GI Pathology FLASHCARDS 🥨
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
* **What happens when someone vomit for days?**
* hypochloremic (hyper chloride) in blood
* lower pH in the stomach
* lower pH in the stomach
2
New cards
what is the PAS staining
* Staines the lining of the mucus → polysaccharides
3
New cards
What is the function of goblet cells in the GI tract?
Goblet cells secrete mucus that protects the mucosa from damage.
4
New cards
What is the pathology of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)/barrets disease?
GERD is caused by long-term acid reflux, which can lead to the development of Barrett's disease of the esophagus, where the lining of the esophagus is damaged and replaced by abnormal cells, and is a risk factor for developing esophageal cancer.
5
New cards
What is the role of Peyer's patches in the GI tract?
Peyer's patches are patches of immune cells found in the ileum that detect and respond to foreign substances.
6
New cards
What is the main function of the colon?
* absorb water and electrolytes from undigested food, and to eliminate waste from the body.
* bacteria + fermentation
* bacteria + fermentation
7
New cards
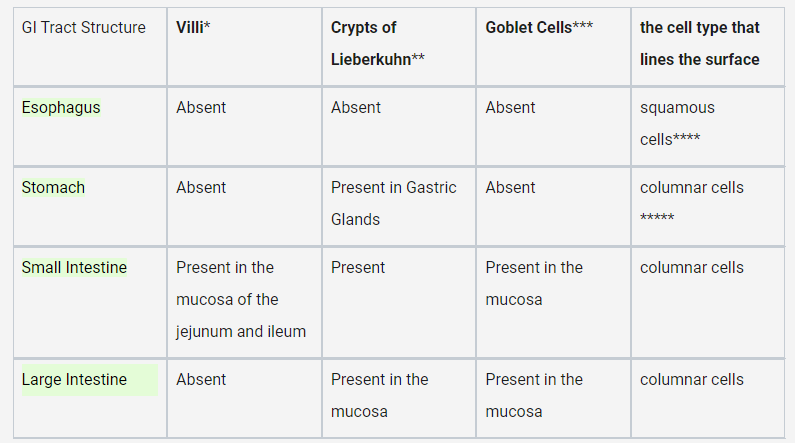
What are the main differences between the structure and function of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine?
* The esophagus lacks villi, crypts of Lieberkuhn, and goblet cells, and has squamous cells lining its surface
* the stomach has gastric glands that produce gastric acid
* the small intestine has villi, crypts of Lieberkuhn, and goblet cells for nutrient absorption
* the large intestine has crypts of Lieberkuhn and goblet cells for water absorption.
* the stomach has gastric glands that produce gastric acid
* the small intestine has villi, crypts of Lieberkuhn, and goblet cells for nutrient absorption
* the large intestine has crypts of Lieberkuhn and goblet cells for water absorption.
8
New cards
What are some of the causes of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)?
* weakened lower esophageal sphincter
* too much acid in stomach
* bad angle between esophagus and stomach
* too much acid in stomach
* bad angle between esophagus and stomach
9
New cards
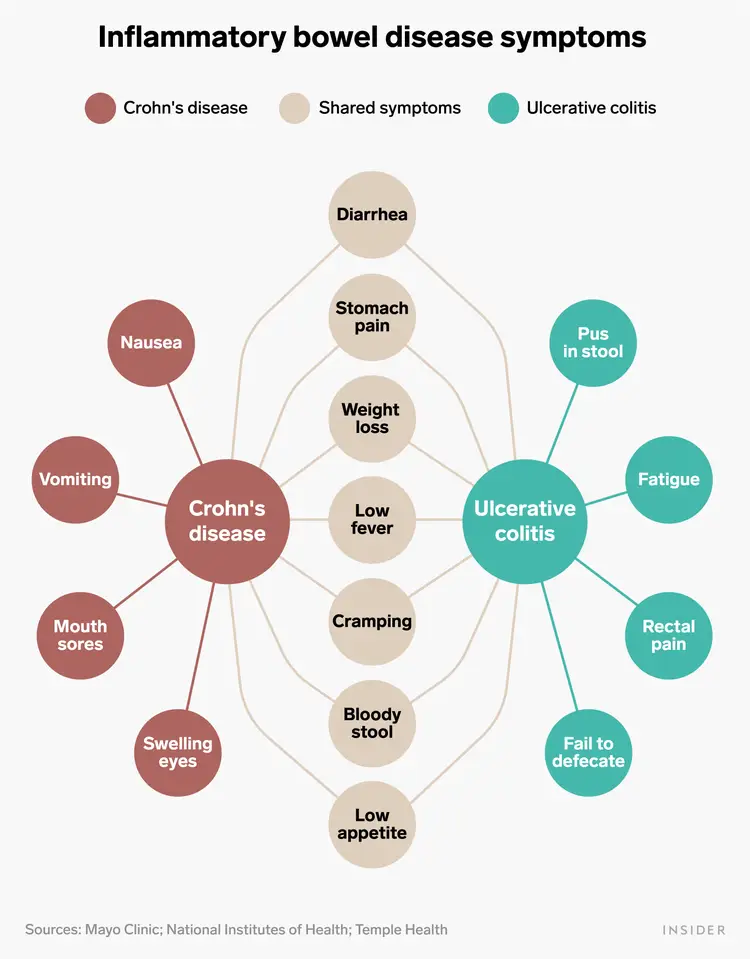
What are some of the common symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) shared by crohns disease and ulerative colitis?
