week 7 - Voltage and ligand-gated ion channels
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is the most diverse family of ion channels?
The most diverse family of ion channels is potassium channels.
How many different genes encode K channel α subunits in the human genome?
More than 70 different genes encode K channel α subunits in the human genome.
What do potassium channels regulate?
Potassium channels regulate cell excitability through different modalities such as frequency and shape of action potentials, secretion of hormones, secretion of neurotransmitters, and membrane potential.
What are the types of potassium channels?
The types of potassium channels are voltage-gated and calcium activated channels.
How many transmembrane domains do potassium channels have?
Potassium channels have 6 transmembrane domains.
What is the assembly type for potassium channels?
Potassium channels can have a Homomeric or Heteromeric assembly.
What does Minoxidil do to K+ channels?
Minoxidil opens K+ channels.
What effect does Minoxidil have on smooth muscle cells?
Minoxidil causes hyperpolarisation in smooth muscle cells, leading to muscle relaxation and hence vasodilation.
What is the intracellular concentration of K+?
A. 1M
B. 10µM
C. 150mM
D. 250mM
150mM
Is intracellular K+ concentration greater or less than
extracellular K+ concentration?
less than
What does Lidocaine block?
Lidocaine blocks voltage-gated sodium channels (Nav1.5, Nav1.7, Nav1.9).
What is the primary target of Lidocaine?
The primary target of Lidocaine is Nav1.5 which is the main cardiac sodium channel.
What are the indications for using Lidocaine?
The indications for using Lidocaine are ventricular arrhythmias, especially after myocardial infarction and local anaesthesia.
Where are Calcium (Ca2+) channels present?
Calcium (Ca2+) channels are present in the membrane of most excitable cells.
What forms the extracellular binding sites for practically all agonists and antagonists in Ca2+ channels?
The α1 subunit forms the extracellular binding sites for practically all agonists and antagonists in Ca2+ channels.
How many families of Ca2+ channels exist, and what are they?
Three families of Ca2+ channels exist :
(1) the high-voltage activated dihydropyridine-sensitive (L-type, CaV1.x) channels;
(2) the high-voltage activated dihydropyridine-insensitive (CaV2.x) channels and
(3) the low-voltage-activated (T-type, CaV3.x) channels.
% of drugs that target major families
nuclear receptor = 16%
kinase = 3%
GPCRs = 33%
Ion channels = 18%
Others = 30%
Potassium channels
•Most diverse family of ion channels.
•More than 70 different genes encoding K channels α subunits in the human genome.
•Regulate cell excitability through different modalities
•Frequency and shape of action potentials.
•Secretion of hormones.
•Secretion of neurotransmitters.
•Membrane potential.
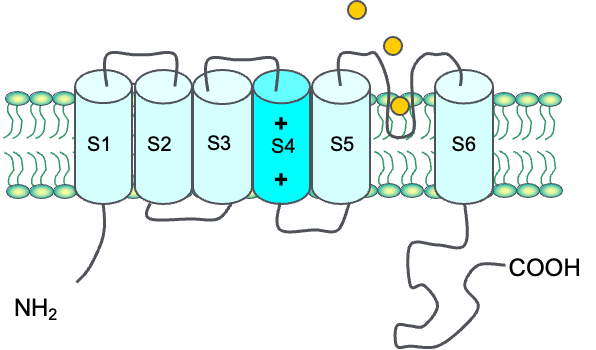
Voltage-gated and calcium activated channels
(6 transmembrane domains)
single polypeptide chain goes through the membrane 6 times
What is the structure of voltage-gated and calcium-activated potassium channels?
Composed of alpha subunits each containing six transmembrane domains (S1-S6).
The S4 segment contains positively charged residues crucial for voltage sensing.
The pore region between S5 and S6 segments is essential for ion selectivity and conductance.
How do potassium channels function?
Channels open in response to changes in membrane potential or intracellular calcium levels, allowing K+ ions to flow out of the cell.
What are the types of assembly for potassium channels?
• Homomeric Assembly: Channels composed of identical subunits, providing specific ion conductance properties.
• Heteromeric Assembly: Channels composed of different subunits, which can modulate the channel’s physiological properties and responses to signals.
Indication
Can be used in the treat of hypertension in combination with a diuretic and β adrenoreceptor blocker
minoxidil
Stimulates hair follicle growth
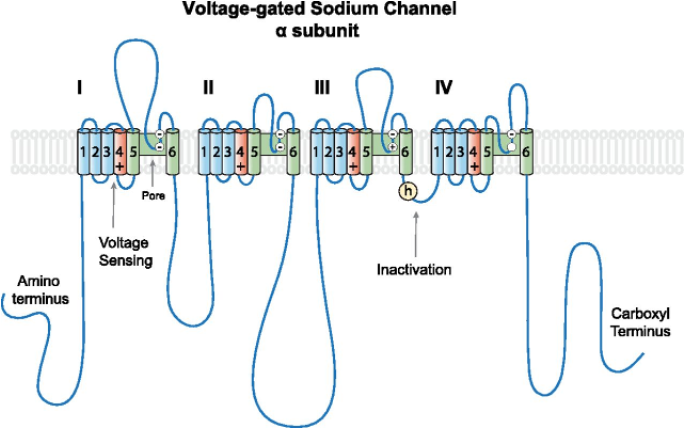
Sodium channels
•Sodium channels were the first members of the ion channel superfamily to be discovered.
• Sodium channels are voltage-gated sodium-selective ion channels present in the membrane of most excitable cells.
• Sodium channels comprise of one pore-forming α subunit, which may be associated with either one or two β subunits.
• Encoded by at least 10 genes.
The α2–δ1 and α2–δ2 subunits
bind gabapentin and pregabalin