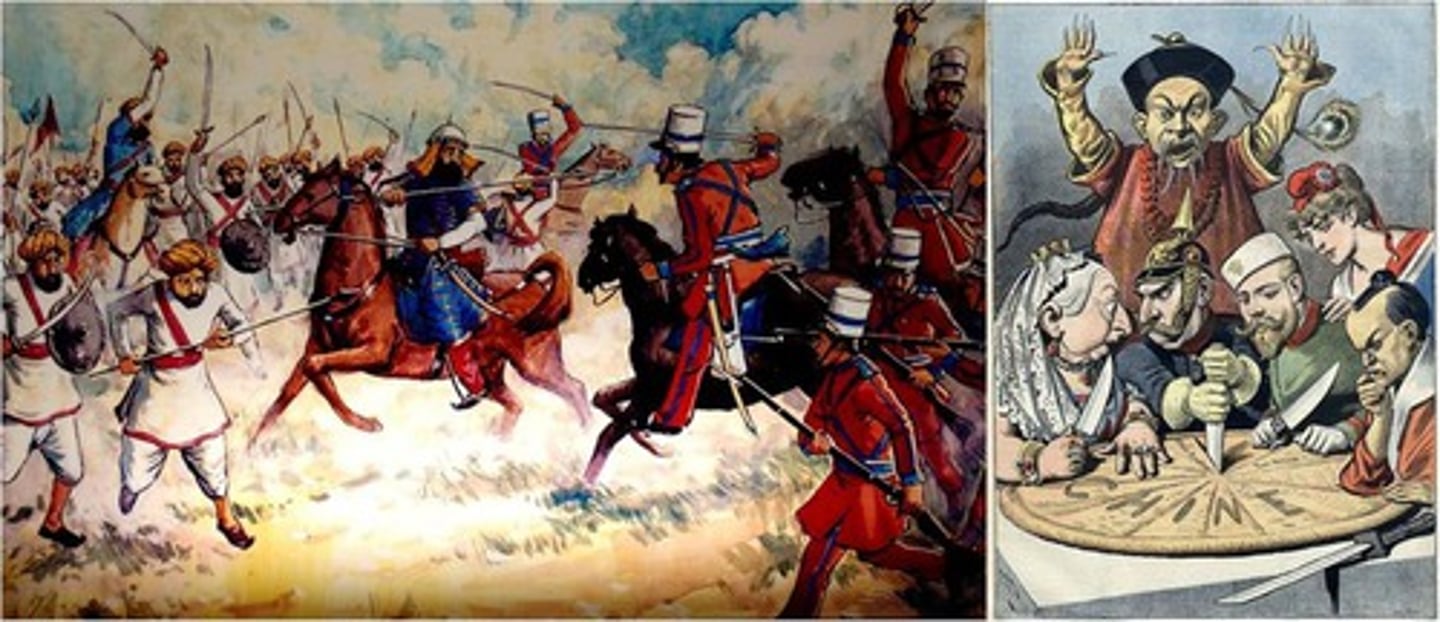

What were the effects of imperialism on China?
Opium War caused China to become a sphere of influence for many industrial nations.
Boxes/Taiping rebellion-remove foreign/imperial influence.

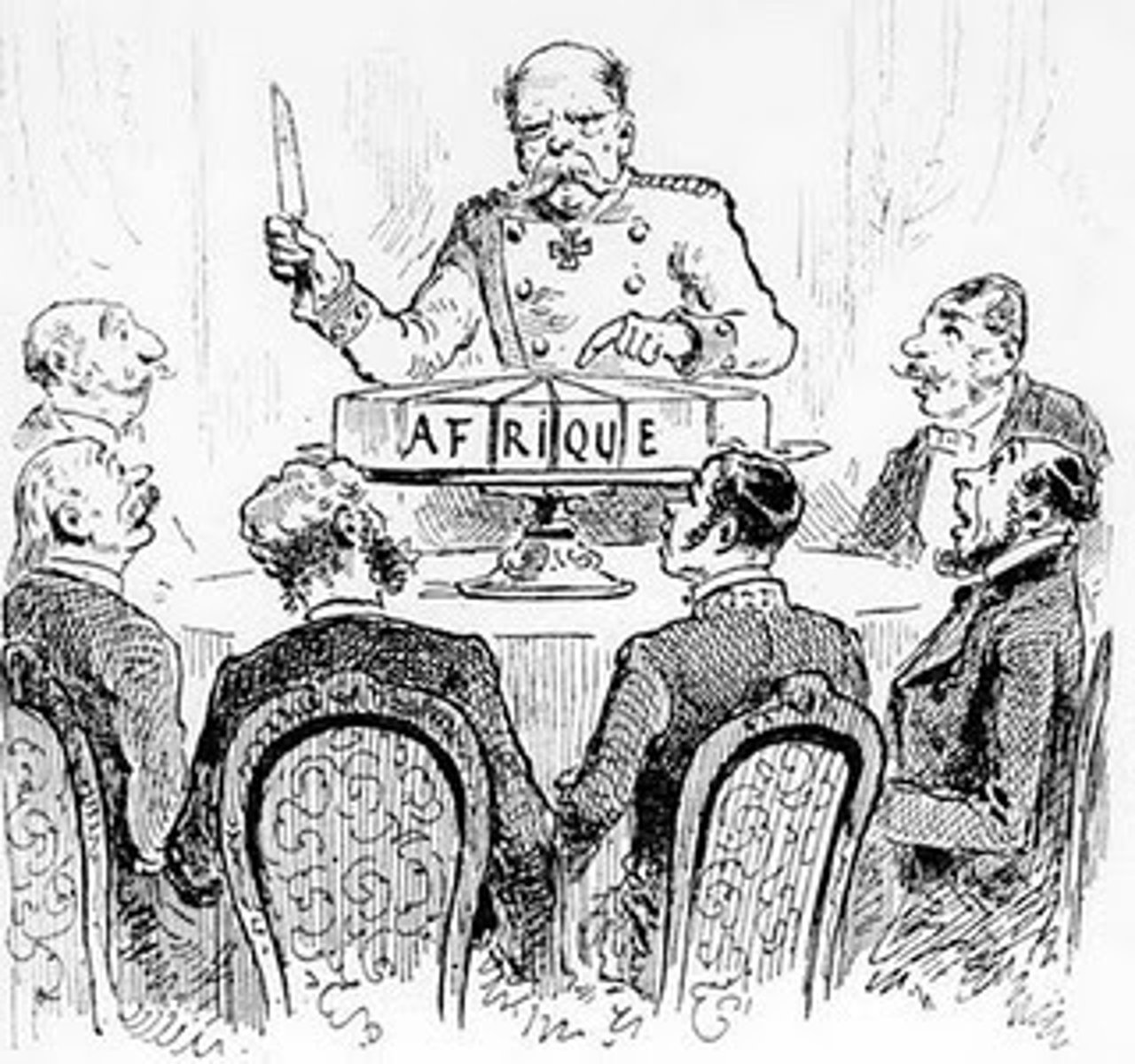
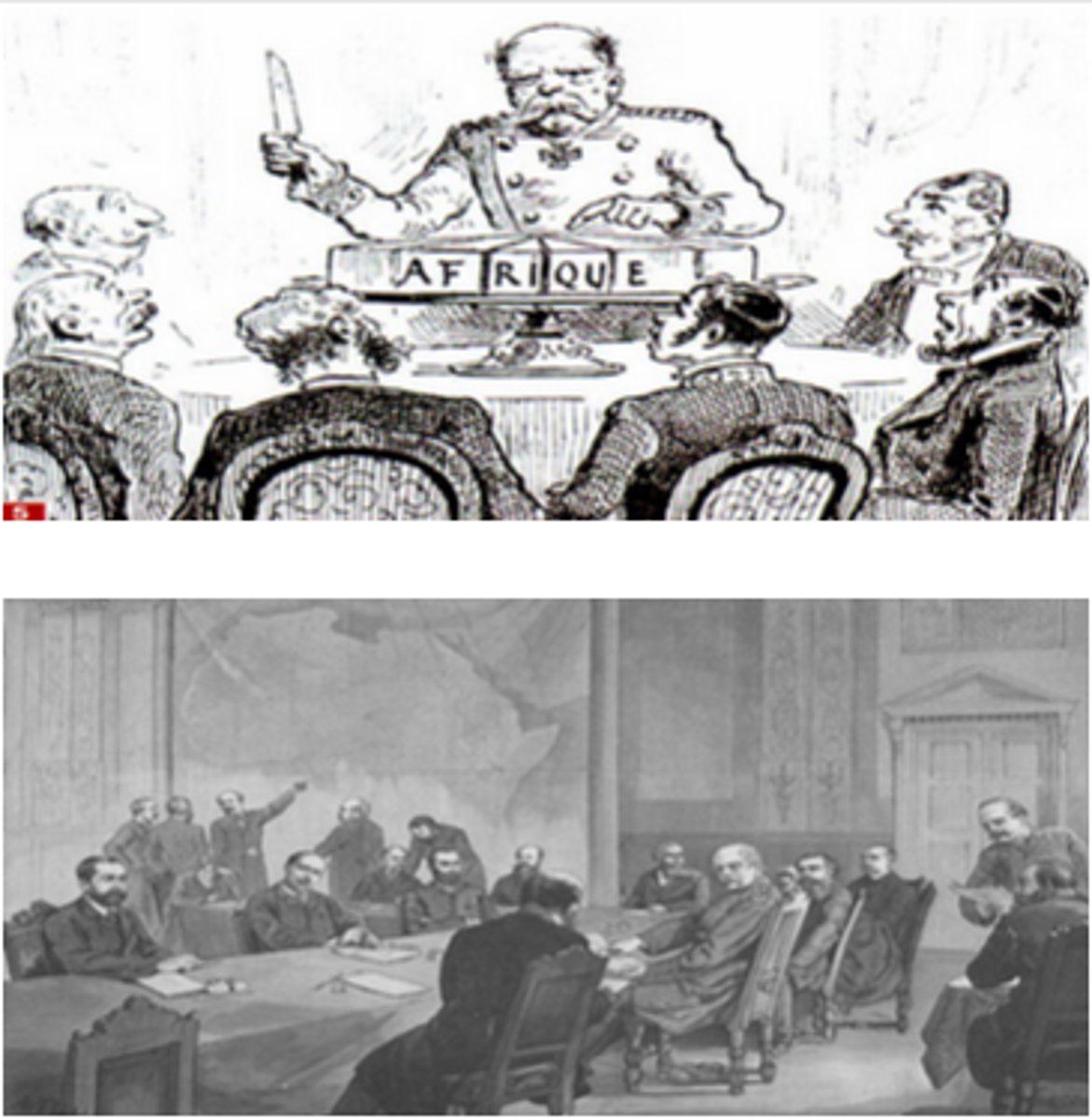
What were the effects of imperialism on Africa?
Berlin Conference-Africa was divided by European nations with no regard to African culture.
Suez canal built as strategic location between Africa and Middle East

