physiology - unit 11.1, 11.3, 12.1
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
What is the circulatory system?
The transport system of our body
What are the 4 main jobs of the circulatory system?
Transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide
Deliver nutrients to parts of the body and transport wastes
Maintain the body’s temperature
Transportation of hormones
What are the 3 main parts of the circulatory system? What are their purposes?
The blood → fluid that transports material
Blood vessels → Transport your blood throughout ur body
the heart → pump that pushes the blood through the vessels
What is the cardiovascular system?
Blood vessels + heart
What are the types of blood vessels? Compare them
Arteries
Carry blood AWAY from heart
Red
Oxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary artery)
High pressure → due to heart’s pumping action
Thicker than veins
Veins
Carry blood to the heart
blue
Deoxygenated (except pulmonary vein)
Low pressure →force pushes blood up through veins through skeletal muscle tissue contracting
so there’s a presence of valves to ensure blood doesn’t flow backwards
Thinner than arteries
Capillaries
Connects arteries to veins
Smallest type of blood vessel
Most important job: exchanges nutrients, waste, water, oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and surrounding cells
What is blood made of? What is each part’s purpose?
Plasma →Carries all other parts of f blood like carbon dioxide, nutrients, waste, hormones and different dissolved proteins that have very important jobs
Erythrocytes (red blood cells) →Contain hemoglobin molecules that help carry oxygen via ions of iron
Leukocytes (white blood cells) →Protect the body against microorganisms and other toxins
Platelets →Help the blood clot when there is a wound using fibrin (which causes blood to stop flowing)
How does the structure of red blood cells (erythrocytes) help them?
Since they don’t have a nucleus:
They have an increased surface area that help them carry more oxygen
Their shape gives them more flexibility to fit through blood vessels
Cannot undergo mitosis
What is pus?
White blood cells + pieces of microorganisms
How do platelets help clot blood of a wound?
They become active when they touch a sharp edge and that makes them rupture/explode
When they explode they release a substance that reacts with proteins in the plasma to create a mesh or net of fibres called FIBRIN
Causing the blood to stop flowing and eventually the fibres will contract and cause your wound to close up
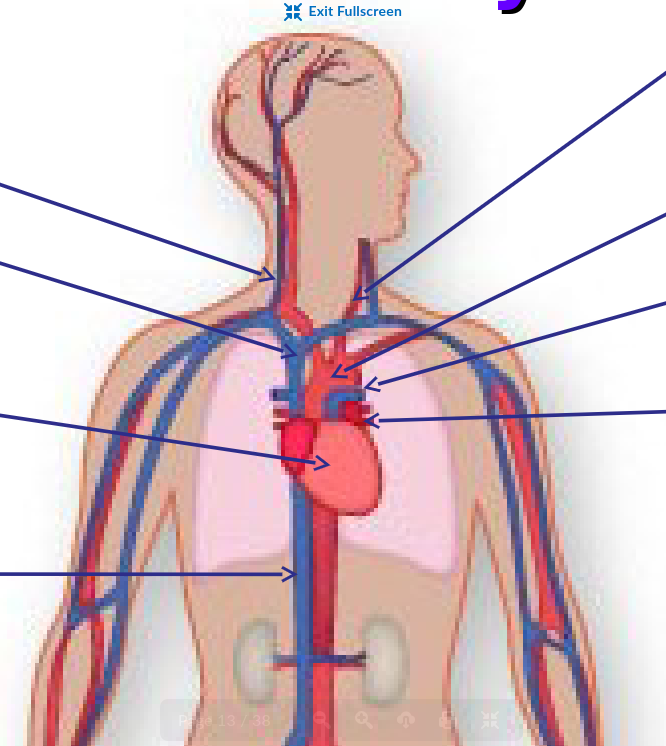
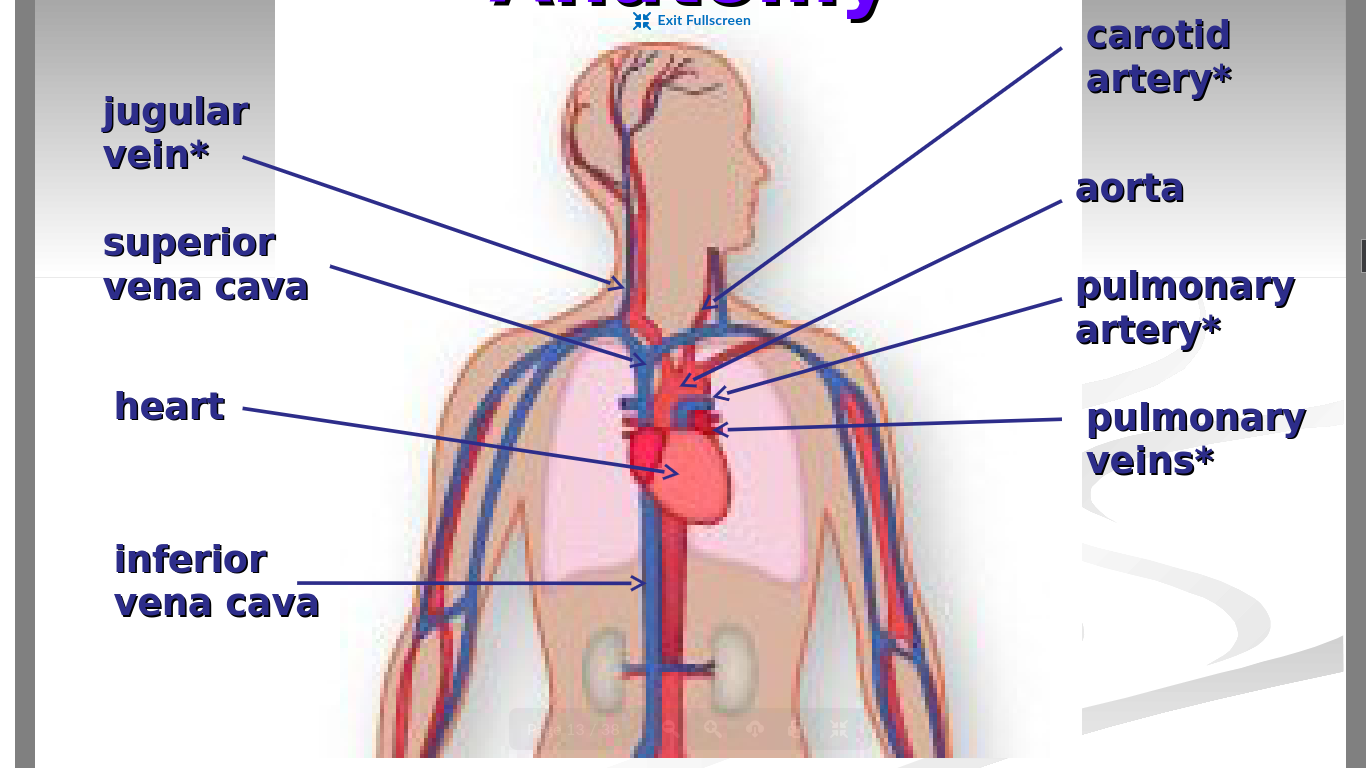
What is the purpose of the aorta in the circulatory system?
