Bonding and Properties of Matter
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Ionic compounds
Giant structure of ions
Held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions
Forces act is every direction (3D)
Properties of ionic bonds / structures
High melting and boiling point → strong electrostatic forces between oppositely charged ions → lot of energy required to break bonds
Don’t conduct electricity when solid → ions in fixed positions
Conduct when molten or dissolved in water → ions are free to move
Ionic compounds neutrality
Ionic compounds are electrically neutral.
→ positive and negative charges balance each other.
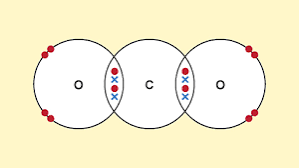
Simple covalent bonds characteristics
Do not conduct electricity (no ions).
Small molecules.
Weak intermolecular forces: Low melting and boiling points.
Intermolecular forces when increased molecule size
They increase. (more electrons)
→ melting/boiling points to increase as well → more energy needed to overcome these forces
Polymers
Large molecules with atoms linked by covalent bonds.
Strong intermolecular forces → solid at room temperature
Giant covalent structures characteristics
Solids: atoms covalently bonded together in a giant lattice
High melting/boiling points → strong covalent bonds.
Mostly don't conduct electricity (no delocalised e−).
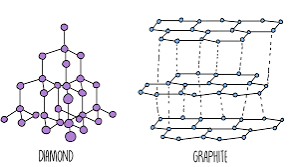
Examples of giant covalent substances
Diamond, graphite, silicon dioxide.
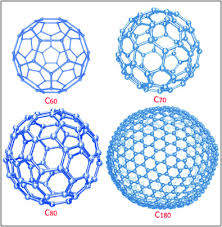
Fullerenes
Hollow shaped molecules based on hexagonal rings.
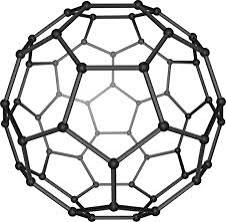
C60
A spherical shape, simple molecular structure known as Buckminsterfullerene.
Nanotubes
Cylindrical fullerene with high length to diameter ratio.
High tensile strength
Strong bonds present in nanotubes.
What causes conductivity in nanotubes?
Delocalised electrons.
Graphene
A single layer of graphite.

Diamond (giant covalent structure) characteristics
Has four strong covalent bonds for each carbon atom
very hard
very high melting point
does not conduct electricity (no delocalised electrons)
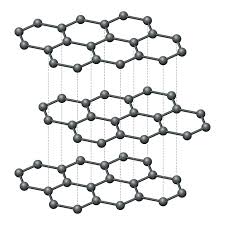
Graphite (giant covalent structure) characteristics
Has three covalent bonds for each carbon atom
high melting point
layers are free to slide → weak intermolecular forces → soft → used as lubricant
conducts heat and electricity → one delocalised electron per each carbon atom
Alloys and being harder than pure metals
Mixtures of metals with other elements, usually metals.
Different sized atom distort layers → harder for layers to slide over each other
Three states of matter
Solid, liquid and gas.
Nanoscience
Science that studies particles that are 1 - 100nm in size.
Nanoparticle
Small particles; 1-100 nm
Uses of nanoparticles
Medicine (drug delivery systems)
electronics
lubricants
catalysts
Sun tan cream, deodorant