What were the effects of imperialism on Japan?
Mejii Restoration.
Became modernized and controlled Asian countries like China and Korea.
Satisfied imperialist goals.
What were the causes of World War I?
MANIA:
Militarism, Alliances, nationalism, Imperialism, Assassination

How did militarism cause World War I?
Countries increased the size and strength of their military to prepare for war

How did alliances caused World War I?
Countries formed secret agreements to protect each other. Germany defends allies, forces France and England to defend their allies of Russian and Serbia.
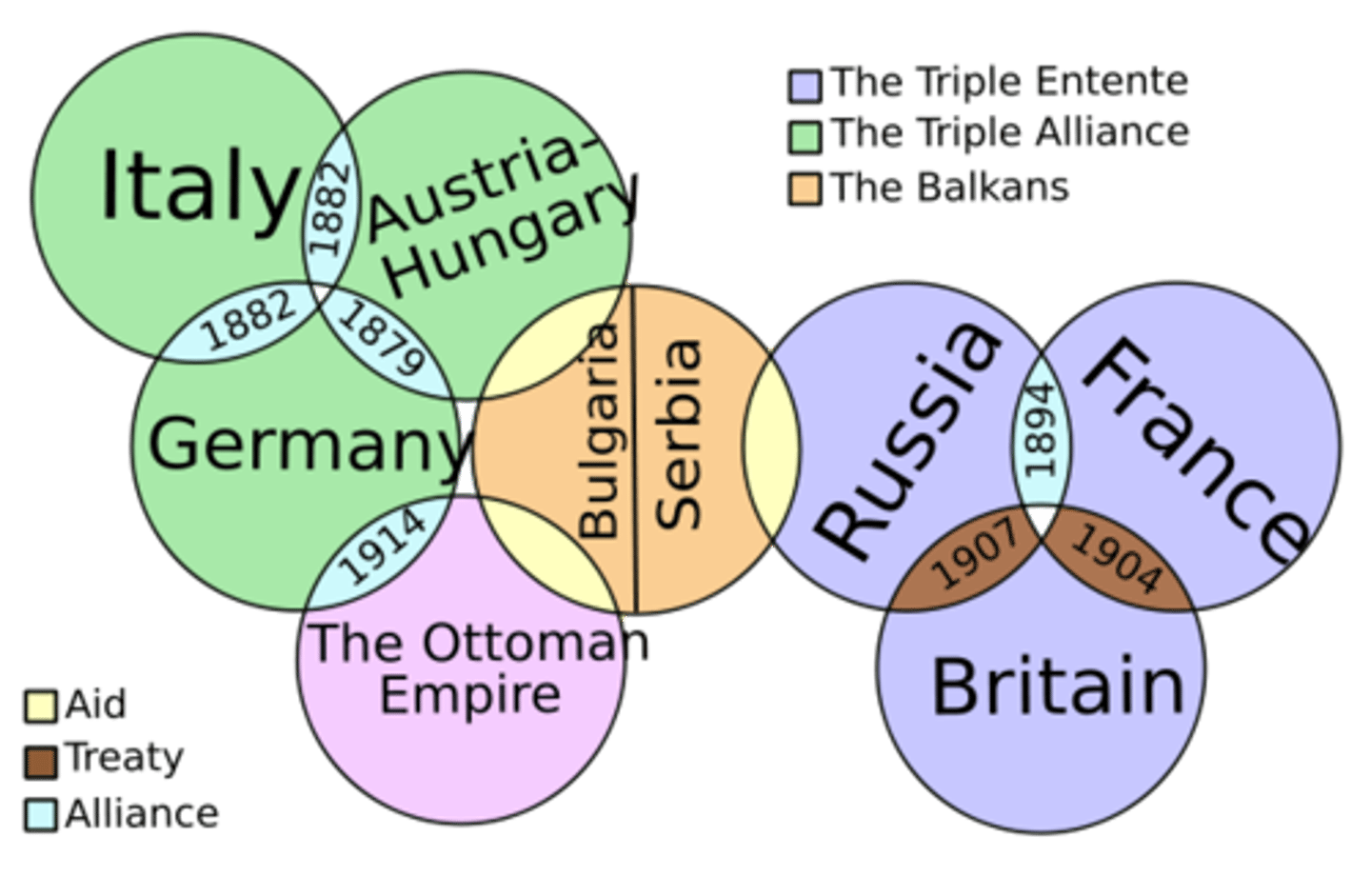
How did Nationalism cause World War I?
Pride and loyalty in your country leads to Serbian nationalists to kill Austria-Hungary's leader, because they want independence.

