Business Role in Society 2 Notes
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Business Model
A system of how a company creates and captures value
A company takes the elements in its surroundings, transforms them and puts them back into the surroundings
Using the managerial functions of planning, organizing, integrating staff, directing and controlling, it transforms the elements or inputs
Value Creation
The process of transforming elements in the surroundings to create value for customers
Managerial Functions
Planning, organizing, integrating staff, directing, and controlling to transform inputs
External Environment
The context in which a company operates, including industry, economy, and society
Strategic Decisions
Choices made by a company regarding offerings and results from a systemic perspective
Holistic Approach
An analysis unit that emphasizes understanding business at a system level
Value Capture
The process of obtaining financial returns from value created
E-commerce Growth
The rise of online business models in the 1990s due to the Internet
Innovation in Business Models
Companies with higher financial performance focus more on innovating their business models
Tools for Business Model Development
Methods like brainstorming, maps, Plan Cruncher, Business Model Canvas, and Lean Canvas
Brainstorming
A group activity to generate and share ideas in a safe environment
Mental Maps
Flow diagrams that illustrate the organization and relationships within a company or project
Plan Cruncher
A one-page summary highlighting key aspects of a business idea
Business Model Canvas
A tool consisting of 9 blocks representing key areas of a company
Lean Canvas
A modified version of the Business Model Canvas focusing on problems, solutions, key metrics, and unfair advantages
Value Proposition
The main reason a customer would buy a product
Market Segments
