Bio Lab Midterm
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What is the Harvard Step Test? (Lab 1)
A test where a subject steps up and down at a constant rate for 3 to 5 minutes. The pulse rate is measured before and after exercise as well as in 1,2,3 minute intervals— in other words,
Basic laboratory rules are..
1) If your hair is long, pull it back'
2) where appropriate clothing attire— no sandals are allowed and make sure most of your body is covered
3) Wear eye protection— if your eyes feel odd, use the eye was
4) Do not eat or drink in the lab
5) put your items below the table
How to dispose of certain substances..
will be added onto later
What are the steps of the scientific method?
1) observation
2) Ask why? (question)
3) Hypothesis
4) Prediction
5) Experiment—> data (results)
6) Analyze the data (analysis)
7) Conclusion (Accept or deny hypothesis)
What is an hypothesis?
A possible explanation/ estimated guess (always starts with maybe)
ex: maybe the females are more fit compared to the males (lab 1)
What is a prediction?
An estimated outcome based on the hypothesis (always starts with if/then)
ex: If females are more fit than males, then their overall pulse recovery rates will be less than the males.
What is the independent variable?
the variable that is being tested/ it cannot be changed
ex: the ___ is time (lab 1)
What is the dependent variable?
the variable that is measured (effects)
ex: the _____ is the average bpm (lab 1).
What is the controlled group?
The group that receives the placebo/ not the real experiment
ex: the ____ are the males (lab 1)
What is the controlled variable?
A variable that is constant
ex: the _______ are the time rests with the step test (lab 1)
What is the experimental group?
The group that receives the experiment
ex: the_____ is the females (lab 1)
The metric conversion…
KHDUDCM
kilo, hector, deka, unit, deci,centi,mili
What is magnification?
the ability to make small objects seem larger, such as making a microscopic organism visible
What is resolution?
the ability to distinguish two objects from each other.
What are lens?
an optical device that can refract light; The refraction depends on the shape of a lens,
red: 5x
yellow:10x
blue: 40x
black/white: 100-250x
What is total magnification?
the product of the objective and ocular lenses
(Objective lens X Ocular lens = Total magnification)
What is the field of view?
The maximum area visible when looking through the microscope; diameter measure
it gets smaller when magnification increases
What is parcentric
This means that an object in the center of the field of view at one magnification is in the center of the field of view at any of the other magnifications.
ex) Microscopes are designed to be parcentric.
What is parfocal?
This means that the focus for each lens is very similar.
ex) Microscopes are designed to be parfocal.
What is depth of field?
The distance between the lens and the object
How to calculate the size of field of view?
Diameter of the field of view (mm) = F / M, where F is the number of field of view (FOV) of the eyepiece, and M is the magnification (mag.) of the objective.
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
The eukaryotic cells have nucleuses while the prokaryotic cells do not
What is the test for carbohydrates?
Benedict’s test…
add benedict’s solution w/ the unknown solution and boil; if the solution is any color that is not blue, monosaccarides are present
What is the test for protein ?
biuret test.. add the biuret solution into the unknown solution and observe a color change, if the change is purple, protein is present
what is the test for lipids?
lipid panel..place the solution onto a paper, if there is an absorption, the lipid is present
What are the building blocks for polysaccharides?
Monosaccharides are the building blocks for polysaccharides. They are simple sugars, such as glucose and fructose, that can be linked together through glycosidic bonds to form larger carbohydrate molecules.
What are the building blocks of proteins?
Amino acids
What are the building blocks of lipids?
Fatty acids and glycerol.
What are the building blocks of nuclecic acids?
nucleotides. They consist of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
the basics of electromagnetic spectrum
Range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Each type has different wavelengths and energies, with radio waves having the longest wavelength and lowest energy, and gamma rays having the shortest wavelength and highest energy.
