Paper 3 all
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What was the aim of the Michelson-Morley Experiment?
To detect the presence of ether and measure the speed of light as it changed with different rotations in respect to the ether.
What was the expectation of the Michelson-Morley experiment and how did it differ from the result?
It was expected that when rotating the blocks and mirrors by 90 degrees, the interference pattern should change as the speed of light should be changing, due to the ether.
There was no change in the interference pattern, so the speed of light was determined to be constant and ether did not exist.
State Einstein’s two postulates of special relativity.
The laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames of reference.
The speed of light in a vacuum is constant and independent of the motion of the source or observer.
What is time dilation?
Time runs slower for an observer when observing a moving object than it does for the object itself.
This effect increases greatly as you approach relativistic speeds.
Why is time dilation a consequence of special relativity?
Since the speed of light is the same for all refernece frames. the time experienced by an observer will differ depending on their relative velocities and frames of reference.
Define proper time
Time observed by an object, or an observer that is stationary with respect to the moving object.
How does muon decay provide evidence for time dilation?
Intensity of muons with distance decreases less than expected. This is because the half life to human observers is much larger than the actual half life of the muon due to time dilation.
How does special relativity effect lengths (Use a rod as an example)?
AN observer parallel to an moving object will observe a shorter length than an observer at rest relative to the rod.
Outline Newton’s Corpuscular theory?
This theory pustulates that light is made of small particles (corpuscles).
He proposed that white light ism made up of different colours, which can be separated by a prism.
Outline Huygens wave theory on light
This theory postulates light behaves as a wave.
All points on a wavefront produce their own secondary waves (Wavelets).
Light was a longitudinal wave but as longitudinal waves require a medium to travel through (space was ‘empty’), Huygens suggested space was filled with an invisible massless substance, aether this allowed the light to travel through space.
Explain reflection based on Newton’s corpuscular theory.
Newton suggested that corpuscles behave as balls that bounce off surfaces.
This occurred because the corpuscles carried momentum and so would change direction upon hitting a reflective surface, obeying the conservation of momentum.
The speed only changes in the direction perpendicular to the surface, it must be reflected at the same angle.
Describe the differences between Newton’s and Hyugen’s theories
Newton believed light diffracts due to an attractive force on the corpuscles causing an increase in vertical speed as it enters the material,
the change in that vertical speed (speed in the direction perpendicular from the surface) is what causes a change in angle when leaving the medium.
Hyugen suggests that wavefronts hit the boundary at an angle,
causing the light to take an infinite amount of time to slow down at the boundary.
How did Young’s experiment support Hyugen’s wave theory.
The double slit experiment displayed a pattern of fringes due to interference between different wavefronts.
Young’s experiment occurs due to diffraction which only waves can do.
Therefore Huygen was correct in his wave theory.
How are fringes formed in Young’s double slit experiment?
Monochromatic light passes through the two slits.
The two slits act as coherent light sources,
this causes bright fringes (Maxima) at points where light is in phase and constructive interference occurs, and dark fringes (Minima) where destructive interference occurs where light is out of phase.
Why does Newton’s Theory fail to explain Young’s interference pattern?
If Newtons corpuscular theory was correct then there would only be fringes at the points where light passes through the fringe spacing but instead a pattern of repeating light and dark fringes is observed. Newton’s theory was inaccurate.
What lead to Newton’s theory being rejected?
His theory was rejected due to the inability to explain interference and diffraction patterns observed in experiments like Young's double slit experiment.
Also, after Young’s discovery, light speed was measured in water and found to be less than air.
What did Maxwell predict about electromagnetic waves?
Maxwell predicted that electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light and consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other and the direction of propagation.
He also derived the equation for the speed of an EM wave and determined that light was an EM wave along with UV, Infrared and others.
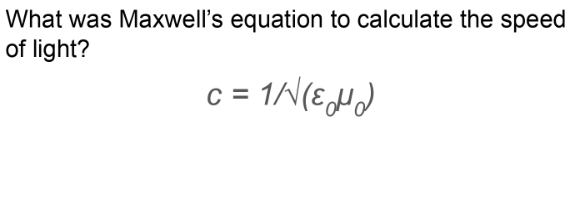
What are the permittivity and permeability of free space?
ε₀ (permittivity)-represents the strength of an electric field due to a charged object in free space.
μ₀ (permeability)-represents the magnetic flux density due to a current carrying wire in free space.
How are stationary waves produced?
When a wave is reflected against a transmitter two coherent progressive waves travelling in opposite directions interfere.
This causes points of maximum displacement (antinodes) and points of minimum displacement (nodes).
How did Hertz discover radio waves?
Hertz discovered radio waves by producing them when a high voltage spark jumped from one metal plate to another.
The spark produced radio waves which he detected using a dipole detector.
As the radio waves produced a voltage across the dipole, it caused a spark in the detector.
