Bones of the Lower Limbs
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
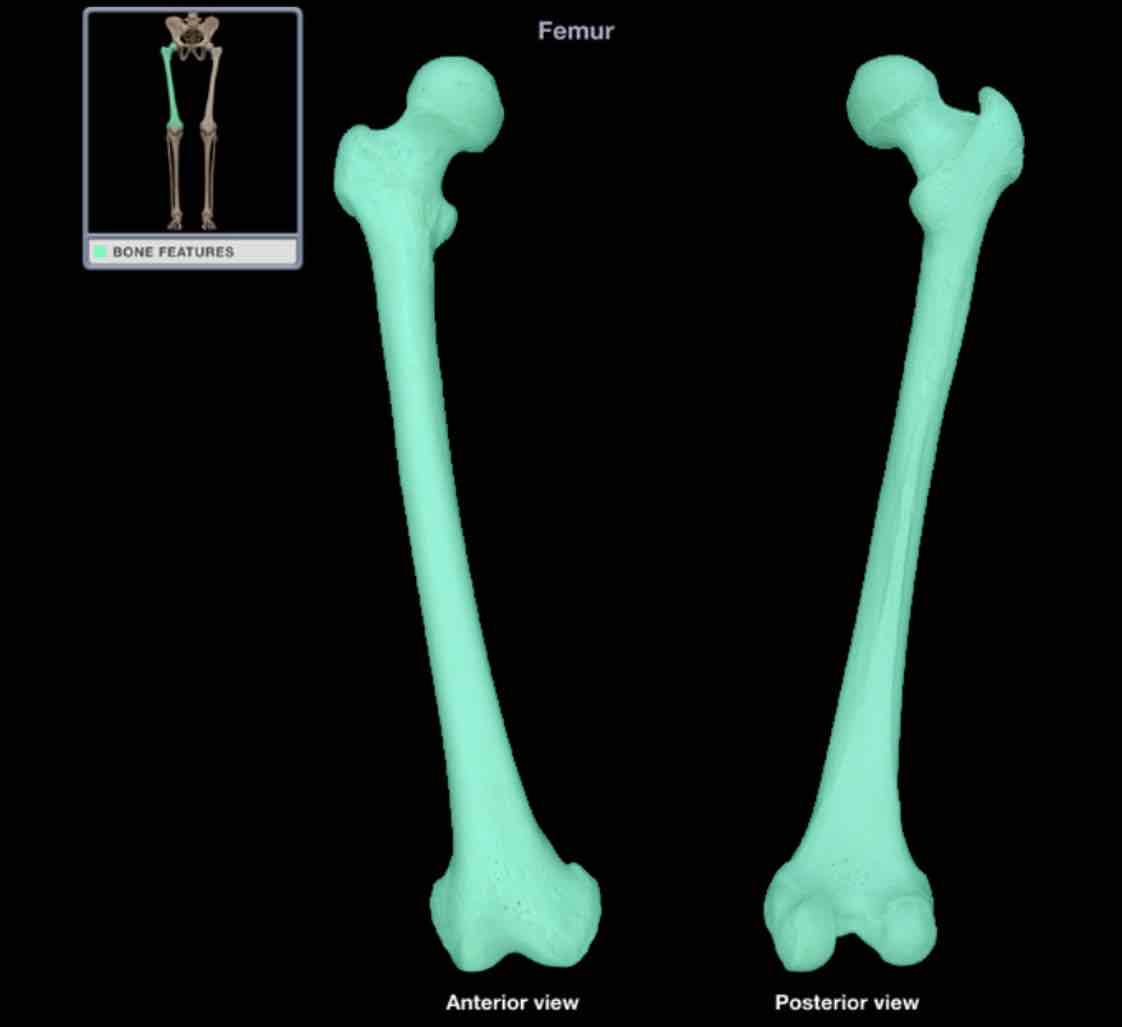
Femur
Location: though
Description
long bone
characteristic features include head, neck, shaft, greater and lesser trochanters, linea aspera, and medial and lateral condyles
head forms part of hip joint
distal end forms part of knee joint
Comment:
only none of thigh
longest bone in body; length accurately predicts height of individual
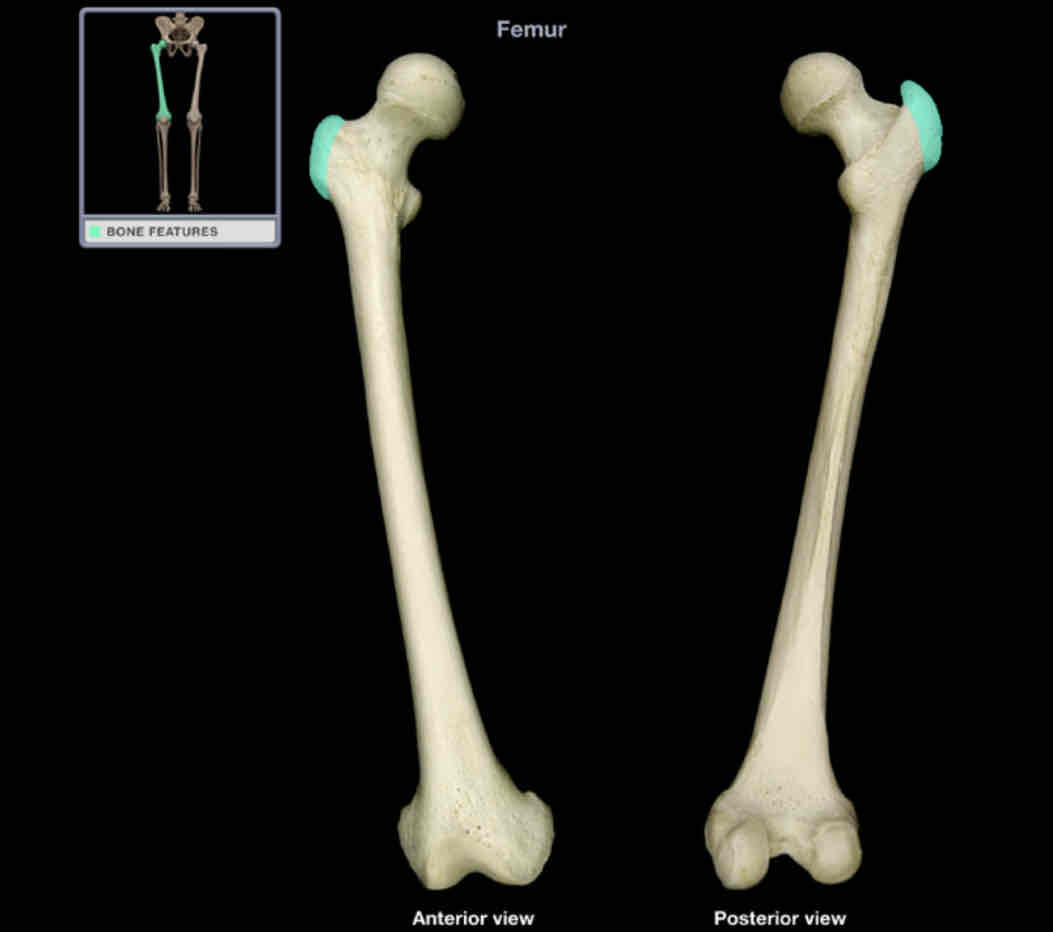
Greater trochanter
Location: femur (proximal)
Description:
large, quadrangular projection at junction of neck with shaft
comment:
provides attachment for many muscles of gluteal region (exception: gluteus maximus)
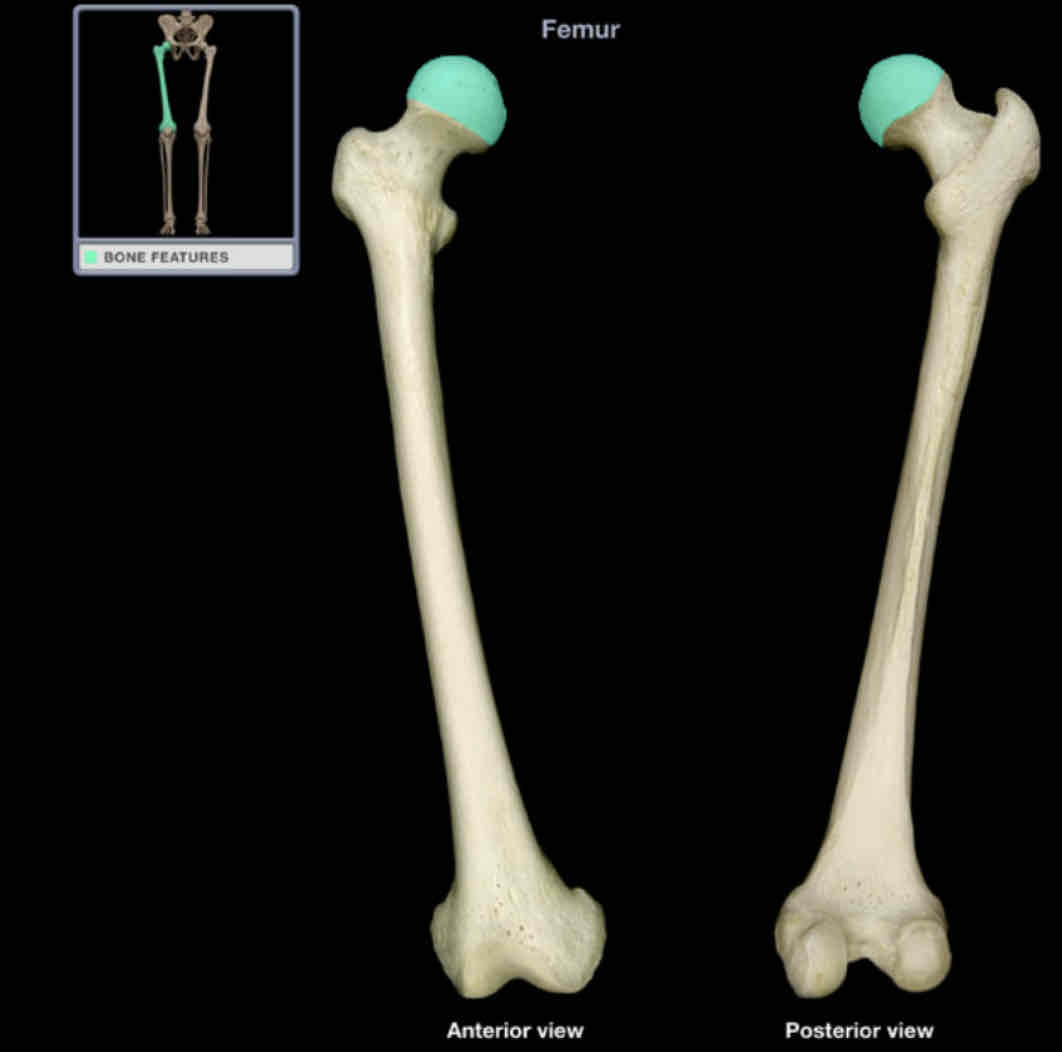
Head of femur
Location: femur (proximal)
Description:
smooth, spherical shape
