RADIO NONTRAUMA ABN of APPENDICULAR SKELETON
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
what are conventional radiographs good for?
visualization of bone cortex
disadvantages of conventional radiograph
can't visualize entire circumference of bone in a single shot; not sensitive for demonstrating MSK abn (it CAN detect soft-tissue swelling if it is SIGNIFICANT)
what is a good imaging modality to visualize BM & soft tissues, muscles, tendons, ligaments?
MRI
bone density
amount of bone mineral (Ca2+ phosphate) in bone tissue (matrix)
what do osteoclastic & osteoblastic activity rely on?
viable blood supply
what does bone respond to?
mechanical forces (repeated use, trauma, overuse)
example of diffuse, increased density
diffuse osteoblastic metastases sclerotic
examples of focal, increased density
localized osteoblastic metastases/tumor, AVN of bone, Paget's Disease, CPPD
examples of diffuse, decreased density
osteoporosis, hyperparathyroidism
examples of focal, decreased density
localized osteolytic metastases, multiple myeloma, osteomyelitis
bone metastases
m/c than primary bone tumors, usu widespread
m/c/c of osteoblastic mets in older men
prostate CA (multiple>single)
AVN of bone
poor blood supply --> cell death --> collapse of bone
how does AVN appear in later stages?
INCREASED DENSITY
where does AVN m/c occur?
scaphoid in wrist, femoral head, humeral head
what is the most sensitive modality for detecting AVN?
MRI
causes of AVN
Intravasc: sickle cell & PCV
Vasc: vasculitis (lupus & radiation induced)
Extravasc: trauma (frx)
