All of Osteoporosis and Osteosarcoma
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
What do osteoclasts do?
Break down bone
What do osteoblasts do?
Build new bone
When is the peak adult bone mass get reached?
Early 20’s to 30/35
When is the greatest amount of bone mass decline?
Immediately after menopause
When is the average age of menopause?
52
What is osteopenia?
A bone condition characterized by bone loss that is not as severe as in osteoporosis
What is the definition of osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is characterized by low bone mass, microarchitectural disruption, and skeletal fragility, resulting in decreased bone strength and increased risk of fracture
Why is a need for an early diagnosis of osteoporosis important?
The availability of therapies that can slow or even reverse the progression of osteoporosis
What does osteoporosis “literally” mean?
Porous bone
What are the descriptions of bone, and what do they lead to (not part of the definition)?
Brittle, porous, and prone to fracture
What is osteoporosis known as in the medical field?
Silent disease
When are symptoms first shown for osteoporosis?
First fracture
What is the rate of bone formation and bone resorption for osteoporosis?
Bone formation is normal and bone resorption is increased
What happens to the bone and structural integrity from osteoporosis?
Incapable of maintaining structural integrity of the skeleton due to depleted bone integrity
The bone density and architectural changes of osteoporosis lead to what?
Impaired skeletal strength and markedly increase risk of fracture
How many people have osteoporosis fractures annually?
2 million
What is the most common type of osteoporosis fracture?
Vertebral compression fracture
What is the second most common type of osteoporosis fracture?
Distal radial fracture
What is the third most common type of osteoporosis fracture?
Hip fracture
What is the fourth most common type of osteoporosis fracture?
Pelvic fracture
What is the main cause distal radial fractures (Abbreviation)?
FOOSH
What does FOOSH stand for?
Fall on an outstretched hand
What kind of fracture is the most life changing?
Hip fracture
What two things do hip fractures effect (Think about the person’s life)?
Morbidity and mortality
What is morbidity?
Suffering from disease
What is mortality?
Death
How many people have osteoporosis in the USA?
10 million
How many women have osteoporosis out of the 10 million?
8 million
What is a pathologic fracture?
Fragility fracture
What are the main causes of fragility fractures?
Osteoporosis and multiple myeloma
How much trauma is needed for a fragility fracture?
Minor trauma
What is used to treat fractures?
ORIF
What does ORIF stand for?
Open reduction and internal fixation
What is primary osteoporosis?
Bone loss that occurs during the normal human aging process
What is secondary osteoporosis?
Bone loss that results from specific, well-defined clinical disorders
What are the most common risk factors for osteoporosis (the four things he listed)?
Aging, taking corticosteroid, alcohol, and post menopausal
What is the main cause of secondary osteoporosis?
Taking corticosteroids
What are common causes of osteoporosis (name them all besides the medications and medical conditions, but I do feel like if you can do the other questions I made you are set)
Female gender, Asian or Caucasian decent, age over 50, estrogen deficiency (post menopausal - 15 years after menopause secondary to decreased estrogen), early menopause (Age less than 45), Low BMI (less than 19 - anorexia), maternal family history of osteoporosis (fractures), inactive lifestyle (lack of weight bearing exercise several times a week), decreased calcium (less than 4 serving daily), decreased vitamin D, smoking (tobacco produces estrogen destroying enzymes which lead to bone loss), nicotine decreases the activity of osteoblasts, and ETOH consumption (regular or excessive amounts (over 7 drinks weekly) decreased pancreas and liver’s efforts to absorb calcium and vitamin D)
When is post menopause?
15 years after menopause
What medications increase your chance of osteoporosis?
Steroids, thyroid medications, hormone suppressants (Lupron), and cancer treatment
What medical conditions increase your chance of osteoporosis (One of my answerers are different than the packet, he misspelled something)?
Rheumatoid arthritis, eating disorder, hyperthyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, and osteogenesis imperfecta
What are all the symptoms of osteoporosis?
Asymptomatic
What kind of events cause someone to realize they have osteoporosis?
Pathologic or fragility fractures
What is the quote from Rosen and Drezner about symptoms?
Osteoporosis has no clinical manifestation until there is a fracture. This is an important fact because many patients without symptoms incorrectly assume that they must not have osteoporosis.