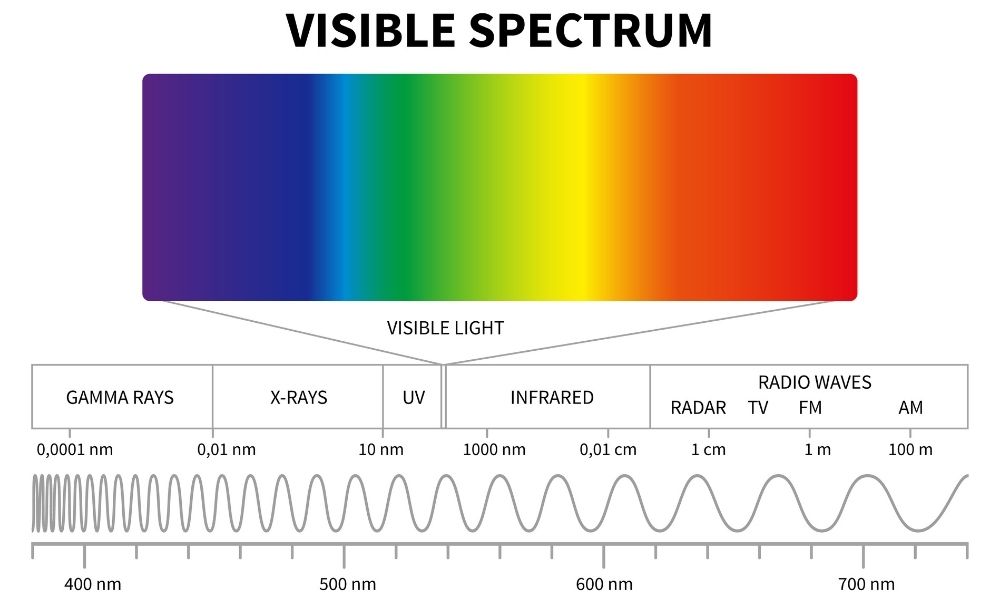
the basics of visible light
The part of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye.
It consists of different colors, ranging from violet to red, with each color having a specific wavelength and frequency. Visible light is responsible for our perception of color and is essential for vision.
(ROYGBV)
The basics of wavelength
The distance between two consecutive points on a wave. It determines the color of light and the pitch of sound. Symbol: λ (lambda).
smaller the wavelength, the more energy it has
bigger the wavelength, the less energy it has
Gamma rays (violet) have the smallest wave length
Radio rays (red) have the largest wave length
basics of absorption
Process where one substance is taken in and incorporated into another, usually a liquid or solid. It occurs at the molecular level and involves the movement of substances across a surface or through a barrier. Examples include nutrients being absorbed by the body during digestion or a sponge soaking up water.
(the absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the solute in the solution)
Basics of transmission (in bio)
light transmitted through the sample —tested by a spectrophotometer
What is the Bradford protein test?
Bradford reagent dye is added to a solution to determine the absorbance
What is spectrophotometry?
Measurement of the amount of light absorbed or transmitted by a substance at different wavelengths.
Used to analyze the concentration of a compound in a sample and determine its properties, such as purity and reaction kinetics.
What is the purpose of a blank?
A blank solution for a spectrophotometer is a solution which can be used to measure the amount of absorbance that occurs in the absence of the molecule which you intend to measure.
What does a blank contain?
20 uL phosphate buffered saline (PBS) + 1000 uL Bradford reagent dye
Why do you measure absorption at A595 instead of A470?
In the presence of protein, the change to the anionic blue form of the dye shifts the Amax to 595 nm. Since the amount of the blue anionic form is proportional to the amount of protein in the sample, the quantity of protein in a sample can measured directly by measuring the absorption at 595 nm.
What is the purpose of a standard curve?
The purpose of a standard curve is to establish a relationship between known concentrations of a substance and their corresponding measurable values. It allows for the quantification of unknown concentrations by comparing their values to the curve.
How to calculate protein concentration?
absorbance- y intercept —→ ans/slope (diluted solutions) or just stare at the graph
multiply the absorbance with the bradford reagent and divide that by 1 mL (for UNDILUTED solutions)
What is a solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution
What is a solvent?
substance (molecule) with the ability to dissolve other substances (solutes) to form a solution
What is selectively permeable?
certain molecules can penetrate through the membrane
What is diffusion?
the spreading of something more widely.