Oxygenated blood leaves the heart from here and is carried to the tissues of the body
Largest artery in the body
On left side of the heart
What is the largest artery of the body?
aorta
What is the purpose of the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava in the circulatory system?
SVC → Carries deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body back to the heart
Leads to right side of heart
IVC →Carries deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body back to the heart
Also leads to the right side of the heart
What is the purpose of the carotid artery in the circulatory system?
Provides oxygenated blood for the head and neck
two in total
one on each side of body
What is the purpose of the jugular vein in the circulatory system?
Brings deoxygenated blood from the head and neck back to the superior vena cava and to the right side of the heart
two in total
one on each side of the body
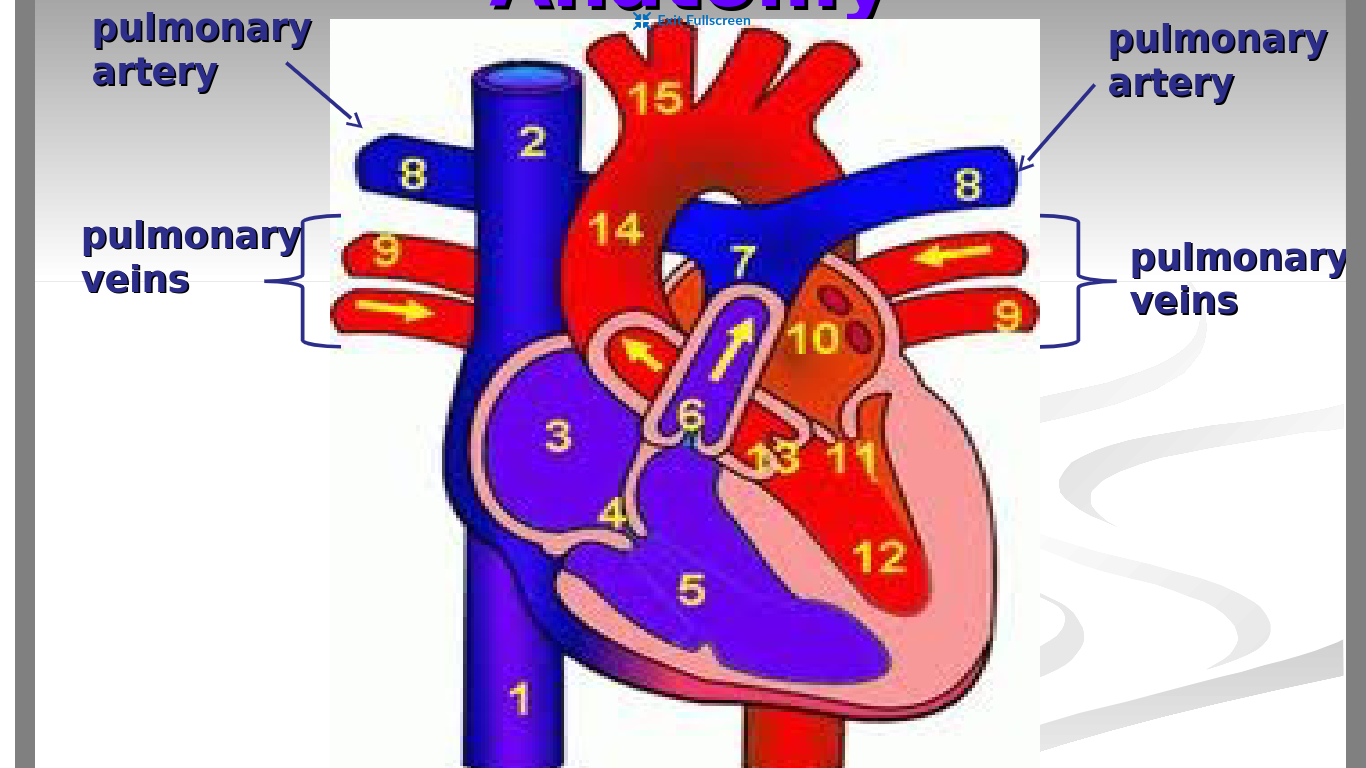