Who made this quote “Osteoporosis has no clinical manifestation until there is a fracture. This is an important fact because many patients without symptoms incorrectly assume that they must not have osteoporosis.”
Rosen and Drezner
What is the first kind of diagnosis for osteoporosis (diagnosis A)?
Fragility fracture, particularly at the spine, hip, wrist, humerus, rib, and pelvis
What is the second kind of diagnosis for osteoporosis (diagnosis B)?
T-score -2.5 or higher standard deviations at any site based upon bone mineral density measurement by DXA scan
When can a clinical diagnosis of osteoporosis?
If there is a elevated rick for fracture
When can a clinical diagnosis of osteoporosis be made in the United States?
FRAX 10-year probability of major osteoporotic fracture is 20% or higher or the 10-year probability of hip fracture is 3% or higher
What is the T-score rating for a normal individual?
-1.0 or higher
What is the T-score rating for an individual with osteopenia?
Between -1.0 and -2.5
What is the T-score rating for an individual with osteoporosis?
-2.5 or less
What is the T-score rating for an individual with severe osteoporosis?
-2.5 or less with a fragility fracture
When should you repeat a DXA scan for a T-score of -1.0 to -1.5?
Every 5 years
When should you repeat a DXA scan for a T-score of -1.5 to -2.0?
Every 3-5 years
When should yo repeat a DXA scan for a T-score of -2.0 or lower?
Every 1-2 years
What population is a T-score based on?
Young adult
What population is a Z-score based on?
Age-matched population
What is T-score and Z-score based on (from the patient, and no abbreviation)
Bone mineral density
What Z-score should prompt careful scrutiny for coexisting problems?
-2 or lower
What does DXA stand for?
Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry
What are the three benefits that make a DXA scan the gold standard?
Low radiation, fast, and open
What are DXA scans used to determine the density of?
Lumbar spine and hip
Who is having DXA scans?
Patients who are at risk of osteoporosis or osteomalacia, have pathologic fractures, and radiographic evidence of diminished bone density
What does a DXA scan deliver?
Negligible radiation with an accuracy that is considerate
What lifestyle factors contribute to bone loss?
Smoking, excessive alcohol, physical inactivity, and poor nutrition
Most of the conditions can causing osteoporosis can be excluded with a what?
Careful history and physical examination
What should be measured in a physical examination for osteoporosis?
Height and weight
What does FRAX stand for?
Fracture risk assessment tool
What does FRAX estimate?
10-year probability of hip fracture and major osteoporotic fractures for untreated patients between ages 40 and 90
X-rays are ___________ to the detection of osteoporosis unless very sever or if there is an acute fracture?
Very insensitive
What are the baseline laboratory tests that are performed to judge the risk of osteoporosis?
Thyroid function, vitamin D assessment, serum protein electrophoresis, 24-hour urine calcium, testosterone level, and LH and FSH
Where do we get vitamin D
Sun
What is vitamin D good for when dealing with osteoporosis?
Calcium absorption
Where do we absorb calcium for vitamin D?
Small intestine
Why is LH and FSH important tests to do for osteoporosis?
Evaluates for hypogonadism which is associated with osteoporosis
What testosterone is measured in a testosterone level test?
Free testosterone
What does an LH and FSH tests stand for?
Luteinizing Hormone and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone
Write the quote from the International Osteoporosis Foundation (I learned he likes to use names just like the way I worded this question, so make sure you know who wrote the thing, so you know what to write)
Osteoporosis, which literally means porous bone, (porous bone matrix) is a disease in which the density and quality of bone are reduced (bones are brittle, porous, and prone to fracture). As bones become more porous and fragile, the risk of fracture is greatly increased. The loss of bone occurs silently and progressively. Often there are no symptoms until the first fracture occurs.
What is the quote from Rosen and Drezner from UpToDate about diagnosis (I heard we need to know quotes, which they got one of last year, this one, and a few others are important due to boldness and highlighting)?
Early diagnosis and quantification of bone loss and fracture risk are important because of the availability of therapies that can slow or even reverse the progression of osteoporosis
Who said this quote “Early diagnosis and quantification of bone loss and fracture risk are important because of the availability of therapies that can slow or even reverse the progression of osteoporosis”
Rosen and Drezner
Write the number and the fracture going from most frequent to least frequent in the top four (I don’t think we need to know numbers as much as you do)
547,000 Vertebral compression fracture, 397,000 distal radial fracture, 300,000 hip fracture, and 135,000 pelvic fracture
What are the signs of a hip fracture?