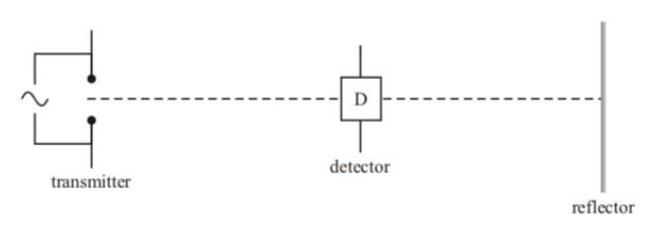
Explain why the strength/reading of the detector varies repeatedly between a minimum and maximum as it travels along the line.
As the transmitter emits a wave it is reflected of the reflector,
producing 2 coherent waves acting in opposite directions that interfere.
This interference causes points of maximum displacement (antinodes) and minimum displacement (nodes).
As the detector moves along the line its reading increases the closer it gets to an antinode and decreases as it moves closer to a node.
What did Hertz discover about radio waves after further experiments?
They can be reflected by metal,
produce stationary waves,
Cannot be stopped by insulators, (So do not have charge)
Can be polarised.
From this he concluded they were EM waves.
How did Hertz determine the speed of radio waves?
Hertz measured the distance between adjacent nodes (1/2 wavelength).
He then multiplied by the frequency of the waves to determine their speed.
This was similar to Maxwell’s predicted value from his equation.
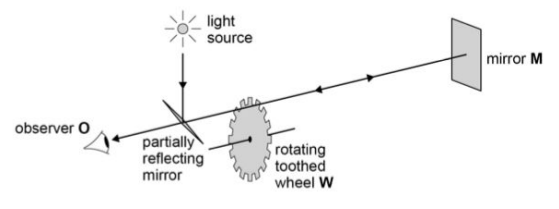
This is the apparatus that Fizeau used to determine the speed of light.
(1) State what he observed when the speed of rotation is low.
(2) This continued until a certain speed was reached.
,State his observation when the rotation speed reached that certain speed.
(1) When the rotation speed was low, the light was able to return through the original gap.
(2)The light is blocked by the cog so is unable to pass through the gap, indicating the speed of light.
Define a Black body and state it’s relevance in the ultraviolet catastrophe.
A Black body is an idealized physical object that absorbs and emits all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence.
It was hypothesised that a perfect black body would emit radiation at all wavelengths, leading to the prediction of infinite energy emission at ultraviolet (very low) wavelengths, which contradicted experimental observations.
How did Planck resolve the UV catastrophe?
He suggested that EM radiation is released in quanta of energy called photons proportional to it’s frequency and not continuous therefore it is not infinite.
When was the photoelectric effect first discovered?
Hertz observed that the strength of the sparks varied with different types of EM waves on the detector, however the strength remained constant if the same EM wave remained incident on the detector.
If frequency is below the threshold, would photoelectrons still be emitted with enough intensity?
Electrons are emitted by 1-1 interactions with photons when they carry a sufficient amount of energy which is proportional to their frequency. Therefore regardless of the intensity photons will not be emitted.
What does maximum kinetic energy of an electron depend on?
It depends on the frequency of light used because f is directly proportional to E.
How does increasing intensity of light affect the rate of photoelectron emissions?
A higher intensity means more 1-to-1 interactions with the electrons, therefore more photoelectrons are emitted, increasing the rate of emission.
Why does the photoelectric effect oppose wave theory?
The effect causes instantaneous release of electron given that the frequency is above a certain threshold.
Wave theory suggests emission won’t always happen instantaneously and predicts that any frequency of light will eventually cause electrons to be emitted.
This is against the experimental results of Hertz and so opposes the wave theory.
What is stopping potential and how is it measured?
Stopping potential is the minimum voltage needed to stop the flow of photoelectrons emitted from a metal surface in the photoelectric effect.
It is measured by applying an electric potential difference that balances the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons.

State De Broglie’s hypothesis
De Broglie's hypothesis states that particles, such as electrons, exhibit wave-like properties, and their wavelength is inversely proportional to their momentum.
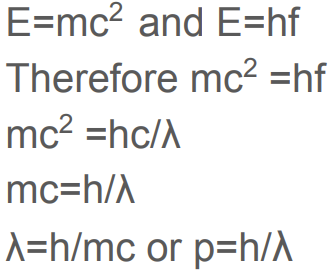
What was observed by the electron diffraction experiment and why was this observed? State The significance of this experiment.
Electrons produced a pattern of concentric rings, due to the constructive and destructive interference that occurred when the electron beam is diffracted.
Significance: Only waves were known to diffract. This supported de Broglie’s hypothesis that particles could also behave like waves.
How is the cathode ray in an electron diffraction experiment created?
A filament is supplied with energy from a power supply, increasing the current and the temperature of the filament.
This supplies the filament with enough kinetic energy to emit electrons from the surface of the metal.
These electrons are accelerated from cathode towards the anode using a p.d.
When the electrons have fully accelerated they will all be travelling with the same kinetic energy which is equal to the work done by the p.d.