How did Imperialism cause World War I?
Nations compete and fight for colonies around the world.

How did Assassination cause World War I?
The killing or assassination of Archduke Ferdinand in the Balkans, also known as "the powder keg of Europe".
Immediate cause and spark that started World War I.
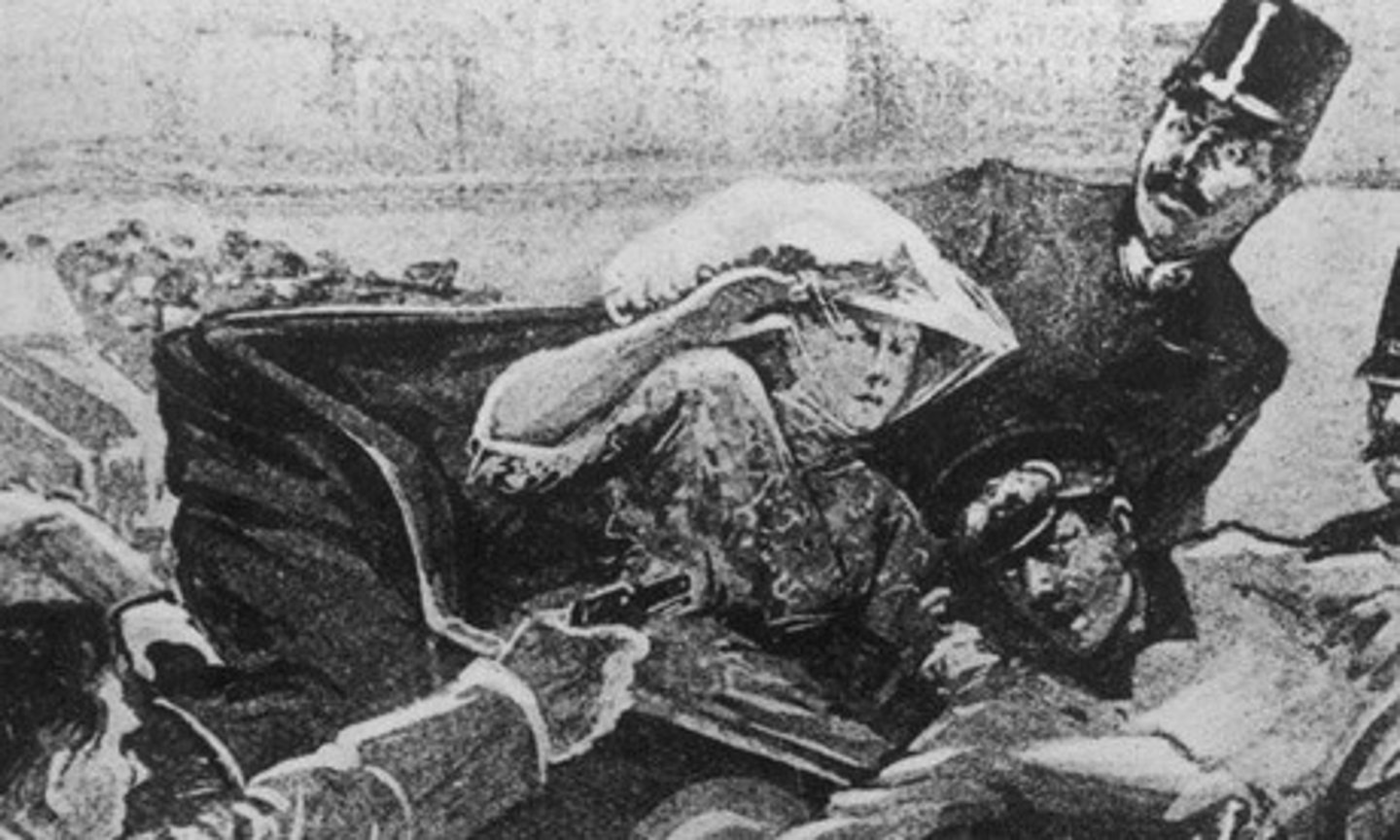
What new warfare was introduced during WWI?
Chemical Weapons-biological weapons like poison and mustard gas.
Machine Guns led to Trench Warfare.
Trench Warfare-trenches dug to avoid open fire
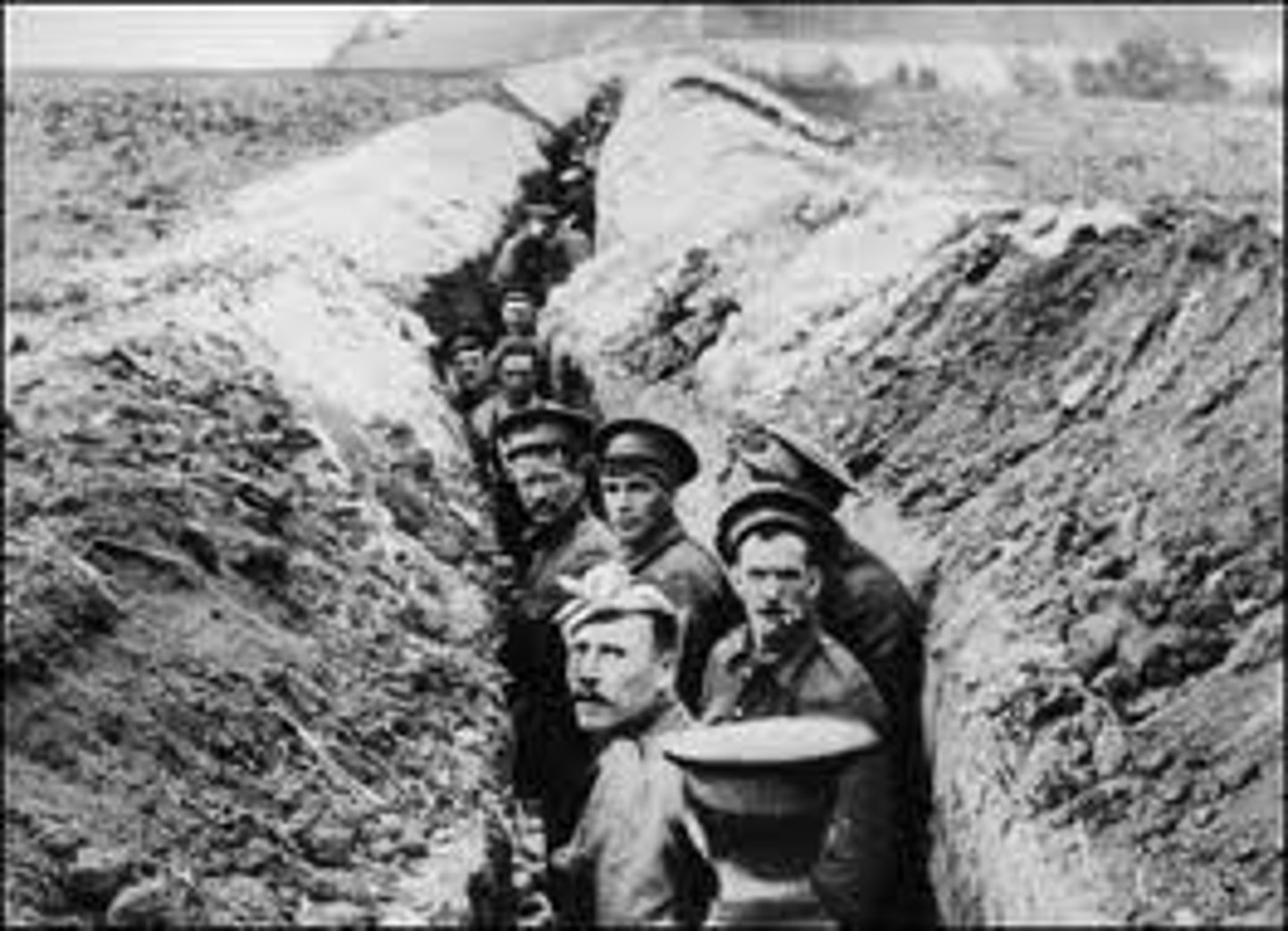

How did WWI end?
Treaty of Versailles-Germany was harshly punished.
Germany accepts blame.
Germany has to pay reparations.
Germany reduced military size.
Germany loses land.
Treaty causes rise of Hitler and World War II.