Identifying the main target audience and their specific needs
Customer Relationship
The type of relationship a company wants to build with its customers
Channels
The methods used to deliver products/services to customers
Key Activities
Essential activities required for the production or sale of a product/service
Key Partners
Entities that help a company maximize operations, such as suppliers and strategic alliances
Key Resources
Required assets needed to create value for customers
Cost Structure
The monetary consequences of operating a business model, including fixed and variable costs
Revenue Streams
Various ways a company can generate income
Business Patterns
Concepts capturing design ideas that can be reused in business models
"Free" Business Model
A model where at least one segment benefits from a free offer
"Open" Business Models
Models that create value
A company is more than just
a product or service
Systemic perspective
The survival of any company implies strategical decisions towards what’s being offered, how and what results are getting from a:
A business model it’s a new analysis unit that’s different from:
The product
The company
The industry or network
It emphasizes an holistic approach at system level to explain how companies do business
What does a business model try to explain
The value creation and value capture
Origin of the concept of business model
With the growth of the internet in the 90’s. And therefore, the e-commerce became a thing
A business model intervenes between technical and economical scopes
Aportaciones técnicas: ej. rendimiento de factibilidad
Modelo de negocio: mercado, propuesta de valor, cadena de valor, costo y beneficio, red de valor, estrategia competitiva
Salidas económicas: ej. valor, precio, beneficio
Tools to develop business models
When we are designing our business model, its very common that our ideas come in random waves and it can cause us to rule them out or forget them. Sometimes, we can’t communicate only with words