contains fovea for ligament of head of femur (also know as fovea capitis)
continuous with neck of femur
Comment:
articulates with acetabulum of hip bone to form hip joint
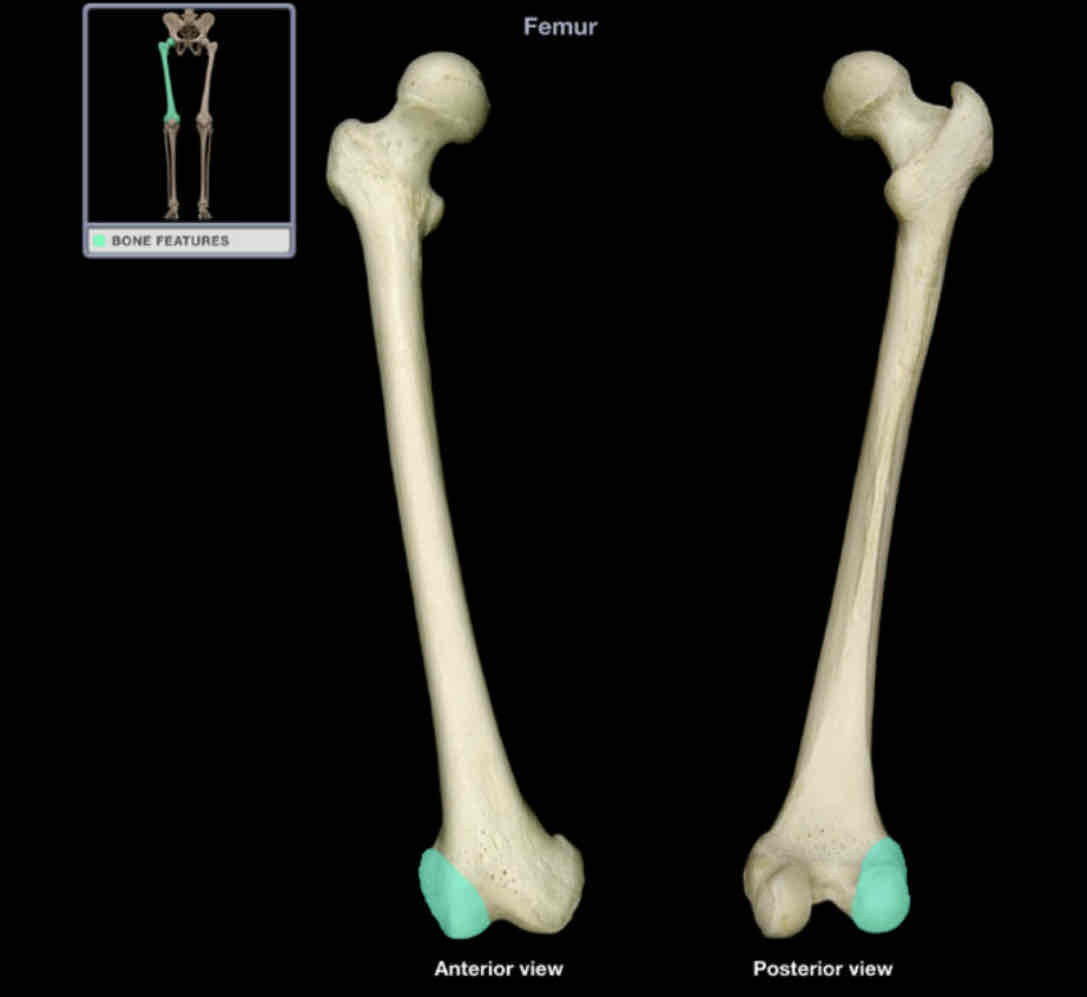
Lateral condyle of femur
Location: femur (distal)
Description:
lateral enlargement of distal end
smooth surface articulates with tibia and patella
Comment:
provides attachment for lateral head of gastrocnemius and popliteus muscles, and fibular collateral ligament of knee
Latin: condyle = knuckle
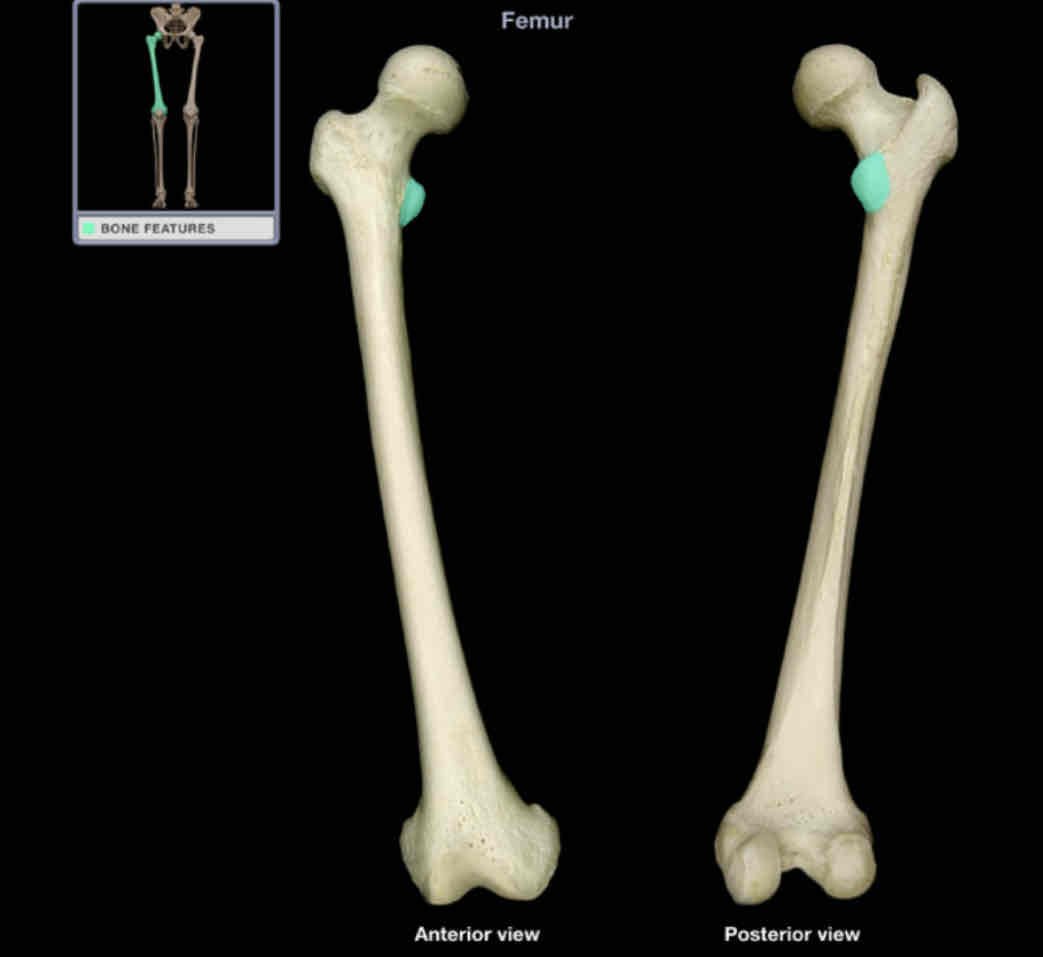
Lesser trochanter
Location: femur (proximal)
Description:
pyramidal process on medial shaft
Comment:
provides attachment for a single muscle - iliopsoas
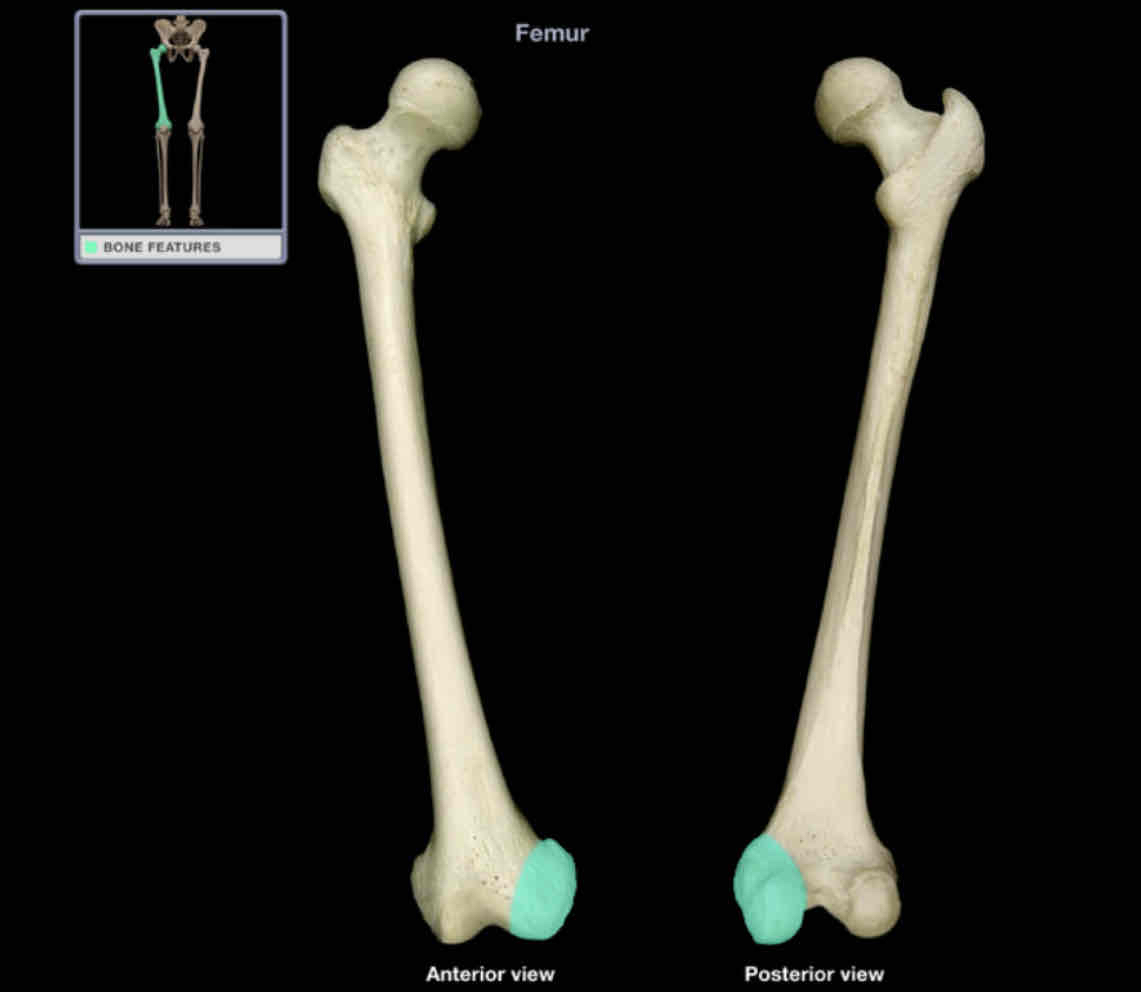
Medial condyle of femur
location: femur (distal)
Description:
medial enlargement of distal end