One leg shorter and externally rotated
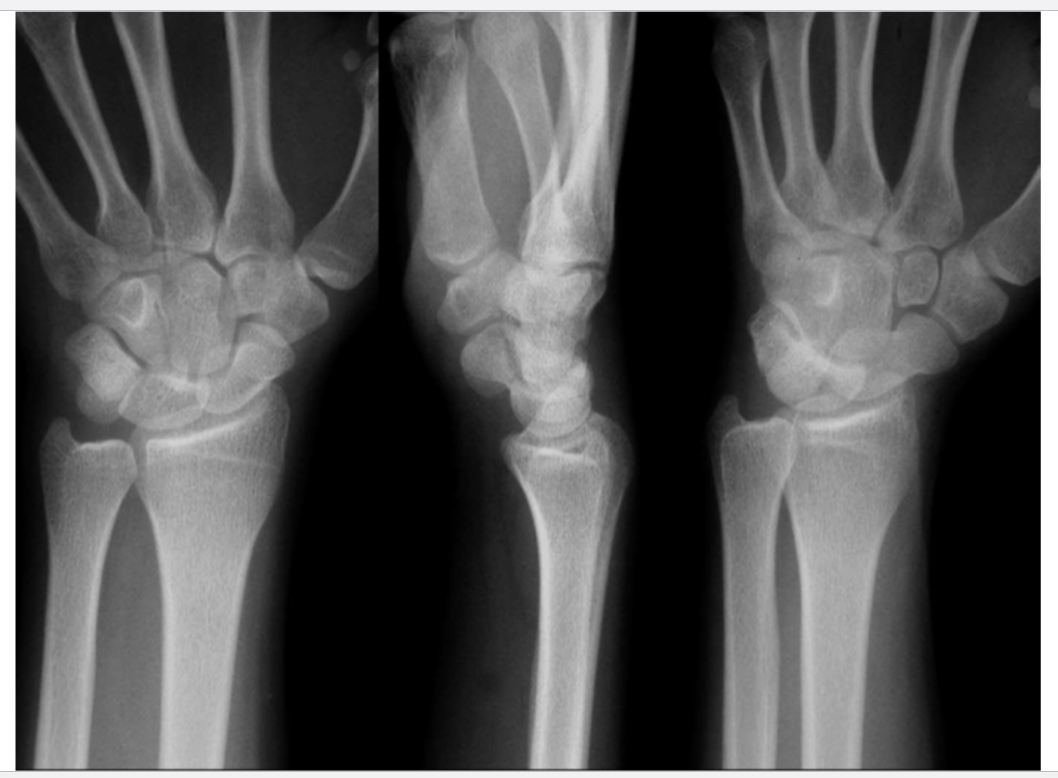
What is this?
Normal
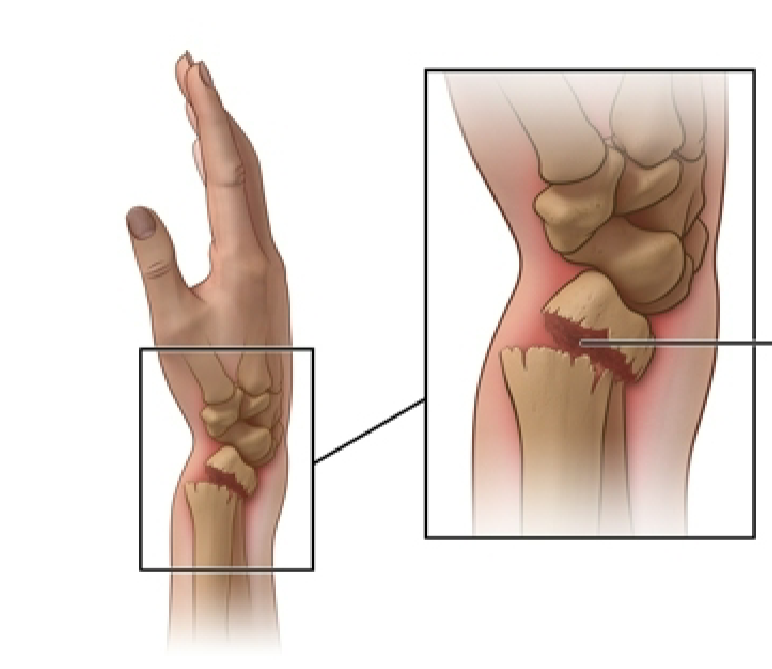
What is this?