What were some of the effects of poor leaderships, which caused the Russian/Bolshevik Revolution?
Bloody Sunday-Czar or leader killed innocent Russians.
Losing the Russo-Japanese War.
Economic differences between social classes.
World War I failures.
What did the Bolsheviks do?
promised land to the poor.
Lenin promised "peace, land and bread."
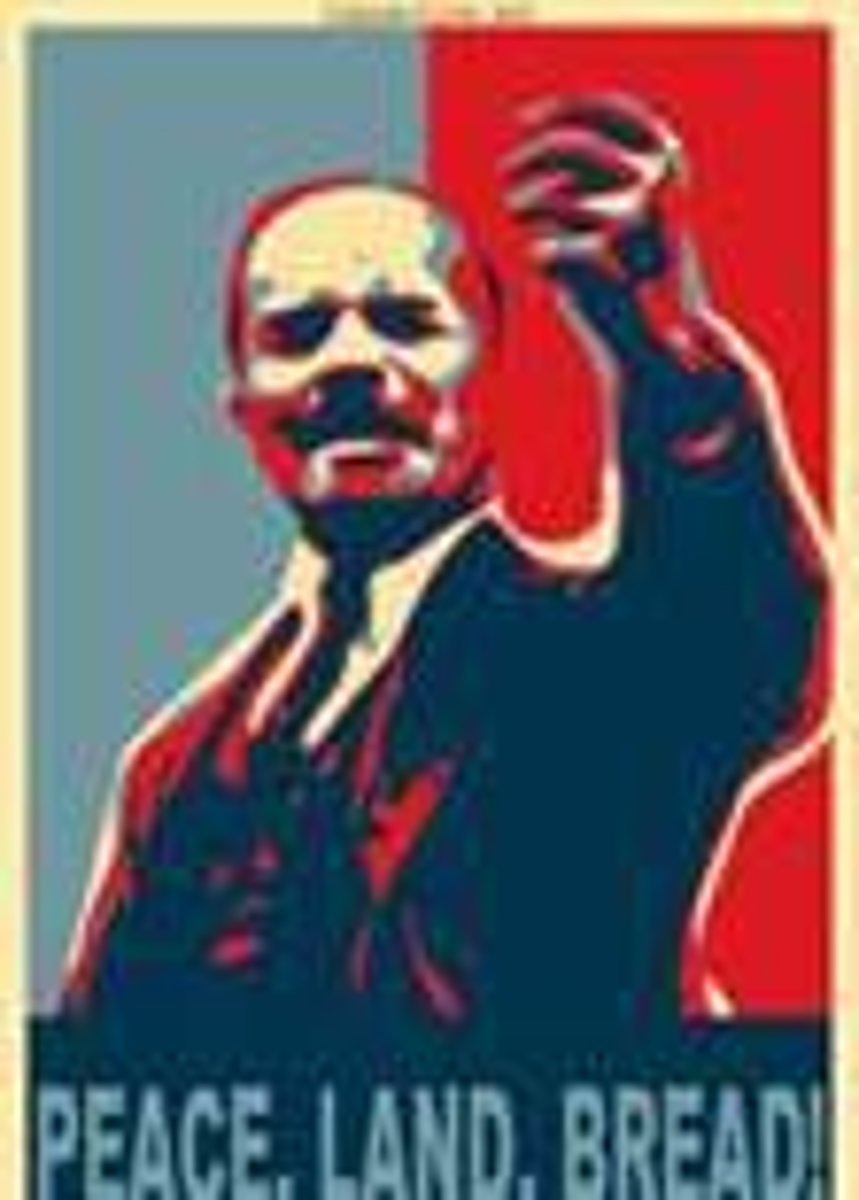

What were the effects of the Russian Revolution?
Lenin's communist Russia-first communist government Ever!!!
command economy-communism.
government controlled businesses.

How did Joseph Stalin rule the Soviet Union?
Censored citizens.
Secret Police-caused Terror.
5 year plan-increase agricultural or farming and industrial or factory output meaning heavy industry.
Collectivization-widespread food shortage and forced famine or starvation in Ukraine.

What caused totalitarianism?
Economic or $$$ and social problems like the Great Depression and loss of faith in democracy
What is totalitarianism?
citizen gave up freedom for stability or safety.
leaders have total control.
state/ country was more important than individuals.
censorship, arrests, secret police force.
denied basic human rights.

What are some examples of totalitarian leaders and what countries were they rulers in?
Benito Mussolini in Italy
Adolf Hitler in Germany
Hirohito in Japan
Joseph Stalin in Russia
Castro in Cuba
Mao Zedong in China

How did Hitler cause World War II?
Policy of Appeasement-Europeans gave Hitler land in exchange for peace.
Europeans promised to fight Hitler if he invaded Poland.
Hitler invaded Poland causing/starting World War II

How did the Russians defeat Hitler?
Russia's large size.
Russia's harsh winter and climate.

What was the Holocaust?
European and German Jews used as an excuse for German struggles after World War I.
Planned extinction/killing of European Jewish population by the Nazis.

What was the 3 step process of Genocide-killing off a race or whole group of people?
1. take rights way-Nuremberg laws.
2. isolate from society-Ghettos and concentration camps.
3. the Final Solution-extermination camps-gas chambers, shooting squads, death marches.

What were the effects of WWII?
European domination decreased, Europeans were no longer so powerful.
Nationalism in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East led to decolonization or colonies gaining independence.
Nuremberg Trials- German officials punished for human rights violations.
Cold War-Russian vs. U.S.A.
What were the 2 sides during the Cold War?
Capitalism-U.S. and NATO, Allies Versus Communism- USSR or Russian and Warsaw Pact

What were the ideas used during the Cold War?
USSR or Russia used military pressure to create Communist governments in Eastern Europe.
Arms Race, weapons and Space Race, NASA wins.

Why didn't the U.S. and USSR or Russia fight?
US and Soviet Union/USSR/Russia avoided war to prevent global nuclear destruction, they didn't want any nuclear bombs.