* diarrhea
* stomach pain
* weight loss
* low fever
* cramping
* bloody stool
* low appetite
* stomach pain
* weight loss
* low fever
* cramping
* bloody stool
* low appetite
10
New cards
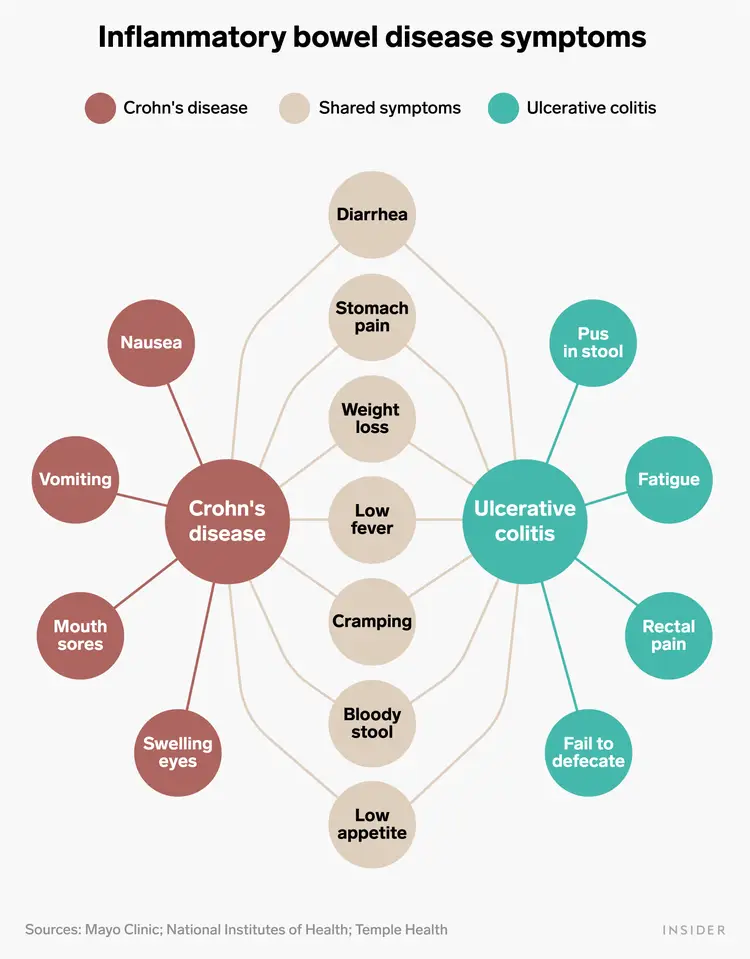
what are some symptoms specific to crohns disease and ulcerativ colitis
crohns :
* nausea
* vomiting
* mouth sores
* black blood in stool
ulcerative colitis
* fatigue