Idiopathic: exogenous steroids, cushings, legg-calve-perthe disease (delayed bone growth by time child is 2 is 1st presentation)
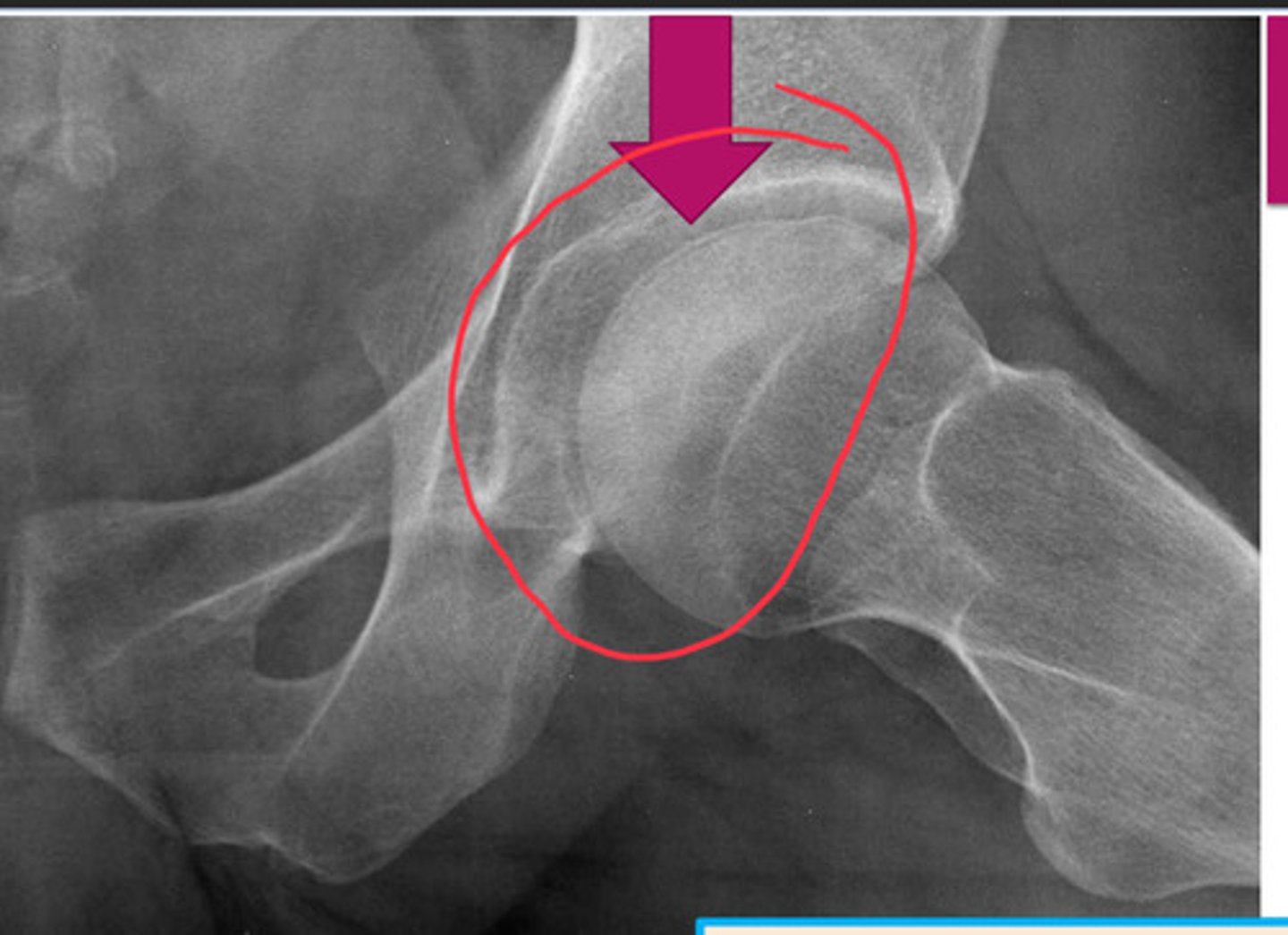
crescent sign
occurs when surface of articular surface is flattening (DO NOT MISS! PRECURSOR TO WORSENING DISEASE!)
pictured: AVN of femoral head
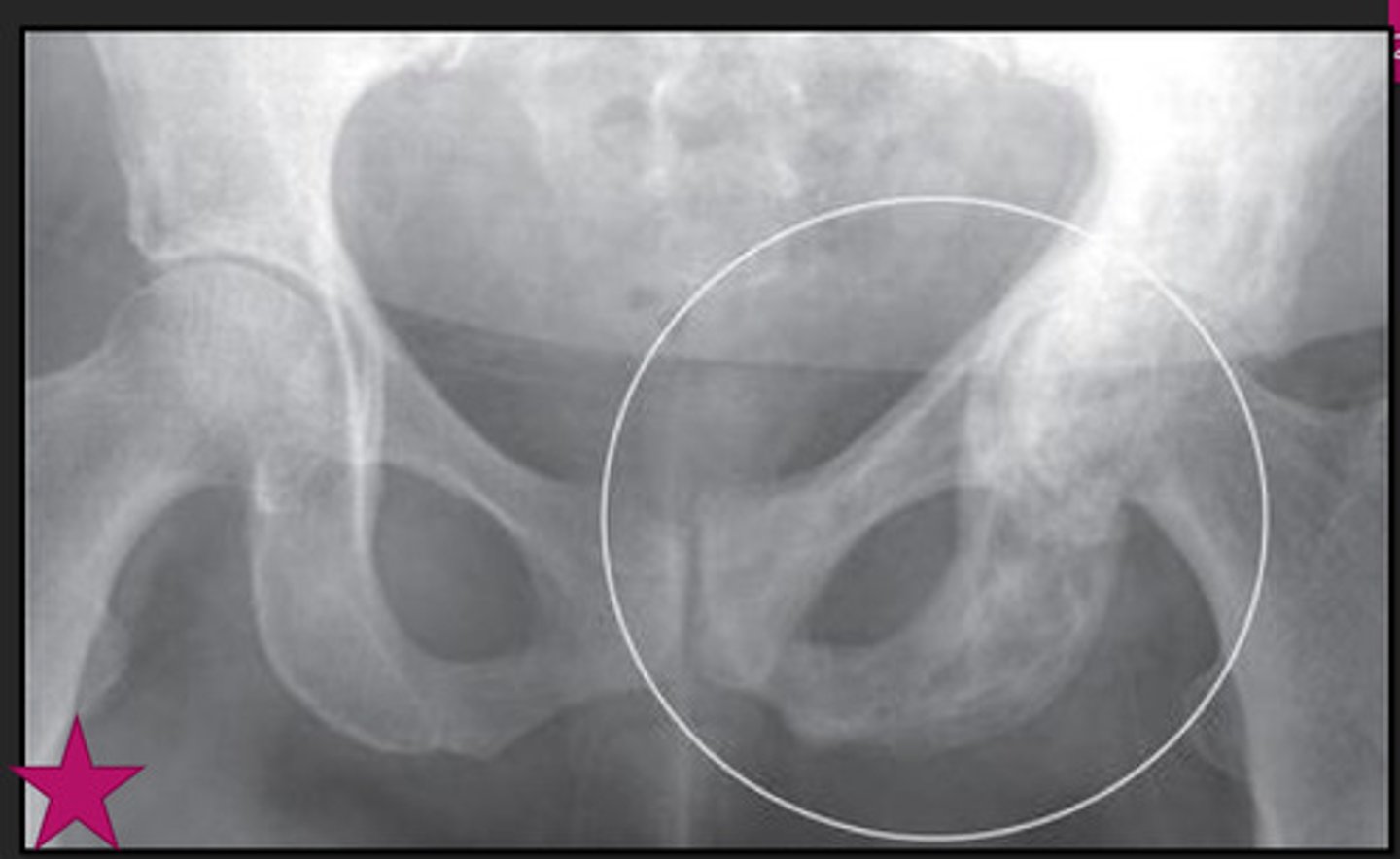
Paget's Disease
chronic disease of bone, m/c in older men; characterized by varying degrees of inc bone resorption & inc bone formation
will affect spine & pelvis; can dx by pain & XR alone
imaging hallmarks of Paget's
thickening of cortex & coarsening and thickening of trabecular pattern
Paget's imaging
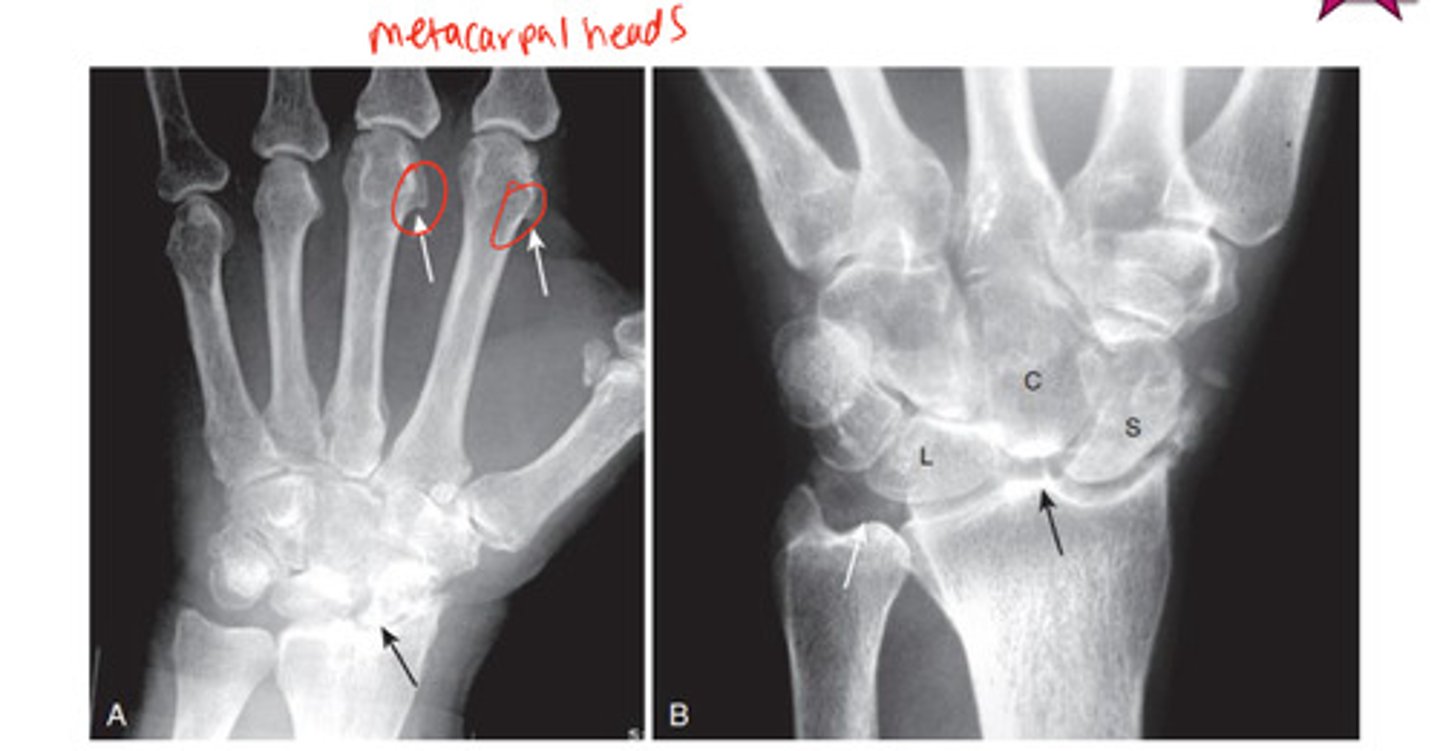
CPPD imaging
Ca2+ pyrophosphate disease- causing hook shaped deformity along 2nd & 3rd metacarpal head from osteophyte
Osteoporosis
skeletal disorder characterized by LOW BMD (postmenopausal & age related bone loss)
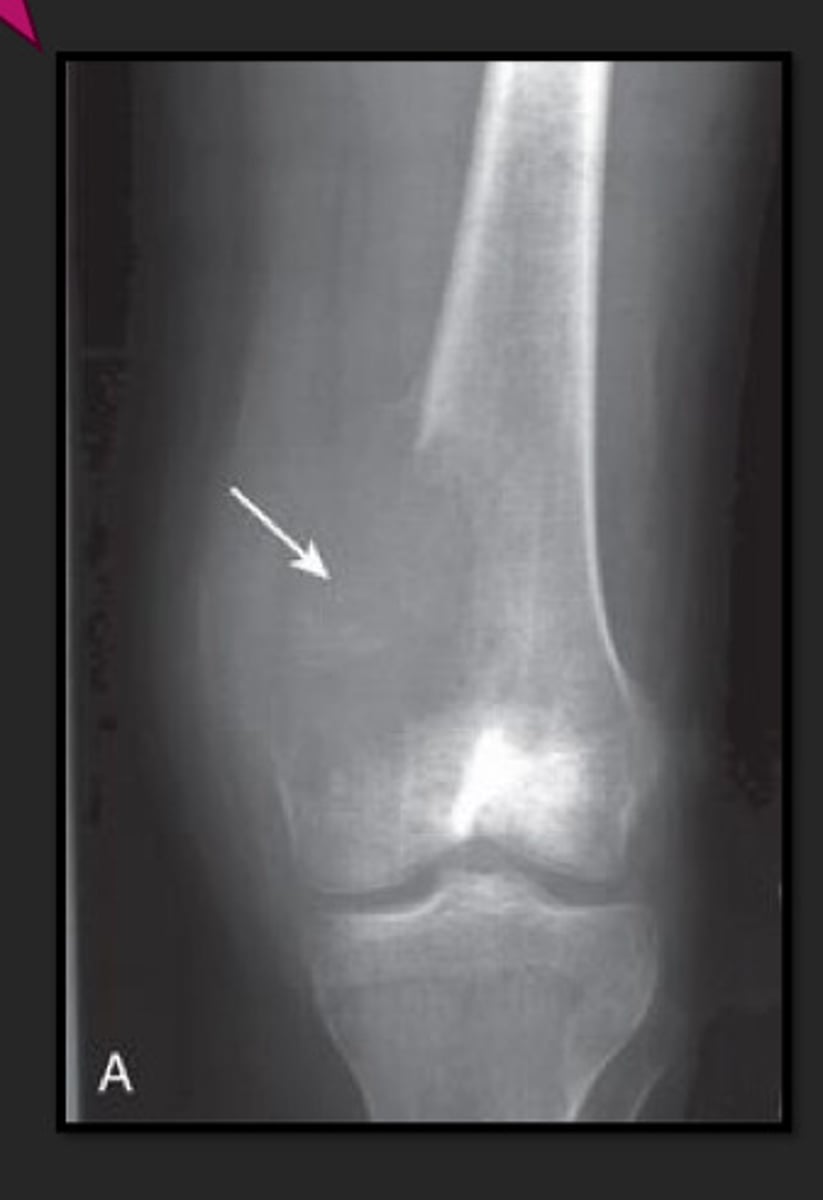
focal lesions
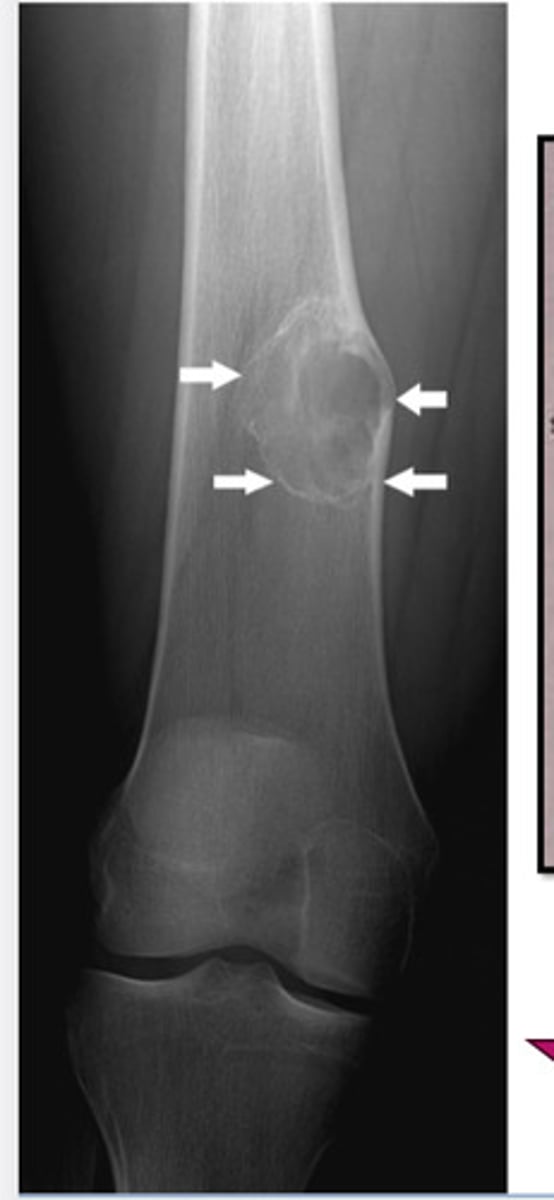
geographic local pattern of bone destruction
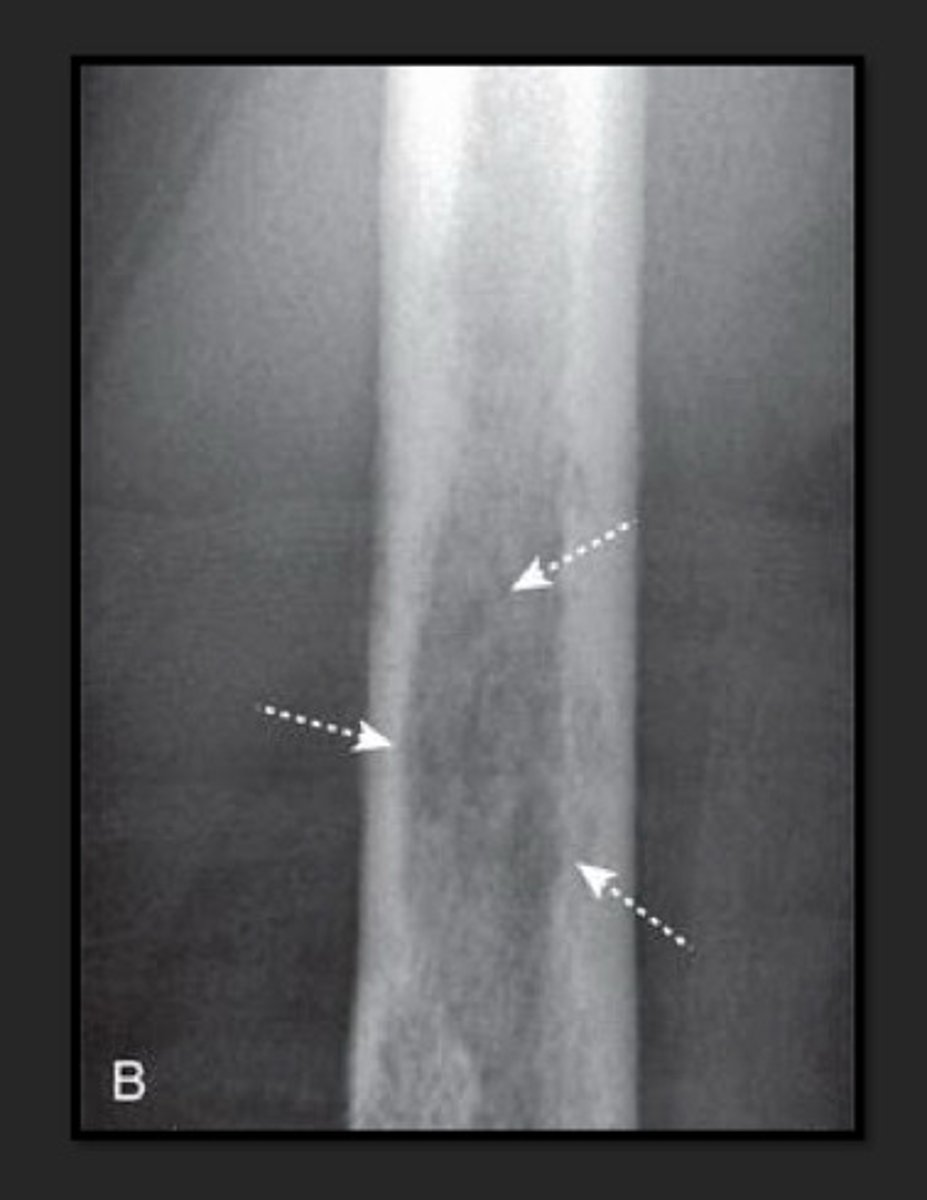
mottled local pattern of bone destruction
"moth eaten appearance"
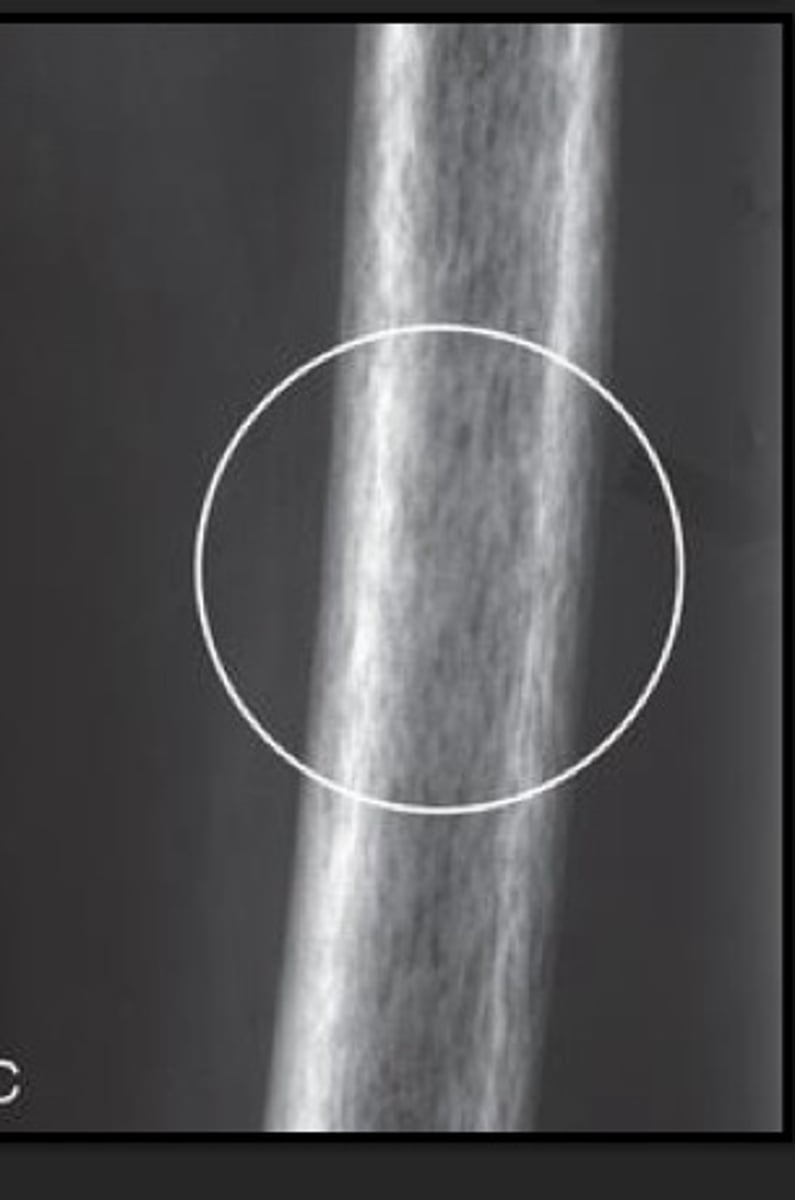
permeative local pattern of bone destruction
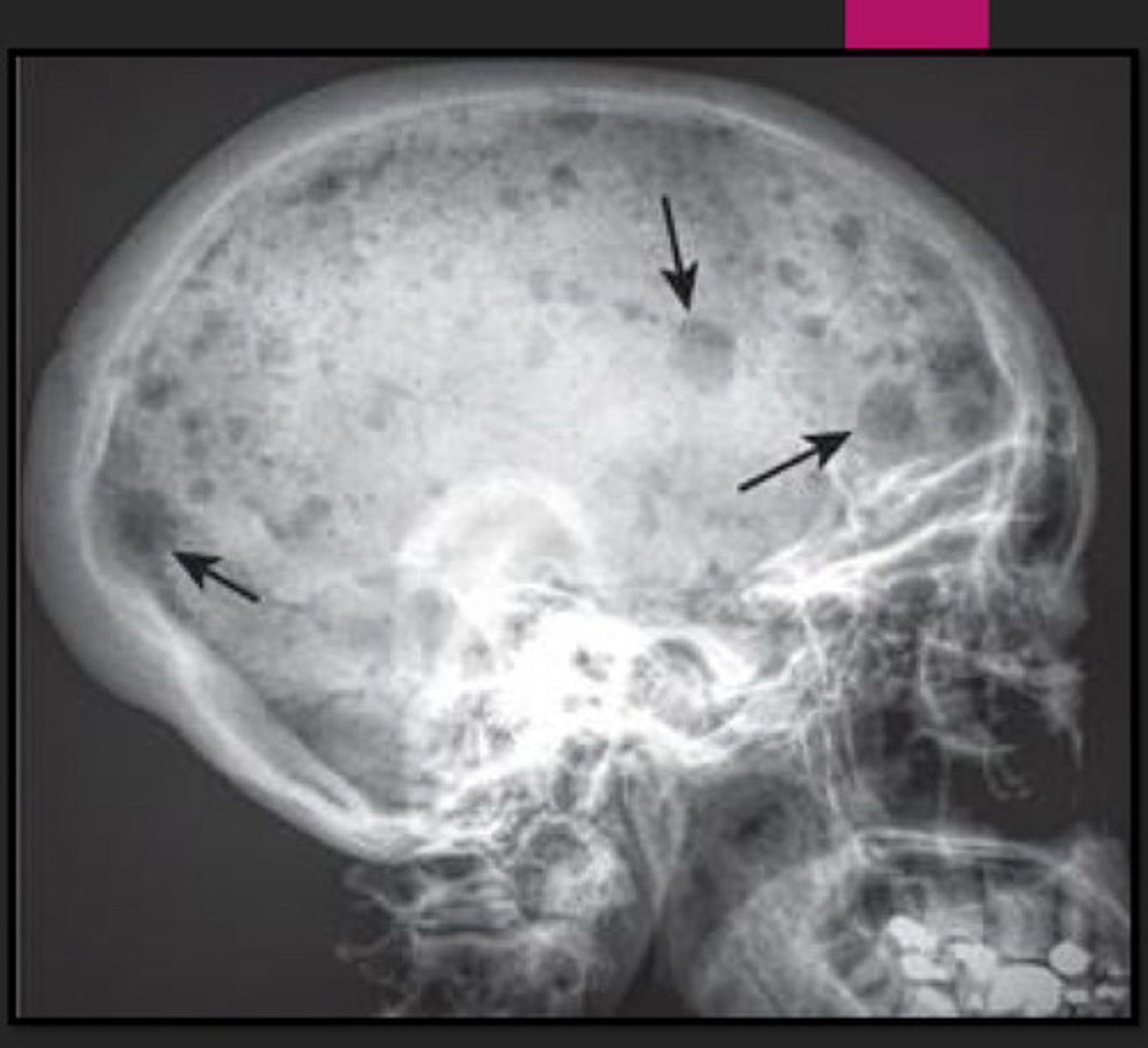
Multiple Myeloma
m/c primary malignancy of BM in adults; dec density & patchy areas of lytic lesions
disseminated
multiple, small sharply circumscribed (described as "punched out") lytic lesions of approx the same size
what is MM associated w/?