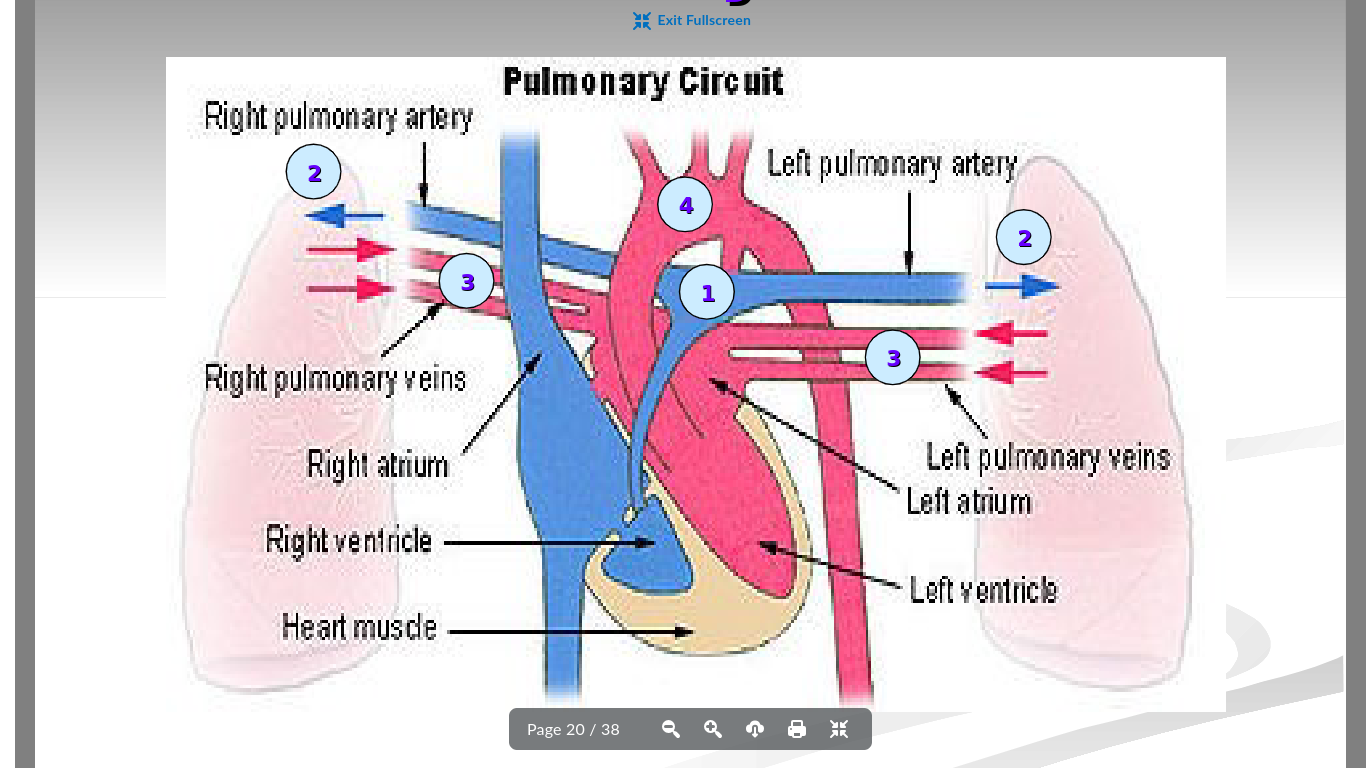
What is the purpose of the pulmonary artery in the circulatory system?
carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to get oxygen
only artery that is colored blue and has deoxygenated blood
two in total - one on each side of body
What is the purpose of the pulmonary vein in the circulatory system?
To bring oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
only vein that is red and has oxygenated blood
four in total - two on each side of body
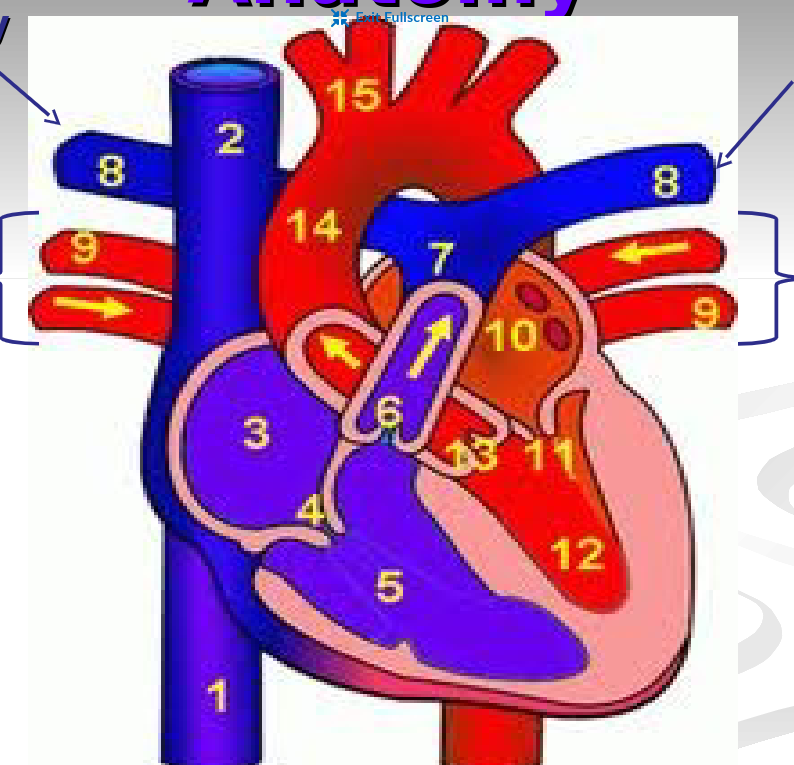
Compare the pulmonary and the systematic circuit
pulmonary circuit →system of blood vessels that carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs and oxygenated blood returns to the heart
Main blood vessels involved: pulmonary arteries and pulmonary veins
Systematic circuit →system of blood vessels that carries oxygenated blood to all parts of our body and deoxygenated blood back to the heart