To solve those limitations and to enhance the results, there are some tools to develop business models
The 5 tools to develop business models
Brainstorming
Maps
Plan Cruncher
Business Model Canvas
Lean Canvas
Brainstorming
It’s a bunch of ideas generated by a work group that are gather in a safe and ideal place to share thoughts and ideas without worrying about whether they are accepted or not
The proposed ideas become public and anyone can share their opinion and propose modifications
Mental Maps
Flow diagrams that show the organization and the relationship between the different components of the company/project

Plan Cruncher
One page summary that show the highlights that turn an idea into a great business
It uses icons and few text
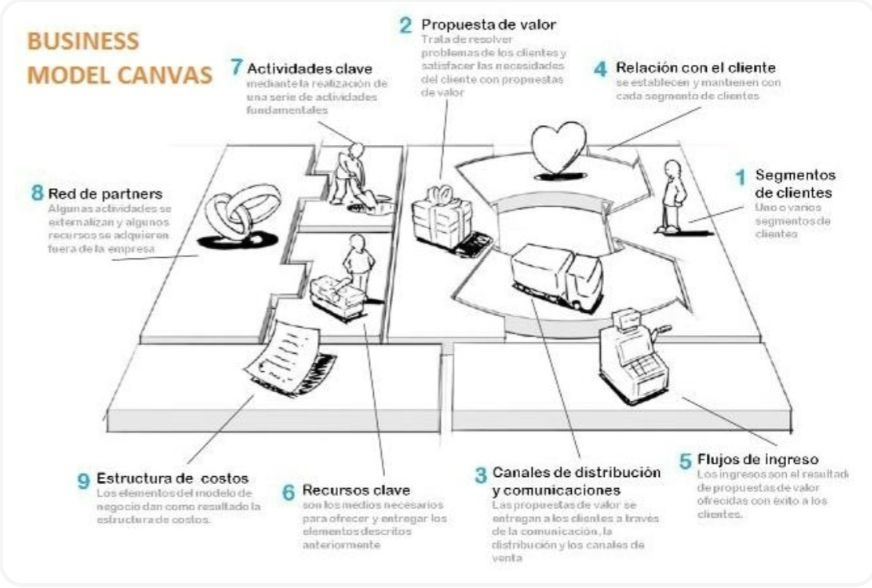
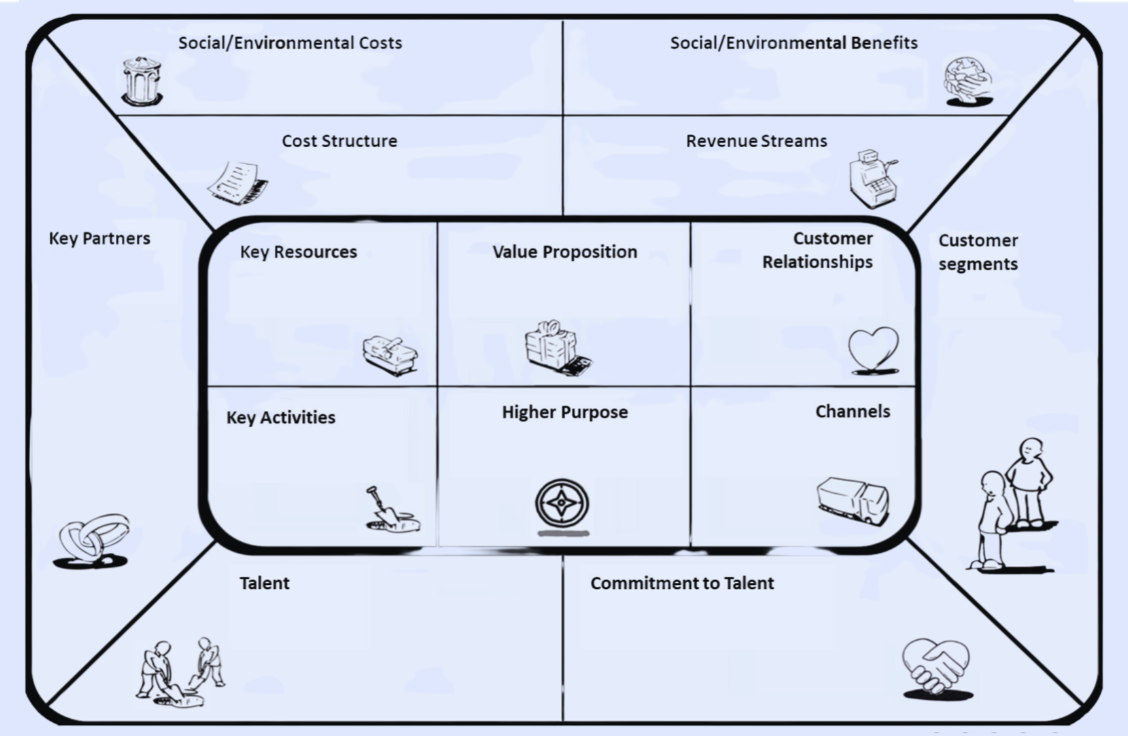
Business Model Canvas
Tool formed by 9 blocks that represent each key area of the company
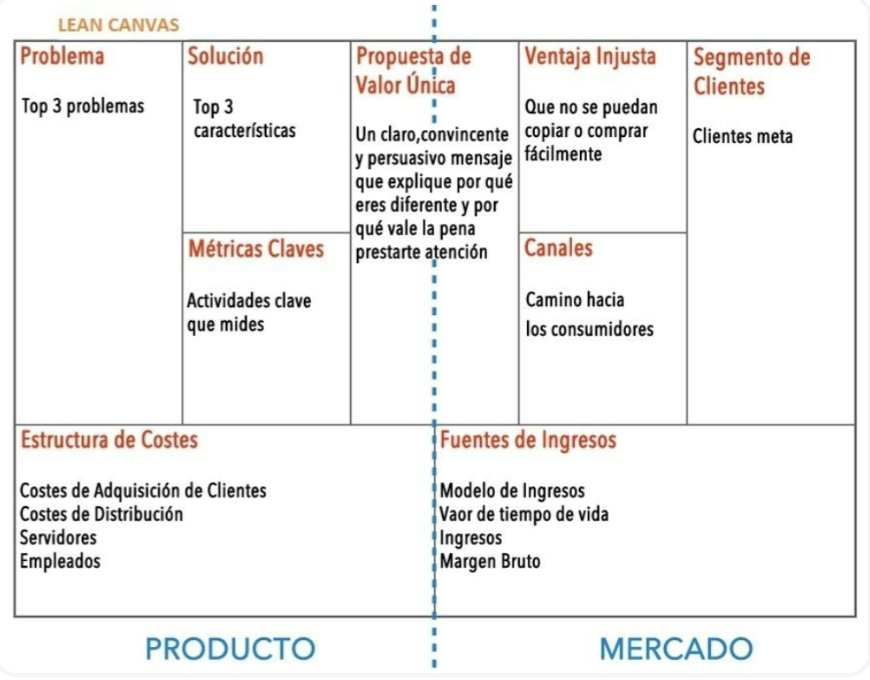
Lean Canvas
Its similar canvas to the BMC but with some changes:
The alliances are substituted by problems
The key activities changed by the solution
The key resources change for the key metrics or KPI’s, that will become a key element when pivoting
The relationship block is substituted by unfair advantage
Propuesta de valor
La principal razón por la que alguien compraría tu producto
“Un modelo de negocio fundamentado en la innovación se basa en encontrar y fomentar nuevas formas de crear, entregar y captar valor” - A.Osterwalder
Principales causas del fallo en emprendimientos
52% modelo de negocio, 29% motivos financieros, 19% otros
Un modelo de negocios describe los funamentos de cómo una organización crea, desarrolla y capture valor
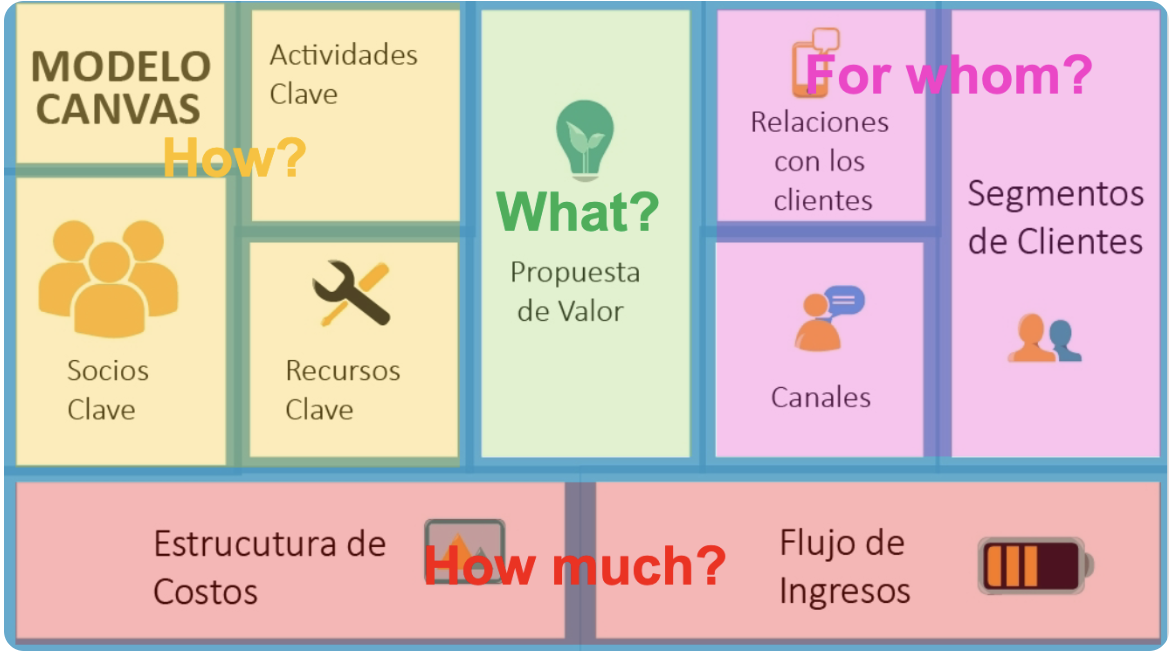
Business Model Canvas Areas
How?
What?
For whom?
How much?
Business Patterns
