Specimen Handling and Processing in Medical Technology
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Pre-analytical phase
Critical phase before specimen analysis for quality results.
Specimen rejection criteria
Reasons for rejecting specimens include hemolysis and contamination.
Delivery time limits
Specimens must reach the lab promptly, ideally within 2 hours.
OSHA requirements
Protective equipment mandated during specimen processing.
Mixing tubes by inversion
Gentle inversions of tubes to mix contents properly.
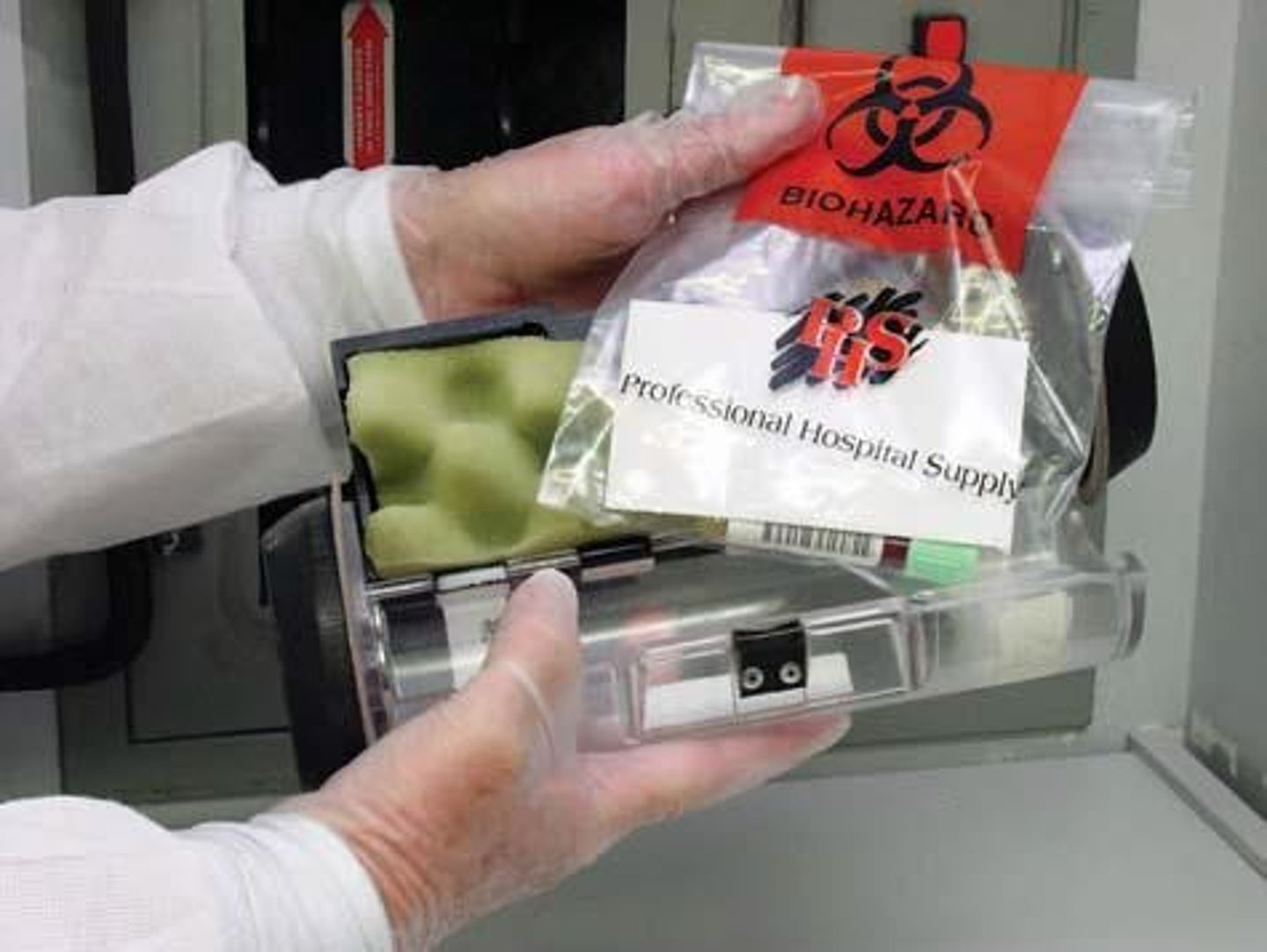
Transporting specimens
Use biohazard bags for blood; leak-proof for nonblood.