Main blood vessels involved: all other blood vessels in the body
Describe the steps of the pulmonary circuit
Deoxygenated blood leaves pulmonary arteries to go to lungs
Arteries become capillaries and receive oxygen from lungs
Oxygenated blood returns to the heart
Oxygenated blood can now enter systematic circuit where it is delivered to all parts of your body
Describe the steps of the systematic circuit
Oxygenated blood leaves the heart from the aorta
Blood travels through arteries to be delivered to parts of your body
Arteries become capillaries so they can deliver oxygen to body cells
Deoxygenated blood travels back to the heart through veins
Deoxygenated blood finally re-enters heart through the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava and is ready to return to the pulmonary circuit

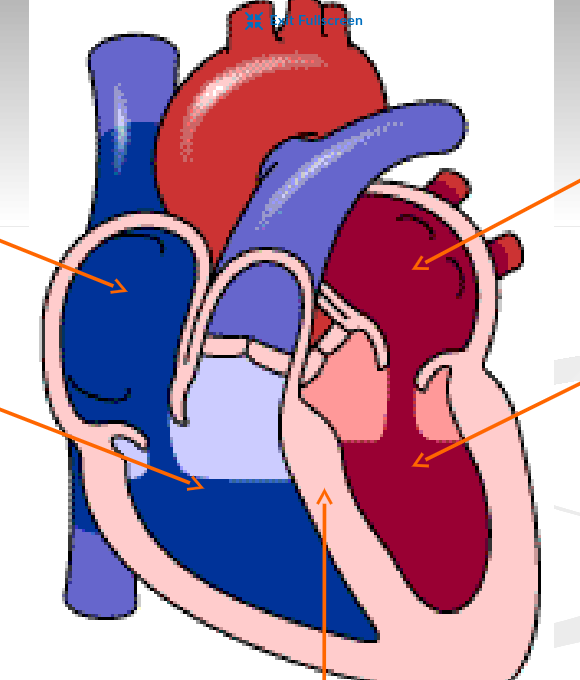
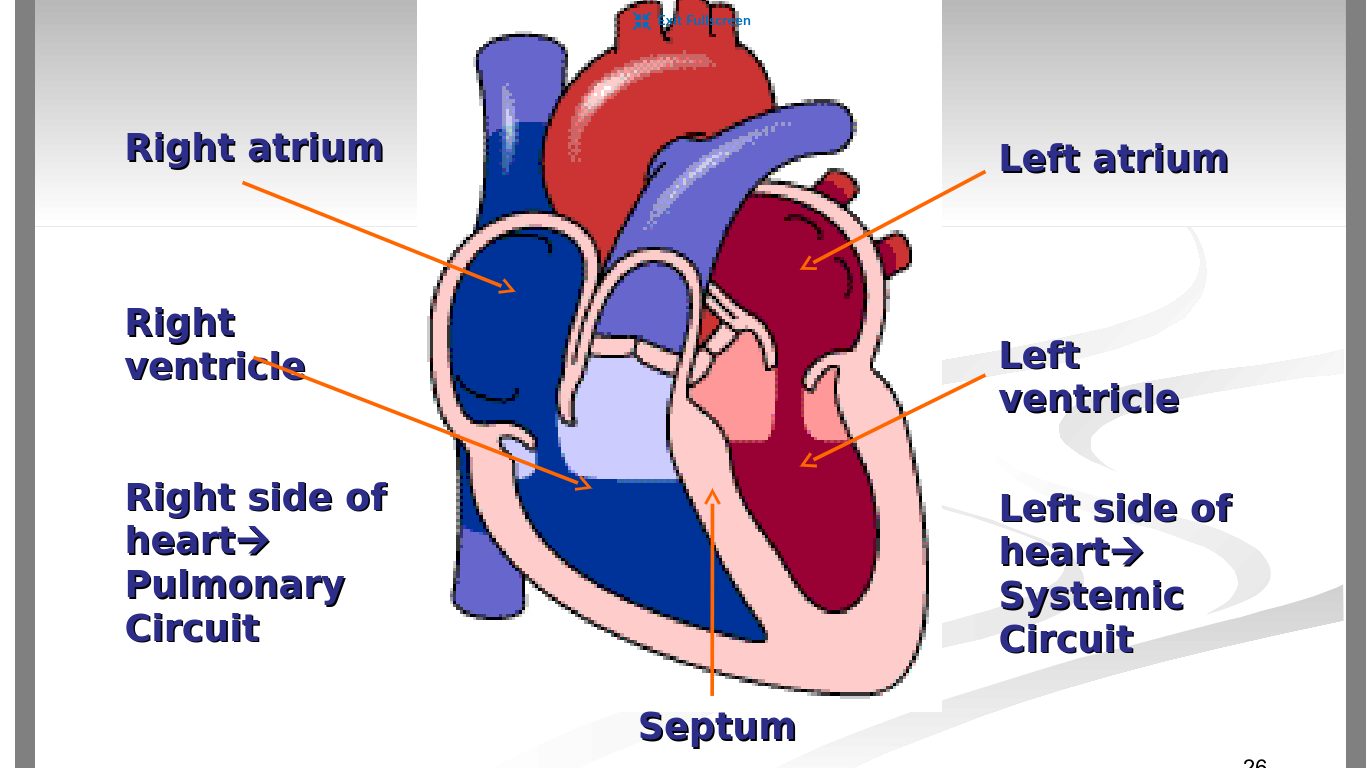
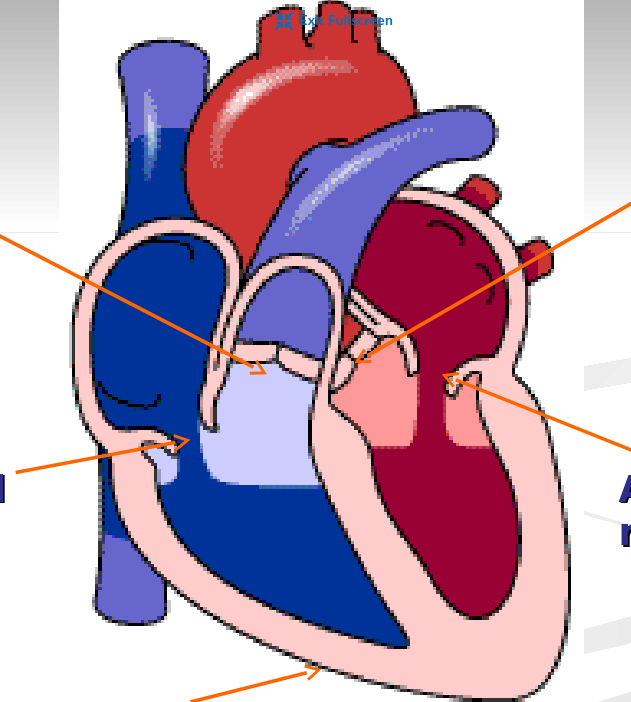