Colles fracture

What kind of fracture would this lead to?
Colles fracture
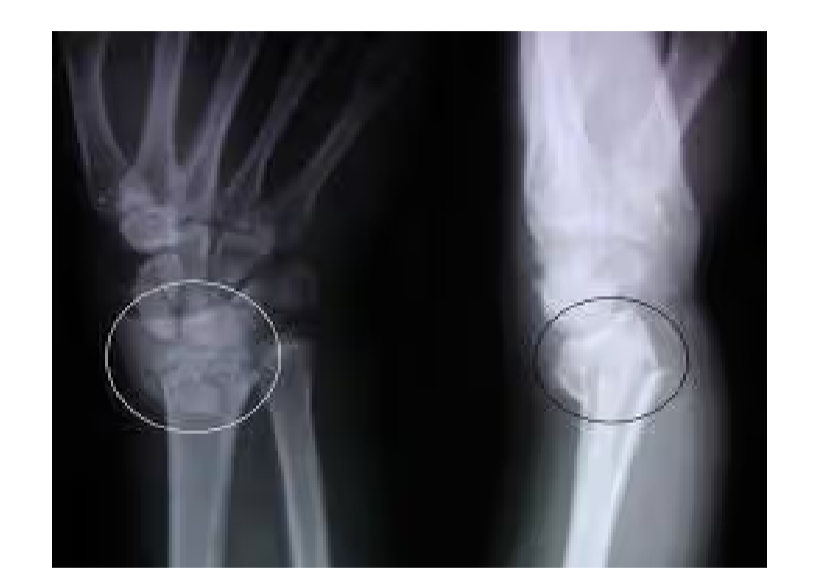
What is this?
Colles fracture
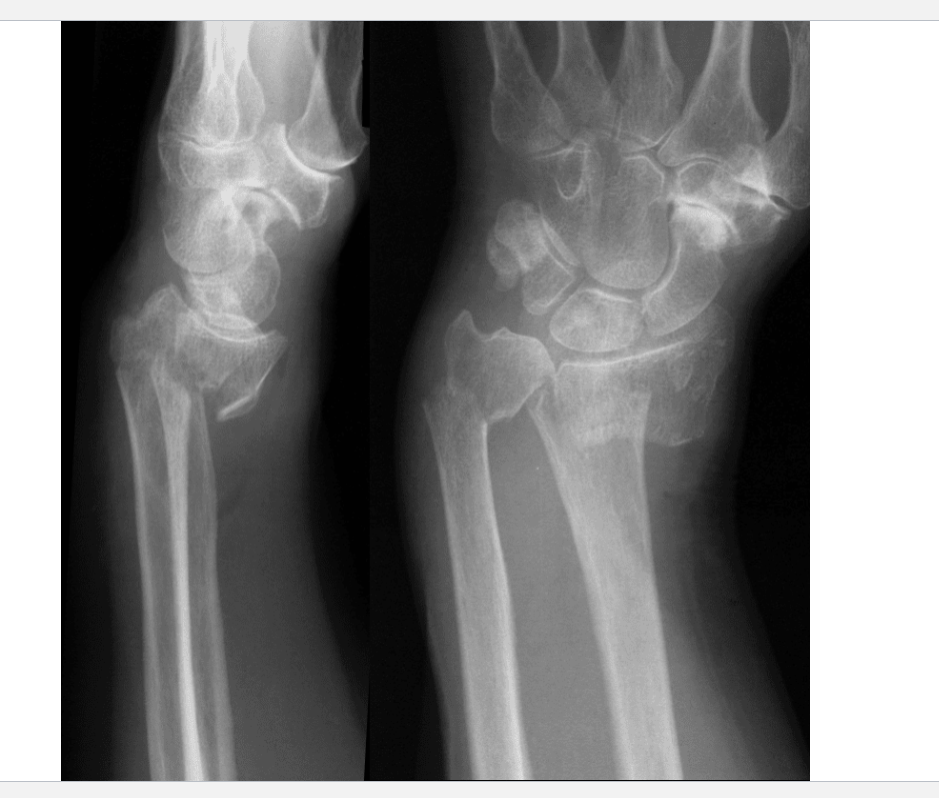
What is this?