smooth surface articulates with tibia and patella
Comment:
provides attachment for medial head of gastrocnemius and adductor magnus muscles, and tibial collateral ligament of knee
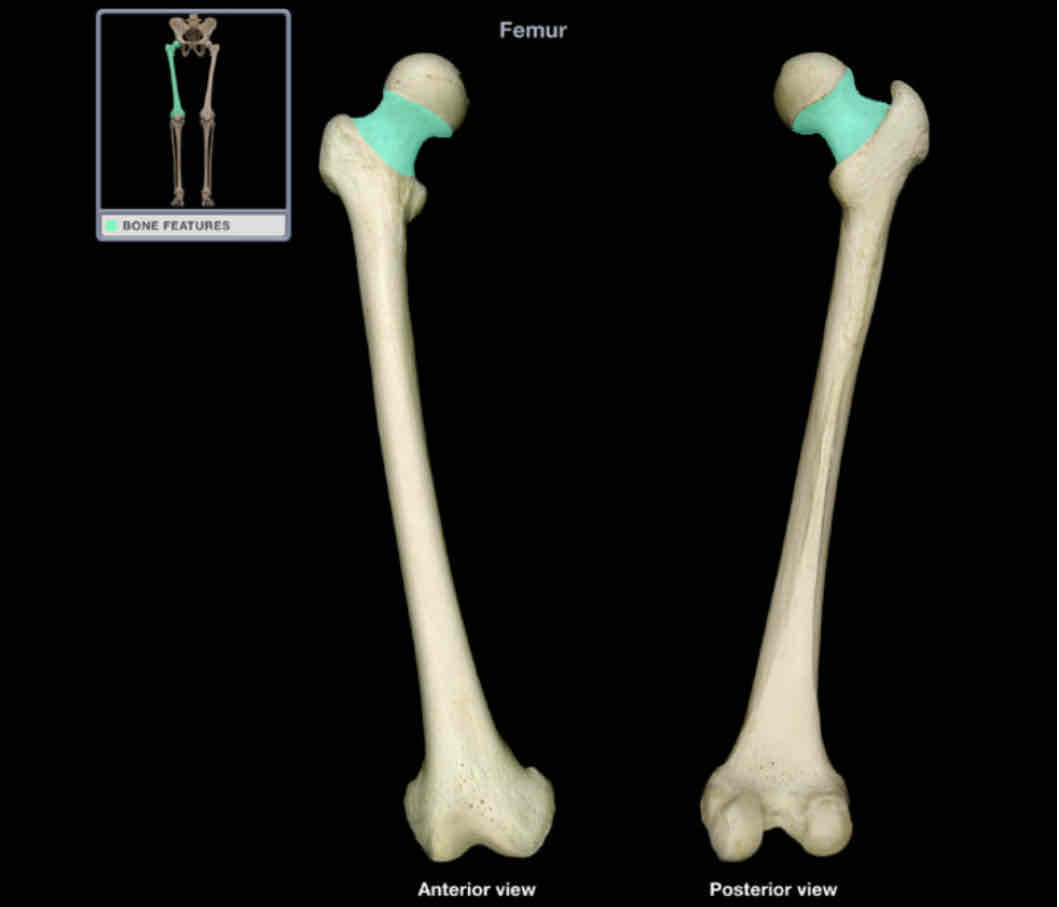
Neck of femur
location: femur (proximal)
Description:
oblique part between head with shaft
Comment:
common site of fracture, especially in elderly
poor blood supply leads to slow or inadequate repair of fracture
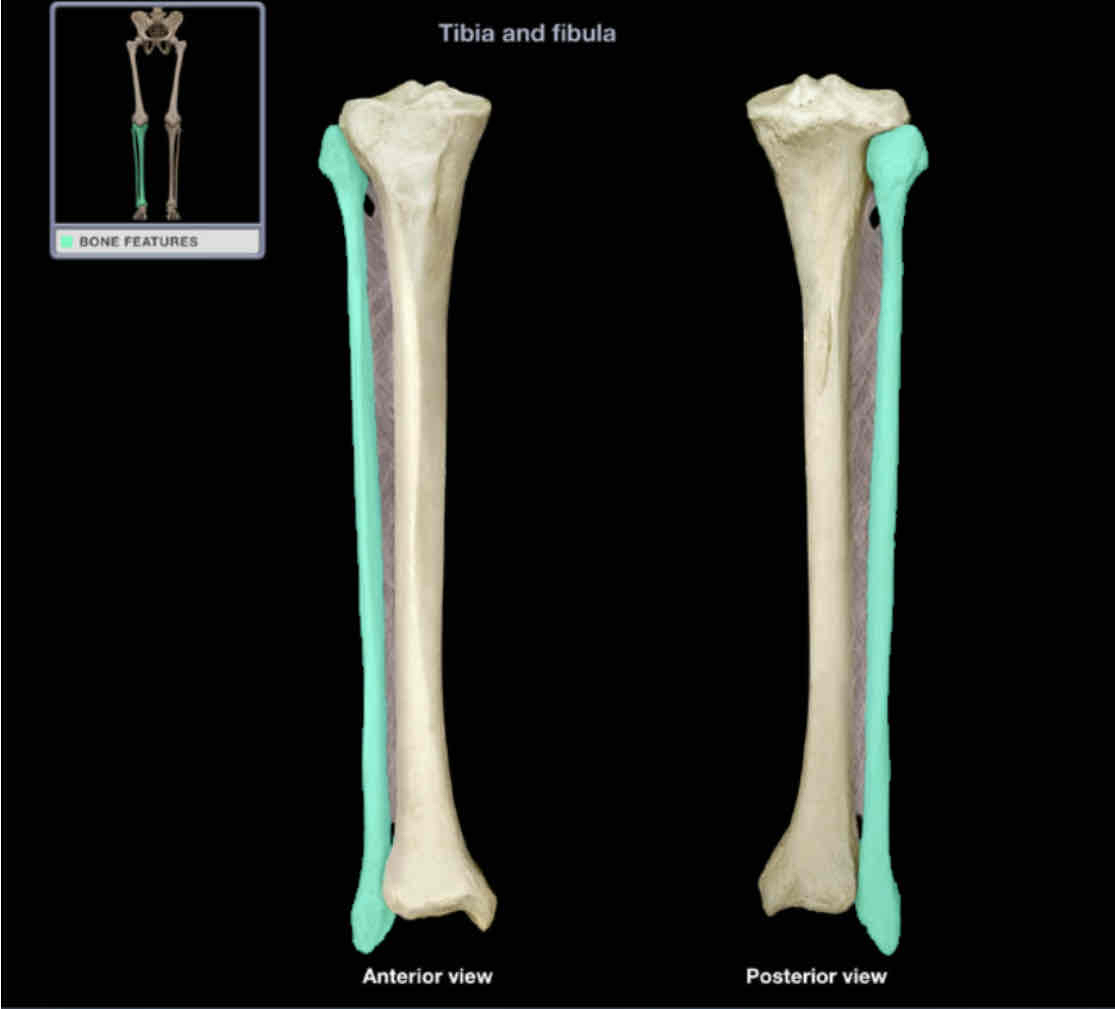
Fibula
Location: leg (lateral)
Description:
long, thin bone
articulates with tibia (proximal) and talus (distal)
characteristic features include head, neck, shaft, and lateral malleolus
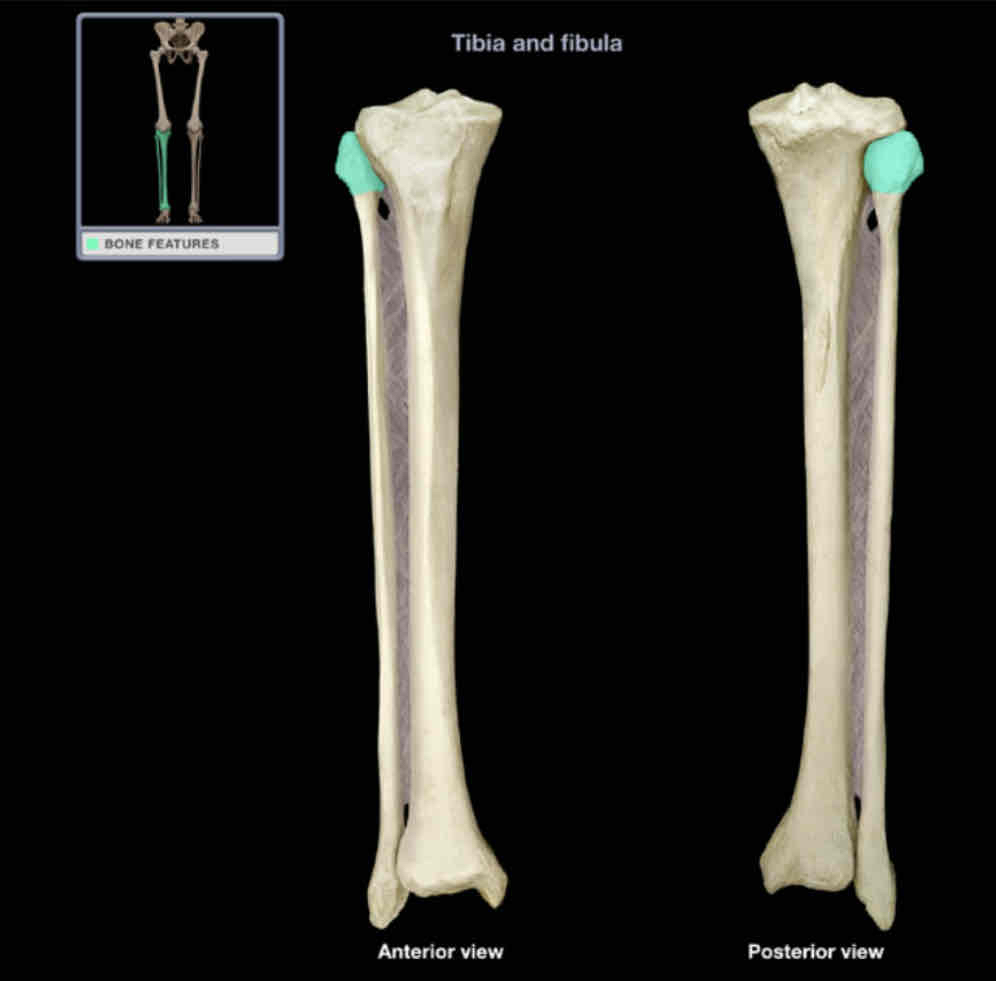
Head of fibula
Location: fibula (proximal)
Description:
rounded subcutaneous projection
articulates with lateral condyle of tibia
Comment:
provides attachment for fibular (lateral) collateral ligament of knee and biceps femoris muscle
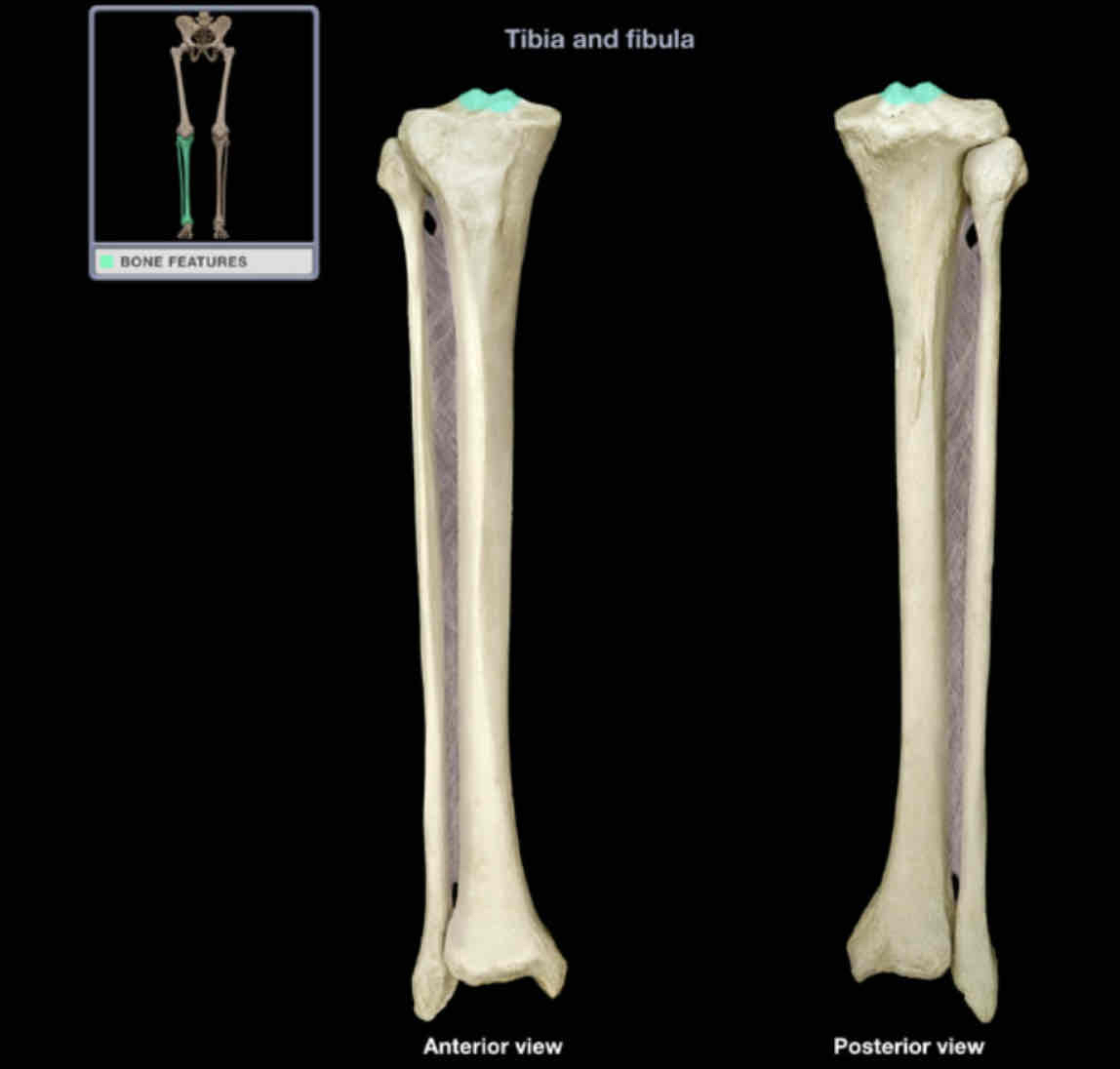
Intercondylar eminence
Location:
tibia (proximal)
between articular surfaces of condyles
Description:
roughened area
Function:
provide attachment for lateral and medial menisci, and anterior cruciate ligament
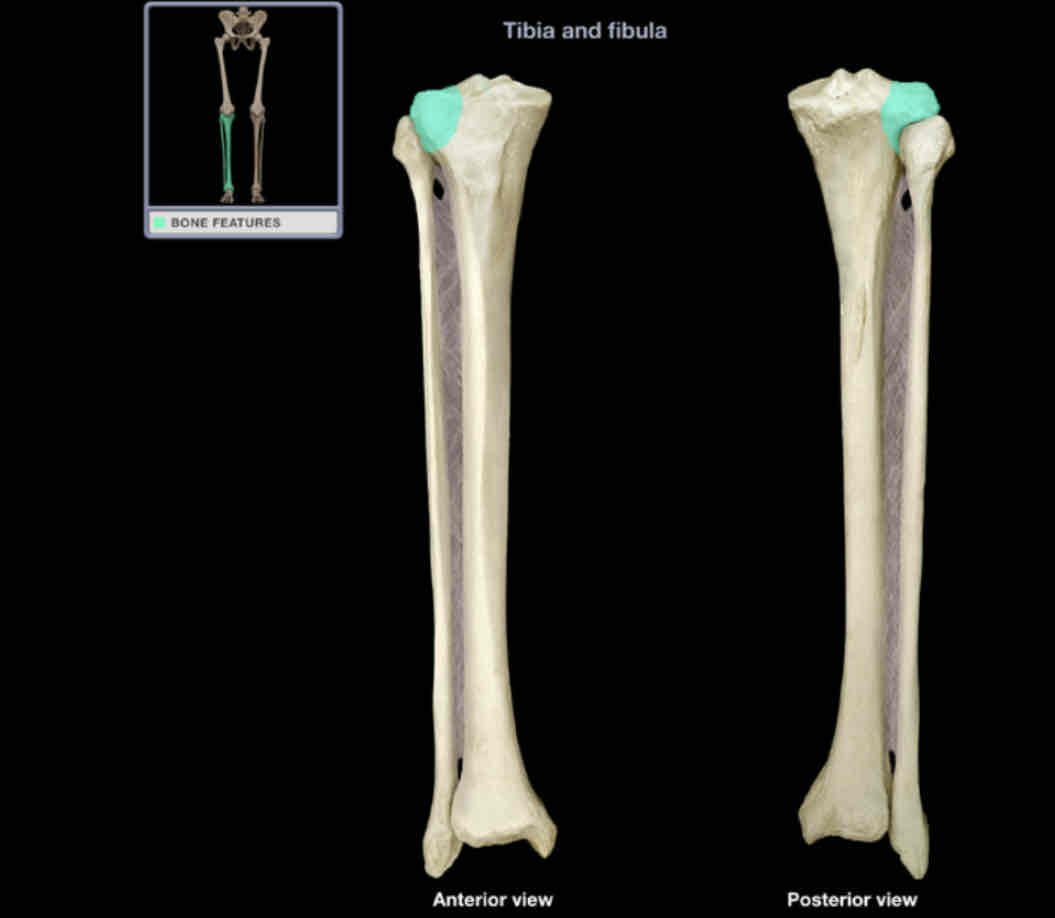
Lateral condyle of tibia
Location: tibia (proximal)
Description:
lateral enlargement of proximal end
has surfaced for articulation with lateral condyle of femur and with fibula
provides attachment point for iliotibial tract
Comment:
lateral condyle of tibia more prominent than medial
Latin: condyle = knuckle
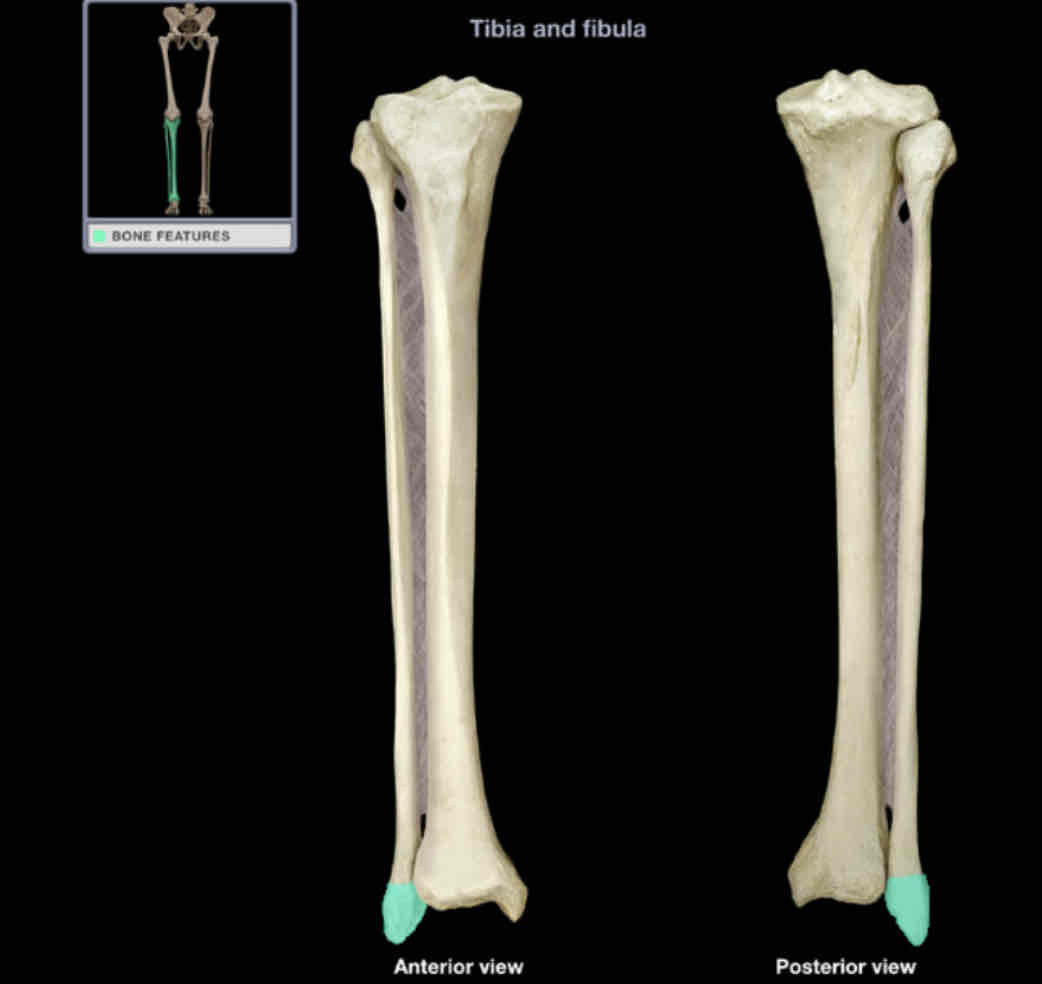
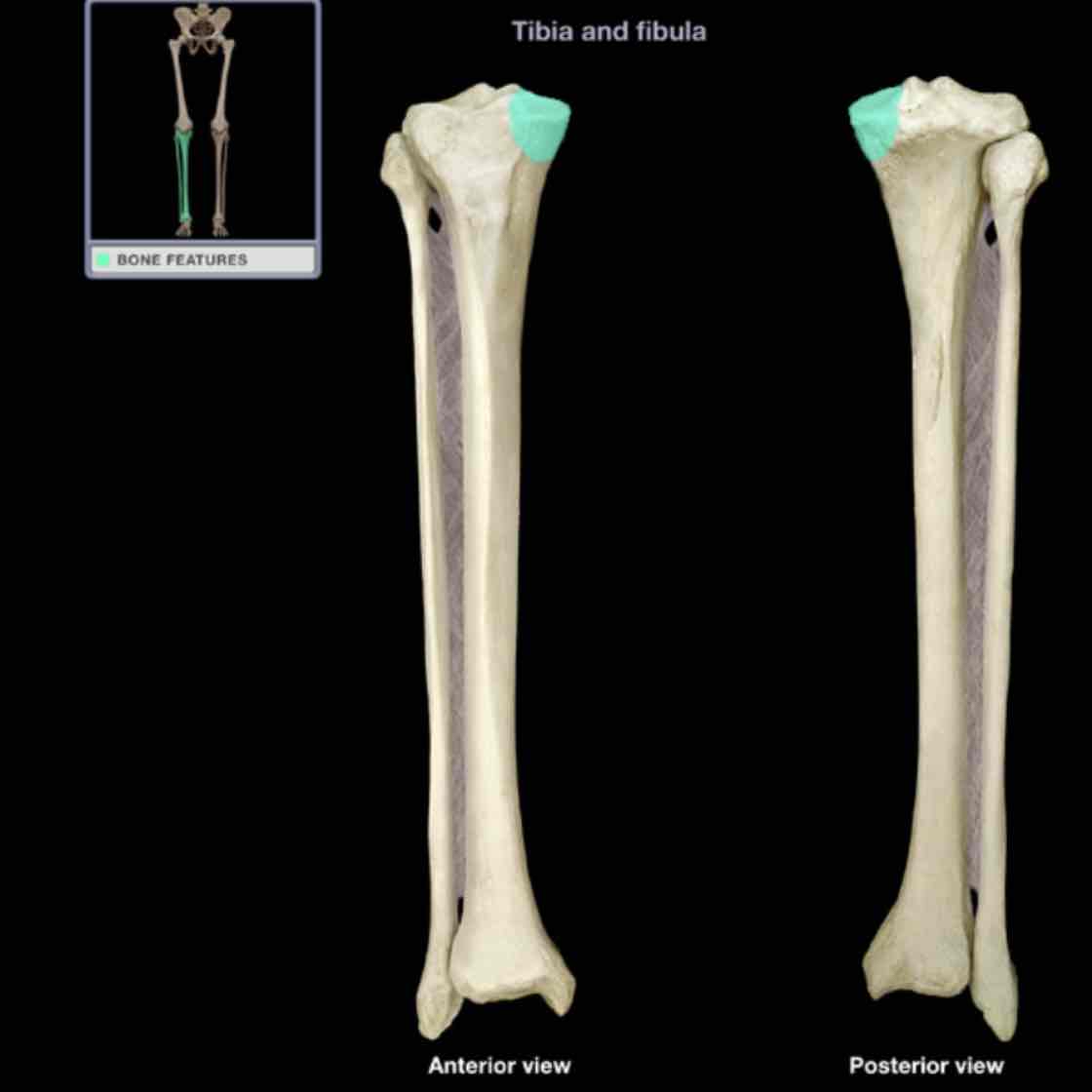
Lateral malleolus
Location: fibula (distal)
Description:
rounded, subcutaneous projection
contributes to ankle joints
Medial condyle of tibia
Location: tibia (proximal)
Description:
medial enlargement of proximal end
has surface for articulation with medial condyle of femur
Function:
provides attachment for semimembranosus muscle and tibial (medial) collateral ligament
Comment:
lateral condyle of tibia more prominent than medial
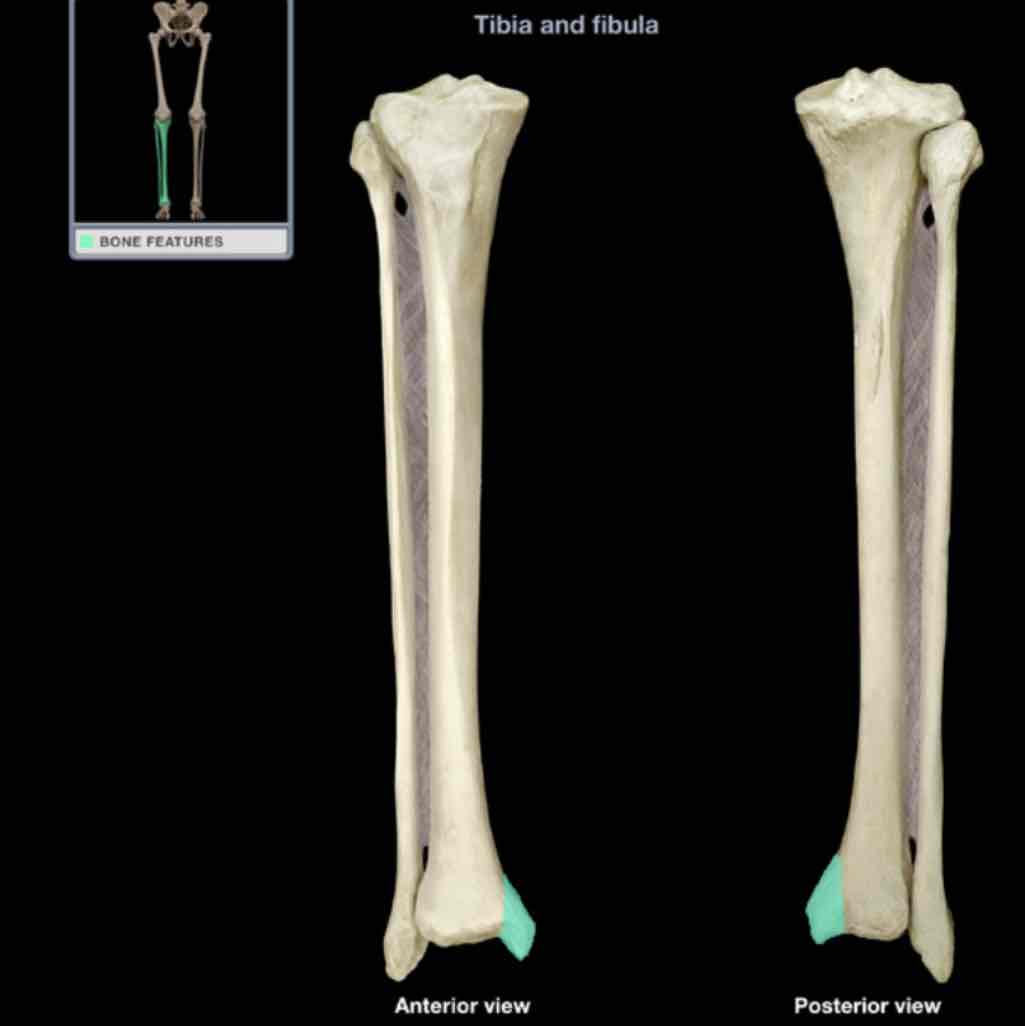
Medial malleolus
Location: tibia (distal)
Description:
rounded, subcutaneous projection
contributes to ankle joint
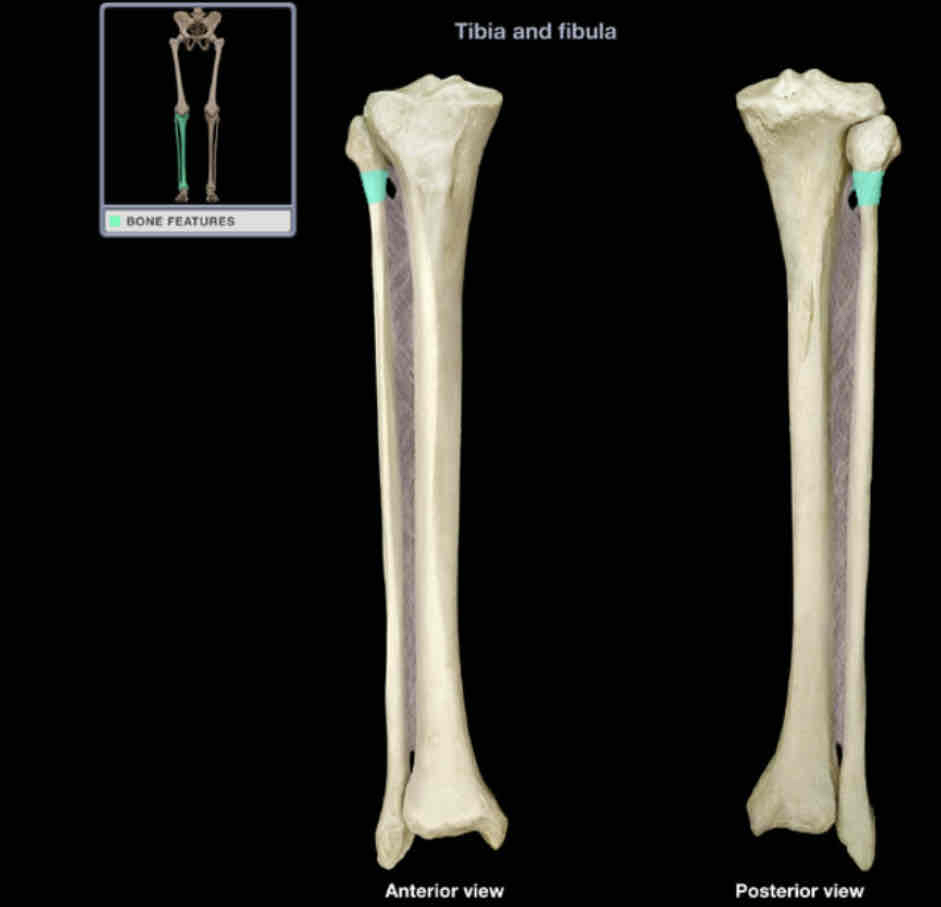
Neck of fibula
Location:
fibula (superior)
between head and shaft
Description:
constricted part between head and shaft
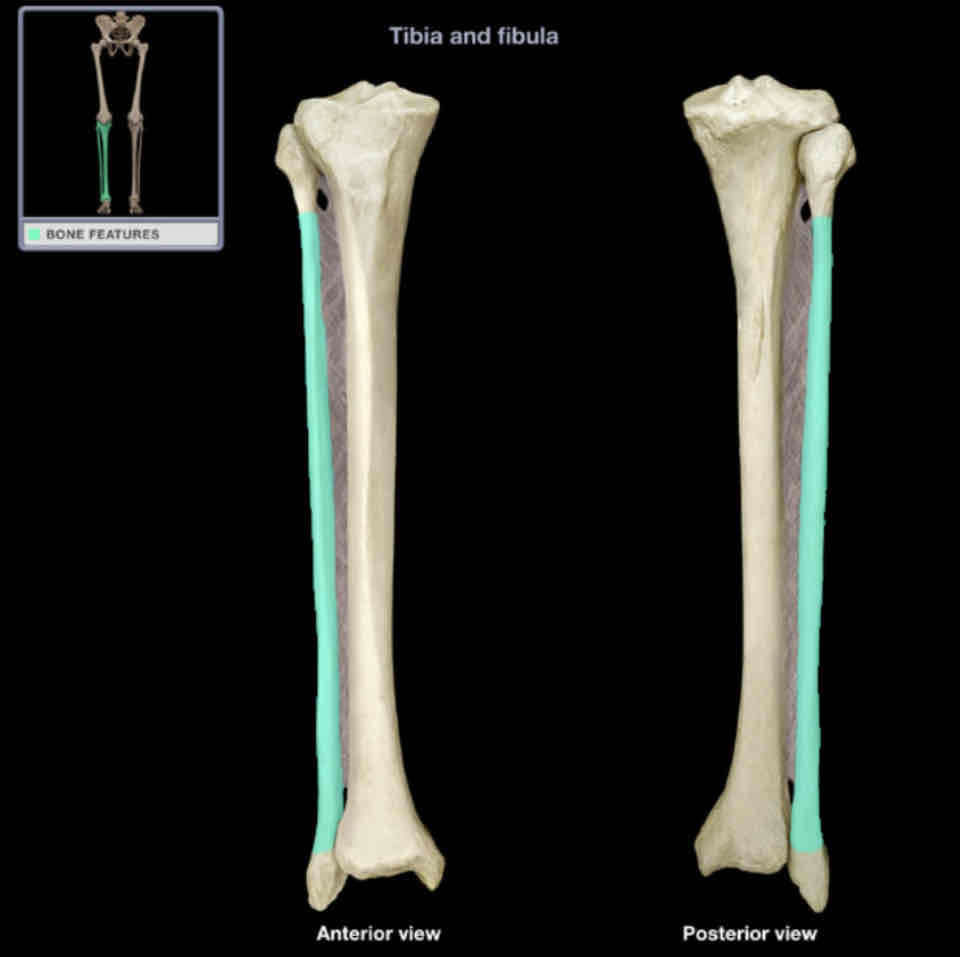
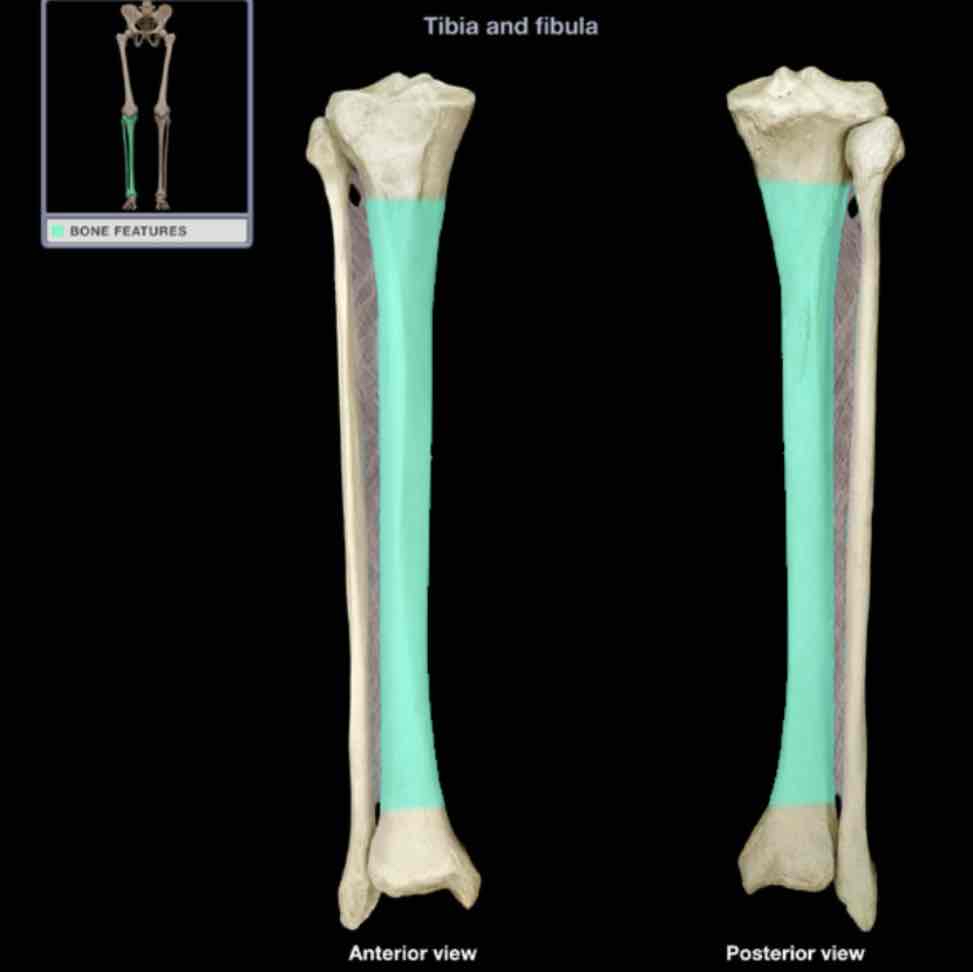
Shaft of fibula
Location:
fibula
between neck and lateral malleolus
