SPI and Trends
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
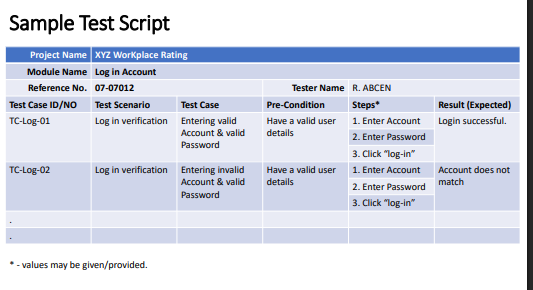
Test Scripts
Software Process Improvement (SPI)
refers to the application of a systematic approach in the identification, evaluation, and improvement of software processes
identification, evaluation, and improvement
Software Process Improvement (SPI) refers to the application of a systematic approach in the _ _ _of software processes.
goal of SPI
The is a systematic methodology to improve the quality, efficiency, and effectiveness of software development and maintenance
quality, efficiency, and effectiveness
The goal of SPI is a systematic methodology to improve the__ _ _of software development and maintenance.
• Identify the need for improvement
• Establish goals and objectives
• Develop a plan
• Implement the plan
• Monitor and evaluate the improvement effort
Steps in SPI
• Identify the need for improvement
- process assessment involving gathering data on the current state of the software development process.
• Establish goals and objectives
- SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-boxed)
• Develop a plan
- includes a timeline, resources, and responsibilities.
• Implement the plan
- implements the changes (often couched as experiments) that have been identified and putting the collection of metrics in place to see if they are effective.
• Monitor and evaluate the improvement effort
- collecting metrics data on the effectiveness of the changes that have been implemented and making adjustments as needed based on feedback.


Artificial Intelligence soar high
Levelled up use of Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
Blockchain
Progressive web apps
5G technology
IoT
Low Code Development Apps
Python Dev
Web 3.0
IoB (Internet of Behavior)
FinOps and GreenOps
Enterprise Developers will Rely More on Distributed Computing
NFT Tokens
Cloud-Native Technologies Continue to Evolve
Microservice Architecture
Adoption of Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Major Cybersecurity with DevSecOps
Kubernetes
New Programming languages
Software Development Trends
1. Automated Machine Learning – From healthcare and finance to retail – AutoML will help simplify complex data sets while also significantly reducing training time for models.
2. Generative AI – Data from all sources, including images, videos, and sounds, will soon be used to create entirely original content, enabling businesses to generate new data for any purpose.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP) – NLP technologies will revolutionize human-computer interaction by bridging the gap between man and machine through natural language understanding capabilities.
4. Ethical AI – Ethical AI will help bridge the trust gap between users and technology by reinforcing cybersecurity measures so that confidence in automated systems can continue to grow.
5. AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS) – With offerings from Google’s TensorFlow and Amazon SageMaker to Microsoft AzureML, companies will be leveraging cloud-based platforms to capitalize on a variety of AI services.
Artificial Intelligence Becoming an Everyday Assistant
FinOps , GreenOps
__focuses on driving efficiency across various financial processes, while _emphasizes implementing eco-friendly practices for long-term value creation.
IoB
brings various important data, such as user behaviors, interests, and preferences, from BI (Business Intelligence), Big Data, and CDPs.
Infrastructure as Code
is one type of process that allows you to manage and provision computer data centers with the help of machine-readable definition files.
Development + Security + Operations
=DevSecOps
DevSecOps
is an automation, platform design, and culture approach that integrates security as a shared responsibility across the IT lifecycle. I
Kubernetes
also known as K8 or Kube,
Kubernetes
is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates many processes, such as scaling, deploying, and managing containerized applications.
URERB univ research and ethics board
SPI in MMSu
Change Management
analyzing the cost and benefits of proposed changes
Configuration management
policies, procedures, tools for managing changing software