What is Osmosis
the movement of water molecules from a solution with a high concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of water molecules, through a cell's partially permeable membrane.
What is tonicity?
the state of a solution in respect of osmotic pressure.
What is isotonic?
water and solute both go in and out at the same time
(blood cells and plant cells:0.9 NaCl)
what is hypertonic?
When salt goes into the cell
(blood cells shrivel; 0.10 NaCl) (Plant cells plasmolyzed (membrane pulls away from the cell wall); 0.10 NaCl)
what is hypotonic?
when water goes into the cell
(blood cells burst; water) (plant cells are turgid: best solution)
How to tell when a cell is plazmolyzed?
the plasma membrane detaches from the cell wall
(plant cell..0.10 NaCl)
How to tell when the cell is turgid?
plant cell looks swollen from the turgor pressure put on the cell wall— lots of water in the cell
(Plant cell..pond water)
How to tell when a cell is flaccid?
a cell lacking turgidity
(plant cell..0.9 solution (isotonic solution))
How to tell if a cell is hemolyzed?
If there is no cell (cell burst)
blood cell in water
How to tell if a blood cell is crenated?
a cell shrivels/shrinks
blood cell in 0.10 NaCl
What is catechol oxidase?
An enzyme of the oxidoreductase class that catalyzes the reaction between catechol and oxygen to yield benzoquinone and water.
What is substrate specificity?
the substrate is specific to its enzyme
What is a catalyst?
a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change
What is activation energy?
The initial investment of energy for starting a reaction
What is the cofactor?
a non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role.. inorganic
What is the competitive inhibitor?
When an inhibitor competes with a substrate to bind to the active cite
What is the non competitive inhibitor?
An inhibitor that binds to the nonactive cite of the enzyme
What is denaturation?
the unfolding or breaking up of enzymes, modifying its standard three-dimensional structure.
What is the optimal temperature?
20-35°C (98 f)
What is the optimal Ph?
between 6 and 8 (7)
Why would yeast produce ATP by fermentation rather than cellular respiration?
When yeast cells are kept in an anaerobic environment (i.e., without oxygen), they switch to alcoholic fermentation to generate usable energy from food.
Know the formula for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2.
why it is important to do an absorption spectrum for plant pigments?
To derive the wavelengths most efficiently used by the pigments in different colored leaves.
What are the parts of the chloroplasts?
(1) the intermembrane space between the two membranes of the chloroplast envelope;
(2) the stroma, which lies inside the envelope but outside the thylakoid membrane;
3) the thylakoid lumen.
What is the light dependent cycle?
the light dependent cycle occurs in the thylakoids
H2O is split and merges with light
O2 is created
ATP and NADPH is produced
(requires light and water)
What is the Calvin cycle??
The calvin cycle occurs in the stroma
the ATP and NADPH from the light dependent cycle power it.
carbon becomes G3P which becomes glucose
this cycle produces NADP + (ADP + P)
What is thin layer chromatography?
an affinity-based method used to separate compounds in a mixture
1) application of the sample
2) "developing" the chromatogram by allowing the mobile phase to move up the paper (mark the paper)
3) calculating Rf values and making conclusions.
The sample is spotted onto one end of the TLC plate and placed vertically into a closed chamber with an organic solvent (mobile phase). The mobile phase travels up the plate by capillary forces and sample components migrate varying distances based on their differential affinities for the stationary and mobile phases.
How do you calculate rf?
equal to the distance traveled by the compound divided by the distance traveled by the solvent front (both measured from the origin).
distance traveled by solute/ distance traveled by solvent
Why are there several pigments in a leaf?
Because they interact with light to absorb only certain wavelengths,
What light does chlorphyll absorb?
Red and blue
A leaf may have different pigments than chlorophlyll because?
Accessory pigments allow a broader spectrum of light to be absorbed by the plant for photosynthesis.