Description:
long, slender part
irregular surface provides attachment for muscles
Comment:
attached to shaft of tibia by interosseous membrane of leg
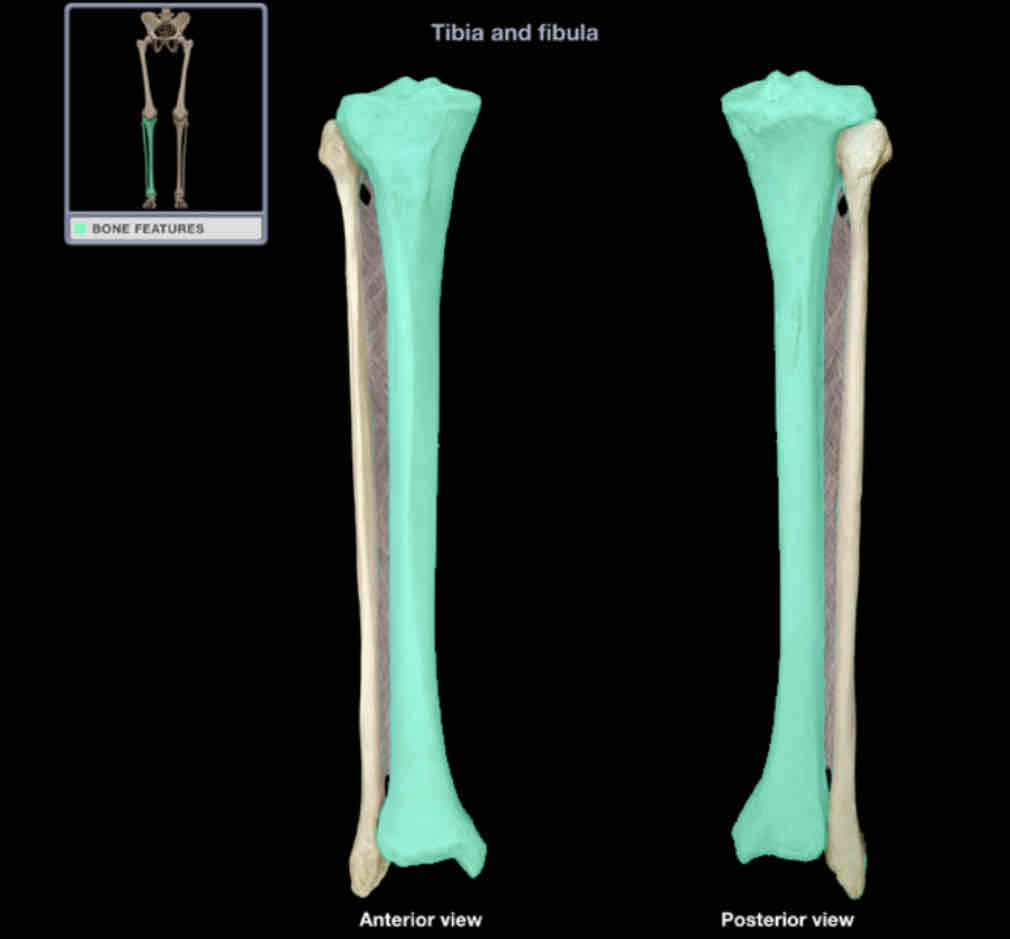
Shaft of tibia
Location:
tibia
between condyles and distal end
Description:
long, thick part
thinnest at junction of middle and distal thirds
features include subcutaneous anterior border and soleal line
Comment:
attached to shaft of fibula by interosseous membrane of leg
Tibia
Location: leg (medial)
Description:
long bone between knee and ankle joints
characteristic features include medial and lateral condyles, medial and lateral plateaus, tuberosity, shaft, and medial malleolus
contributes to knee and ankle joints
Also know as: shin bone
comment:
anterior shaft is subcutaneous
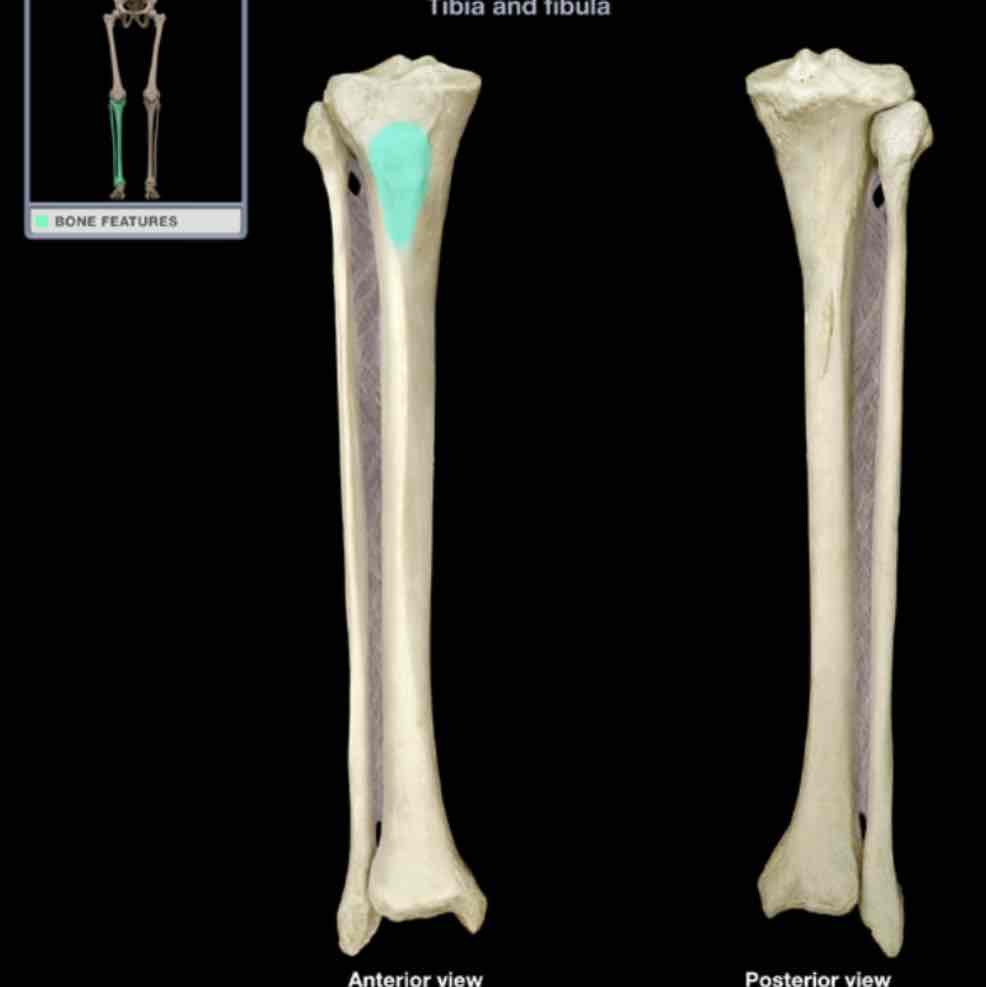