diffuse spinal osteoporosis (hallmark) & multiple compression fractures @ end stages
osteomyelitis
hallmark on radiograph is destruction of articular cartilage, release of synovial fluid; monoarticular; rapidly progressing infx; MRI>XRAY for Dx
WHAT CAN BOTH INC OR DEC DENSITY ON XRAY? *Rule Breaker*
ARTHRITIS
arthritis
affects a joint & bones on either side, almost always accompanied by joint space narrowing
joint disease>bone disease
hallmark of hypertrophic arthritis?
osteophyte formation
3 major types of arthritis
OA/DJD, erosive, infectious
OA/DJD
bone formation @ involved site, may occur w/in confines of bone (subchondral sclerosis) or protrude from bone (osteophyte)
m/c OA/DJD
primary osteoarthritis AKA degenerative joint disease
m/c/c of OA/DJD
mechanical stress or excessive wear & tear in weight bearing joints
erosive arthritis
inflamm & synovial prolif (pannus formation), production of lytic lesions in or near joint
(erosion)
types of erosive arthritis
RA, gout, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis
RA
m/c in F; involves proximal joints of hands & wrists, usu B/L & symmetric
late findings of RA
ulnar deviation of fingers @ MCP, subluxation of MCP & ligament laxity leading to swan neck & boutonniere's deformities
gout
inflammatory changes incited by deposition of calcium urate crystals in the joint
M>F
monoarticular; asymmetrical later in course
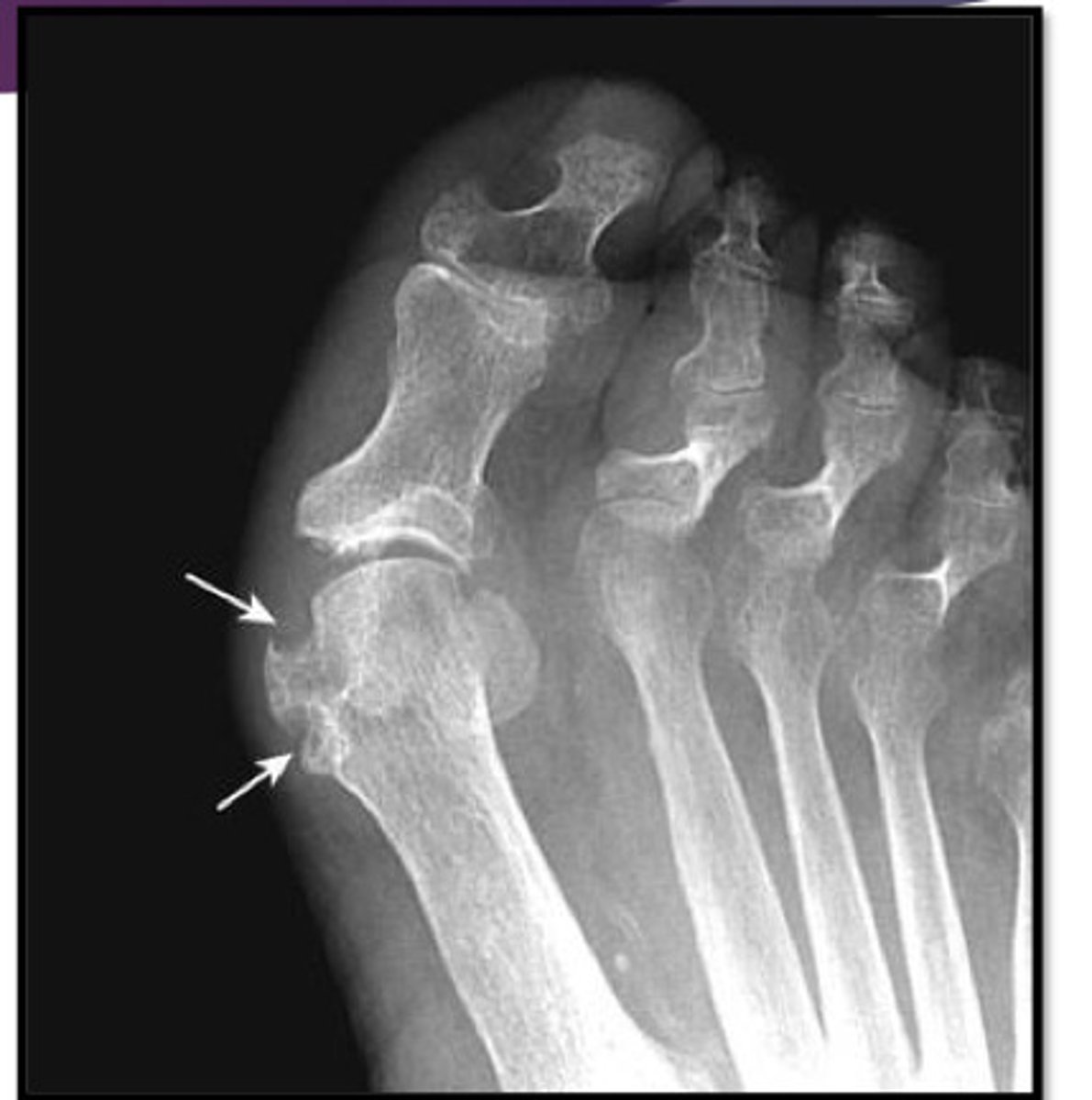
what joint does gout m/c affect?
metatarsal phalangeal of the great toe
hallmark of gout
sharply marginated, juxtaarticular erosion that tends to have sclerotic borders ("rat bites")
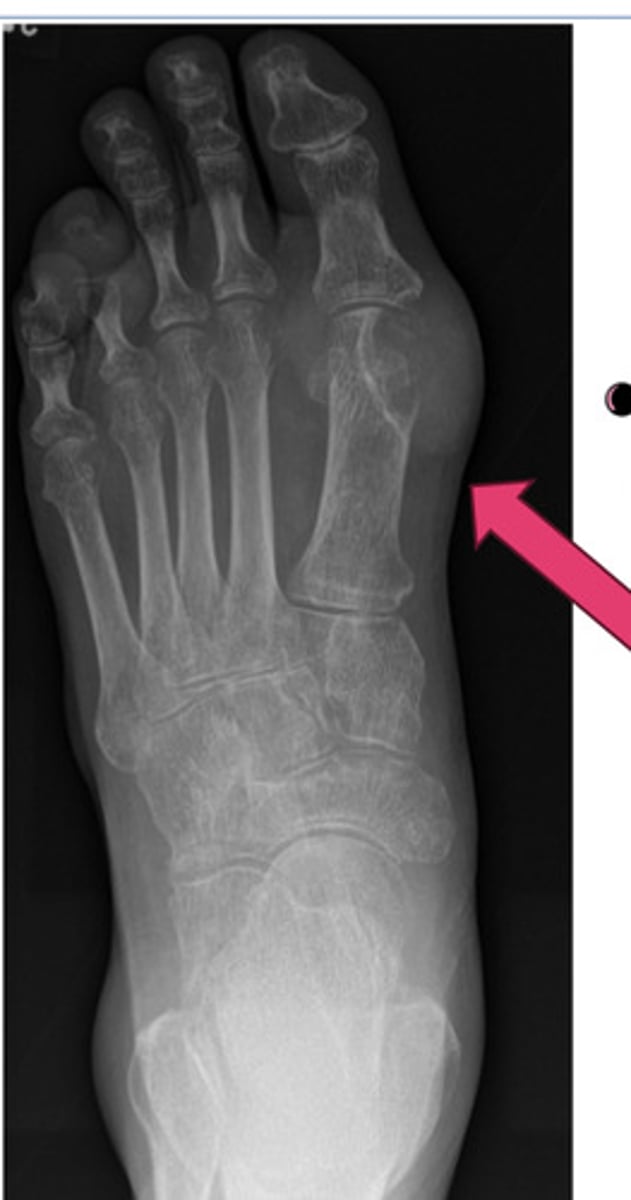
gout imaging
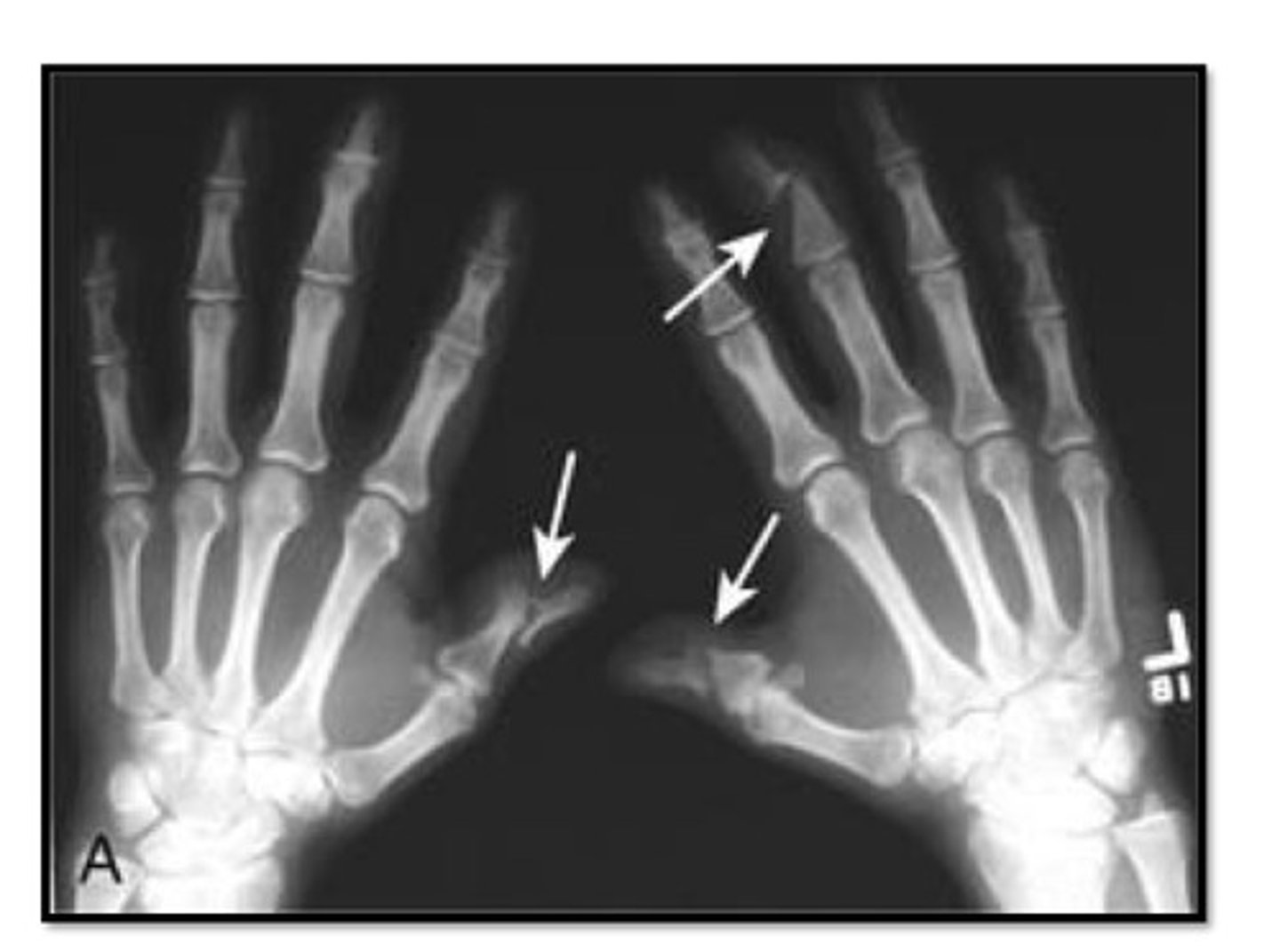
psoriatic arthritis
characterized by erosion & new bone formation that may occur in the same joint
"Pencil in a cup" appearance
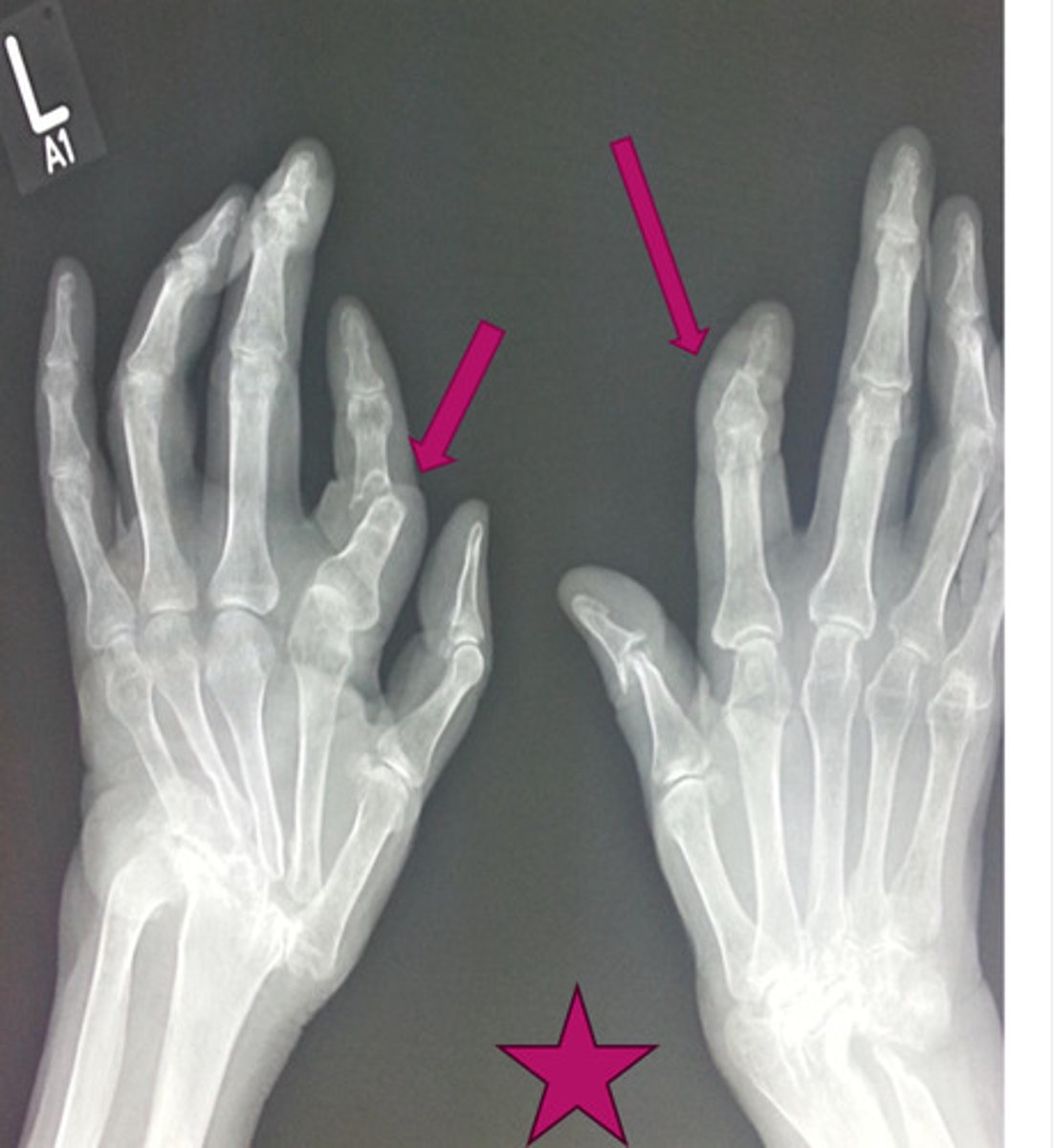
psoriatic arthritis imaging
ankylosing spondylitis
young, males
neck/LBP, worse @ night & better w/ exercise
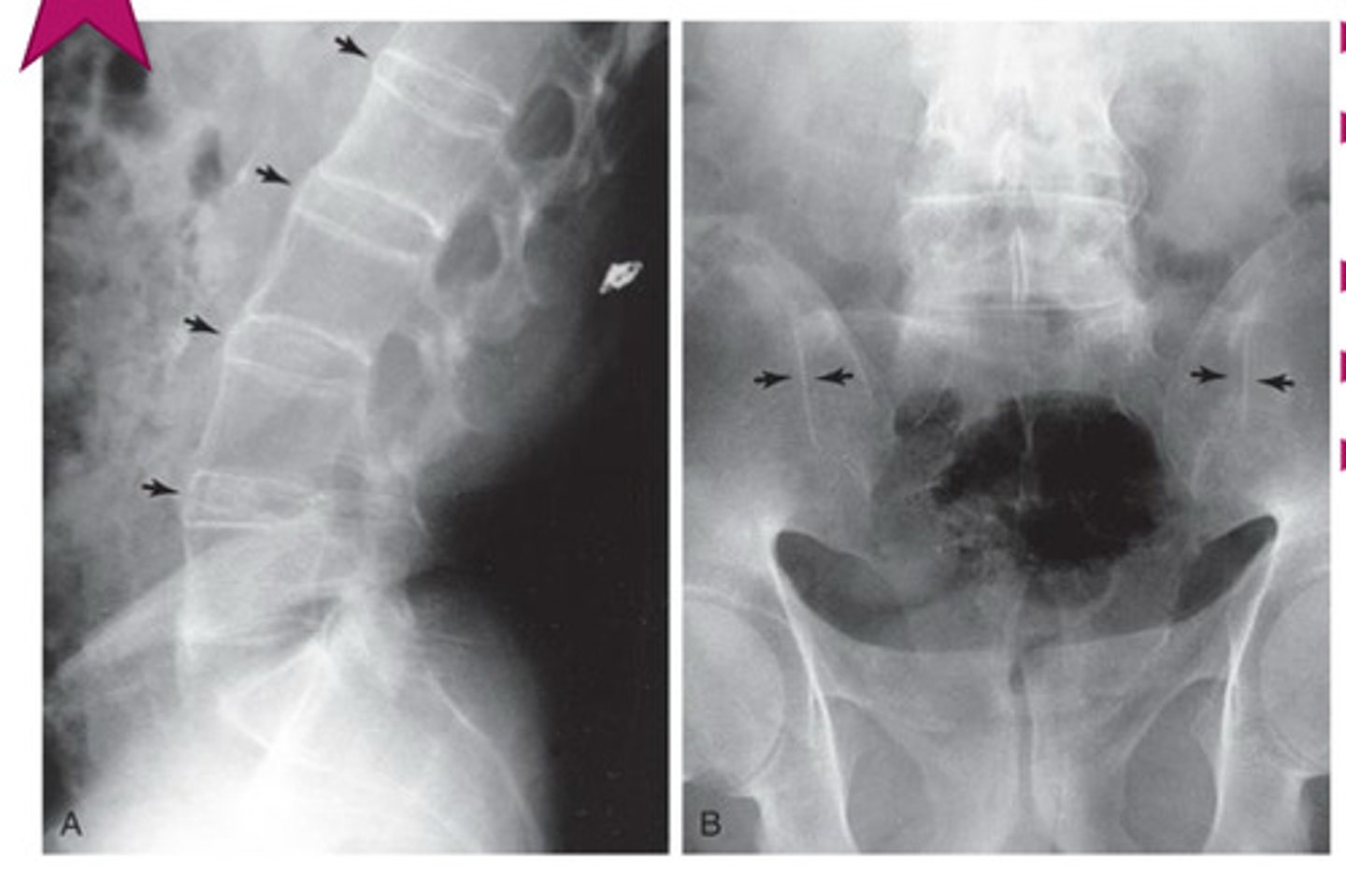
what is ankylosing spondylitis associated w/?
ulcerative colitis
what marker can do patients w/ ankylosing spondylitis test + for?