Propuesta de valor
¿Que valor entregamos al cliente?
¿Que necesidades estamos satisfaciendo?
¿Que paquetes de producto/servicio estamos ofreciendo a cada segmento de clientes?
2.1 Market segments
We have to id our main target, that which is worth the effort. The idea is to find the features or needs of that segment and develop the right strategies to approach them
Massive segmentation
Niche market
Traditional segmentation
Diversify: many segments, each one with a different set of features
Multi-platforms: they serve different segments that are somehow connected
2.2 Customer Relationship
To be successful, a company must id the type of relationship they want to build with their customers
There are several types of relationships:
Personal assistance: stronger relationship
(Devoted) personal assistance, ex. personal shopper
Self-service: indirect interaction
Automated services
Communities: interaction between customers who share their experiences
Co-creation: the customer is part of the production process
2.3 Channels
It includes how do we deliver the product/service to the customer
You can use your own channels, others or both:
Direct
Indirect
Combination
Consider the distribution type:
Massive ex.coca cola
Intense ex. hp
Selective ex. zara
Exclusive ex. mcdonalds
Channels
Direct
Indirect
Combination
Distribution type
Massive ex.coca cola
Intense ex. hp
Selective ex. zara
Exclusive ex. mcdonalds
3.1 Key Activities
It requires to id those activities that are required for the production or sale of the product/service
They are a must
The most important categories are:
Production
Problem solution
Platform or network
3.2 Key Partners
There are always partners that help the company to maximize the operations
It can include: suppliers, financial institutions, legal aid, government, strategic alliances
3.3 Key Resources