Tibial tuberosity
Location: tibia (anterior)
Description:
bony elevation on proximal shaft
Comment:
provides attachment for quadriceps femoris muscles, via patellar ligament
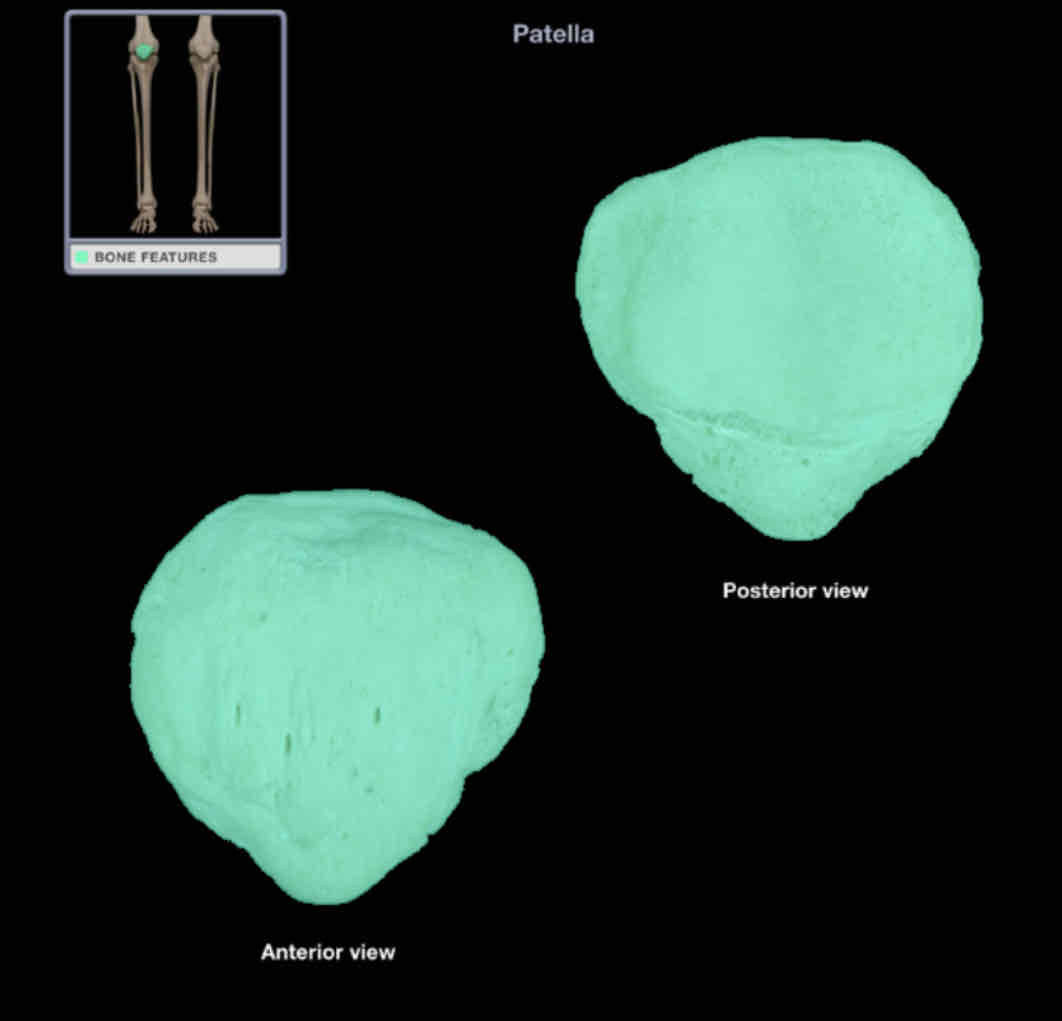
Patellar
Location: knee (anterior)
within tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle
Description:
triangular sesamoid bone
apex of bone directed distally
posterior surface has two articular facets for femoral condyles
together with femur and tibia, forms knee joint
Also known as: kneecap
Comments:
acts as fulcrum to increase angle of quadriceps femoris tendon across knee
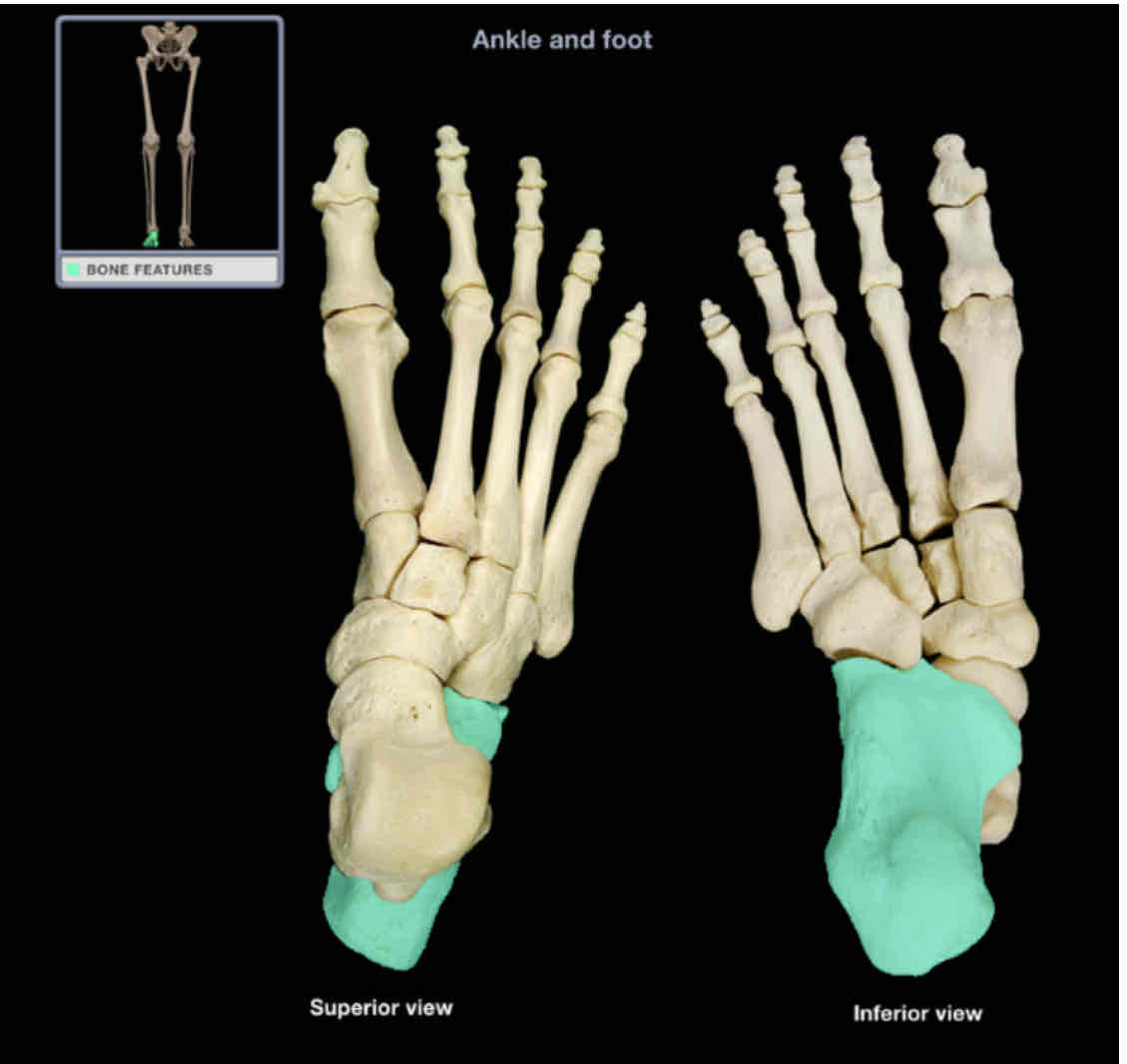
Calcaneus
Location: foot (posterior)
Description:
most posterior tarsal bone
largest tarsal bone
irregular shape
articulates with talus and cuboid bone
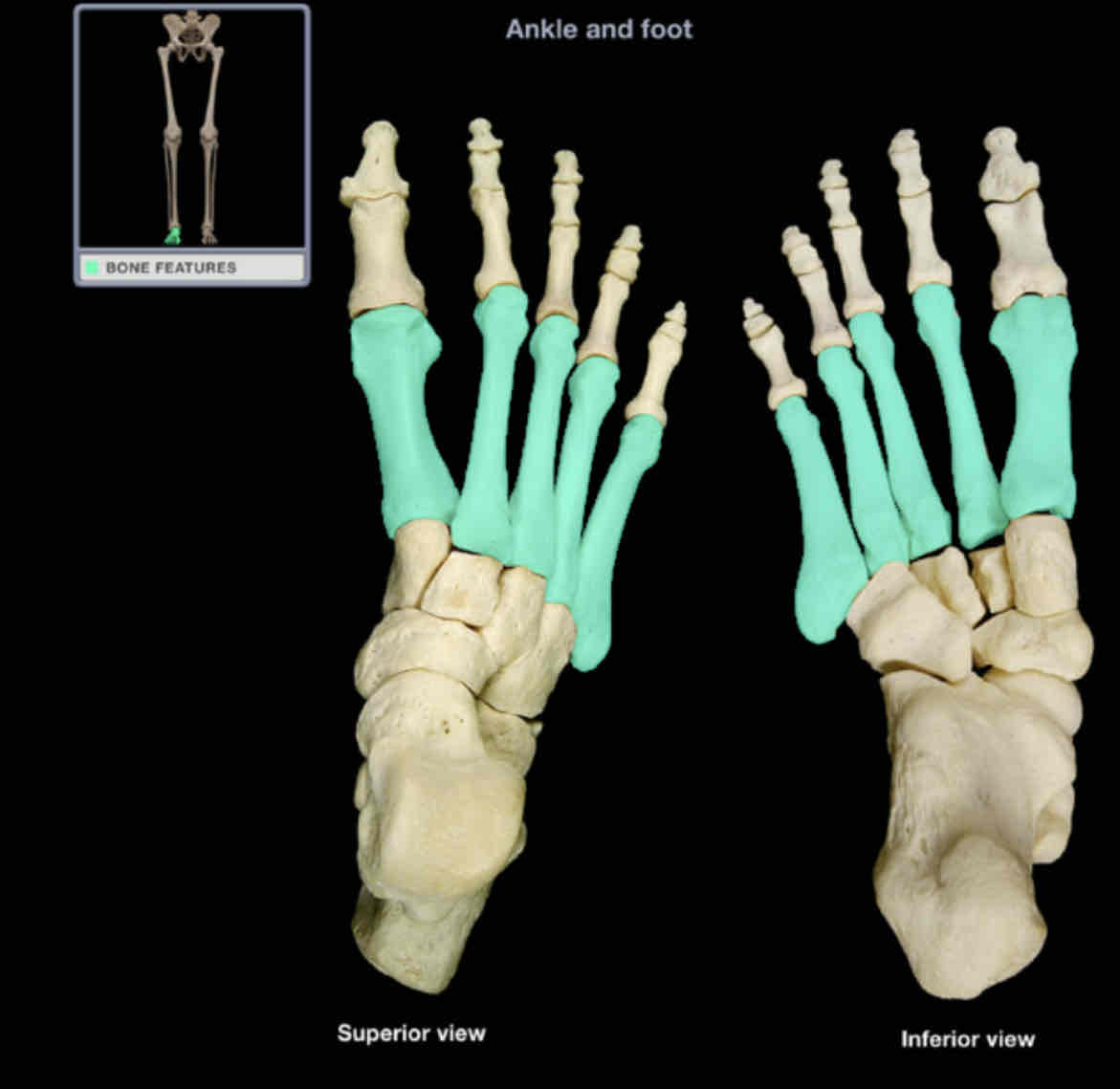
Metatarsals