What is de Broglie’s Wavelength in reference to anode potential?
.
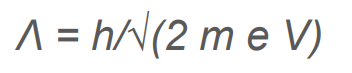
How does increasing the electron’s speed change the diffraction pattern?
Increasing the speed/momentum of the electron, decreases it’s wavelength.
This will produce rings that are closer together.
What anode voltage is required f or electrons to have wavelengths of the same order as a atom?
150V
Define Resolving power.
The ability of an optical system to distinguish between closely spaced objects, often defined as the minimum angular separation that can be resolved.
How are images formed by a TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope)?
An electron beam produced by thermionic emission is accelerated using a anode.
A Magnetic lens uses magnetic fields to deflect electrons near the edge towards the centre. Electrons in the centre continue in their straight path.
A condenser lens focuses electrons into a parallel beam incident uniformly on the sample.
There is than an objective lens that forms an image of the sample.
A projector lens creates the final image on a fluorescent screen.
State the factors that lead to a lower resolution image
Lower anode potential- This would mean the electrons gain less kinetic energy, resulting in longer wavelengths and reduced resolving power.
Thickness of a sample- The electrons pass through thick sample, so have less kinetic energy as they slow down, decreasing their wavelength and reducing detail.
lens aberrations- These reduce the focusing ability of the lens to direct electrons travelling at different speeds due to being scattered.
Why is the pressure in the TEM low?
To reduce the amount of collisions with air particles.
If pressure is high rate of collisions increases, decreasing the kinetic energy of the electron, increasing their wavelength and reducing the resolving power.
How does a STM (Scanning Tunneling Microscope) work?
Uses Quantum Tunneling-a phenomenon where electrons tunnel through a barrier. The closer the barrier to source of emission the higher the probability of tunneling.
A fine probe is placed close to the surface of a material to produce a tunneling current between the surface and the probe.
A small p.d. goes between the probe and the surface so electrons cross the gap from negative to positive.
How are cathode rays made in a discharge tube?
Electrons are released by thermionic emission.
Electrons are repelled by cathode and accelerated towards anode.
Why is light emitted from a discharge tube?
A strong p.d. between the anode and cathode cause atoms in the discharge tube to ionise.
When these positive ions are attracted to the cathode, they accelerate and collide with the cathode.
This causes electrons to leave the cathode and go to excite other atoms, when those atoms excite and de excite they release photons of light.
The speed, v, of each electron leaving the anode in a cathode ray?
Work done on each electron is equal to the kinetic energy gained, which is given by the equation W = qV, where q is the charge of the electron and V is the potential difference.
This increases the speed of each electron as it accelerates to the anode.
State 3 methods used to work out the specific charge of an electron
Using a magnetic field.
m=mv/Be
e/m=v/Br
e/m=2V/B²r²
Why must gas pumped into a electron tube be low?
Low pressure = less molecules.
To ensure that collisions between gas molecules and electrons are minimized, allowing for efficient electron acceleration and less scattering.
This could result in electrons not being able to travel the entire length of the tube.
Who was Thomson and what did he accomplish?
Conducted experiments investigating cathode rays which lead to him discovering the electron and it’s specific charge.
What did Thomson determine about the specific charge of an electron in comparison to an hydrogen ion? Why was it significant?
Thomson determined the specific charge of an electron was 1800x greater than a hydrogen ion.
This meant the electron had either a massive negative charge or a very small mass.
Significance: hydrogen was previously determined to have the highest specific charge of any particle, indicating that the electron is a fundamental component of matter.
Who was Millikan and what was the significance of his experiment?
Robert Millikan was an American experimental physicist renowned for his oil drop experiment, which measured the charge of the electron.
He found that the common factor between the charges found on the droplets was no less than the elementary charge so he determined that the charge of all material is quantised.
What forces act on a droplet in Millikan’s experiment when stationary?
mg=eV/d
The weight of the droplet acting down, and the Electric force which is equal to the weight, acting upwards to balance it.
Explain the journey of a falling droplet including how to cause the droplet to fall from stationary.
A falling droplet begins stationary due to the balance of forces acting on it.
When the p.d. is decreased, the electric force acting upwards becomes weaker, allowing the weight of the droplet to cause it to accelerate downwards.
If the p.d. is shut off completely, the weight of the droplet causes it to accelerate downwards (\/)
As it falls drag increases reducing the rate of acceleration until mg=drag then it has reached it’s terminal velocity.
What did Stoke accomplish?
Stokes formulated the law of viscosity, which describes the drag force experienced by a sphere moving through a viscous fluid, highlighting the relationship between the droplet's size, velocity, and the fluid's viscosity.
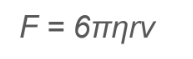
How does Stoke’s Law determine the radius of a droplet?

How did Millikan use the value of the radius to determine the charge of an electron?
He used the radius to determine the mass of the droplet, to calculate it’s weight.
He then was able to determine the p.d. necessary for the droplet to remain stationary.
From that he could calculate the charge using eV/d=mg.