2.5 - Dopamine
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Catecholamines
- monoamines containing catechol w/ side chain amine (ex: dopamine, NE, epi)
- derived from Phe and Tyr
Adrenergic system
uses NE and epi as NT
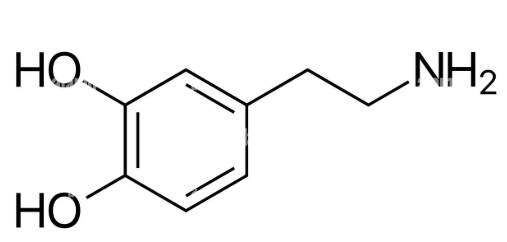
Dopamine (DA)
- important in ANS and CNS activity
- first member of catecholamine NT class
Dopamine synthesis (in neurons)
- Tyr actively co-transported into cell (charged)
- hydroxylation of Tyr by tyrosine hydroxylase (rate limiting step) → DOPA is converted to dopamine via DOPA decarboxylase
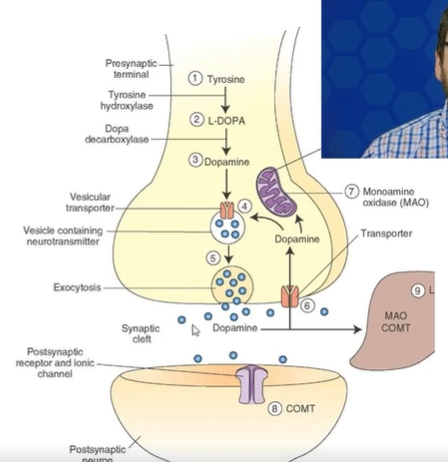
Dopamine transporter
- actively co-transported w// ions (exchange h+ for DA)
- after release 90% of DA is taken up by them into pre and post synaptic cells → terminates signaling
reserpine
inhibits VMAT protein
Amphetamine
inhibits VMAT
Dopamine reuptake fate
reused (presynaptic only) or metabolized into homovanillic acid and DOPAC by COMT and MAO enzymes
dopamine receptors
- all metabotropic 7 transmembrane GPCR-class receptors
- divided into 2 groups: D1-like and D2-like
D1-like receptors
- increase adenyl cyclase
- D1 and D5; excitatory
D2-like receptors
- decreases adenyl cyclase
- D2, D3, and D4; inhibitory
D2 receptors
- important in feedback inhibitory control and control mechanism
- inhibits release of NT from presynaptic cell
- binds to autoreceptor
autoreceptor
presynaptic receptors that respond to dopamine release by the same cell
Dopamine Pathways in the brain
Nigrostriatal, mesocorticolimbic, and tuberoinfundibular
Nigrostristal pathway
- substantia nigra to Striatum; ~75% of dopamine in brain
- regulates voluntary locomotor activity
- ex: Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and Gilles de la Tourette
Parkinson’s disease
degeneration of substantia nigra dopamine neurons
Huntington’s chorea
excess dopamine → involuntary movement
Gilles de la Tourette syndrome
excess dopamine contributes to physical (motor) and vocal (phonic) tics
Mesocorticolimbic pathway
- originates in midbrain and projects to nucleus accumbent, limbic and frontal cortex
- regulates reward (signals natural reinforces; euphoria) and controls motivation
Tuberoinfundibular pathway
- originates in arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus. projects to pituitary gland
- inhibits secretion of prolactin
dopamine antagonists
cause hyperprolactinemia (↑ blood prolactin)
monoamine hypothesis
decreases catecholamine and serotonergic activity may underlie depression
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCA)
- Ex: imipramine (Tofranil)
- block monoamine transporters
- prevent presynaptic neuron from reabsorbing catecholamines and serotonin from synaptic cleft after release
monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MOA-Is)
- ex: pheneizine (Nardil)
- block enzyme MAO, presynaptic terminal enzyme that metabolizes serotonin and catecholamines into inactive forms
- more NT available
dopamine hypothesis
schizophrenia results from excess activity at D2, D3, and D4 dopamine synapses
dopamine hypothesis support
- antipsychotic drugs strongly antagonize postsynaptic D2R
- drugs ↑ dopaminergic activity either aggravate schizophrenia or produce psychosis de novo
- mediate sexual behavior (↑ central DA = ↑ behavior) and vomiting (stimulation of D2R = ↑ vomiting)
opioid addiction
directly activates MOR; inhibits GABA-A, interneurons = ↑ DA in A10
psychostimulant addiction
- ex: cocaine, amphetamine
- increases DA by inhibiting dopamine transporter (DAT) = ↑ DA in synaptic cleft