* rectal pain
* fail defecate
* red blood in stool
* nausea
* vomiting
* mouth sores
* black blood in stool
ulcerative colitis
* fatigue
* rectal pain
* fail defecate
* red blood in stool
11
New cards
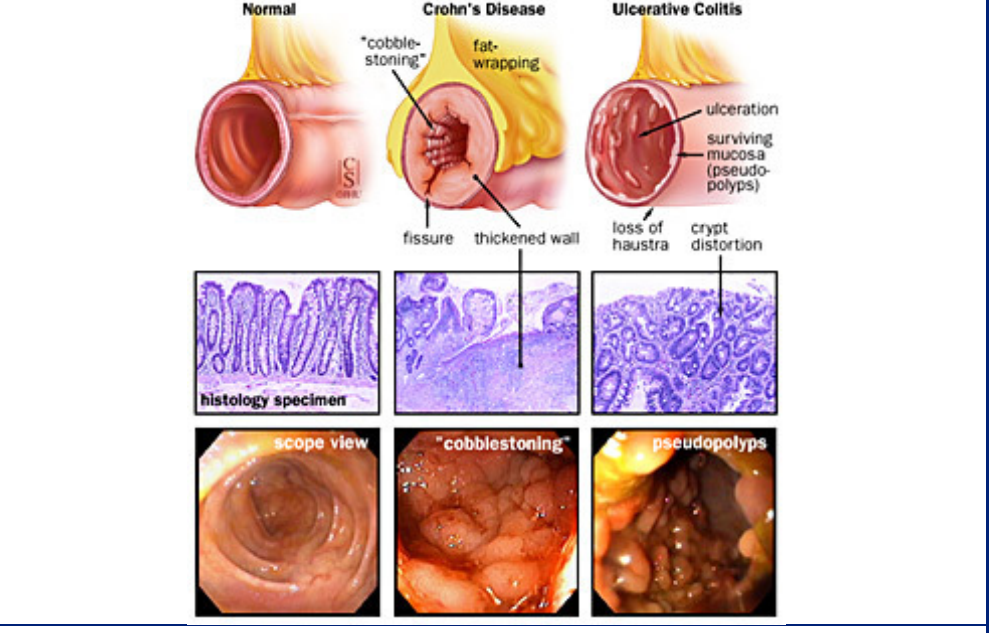
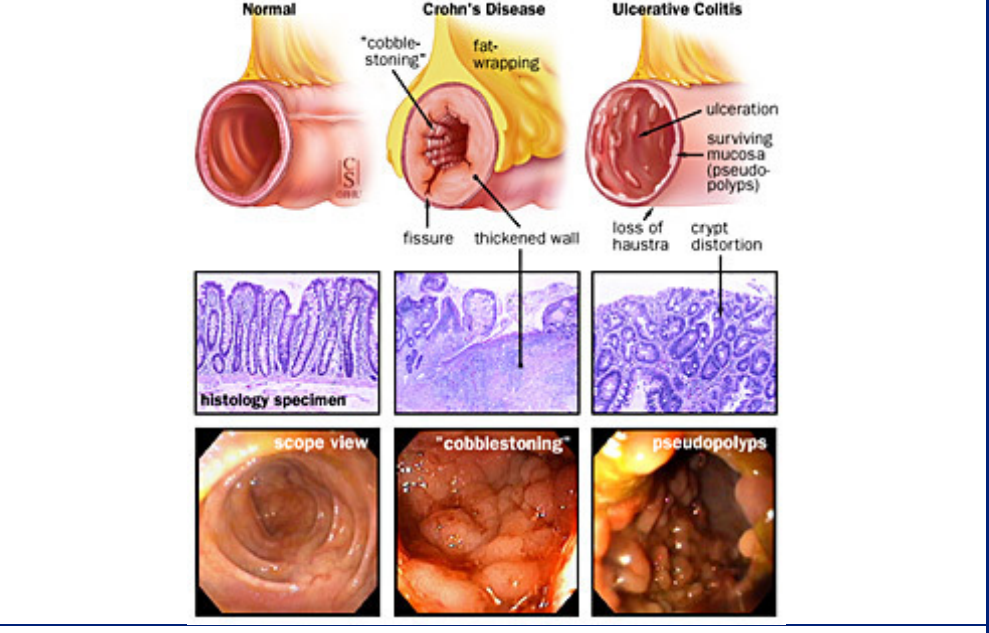
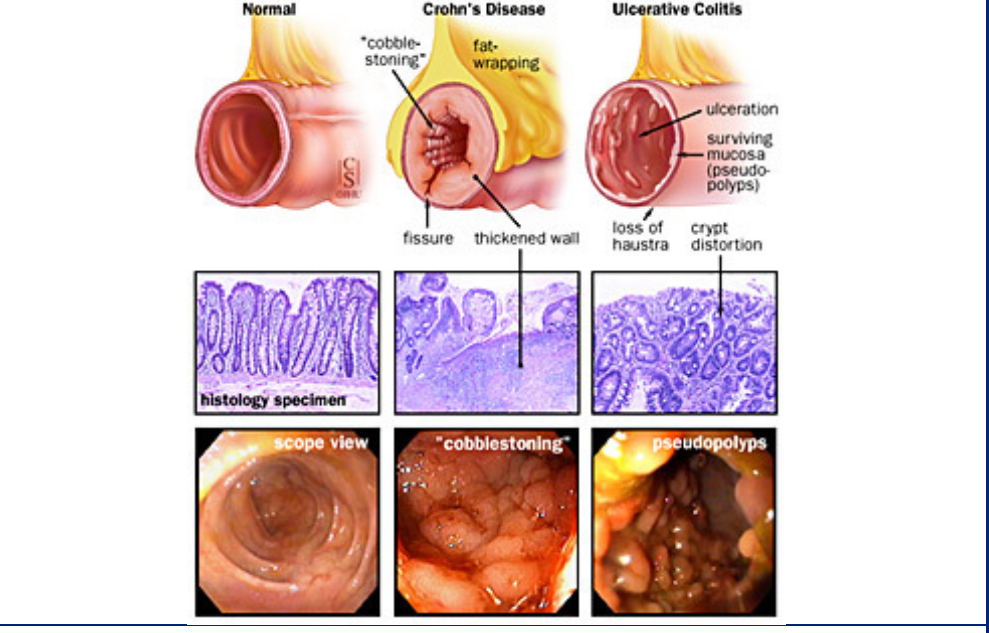
what are some internal factors that are specific to crohns disease?