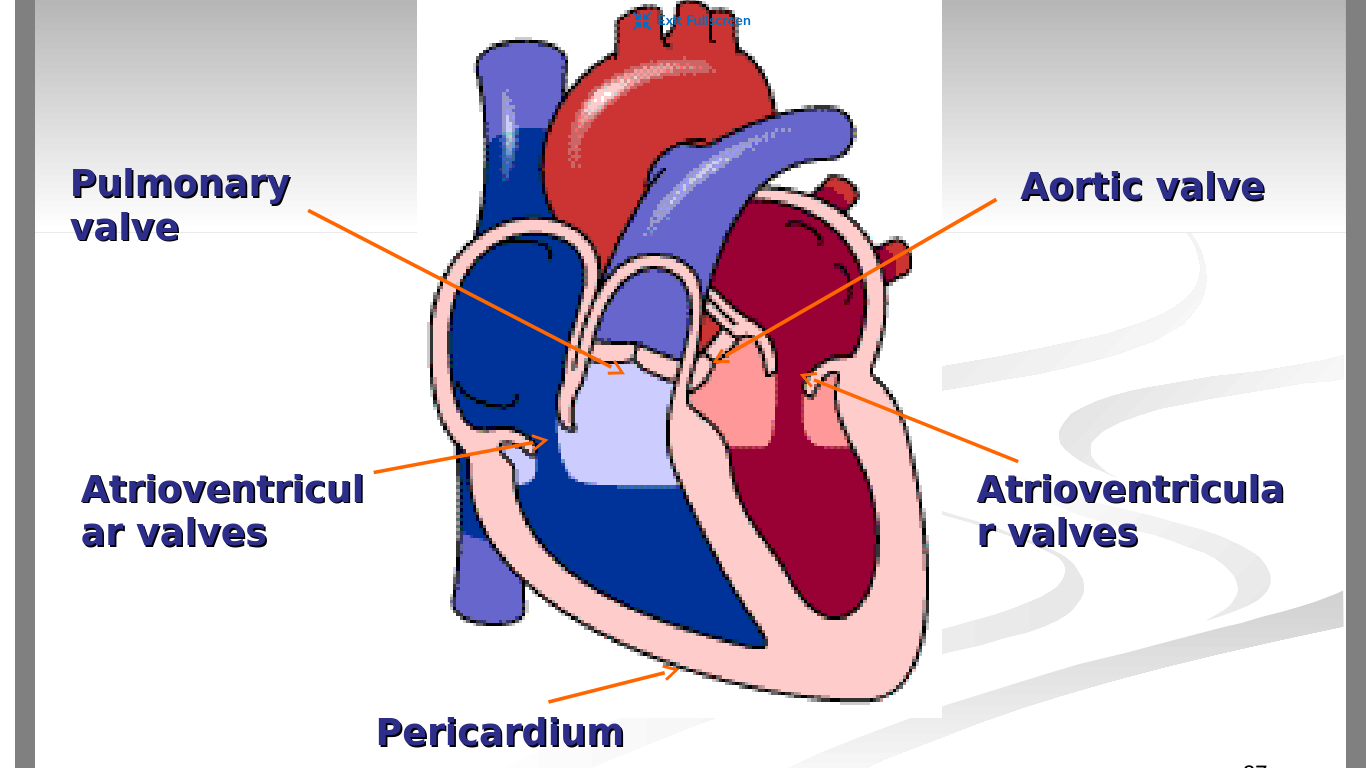
What is the purpose of the atriums and ventricles of the heart
Atrium →Receives blood from the veins and passes it on to the ventricles
Ventricles → More muscular and pumps blood to the arteries
What side of the heart are the pulmonary circuit and systematic circuit on?
Right side → pulmonary circuit
Left side →systematic circuit
What is the purpose of the pericardium of the heart?
it is a protective sad filled with fluid that lubricates (make smooth or slippery) the surface of the heart and roots of major blood vessels
What are the purpose of valves in the heart? Name the different types in the heart
Purpose of valves is to prevent blood from flowing backwards
Atrioventrical valves →between atria and ventricles; one on each side of heart
Pulmonary valves →between right ventricle and pulmonary arteries
Aortic valve →between left ventricle and aorta
What are the purposes of coronary arteries in the heart?