What were some hot spot conflicts during the Cold War?
Berlin Wall-divided communist and democratic berlin.
Korean War-North and South Korea divided at 38th parallel.
Vietnam War-South communist Vietnam wins.
Cuban and Nicaraguan Communist Revolutions-Fidel Castrol in Cuba.
Cuban Missile Crisis.
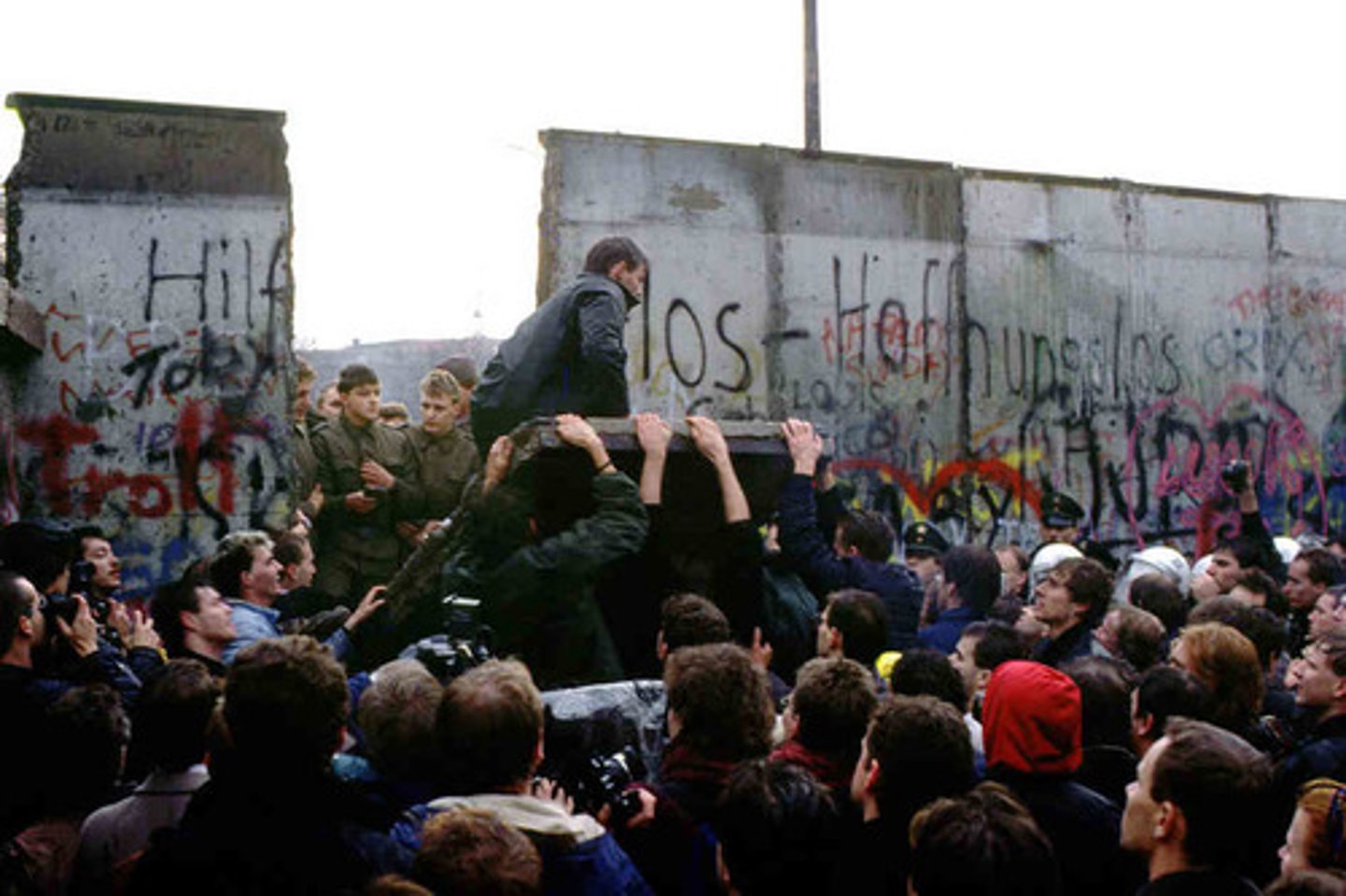
How did Communism collapse or fall apart?
high costs during Cold War.
Russian failures in Afghanistan.
Glasnost and Perestroika-policies to make Russia more democratic and capitalist-Remove Communist ideas.
Fall of the Berlin Wall was the End of the Cold War!!!

Why did Indians want independence?
British controlled Indian business and mistreated Indians.
Desired to remove or get ride of foreign/European imperialism. They didn't want anyone else controlling them.
How did Ghandi and Indians gain their independence?
Indian National Congress-nationalist organization with the goal of freeing India.
Ghandi-Passive Resistance and Civil Disobedience which means fighting back with non-violence and breaking unfair and unjust laws.
Ghandi -Salt March and homespun movement-wear traditional Indian clothing made in India, from start to finish

What were the effects of Indian independence?
India and Pakistan divided or partitioned-India for Hindus and Pakistan for Muslims. Border disputes or arguments for India with Pakistan and China.
India vs. Pakistan conflict over Kashmir-border between nations.

Why did African want independence?
European nations weakened after World War II-decline of empires, the big nations were getting worse.
Human rights violations-limited rights as colonies.
Desire to remove foreign/European imperialism (Europe taking over nations).
How did African nations gain their independence?
Strong leaders such as Jomo Kenyatta, Kwame Nkrumah, and Kenneth Kaunda.
Nationalist movements
Mau Mau in Kenya- rebelled against colonial power

What struggles were Africans faced with after gaining its independence?
clashes or fights with traditional tribes.
Islamic fundamentalism or traditional Muslim ideas vs modernization or western ideas.
ethnic/tribal differences or traditions.
What were some of the negative effect of African Independence?
Africans were not prepared for independence.
Europeans divide Africa with no regard for religious or ethnic groups.
African tribes and families were separated by unfair borders which started wars.
African cultures and traditions were lost due to separation and lack of preservation or keeping it

What was the policy of Apartheid in South Africa?
Apartheid was a series of laws that segregated and discriminated against the majority black population of South Africa.
This policy was started and upheld by the minority white population who held all governmental power.

What were some of the policies of Apartheid?
pass laws, passes were needed to travel from black to white areas.
The Race Classification Act.- Every citizen suspected of not being European was classified according to race.
The Mixed Marriages Act. It prohibited or didn't allow marriage between people of different races.
The Group Areas Act It forced people of certain races into living in designated or specific areas.

