1. Biomolecules
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Monomer
molecule that can be covalently bonded to another identical or similar molecule to form a polymer
Carbohydrate general formula
CH2O
Colours of these biomolecules
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Sulphur
Phosphor
Carbon - black/grey
Hydrogen - white
Oxygen - red
Nitrogen - blue
Sulphur - yellow
Phosphor - orange

Alcohol
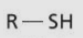
Thiol
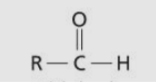
Aldehyde
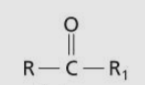
Ketone
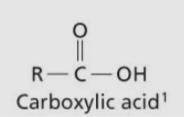
Carboxylic Acid
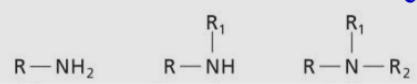
Amine (1, 2, 3)
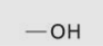
Hydroxyl group

Sulfhydryl group
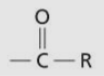
Acyl group

Amino group
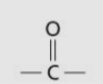
Carbonyl group
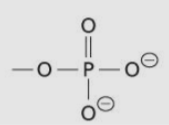
Phosphate group
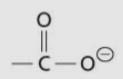
Carboxylate group
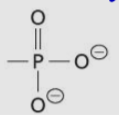
Phosphoryl group
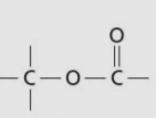
Ester group/linkage
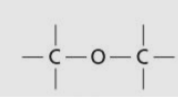
Ether group/linkage
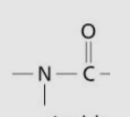
Amide group/linkage
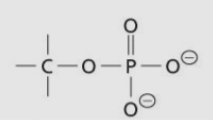
Phosphate ester group/linkage
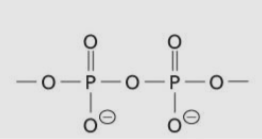
Phosphoanyhdride group/linkage
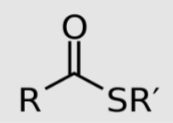
Thioester linkage
Dehydration reaction
loss of H2O from reactants, joins two molecules
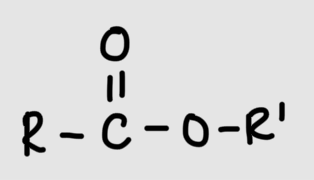
Formation of ester linkage
Carboxyl group + hydroxyl group
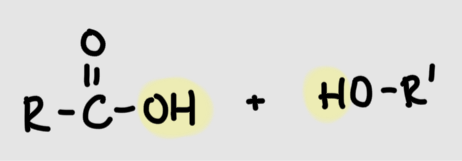
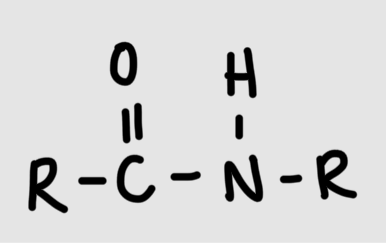
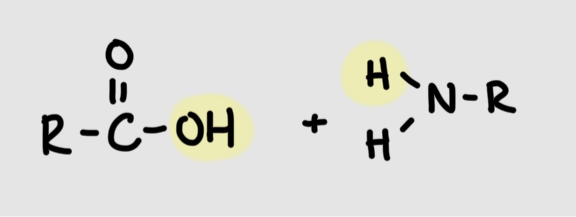
Formation of amide linkage
Carboxyl group + amino groupR
Residue
Monomer that is a part of a polymer. Usually different in structure.W
Peptide bond
Bond joining amino acids monomer into protein polymer
Phosphodiester bond
Bond joining nucleotide monomers into nucleic acid polymers
Hydrogen donor
hydrogen bonded to an electronegative atom (O, N, S)