Pair of arteries that branch from the aorta to the heart itself to provide it with necessary nutrients
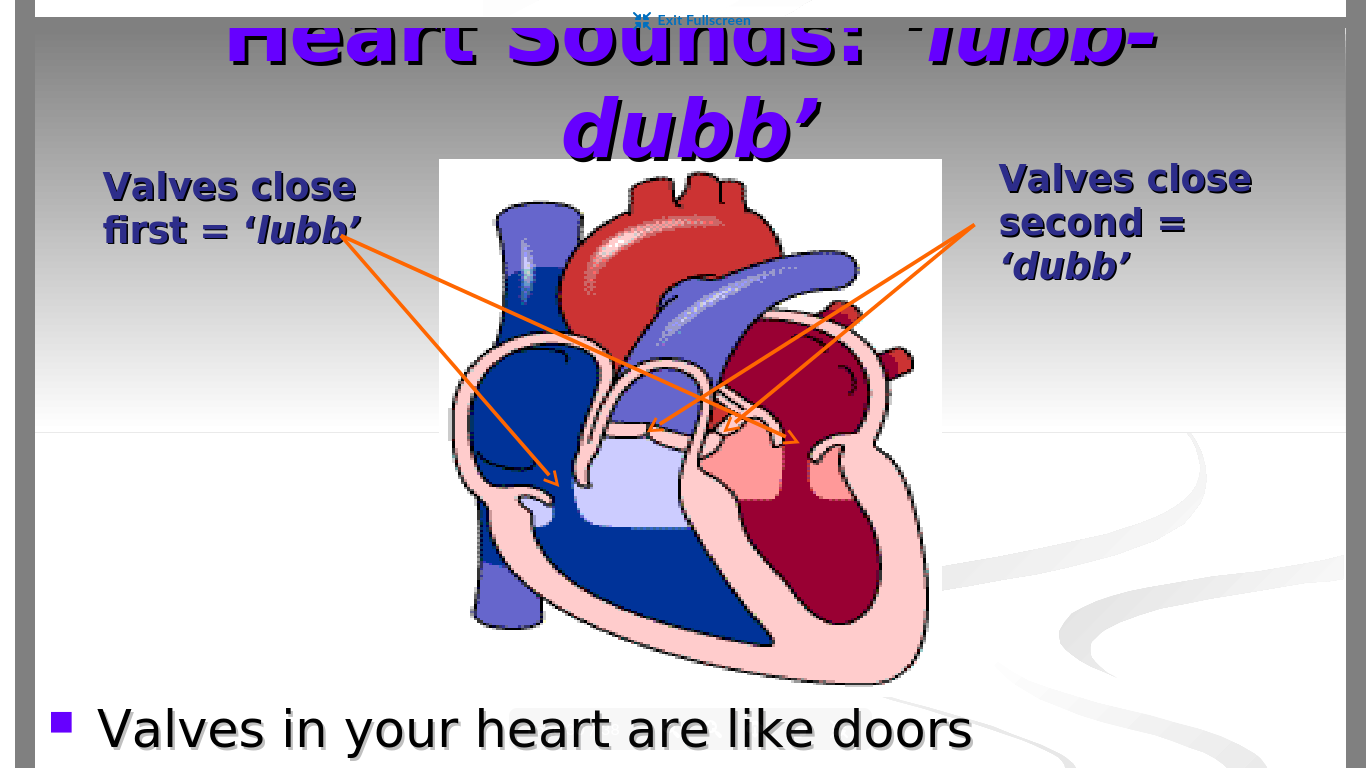
What makes the heart sound “lubb-dubb”
First lubb →atrioventricular valves close first
Second dubb →pulmonary and aortic valves close second
What are the two groups of nerves in the heart that control its beating and heart rhythm
sinoatrial (SA) node →acts as pacemaker and creates and electrical signal controlled by nervous system and endocrine system
Atrioventricular (AV) node →Acts as a messenger that passes signal from SA node down to the ventricles that make the ventricles contract as atria relax
What two steps occur during the beating of our heart?
Diastole →relaxation/growing of the atria or ventricles that allows blood to enter into the atria or ventricles
Blood enters atria from veins and enters ventricles from atria
Systole →contraction/squeezing of the atria or ventricles that allows atria or ventricles to pump blood away
Atria pump blood to the ventricles and ventricles pump blood to arteries
How is blood pressure measured?
with a sphygomomannometer
cuff/sleeve of the sphygmomanometer is wrapped around arm and inflated with a pump to cause your blood flow in your arm’s arteries to stop flowing
Air from cuff/sleeve is slowly released and the doctor waits to hear the sound of your blood start flowing again, as soon as the doctor hears it, they record it. This is called your systolic blood pressure (The maximum amount of pressure in ur arteries)
The cuff/sleeve is deflated even more until the sound stops, when it does the doctor records the pressure. This called your diastolic blood pressure (Lowest amount of pressure in ur arteries)
What 2 factors affect our blood pressure?
Cardiac output →amount of blood pumped by the heart each minute
Increased volume of blood pumped = increased blood pressure
Resistance of arteries →related to elasticity in arteries
increases resistance of blood flow = increased blood pressure
Whats the difference between systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure
Systolic blood pressure →maximum amount of pressure in ur arteries that happen when ventricles undergo systole (squeezing)
Diastolic blood pressure →lowest amount of pressure in your arteries that happen when your ventricles are in diastole (growing)
What is the ratio that blood pressure is recorded as?
Systolic blood pressure/ diastolic blood pressure
ex: 120 / 80
Describe characteristics of plasma
Liquid
Contain dissolved nutrients, waste, and everything
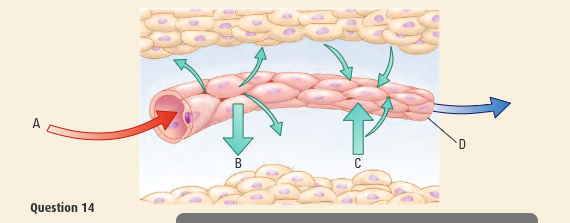
Explain what is happening in A, B, C and D of the diagram
A →oxygenated red blood travels away from heart to other organs and capillaries
B →oxygen and nutrients are distributed via capillaries to surrounding cells
C → CO2 and waste goes into blood
D →deoxygenated blue blood travels back to heart
What is the role of fibrin in blood clotting?
