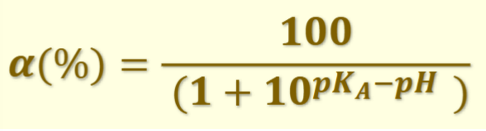Acids and bases
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is an amphoteric compound
A compound that can act as both a base and an acid, donating and accepting protons
What is an electrolyte?
A molecule that will form ions when it dissociates in a suitable solvent
Describe dissociation of acids
Acids give away protons
Dissociation of strong acids have reactions that aren’t reversible
Dissociation of weak acids have reactions that are reversible
Describe dissociation of bases
Bases accept protons
Dissociation of strong bases have reactions that aren’t reversible
Dissociation of weak bases have reactions that are reversible
What is a monovalent, divalent and trivalent compound
Compounds with a charge of 1, 2 and 3
What is a Normal (N)?
A unit of concentration. It is the number of equivalent(s) (Eq) in 1L of solution
N = M × Valence
Describe strong electrolytes
Dissociation is almost complete and they exist almost fully as ions in solution
Describe weak electrolytes
Dissociation is incomplete and they exist as a mixture of unionised and ionised species
What is the equation linking pH and H3O+?
pH = -log[H3O+]
H3O+ = 10-pH
What is the acidity constant?
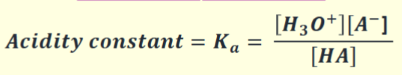
What is the Henderson-Hasselbach equation
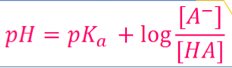
What is the equation for the concentration of a weak acid in a solution?

What is the equation for the degree of ionisation of a weak acid?
Here 'charge' for a weak acid is -1. Whilst charge for a weak base is +1