Hydrogen acceptor
lone pair of electrons associated with an electronegative atom (O, N, S)
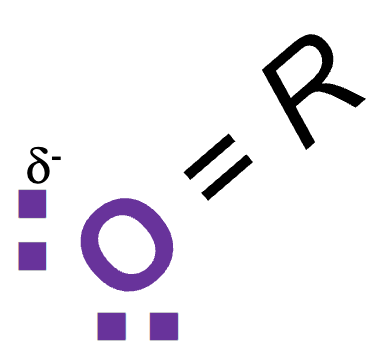
Which is longer: hydrogen or covalent bond? What does this mean?
Hydrogen bond makes it weakerHOw m
How many H-bonds can water form (theoretically)?
4: 2 donor and 2 acceptor
How many H-bonds can ice form vs water?
4 for ice, 3 for water
How many H-bonds can hydronium ion form
4: 3 donor, 1 acceptor
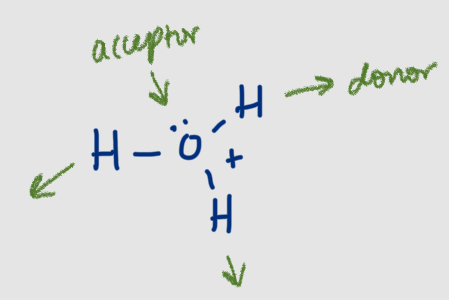
How many H-bonds can hydroxide ion form
4: 1 donor, 3 acceptor
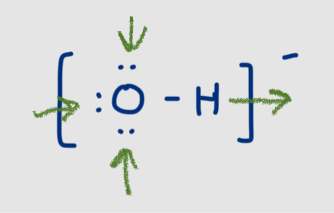
Why are non-covalent molecules important for interactions
Weak bonds easily break and form allowing for quick transformations and interactions with other molecules
Ionic interactions are weaker than covalent interactions. True or false?
True
Different between van der Waals and H bonds
Both are dipole interactions but van der Waals does not include H2O.
What are the types of van der Waals forces. Describe each.
Dipole-dipole interactions: between polar non-charged groups
London dispersion forces: between nonpolar molecules
Rank in order of increasing strength: H-bonds, dipole-dipole interactions, London dispersion forces
LDF < D-D < H-bond
Hydrophobic effect
tendency of water to minimize its contact with nonpolar substances. causes substances to aggregate
Examples of donor groups in H-bonds
N-H, O-H, s-H
Examples of acceptor groups in H-bonds
O with two lone pairs. N with one lone pair. s with one lone pair
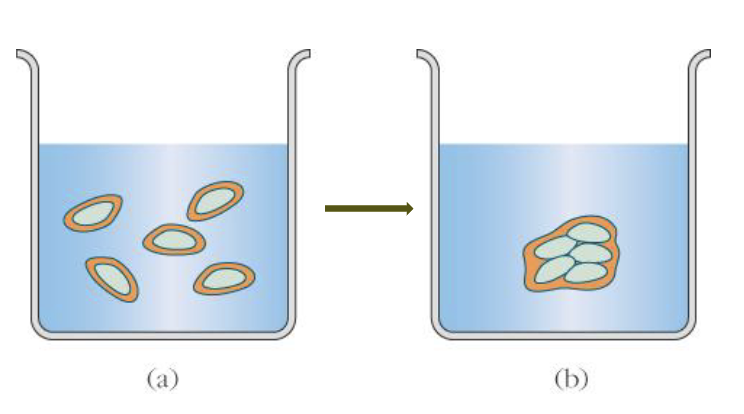
Explain the following image
The non-polar molecule is placed into water and causes water molecules to become constrained around it (orange). Figure a is less favourable for water because there is lower entropy. Due to the hydrophic effect, the non-polar molecules want to interact so they aggregate and result in figure b which is more favourable for water due to the higher entropy it has.Am
Amphipathic/amphiphilic molecules
Experience hydrophilic interactions and hydrophobic effect at the same time. (more hydrophobic is usually amphipathic)
Micelle
Fatty acids with polar head and non-polar tail join to form spherical structure

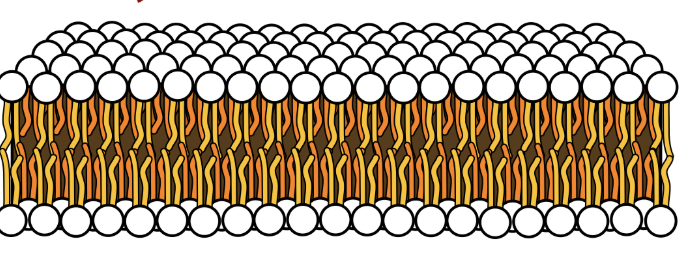
How is a bilayer formed
Membrane lipids join to position polar head towards water and non-polar parts away from water