To stop blood flow in wounded areas
a) What happens when the heart muscle contracts?
b) What happens when the heart muscle relaxes?
a) →The heart is in systole: squeezing of the atria or ventricles
Allows blood to be pumped away from the Atria or ventricles
Atria pumps blood to ventricles; ventricles pump blood to arteries
b) → the heart is is diastole: growing of atria or ventricles
Allows blood to enter the atria or ventricles
blood enters atria from veins; blood enters ventricles from atria

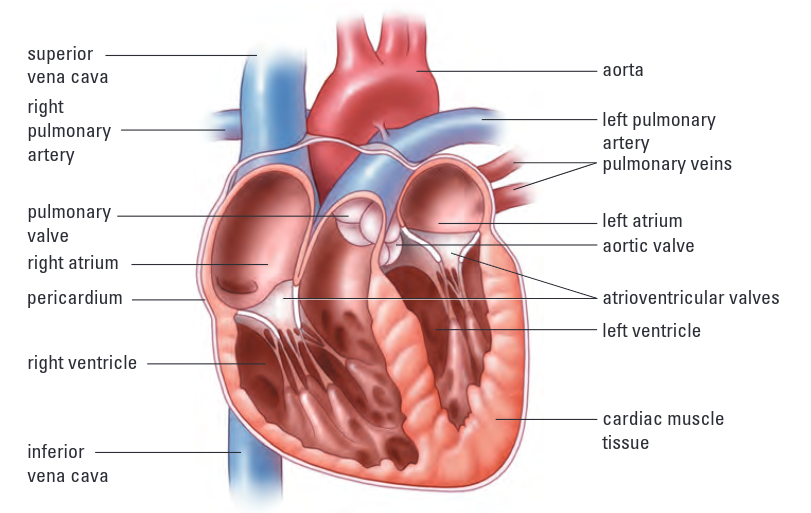
What is the function of valves in the heart
to prevent blood from flowing backwards
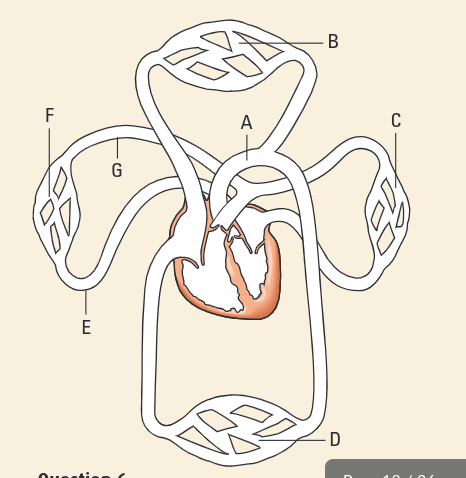
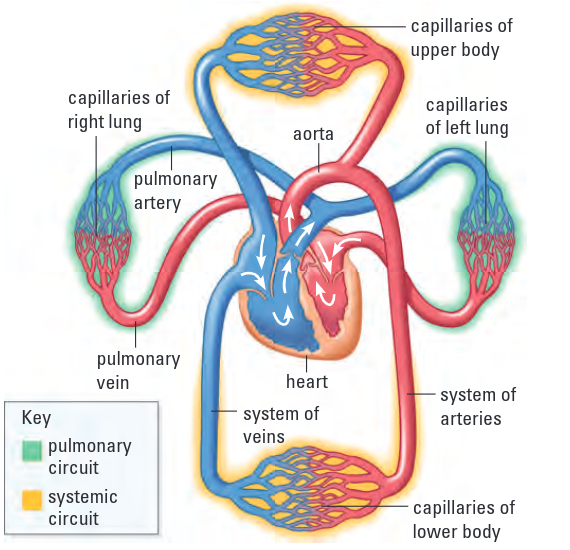
State one way in which the function of the pulmonary artery is different from the function of other arteries in the body
deoxygenated blood
What is the difference between the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava
SVC → deoxygenated blood from upper half body to the heart
IVC → deoxygenated blood from lower half of Body to heart
How are the cells of the heart supplied with the necessary oxygen and nutrients
Pair of arteries branching from aorta to the heart itself called coronary arteries provide the heart with the necessary nutrients
Where in the heart would you find the area known as the pacemaker
Sinoatrial (SA) node
ABout how many times does a heart beat per minute
72
What is a sphygmomanometer?
a tool that measures blood pressure
Define the following
a) diastolic pressure
b) systolic pressure
a) Lowest amount of pressure in your arteries
b) maximum amount of pressure in ur arteries
What factors does blood pressure depend on?
systolic blood pressure / diastolic blood pressure
What is an average blood pressure reading for a healthy adult
120 / 80
Describe the three types of cardiovascular disease
Arteriosclerosis →a group of disorders where the walls of the arteries thicken, harden, and lose elasticity so that they can’t stretch well
Disease of the veins →ex: varicose veins
Heart disease
What is the disease varicose veins
Often seen in the legs where the veins become swollen and twisted because they don’t have proper blood flow
Describe the following types of heart disease:
a) coronary heart disease
b) Arrhythmia
c) valves disorders
d) heart muscle disease
e) aneurysm
f) stroke
a) Blockage of the arteries that provide blood to the heart
b) Problems with your heart rhythm or heartbeat
c) Dysfunction in one or more of ur heart valves
d) Inflammation of an infection of the heart muscle itself
e) Bulge/swelling of the wall of an artery that can burst
f) Blood clot forms in an artery going to the brain
What is the difference between atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis is a category of cardiovascular disease that include diseases that causes arteries to thicken and harden
Atherosclerosis is in this category and it is the blockage of blood flow caused by the collection of plaque
Also main cause of coronary artery disease
What is the main cause of CAD
atherosclerosis →blockage of blood flow in arteries caused by collection of plaque
plaque →yellow sticky substance made up of calcium and fat deposits
What can happen when there is a buildup of plaque in the coronary artery
Causes CAD
Causes artery to become more narrow, which:
Increases blood pressure
Eventually blocks artery so no oxygen or nutrients can reach the heart
What is a myocardial infection
When no oxygen or nutrients can reach the heart, causing the heart to die
What are the 4 symptoms of a heart attack
Shortness of breath (diff breathing)
Nausea
Sharp chest pain
Pain in neck and arm (mostly left arm)
What are the list of things that can increase ur chance of getting CAD
Smoking
Lack of exercise
High blood pressure
High blood cholesterol
Obesity/overweight
Poor eating habits
Diabetes
Genetics
Stress
How is a heart attack diagnosed?