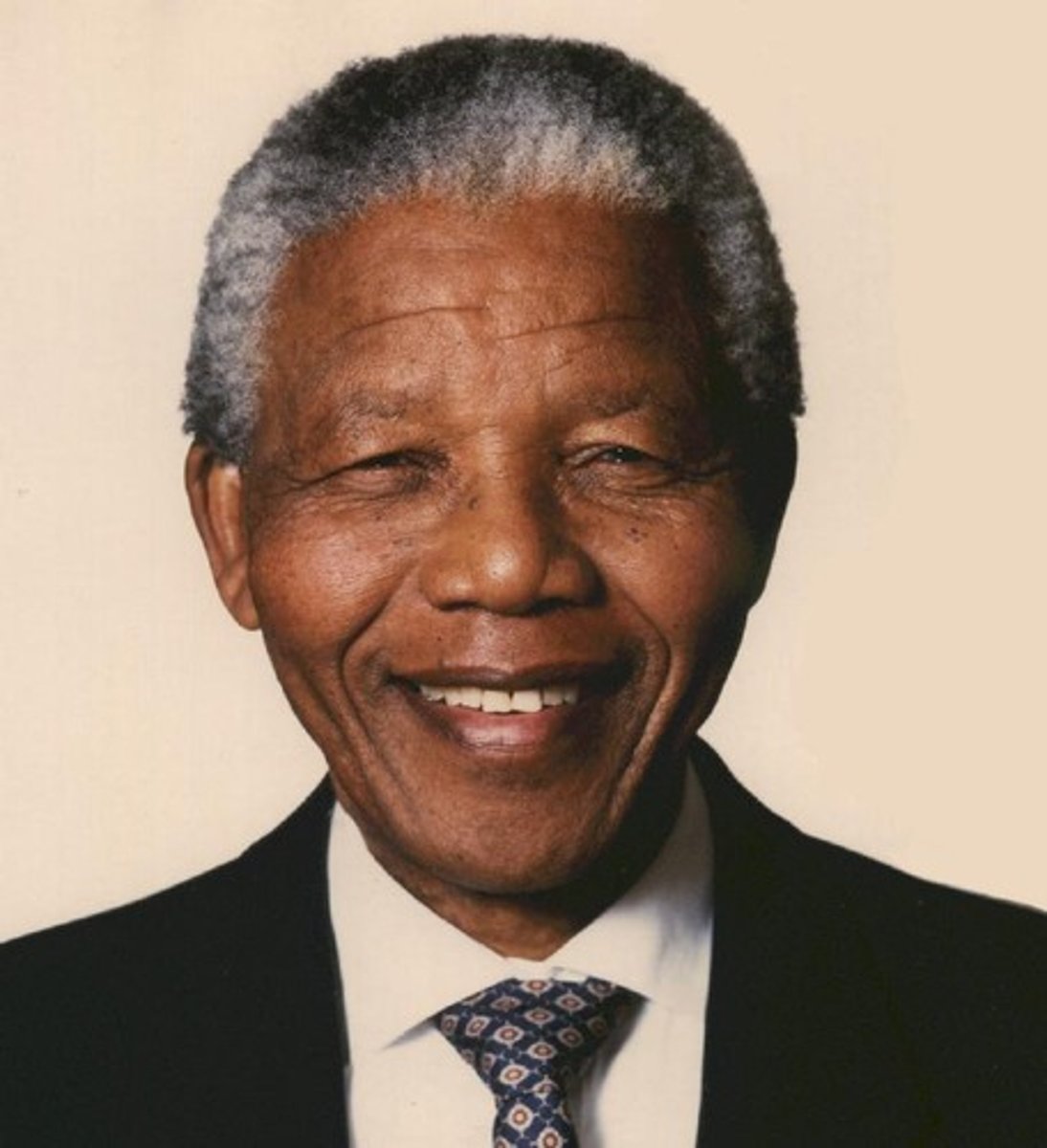
How did Nelson Mandela help South Africa remove Apartheid?
African National Congress-goal was to rule as majority political party.
Mandela first practiced peaceful protests and civil disobedience, but later began violent protests.

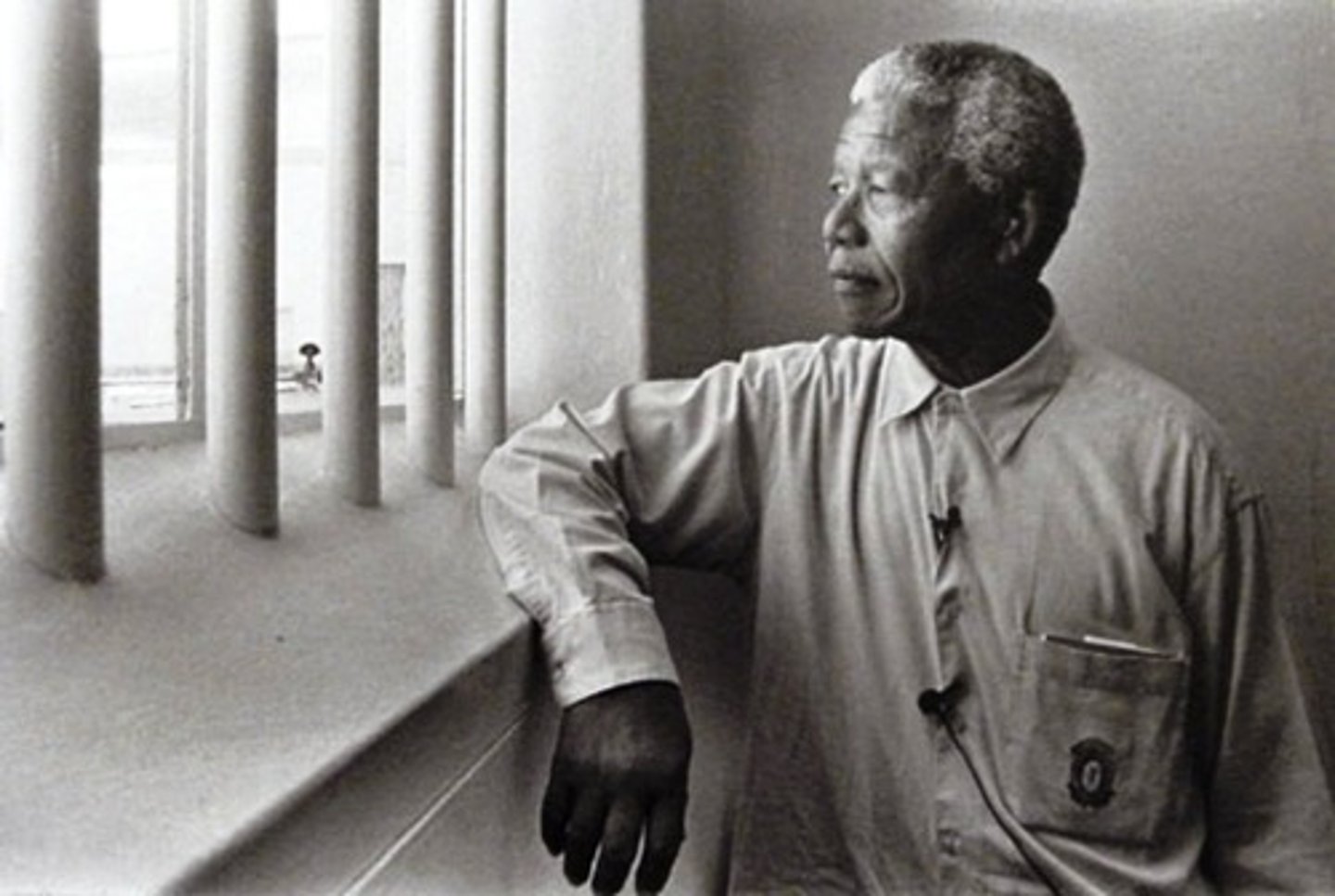
What were the effects of Mandela's protests?
He was imprisoned for fighting against Apartheid.
Nations boycotted or did not buy economic goods from South Africa when Mandela was in jail. ECONOMIC SANCTIONS were placed on South Africa. Mandela was elected President following his release from prison and Apartheid laws were repealed/removed.