Location: foot
Description:
five small, long bones, between tarsal bones to phalanges
designated by Roman numeral (I-V) from medial (great toe) to lateral (little toe)
characteristic features are base (proximal), shaft, and head (distal)
Comment:
heads are surface contact points on plantar foot
ahead of metatarsal 1 is also know as “ball of the foot”
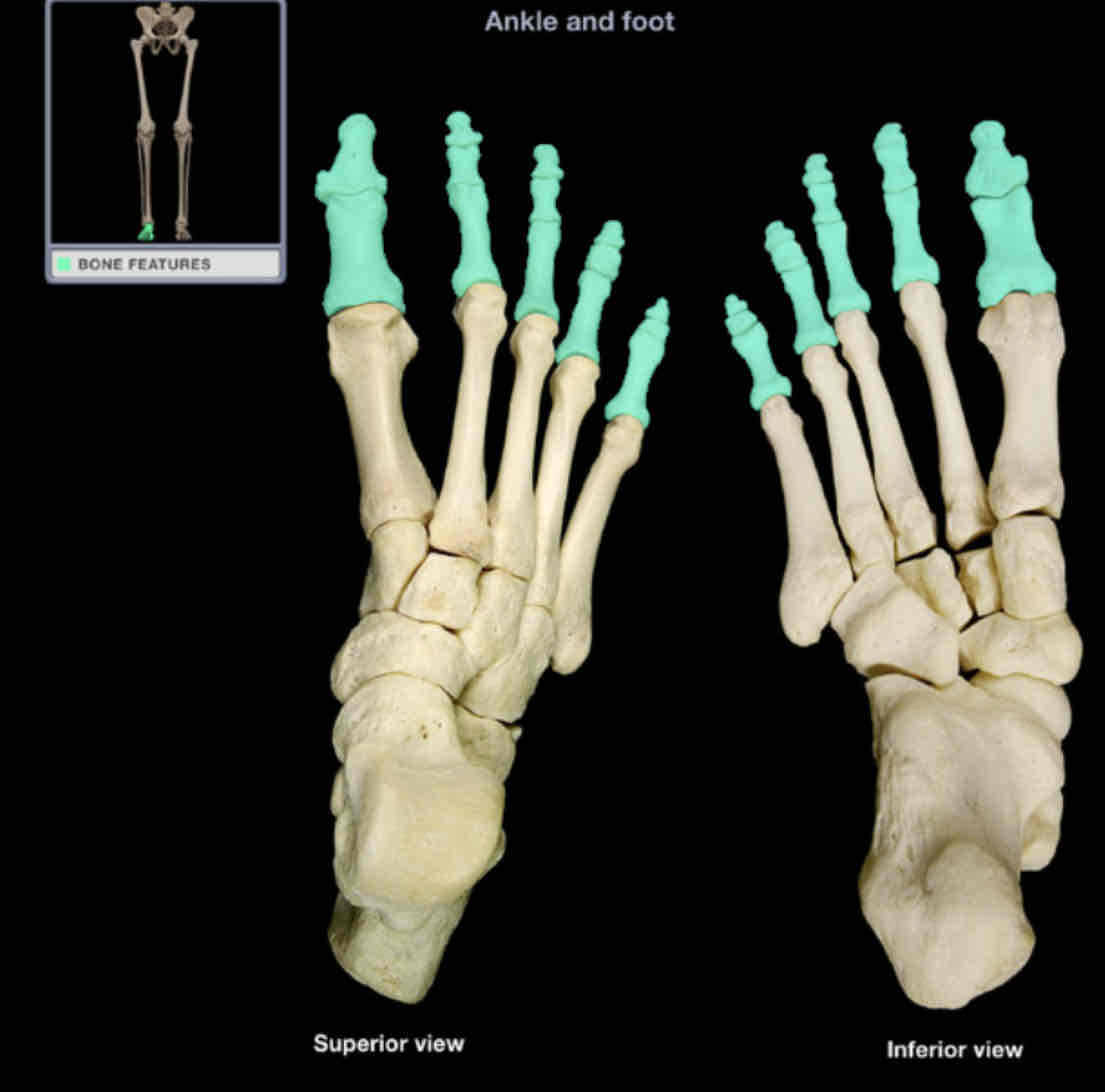
Phalanges of toes
Location: foot (toes)
Description:
small bones of toes
lateral four toes (2-4) have three phalanges each (proximal, middle, and distal)
great toe has two phalanges (proximal and distal)
Comment:
singular of phalanges is phalanx
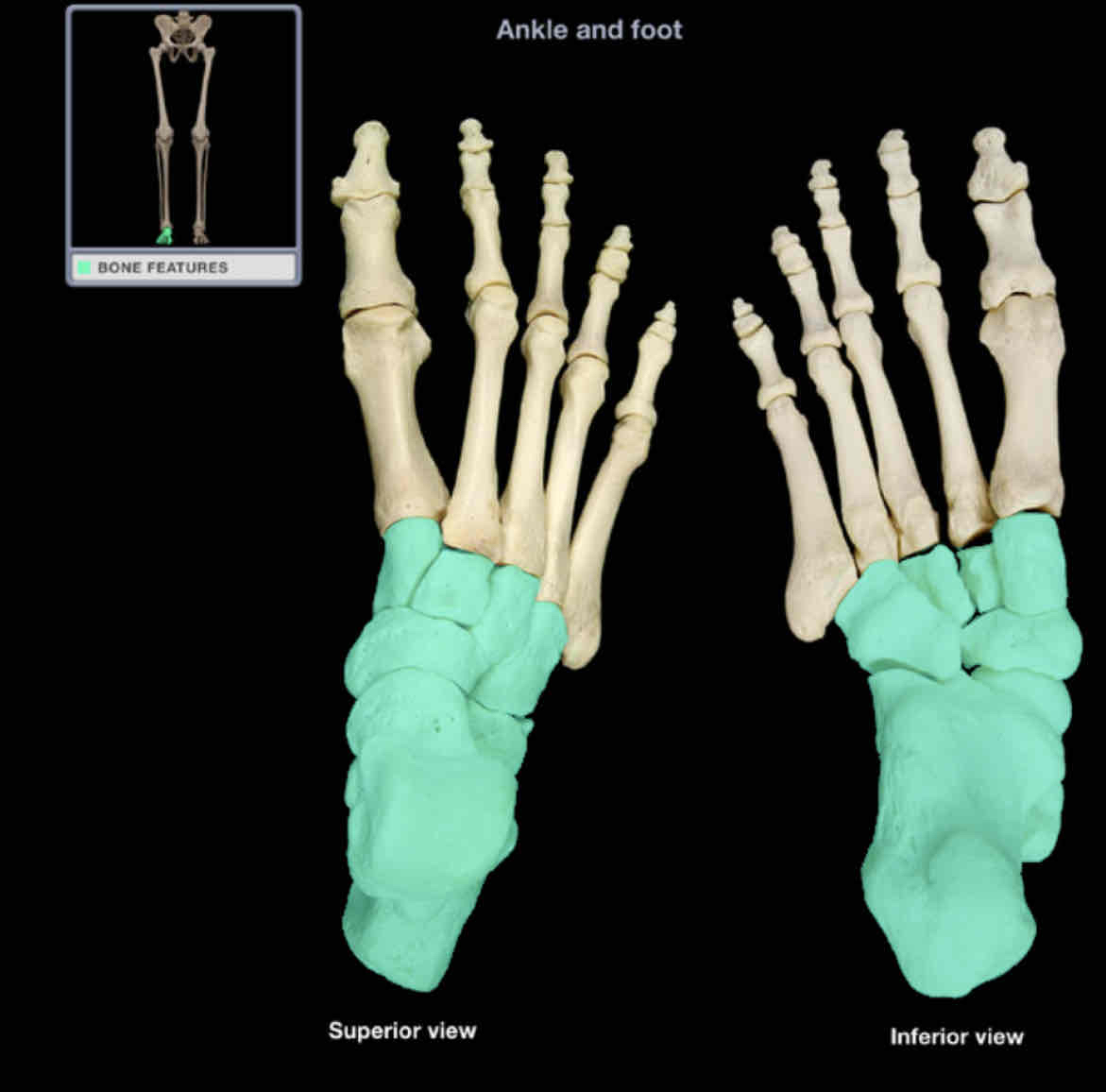
Tarsal bones
Location: foot
Description:
seven irregular-shaped bones
Comment:
includes talus, calcaneus, navicular, cuboid, and three cuneiform bones