First detect the symptoms
Do a blood test to detect certain proteins that are made when your muscle tissues around the heart are damaged
After, the doctor uses an electrocardiograph to detect if ur heart rhythm and rate are normal or if ur heart has been damaged
After the electrocardiograph tells the doctor where the damage occurs (but not how badly blocked it is) the cardiologist performs a procedure called a cardiac catheterization
Small tube (catheter) is inserted into an artery near the groin area
A dye is inserted into the catheter so that it can be seen on x-ray
Catheter is then threaded through the artery into the blocked area in the coronary artery to identify the location of the blockage
How is a heart attack treated?
Anti-clotting drug is provided to prevent more blockage in coronary arteries
Tubes are inserted into nose to increase concentration of oxygen in the lungs
Then cardiologists will perform an angioplasty
Second catheter (containing small metallic mesh tube called a stent) is placed into the first one
The stent opens up and stays in ur artery to prevent it from narrowing
In severe cases, another option is to perform a coronary bypass
This is where the procedure takes a vein from another part of the body and attaches it to the heart to bypass the blocked area of the coronary artery to supply blood to the area past the blockage
What is cellular respiration?
All processes involved in the intake of oxygen and release of carbon dioxide from our cells
What is another name for the following:
a) windpipe
b) voice box
a) trachea
b) larynx
What is the difference between bronchi and bronchioles?
Bronchi →two air passages connected to the trachea that lead to the lungs
Bronchioles →smaller tubes throughout the lungs divided from the bronchi
a) What is the medulla oblongata?
b) What is its role in the breathing process?
a) the part of the part that controls your breathing
b) Sends nerve signals to your diaphragm to contract or relax
Describe the role of carbon dioxide in controlling breathing
Increased CO2 = Increased carbonic acid in plasma →lowers blood pH →increases breathing rate
When you breathe back out the CO2, your blood’s pH raises again, making it normal
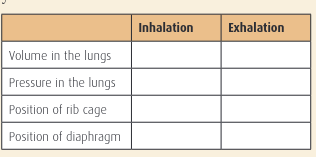
Complete the table
Inhalation:
Volume in lungs →increases
Pressure in lungs →decreases
Position of rib cage →expands
Position of diaphragm →moves down (contracts)
Exhalation:
Volume in lungs →decreases
pressure in lungs →increases
Position of rib cage →gets smaller
Position of diaphragm →moves up (relaxes)
Explain how gas exchange is accomplished in the alveoli
Blood enters network of capillaries in the lungs deoxygenated and high in CO2
Oxygen from alveoli transfers to blood through the capillaries and CO2 from the blood transfers to the alveoli through capillaries
Blood leaves network of capillaries oxygenated and low in CO2
Blood goes back to the heart and gets pumped out to the rest of the body
How do cilia and mucus help your respiratory system to function efficiently
Cilia and mucus help filter the air you breathe in by trapping dust and other foreign substances in your trachea and your nasal and oral cavities
Indicate the name of the cardiovascular disease based on the descriptions below:
a) Problems with your heartbeat and rhythm
b) Bulge in the wall of an artery that can burst
c) Blockage of blood flow in arteries due to plaque
a) Arrhythmia
b) Aneurysm
c) Atheriosclerosis
Briefly describe the two methods for treating a myocardial infarction:
a) Angioplasty
b) coronary bypass
a) when a catheter with a stem is released to an area of blockage and it widens so blood can flow through
b) A vein from another part of your body is placed around the blockage to create a new path for your blood to flow through
True or false:
Blood first entering into alveolar capillaries are high in oxygen and low in CO2
False
True or false:
During inhalation. the diaphragm and rib cage both rise
false
True or false:
Involuntary breathing is controlled by the medulla oblongata
True
True or false:
The vast majority of your blood is made of red blood cells
false
True or false:
Fibrin is an important protein necessary to help your blood clot
True
True or false:
All veins carry deoxygenated blood
false
True or false:
The purpose of the systematic circuit is to pump oxygenated blood to all parts of our body and return deoxygenated blood directly back to the lungs
false →first goes to right side of heart
True or false:
Blood leaving the right atrium is directed to the aorta next
false
True or false:
The pericardium is the tissue that separates the right side from the left side of the heart
false → the septum not pericardium
True or false:
The blood pressure in arteries is higher than the pressure found in veins
true
True or false:
Cilia are small, fleshy hairs lining your trachea that trap and filter air
true
Draw a flow chart to show how your body will homeostatically regulate your breathing rate
Increased CO2 = Increased carbonic acid →lowers blood pH →increases breathing rate →CO2 goes back out of body → pH increases and goes back to normal
Sketch and draw a hemoglobin molecule
big blob with 4 small units of iron (Fe) each bonded to an oxygen
Identify the role of the following structures in the circulatory system:
a) carotid artery
b) Pulmonary veins
c) aortic valve
d) SA node
e) systolic blood pressure
a) Delivers oxygenated blood to the head and neck
b) Returns oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart
c) between left ventricular and aorta
d) pacemaker and sets the rhythm of the heartbeat
e) Highest blood pressure felt in your arteries