HLA-B27
hallmark of ankylosing spondylitis
fusion of lumbar spine & sacroiliac joints (sacroilitis)
bamboo spine ("dagger sign" on AP projection)
ankylosing spondylitis; no spaces b/w vertebrae
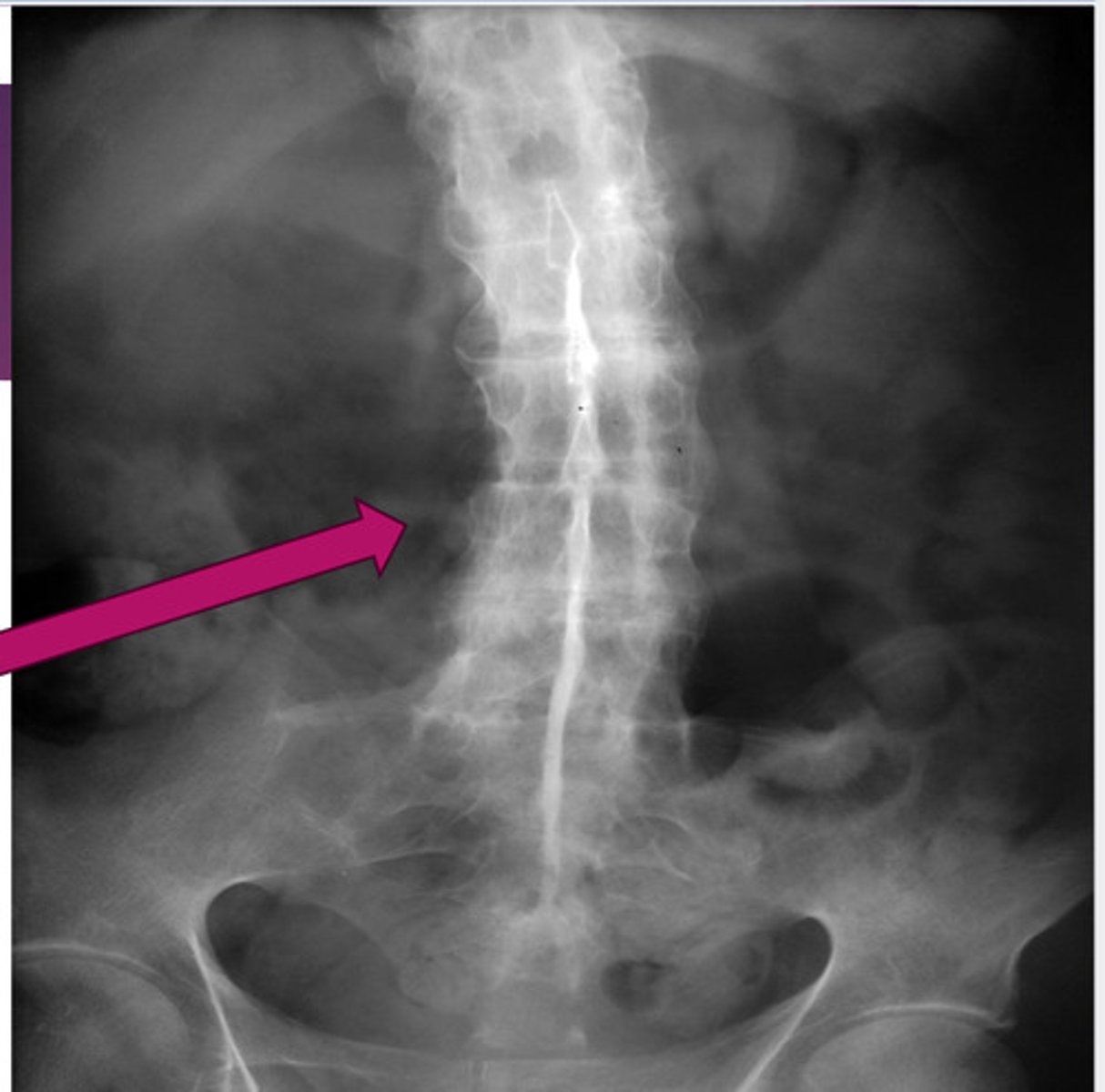
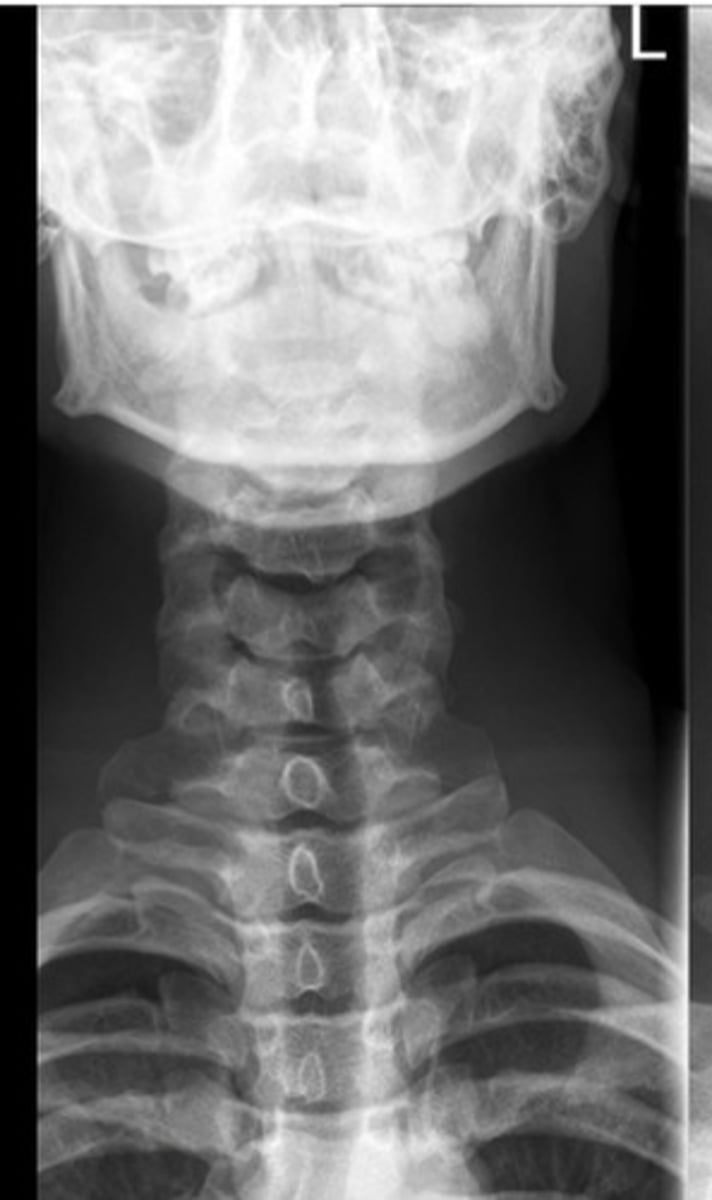
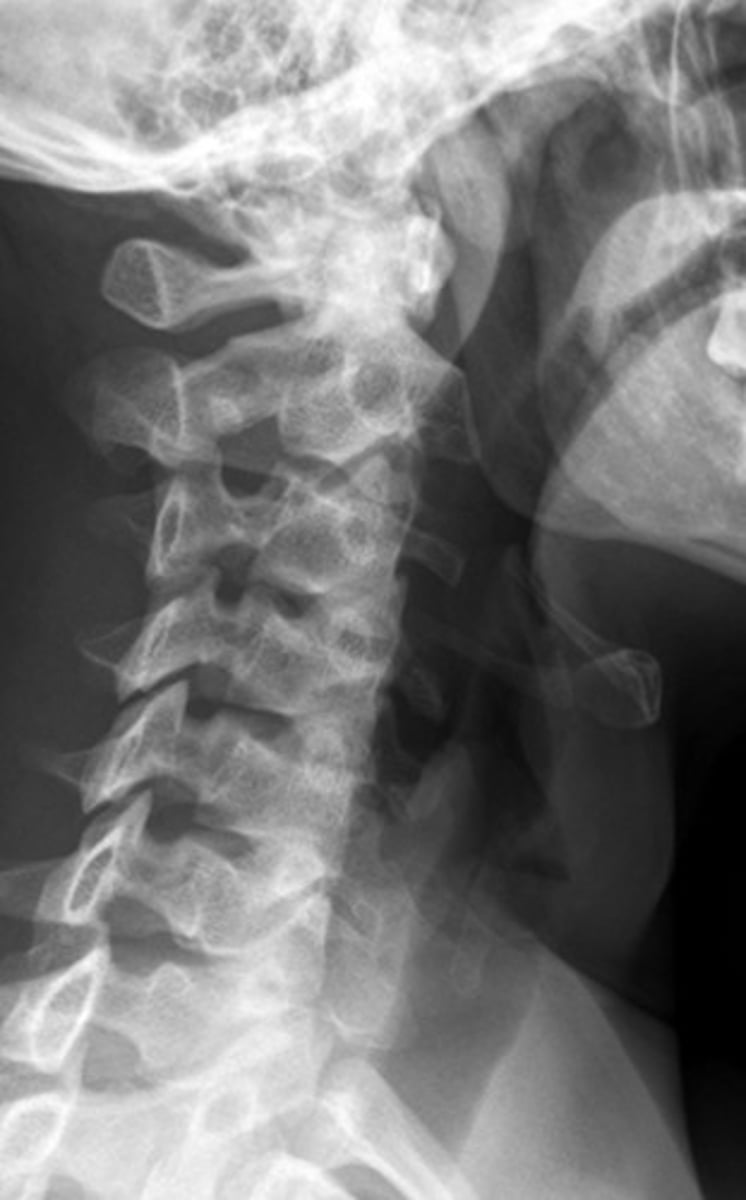
normal C/S
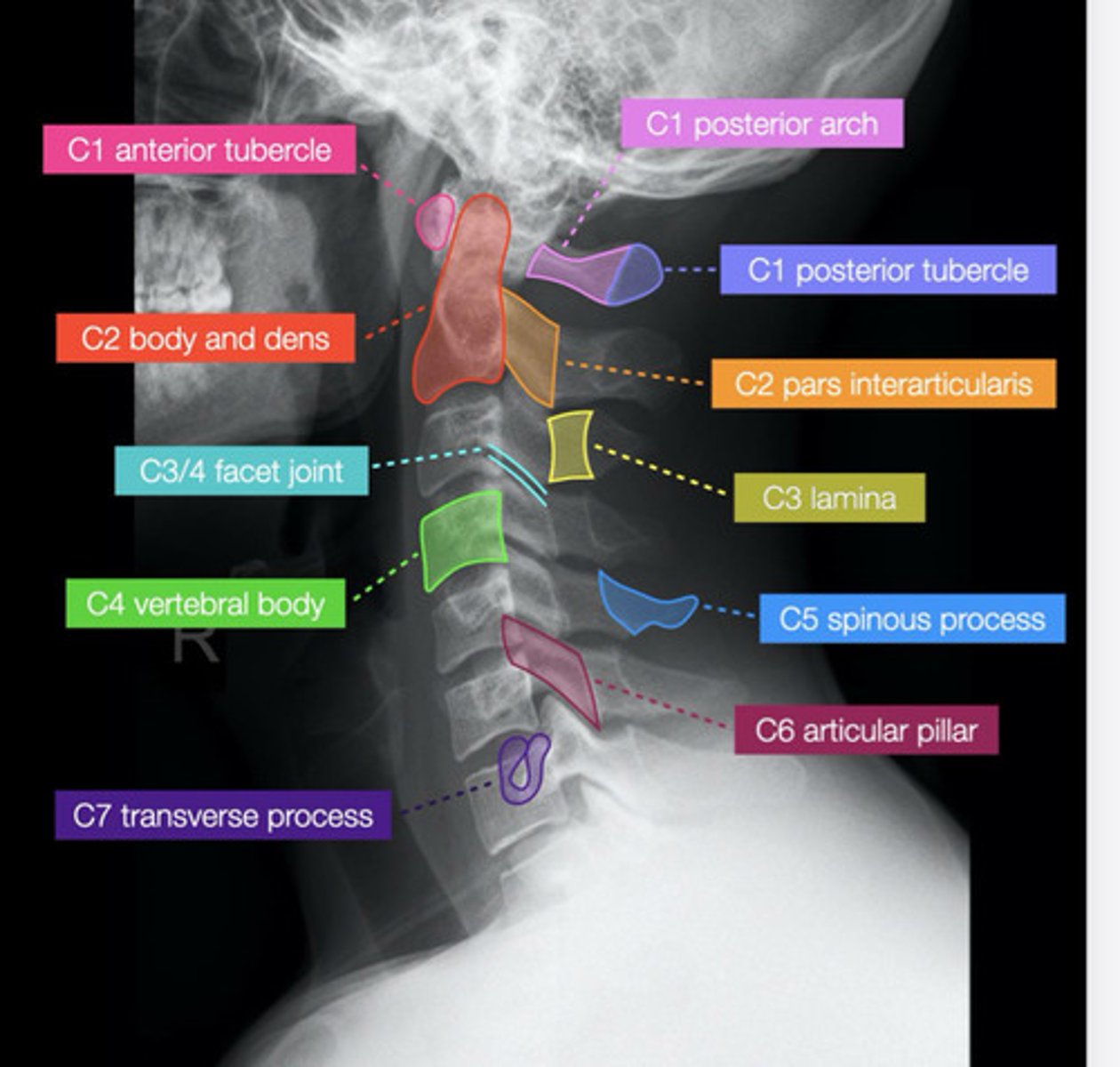
lateral spine xray
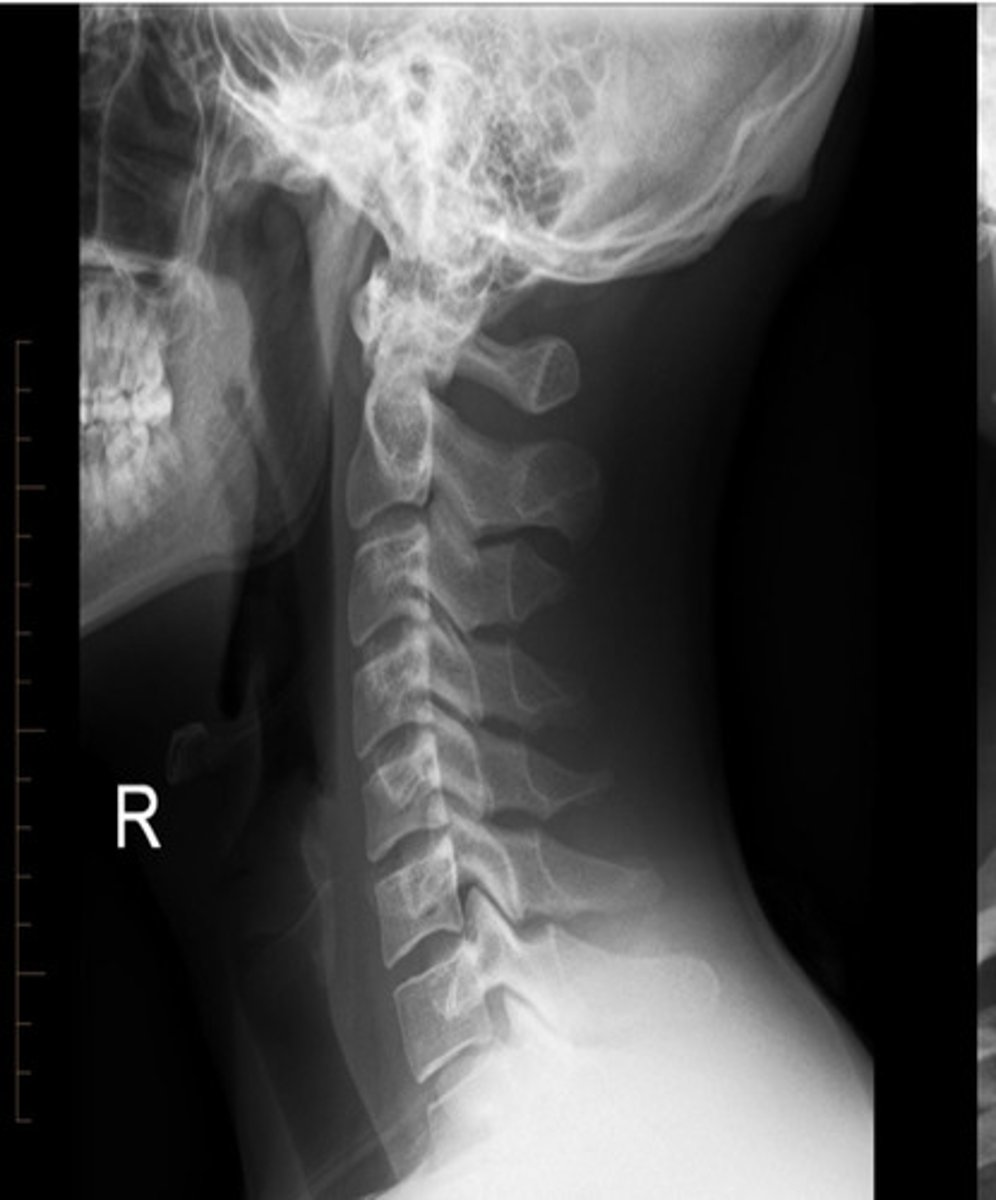
AP spine xray
oblique spine xray
normal thoracic spine xray
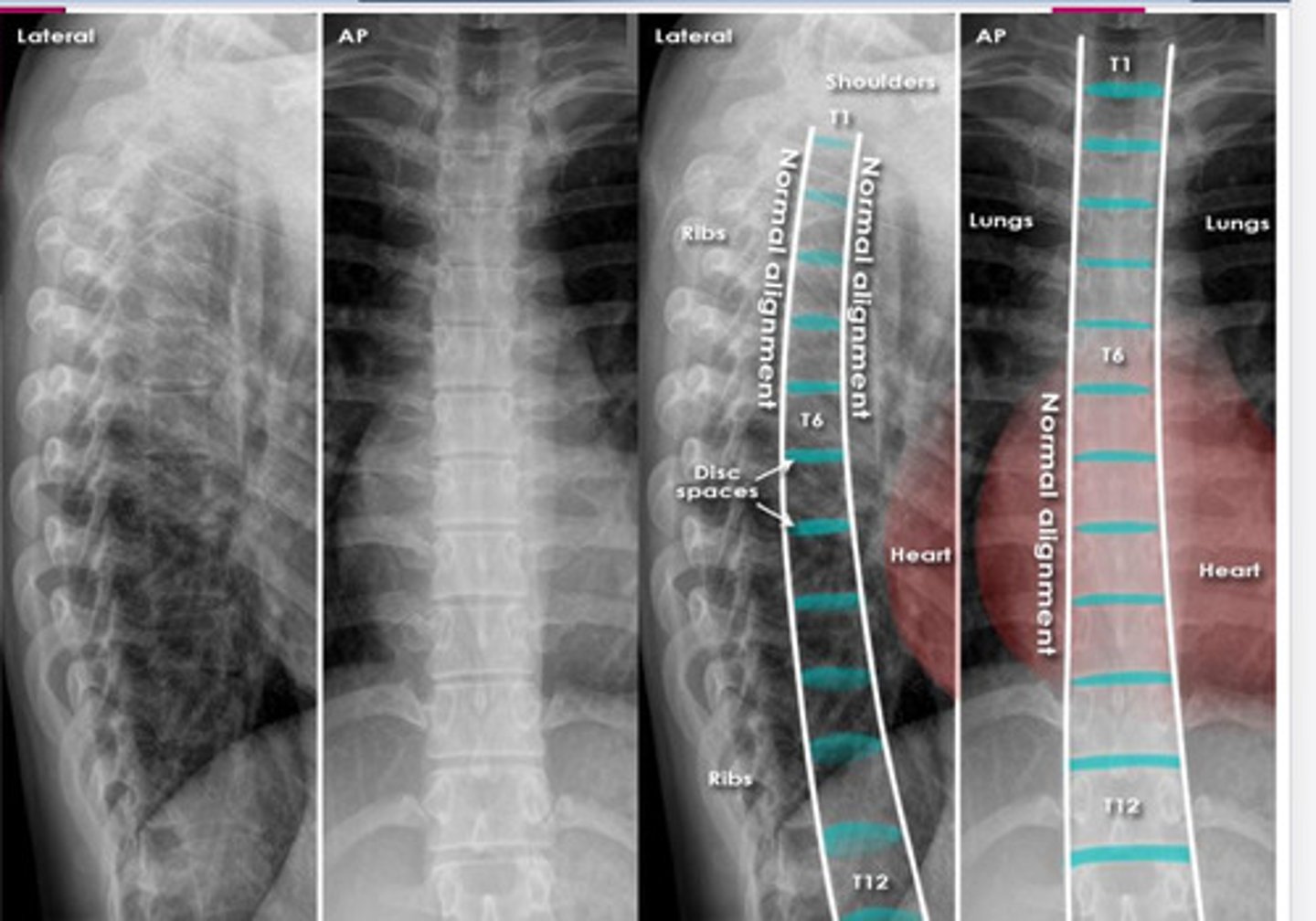
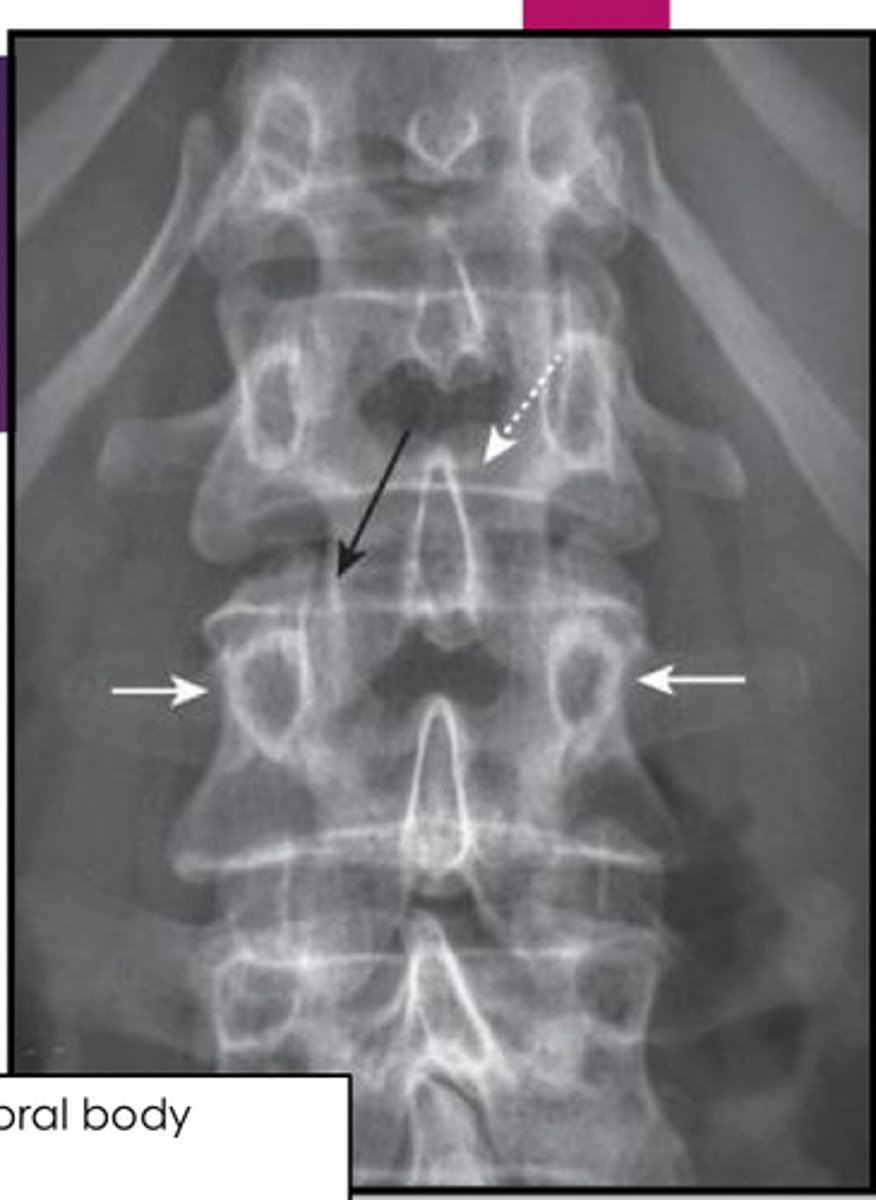
normal L/S xray
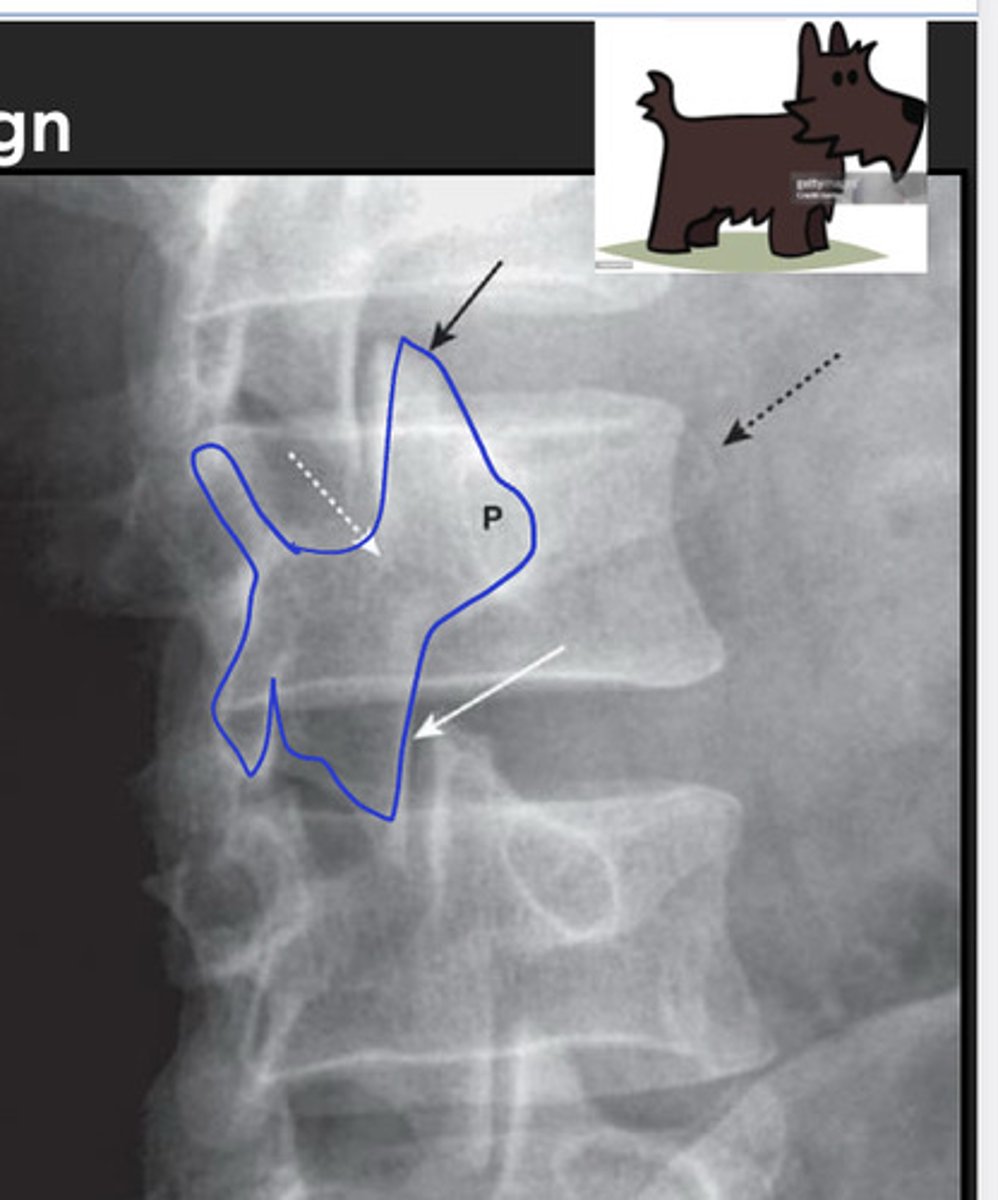
white arrows: 2 pedicles on side of vertebral body
white dotted arrow: spinous process
black arrow: facet joint
scottie dog sign
seen on oblique views; "the best dog in medicine"
DDD (degenerative disc disease)
disc becomes dehydrated & degenerates with increasing age; gradually leads to progressive loss of the height of the intervertebral disc space
compression fractures of the spine
common, W>M & typically 2/2 osteoporosis
how are compression fractures of the spine 1st noticed?
b/c of inc kyphosis or overall loss of body height
study of first choice for compression fractures of the spine
conventional spine radiographs
what parts of the vertebral body are usually involved in osteoporotic compression fractures?
anterior & superior aspects
spinal stenosis
narrowing of the spinal canal 2/2 soft tissue or bony abnormalities (either acquired or congenital; acquired>congenital)
where is spinal stenosis m/c?
cervical & lumbar areas
neurogenic claudication
intermittent pain & paresthesias radiating down the leg & worsened by standing or walking & relieved by flexing the spine by lying supine or squatting
what imaging is obtained 1st for spinal stenosis?
conventional radiographs
what is the imaging modality of choice for spinal stenosis?