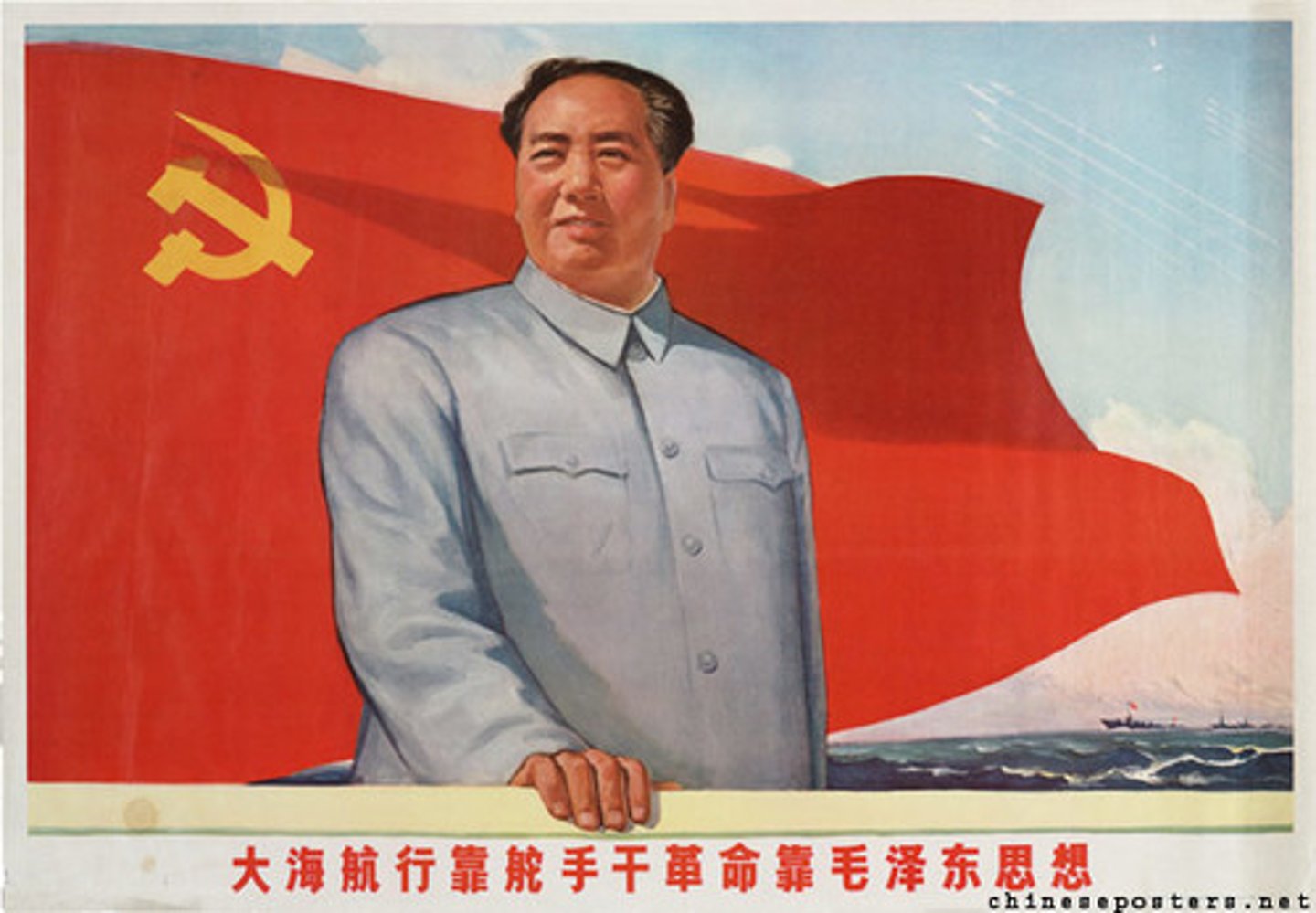
What caused the Chinese Communist Revolution?
Eliminate democratic ideas.
Peasants supported Communism-promised land and power to peasants.
Mao Zedong leading the Communist Chinese Revolutionaries
Long March-Mao escaping anti-Communist Chinese government.

How did Mao Zedong lead Communist China?
The Great Leap Forward-increase industrial productivity-heavy industry.
No religion-religions compete for loyalty.
Cultural Revolution-remove anti-communist ideas and Mao's competition.
Marxism-community work teams on farms.

What were the policies of Deng Xiaoping's Communist China?
Four Modernizations-increase industrial, agricultural, defense and science/tech productivity.
Tiananmen Square Massacre-Government oppression (terrible control) of citizens continued.
Not a democratic government.

How did the Middle East change following World War II?
Zionism-Belief in a Jewish homeland-Israel given to Jewish population. Israeli Jews vs. Palestinian Muslims.
Palestinians want to establish a homeland.
Arab nationalism vs. Jewish nationalism.
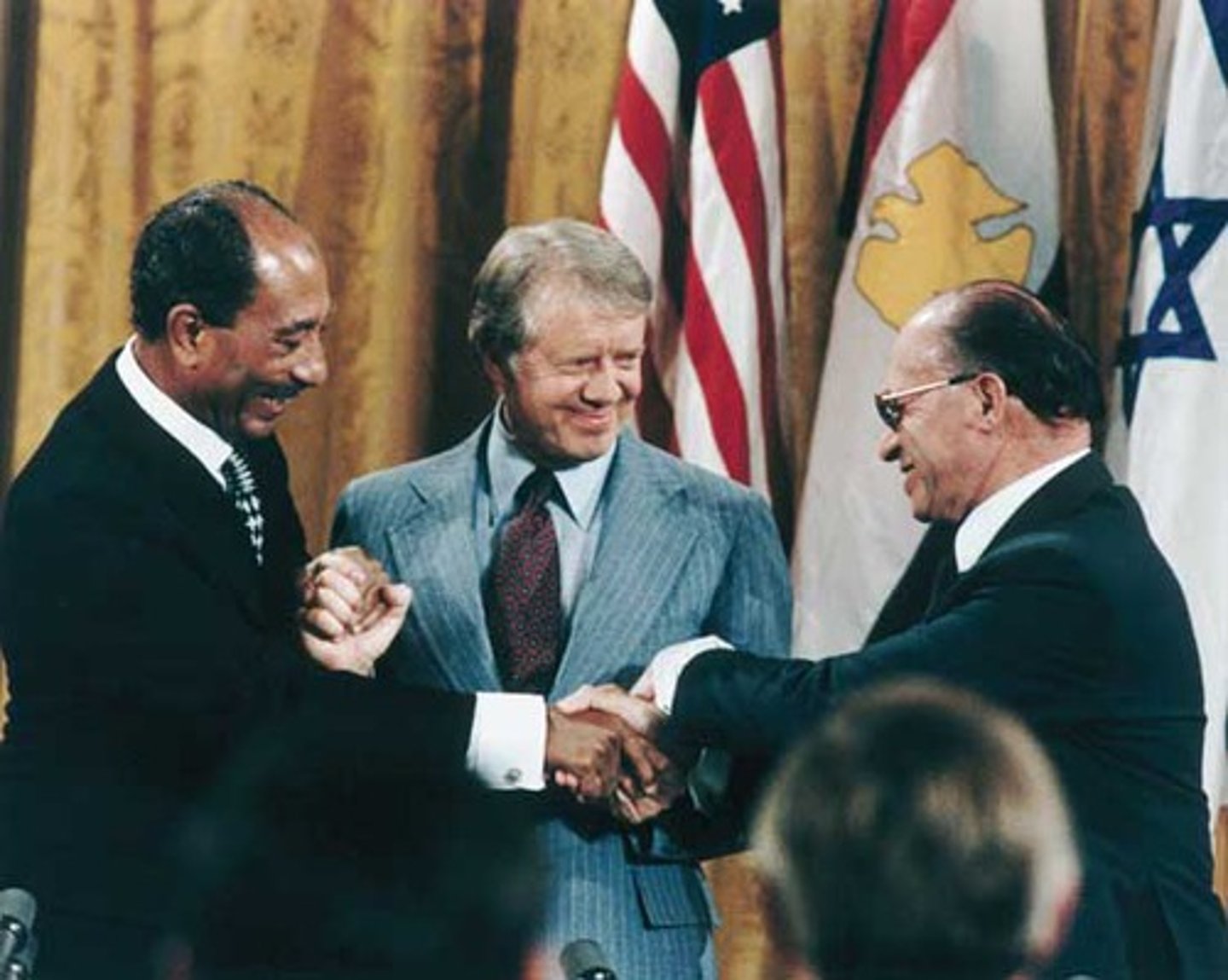
Camp David Accords-peace treaty between Israel and Arabs.