Include in this section all those resources that are needed to create value for the customer. They are considered as required assets to hold and support the company
They can be: human, financial, physical and intellectual
4.1 Cost Structure
In this section you’ll find the most important monetary consequence that occurs while operating business models
It’s important to define whether your business is:
Cost motivated
Value motivated
Consider: fixed and variable costs, scale economies
Cost definitions
Cost motivated
Value motivated
4.2 Revenue Streams
It answers the question: how do we obtain money? There are many ways, some of the more common are:
selling assets
usage fair
subscription
rent/leasing
licensing
commission
advertising
Pattern
“It refers to the concept of capturing design ideas and be able to reuse them” - Christopher Alexander
Business model patterns
In business models it’s related to:
Description with similar features
Similar behaviour
Similar organizations
A pattern in Business Models describes similar characteristics, similar arrangements of business model building blocks, or similar behaviors
90% of all business models are based on 1 of the 55 existing patterns
The business patterns are a source of inspiration
When you have your own business or want to improve one, you should create your own proposal
“Free” as a Business Model
At least, one of the segments gets constantly benefited by the free offer
ex. Spotify
“Open” Business Models
It creates and captures value by systematically collaborating with external partners
It opens the research process to a third-party
ex. innocentive
“Cross-sale” Business Models
The companies can easily offer products or deals that are not necessarily linked to the main industry they’ve chosen
They can generate additional income with relatively little-to-no changes in the infrastructure and existing assets
ex. Ikea
“The long Tail” Business Models