MRI
fracture
disruption in the continuity of all or part of the cortex(hard outer layer) of a bone
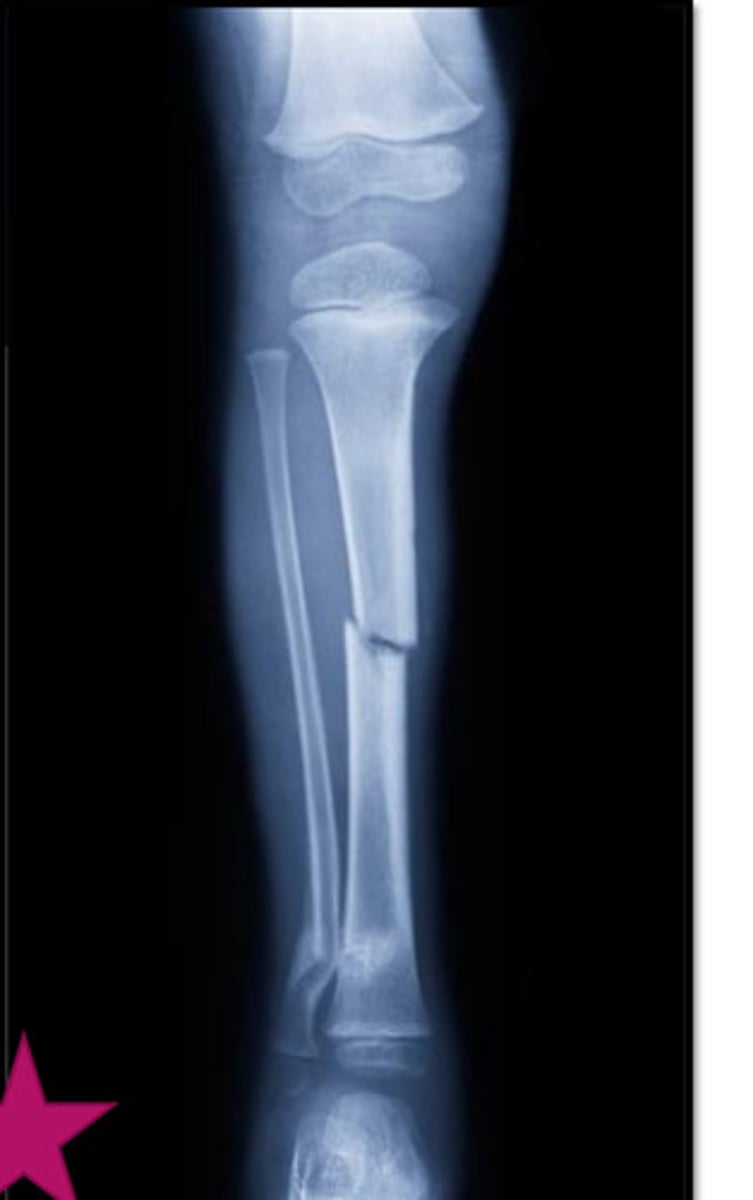
incomplete fracture
only part of the cortex is fractured
complete fracture
through & through
normal xray of growing bone
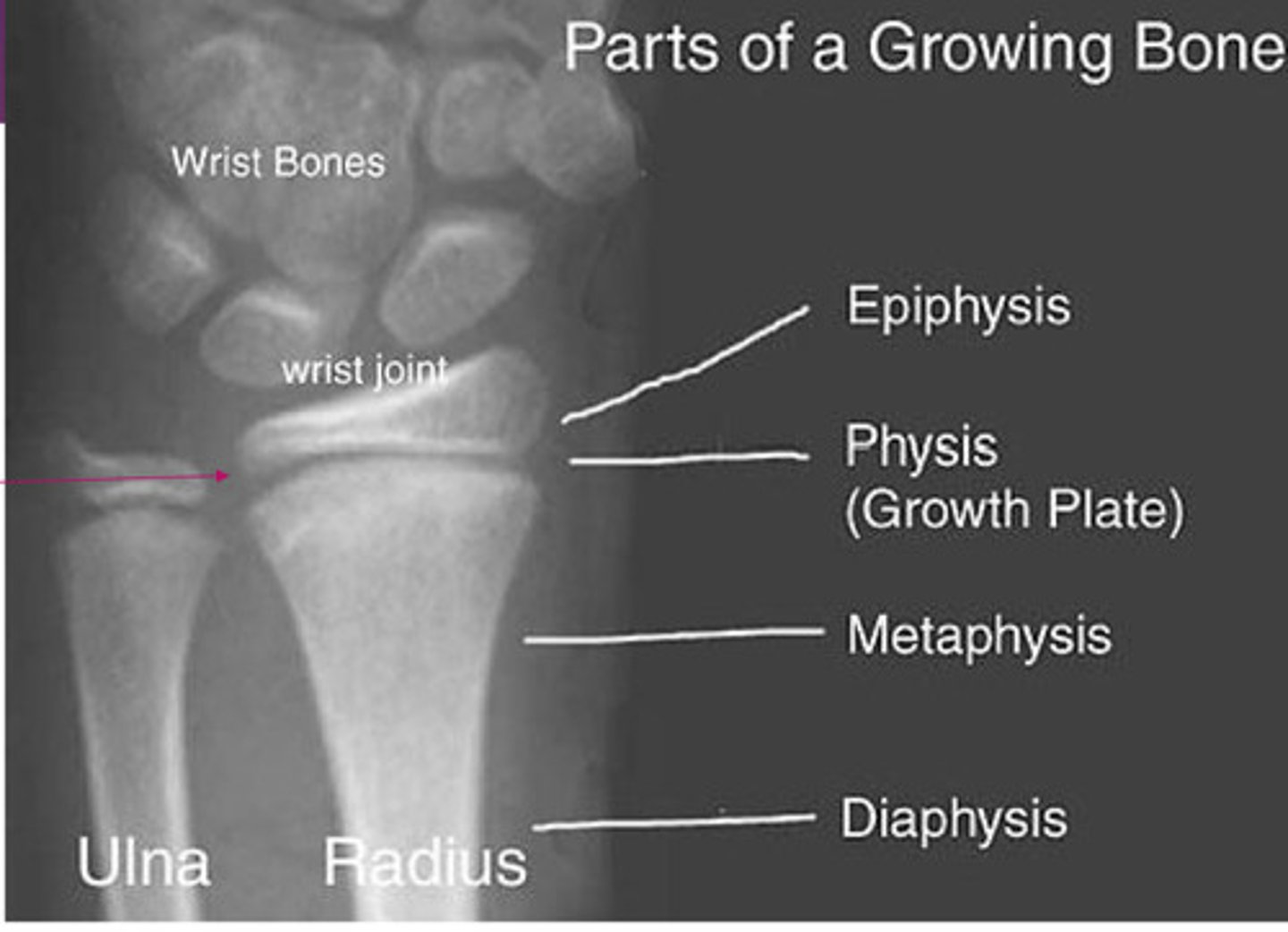
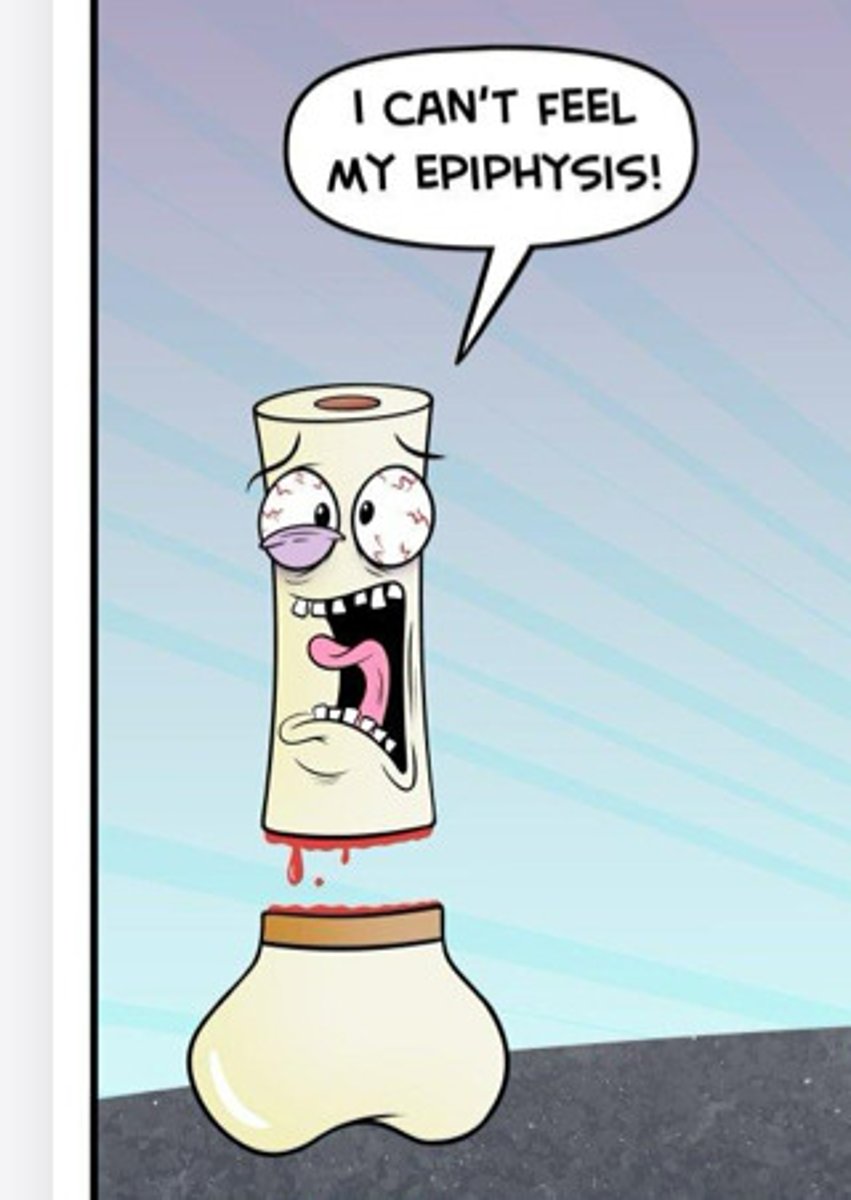
type 1 salter harris fracture
through the growth plate; heals well w/ cast

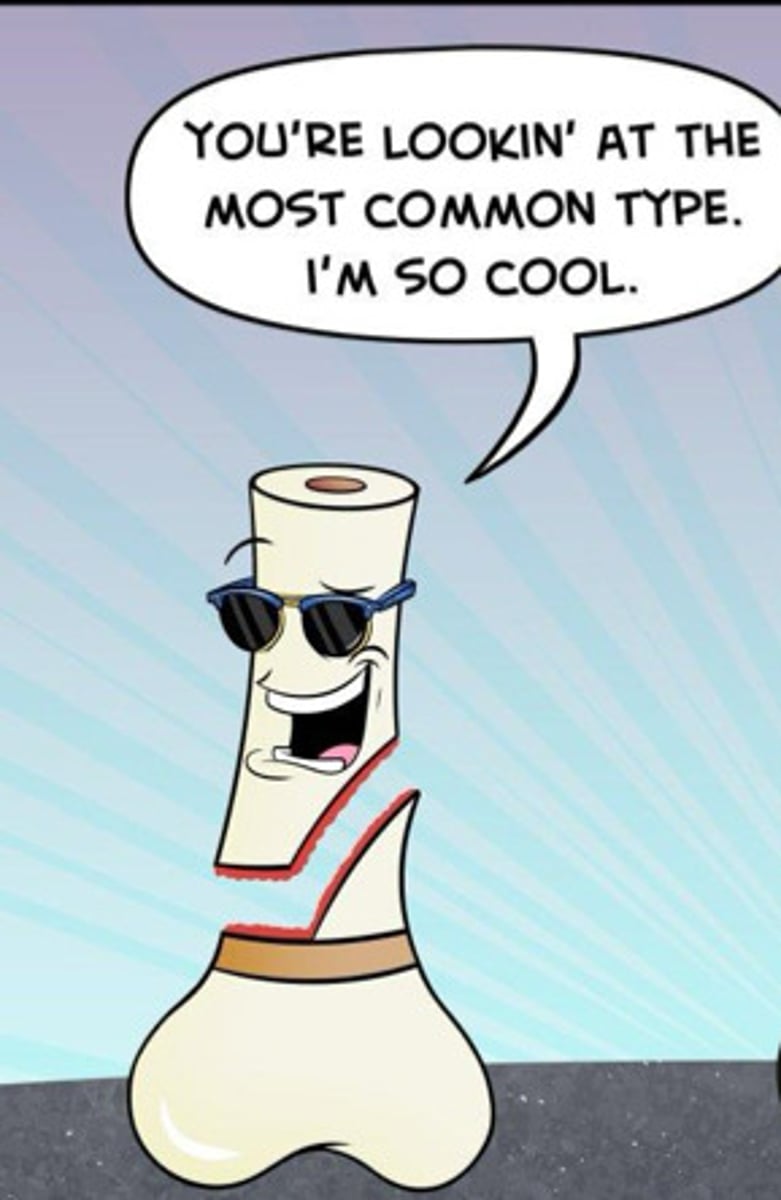
type II salter harris fracture
through the growth plate & metaphysis; heals well w/ cast

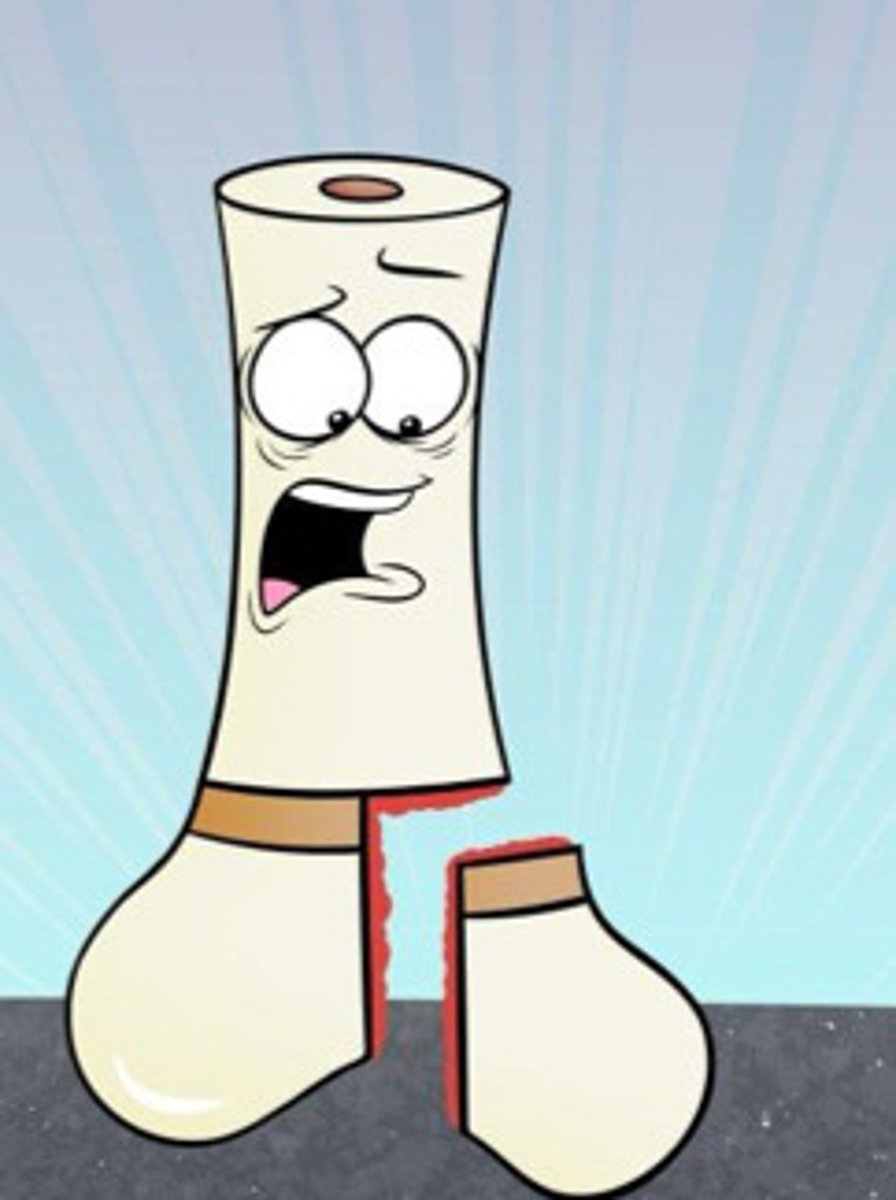
type III salter harris fracture
through growth plate & epiphysis; can develop arthritic changes or asymmetrical growth plate fusion

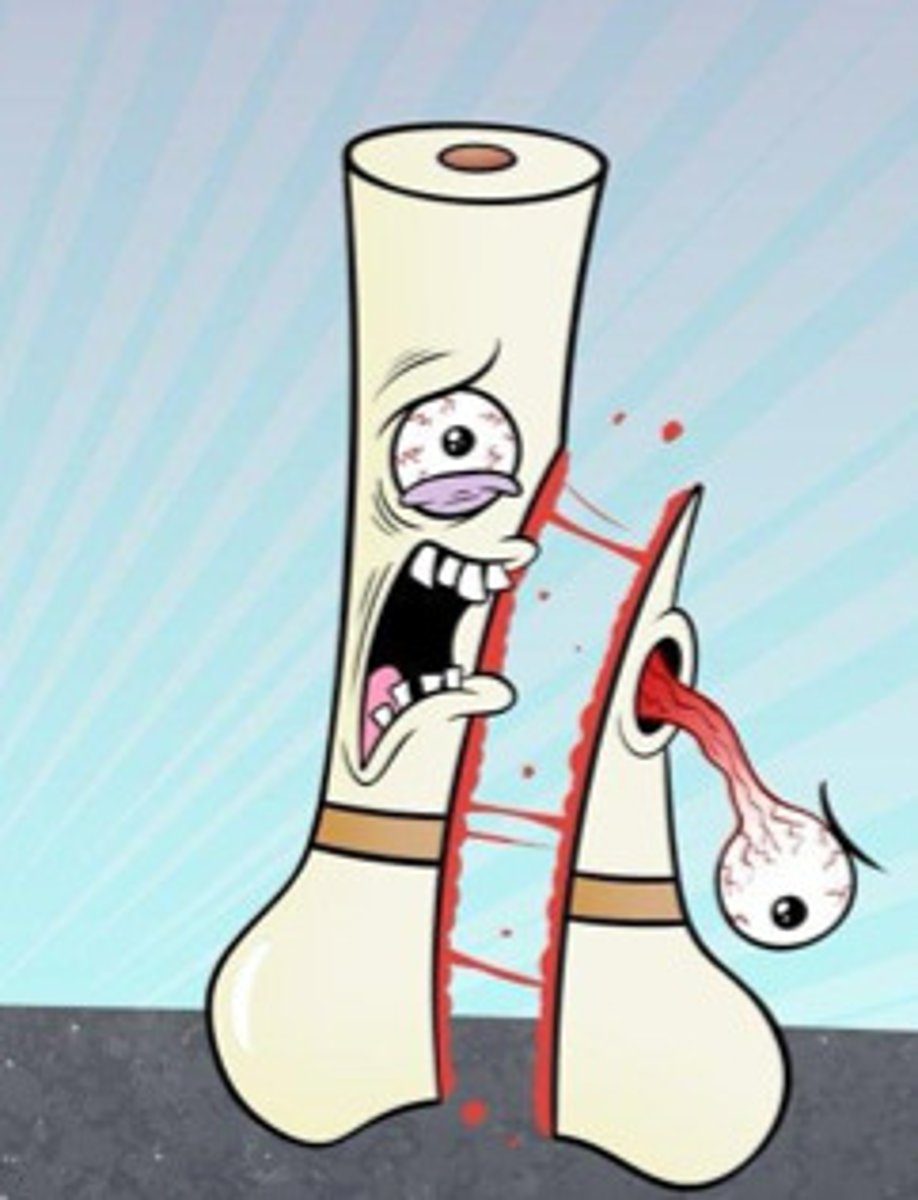
type IV salter harris fracture
through all 3 elements: growth plate, metaphysis and epiphysis; more likely to develop early fusion of growth plate w/ angular deformities & shortening of bone