What is the important resource in Middle East?
Oil/ Petroleum

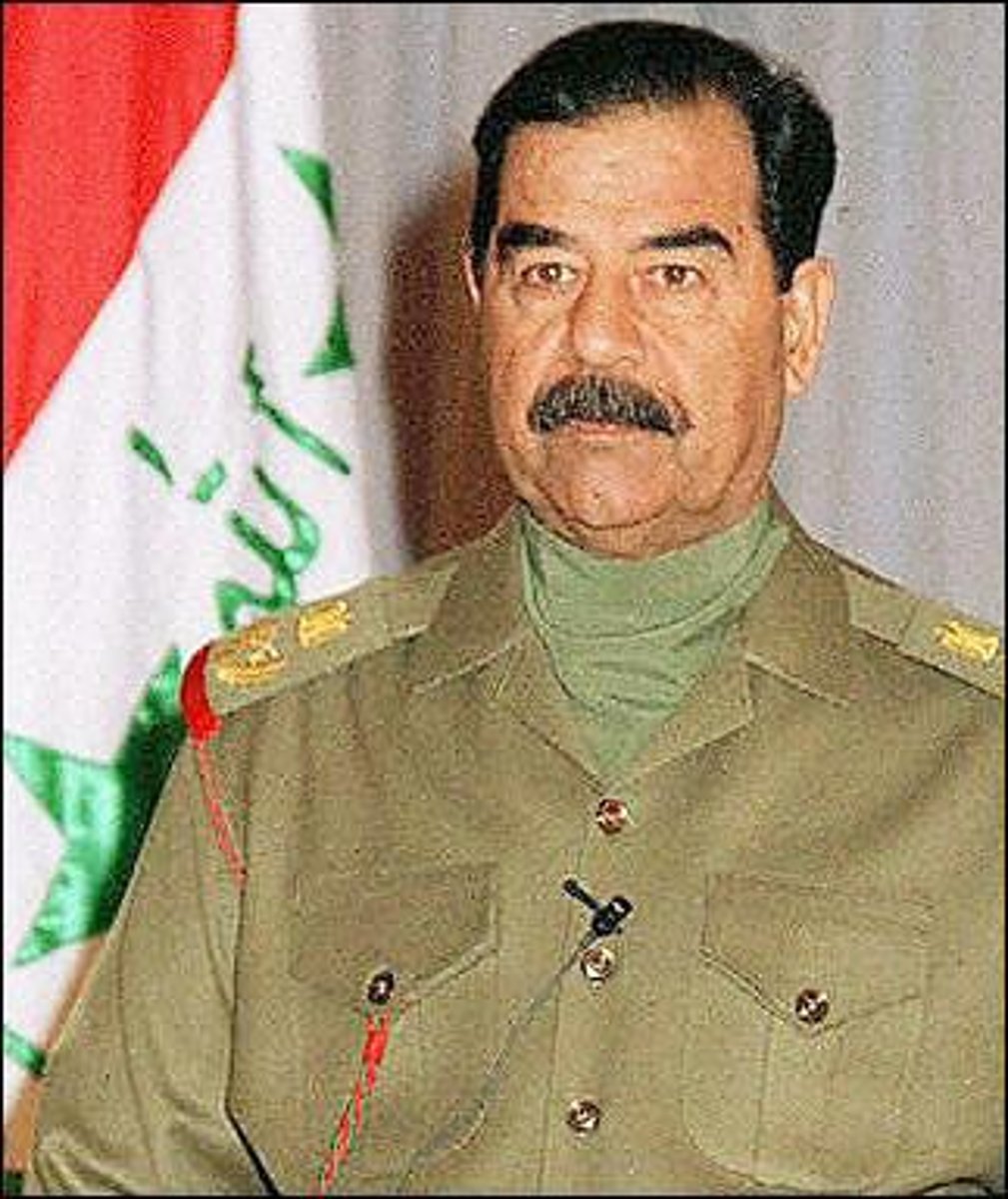
Who was the Iraqi dictator during the Persian Gulf War vs. United States?
Saddam Hussain

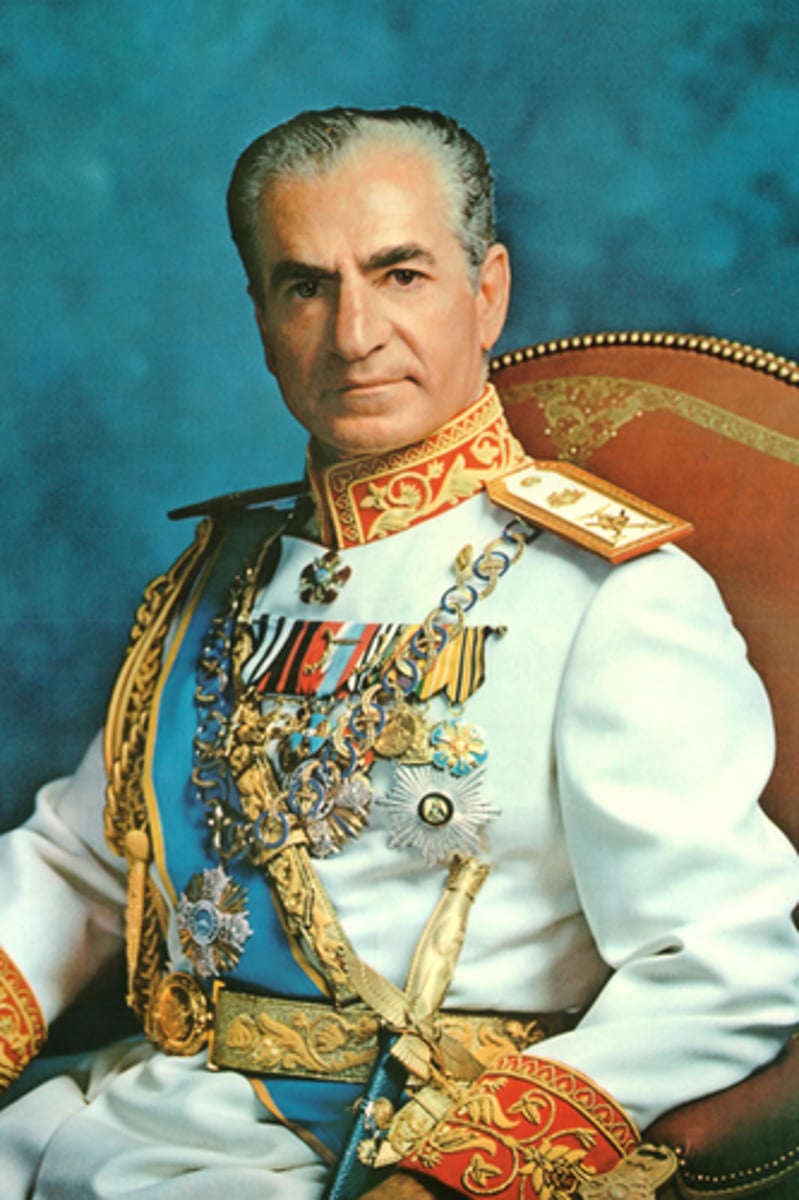
What caused the Iranian Revolution?
Failure of the leader, Shah Reza Pahlavi, to meet needs of the people. Shah supported Western ideas, not Muslim ideas.

Who was Ayatollah Khomeini and why did the Iranians support him?
he became the Iranian leader after the Shah and he supported the Islamic fundamentalism-Sharia law-Muslims wanting to keep traditional beliefs. He rejected Western and modern beliefs.

What were the effects of the Iranian Revolution?
Iran returned to traditional customs/beliefs.
Sharia Law-limited rights for women.
Islamic fundamentalism.