Smith fracture
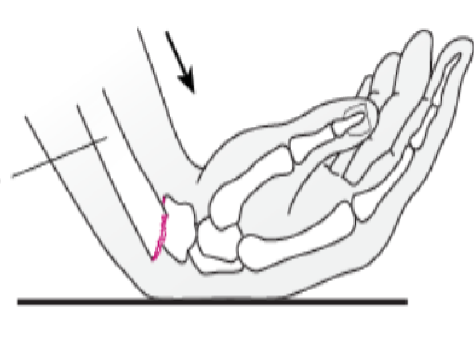
What is this?
Smith fracture
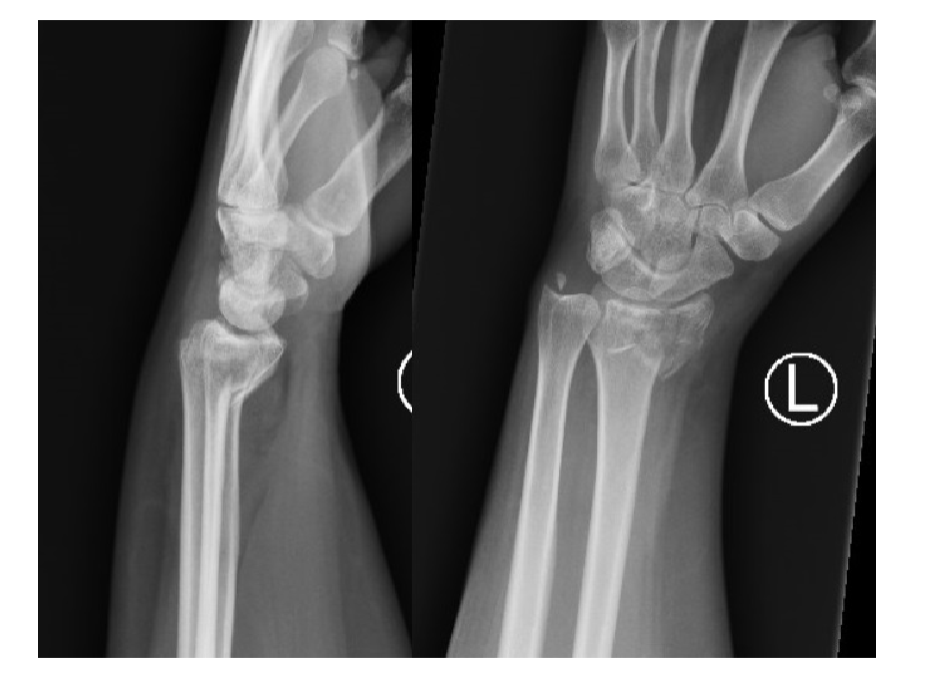
What is this?
Smith fracture
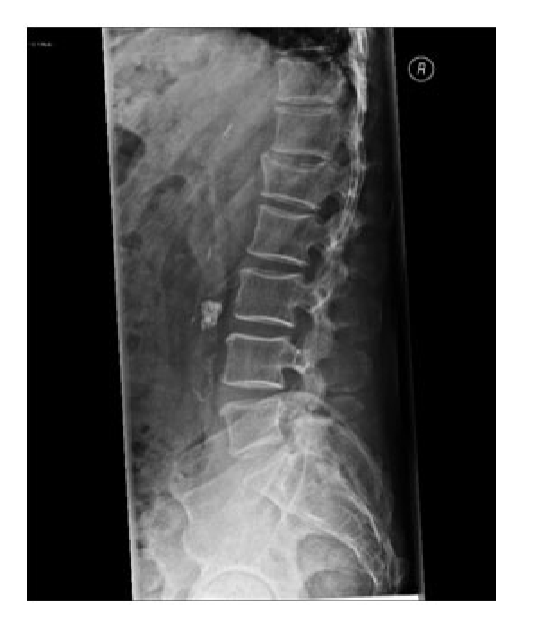
What does this show?