* the disease can skip passages in the colon and cause inflammation → patchy inflammation
* **Fistulas:** abnormal passageways that form between different parts of the body
* → transmural ( tears through the tissue of them muscle) inflammation → feces can end up in urine
* **granulomas**: clusters of cells that form when the body's immune system attempts to contain and eliminate foreign substances or bacteria
* muscle hypertrophy
* cobblestone appearance
* fat wrapping
* serological marker: ASCA
* **Fistulas:** abnormal passageways that form between different parts of the body
* → transmural ( tears through the tissue of them muscle) inflammation → feces can end up in urine
* **granulomas**: clusters of cells that form when the body's immune system attempts to contain and eliminate foreign substances or bacteria
* muscle hypertrophy
* cobblestone appearance
* fat wrapping
* serological marker: ASCA
12
New cards
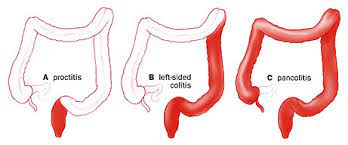
what are some internal factors that are specific to ulcerative colits disease?
* always __originates in the rectum__ and then moves up until half of the colon or the entire colon
* serological markers: pANCA
* ulceration within the mucosa
* in children, it does not have to start in rectum
* serological markers: pANCA
* ulceration within the mucosa
* in children, it does not have to start in rectum
13
New cards
how are the different development types of ulcerative colitis
14
New cards
how does the rectum look like/chnage in Crohns and ulcerativ culitis?
15
New cards
what is tolerance in immunology
tolerance refers to the ability of the immune system to distinguish between self and non-self antigens and to not attack the body's own tissues.
* inflammation vs. tolerance ( too much aggressive inflammatory cells or too few protective cells)
* inflammation vs. tolerance ( too much aggressive inflammatory cells or too few protective cells)
16
New cards
what are 2 non invasive and invasive treatment for IBD
**non-invasive:**
* steroids
* target immunosuppression
**Invasive:**
* only works for UC → take out colon(will always be in rectum)
* steroids
* target immunosuppression
**Invasive:**
* only works for UC → take out colon(will always be in rectum)
17
New cards
what is IBD? and what is its characteristics?
^^Inflammatory bowel disease^^
* systematic inflammatory disease
* cause: due to a genetic defect, all leukocytes attack microbes and food
* **onset:** 20 and 60 → 25% of all IBD starts in childhood !!! ++ The earlier the onset, the more genetic the IBD
* systematic inflammatory disease
* cause: due to a genetic defect, all leukocytes attack microbes and food
* **onset:** 20 and 60 → 25% of all IBD starts in childhood !!! ++ The earlier the onset, the more genetic the IBD
18
New cards
what does the NOD2 receptorees have to do with ibd?
* because innate immune system is not working( NOD 2 intracellular bacterial receptor) there is an overload of B and T cells → underlying explanation of IBD
19
New cards
what are the serorological markers of the two types of IBD
* Crohn’s → **ASCA**
* Ulcerative colitis → **pANCA**
\
* Ulcerative colitis → **pANCA**
\
20
New cards
does the bolus move through the GI tract?
* passively → gravity
* actively → peristaltic muscle movement
\
* actively → peristaltic muscle movement
\