They’re focused on offering a huge variety of (rare) products, each one is sold in low volumes
The real challenge in selling specialized content is to find potential buyers
ex. amazon
“Razon & Blades” Business Models
Business based on replacement/refill
The basic product is cheap, sometimes it’s free, but the add-ons are expensive
ex. Nespresso
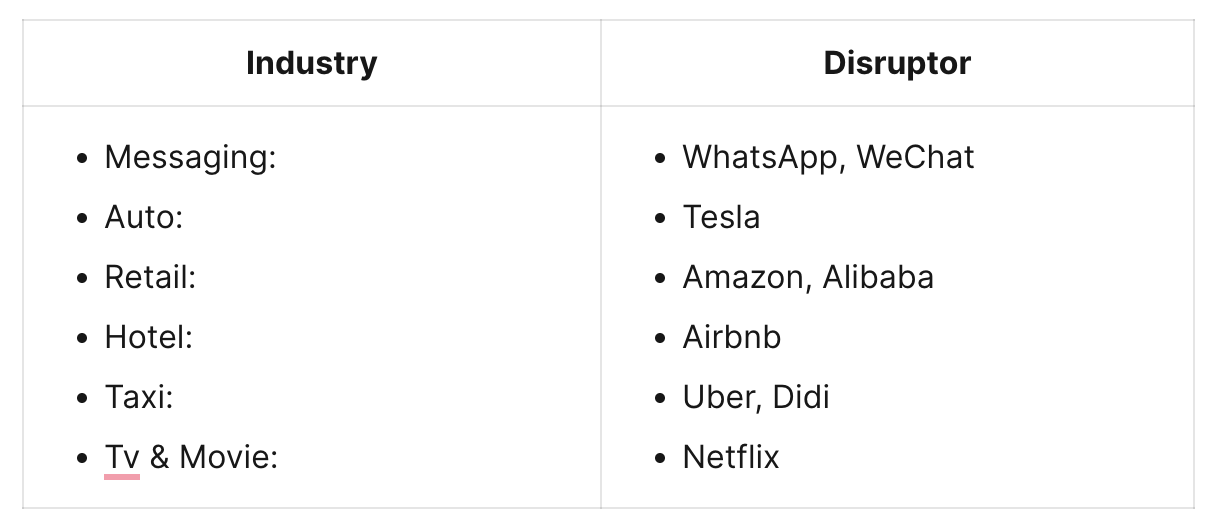
Industry and Disruptors
Disruptors: Entities that significantly alter industry dynamics
Impact: Can lead to industry decline or transformation
Innovation: Often introduce new technologies or business models
Market Share: Disruptors can capture significant market share quickly
Consumer Behavior: Shift in preferences towards disruptor offerings
Adaptation: Established industries must adapt to surviveCompetition: Increased competition drives innovation and efficiency
Examples: Uber (transportation), Netflix (entertainment), Airbnb (hospitality)Response Strategies: Collaboration, investment in innovation, or acquisitionRegulation: Disruptors may challenge existing regulatory frameworks
Example industries and disruptors
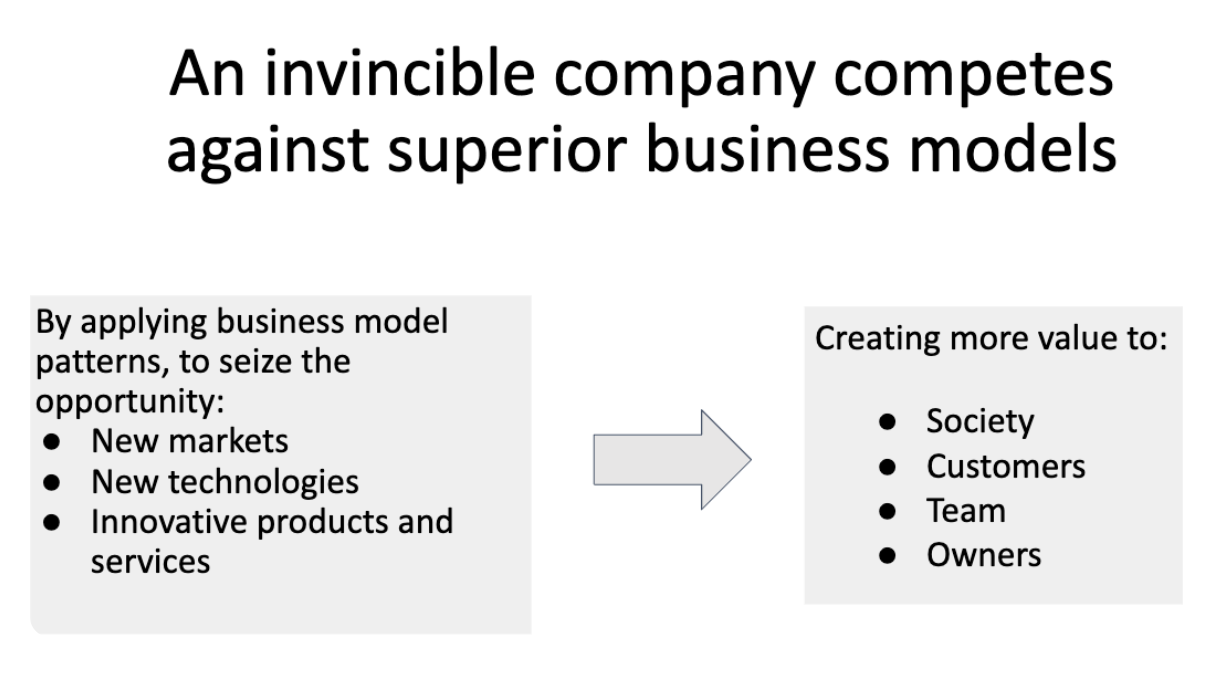
Invincible companies
“Its a company that reinvents itself constantly, before it becomes obsolete”
It beats itself
It explores the future by being excellent in the present
It cultivates an innovation and execution culture
It computes with superior business models
It transcend the industry’s limits
Invincible company’s competition
An invincible company uses tools to explore the present and explore the future
7 actions of the exploration stage
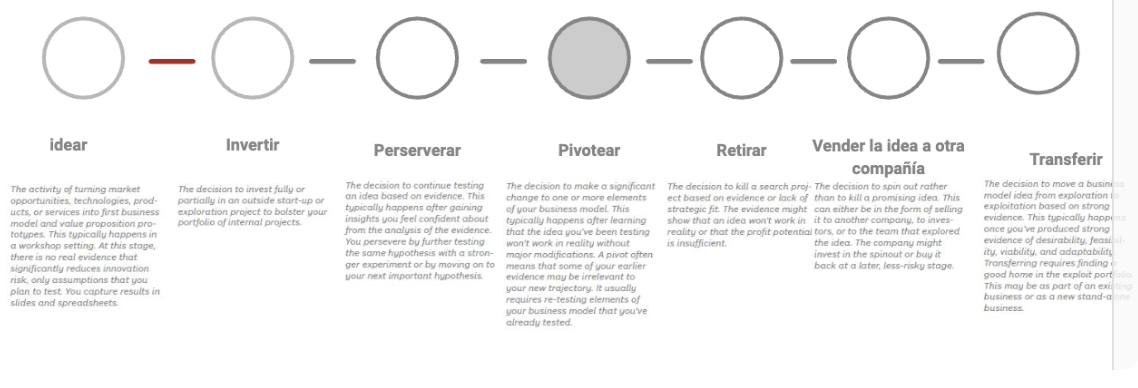
Pivot
It represents the decision of making a significant change to one or more elements of the business models
Example of Pivot

Conscious business models definition

4 pilars of conscious business models
Higher purpose
Stakeholders
Conscious culture
Conscious leaders
Conscious Business Models