Vertebral compression fracture
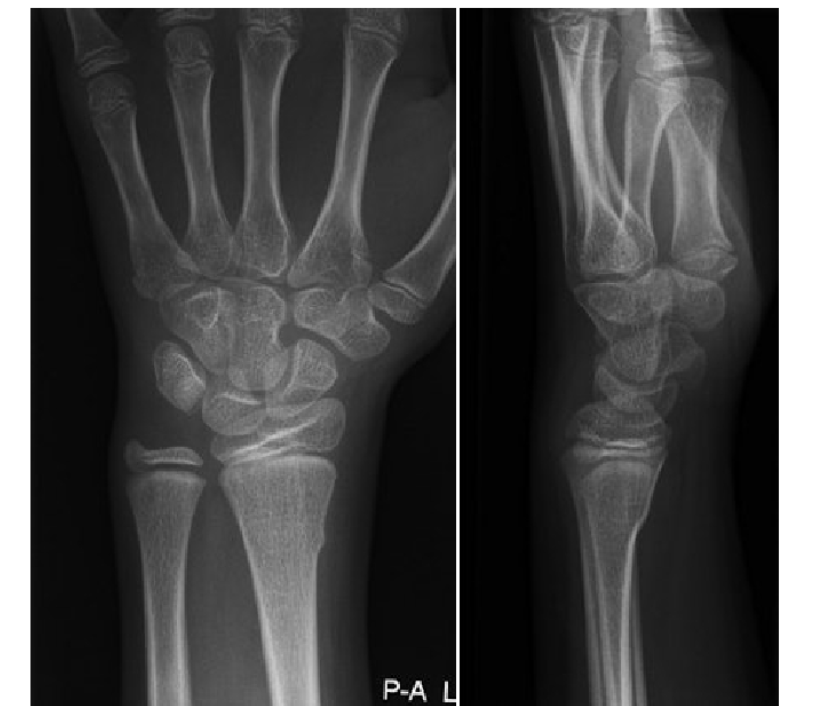
What is this?
Growth plates
What is this?
Cast treatment
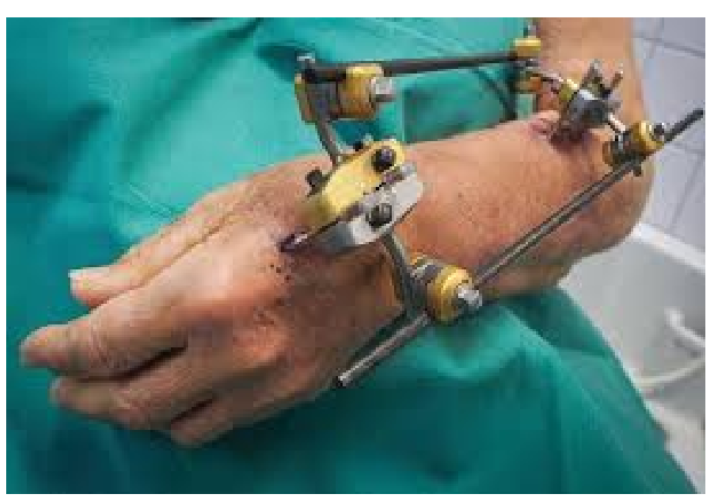
What is this?
External fixation
What is it called when you fix a distal radial fracture without opening the skin?
Closed reduction
What are the nutritional and lifestyle modifications that can be done to prevent osteoporosis?
Diet should be adequate in protein, total calories, calcium, and vitamin D, corticosteroid doses should be reduced or discontinued if possible, high impact physical activity (jogging) significantly increases bone density in both men and women, stair climbing increases bone density in women, weight training (increase muscle strength as well as bone density), and fall avoidance
List 5 high calcium foods (he asked this question as if it’s going to be an exam question, and you can remember this or other things if you find it easier).
Milk, yogurt, cheese, sardines, and salmon
What is the most important preventative lifestyle change for osteoporosis?
Fall avoidance
What are some things you can remove or be watchful for to decrease your chance of falling?
Loose rugs, cluttered floors, pets underfoot, wet or cracked paving, ice, and snow
What are things you can install and use to decrease your chance of falling?
Handrails on stairs, handholds in bathroom, and use of cane or walker