type V salter harris fracture
crush injury to growth plate; more likely to develop early fusion of growth plate w/ angular deformities & shortening of bone; associated w/ vascular injury & cause growth impairment
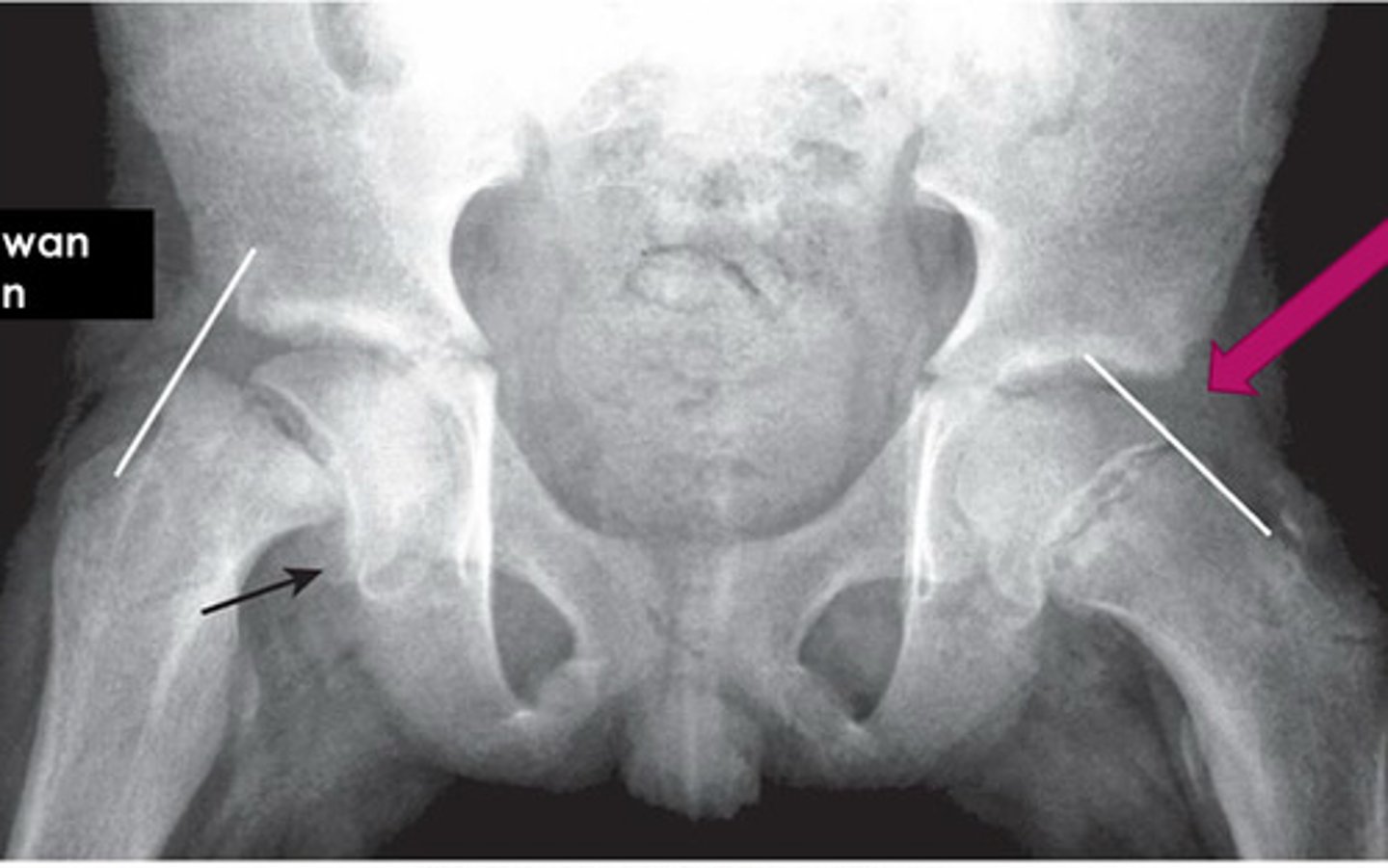
Klein's Line
arbitrary line drawn along superior edges of femoral neck; useful in detecting early slipped upper femoral epiphysis in adolescents; line should normally intersect lateral aspect of superior femoral epiphysis on AP view
what can salter harris fractures be a result of?
child abuse!
what injuries raise suspicion of child abuse?
metaphyseal corner fractures, rib fractures, head injuries
metaphyseal corner fractures
small avulsion fractures from repetitive mvmt of ligament over bone
rib fractures
especially more than 1 & posterior
metatarsal fractures
if not MVA, CHILD ABUSE!! (hard to break)