Chilled specimens
Stored at 2°C-10°C to preserve integrity.
Light-sensitive specimens
Bilirubin specimens must be protected from light exposure.
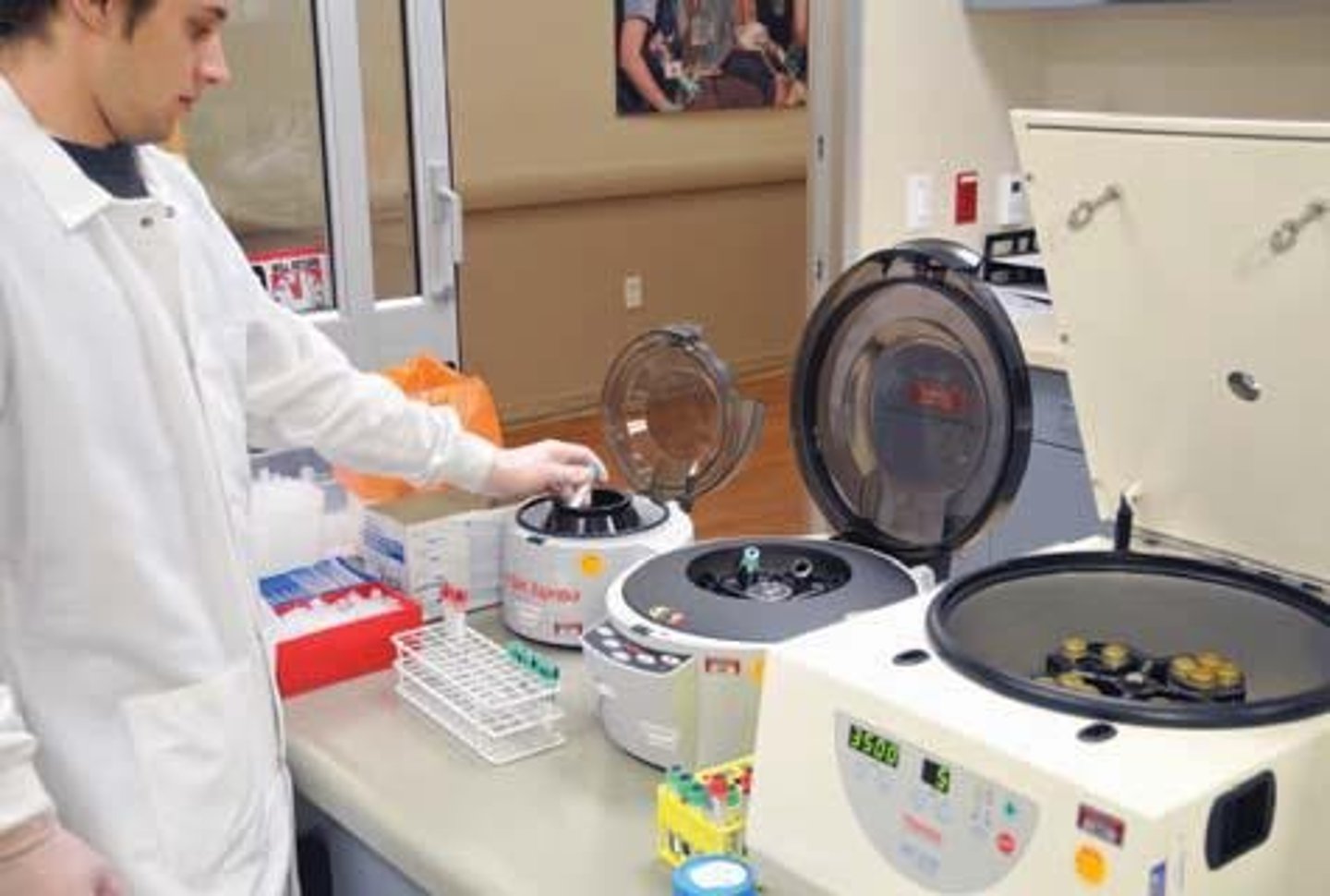
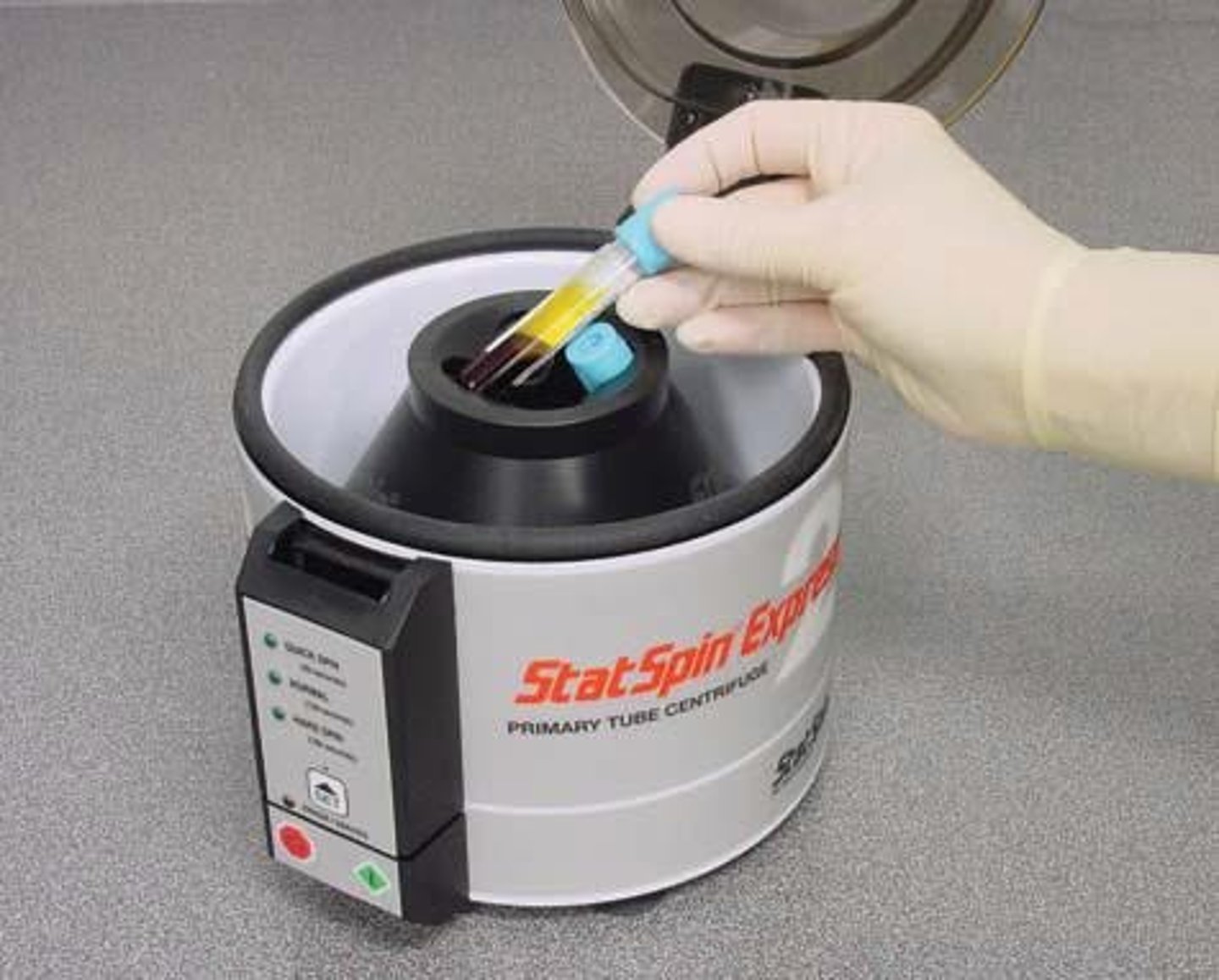
Centrifugation
Spinning specimens at high RPM to separate components.

Aliquot preparation
Portioning specimens for multiple tests or analyses.
STAT specimens
Emergency specimens requiring immediate processing.
EDTA specimens
Used for CBCs, ESR, and reticulocyte counts.
Centrifuge
Machine that spins specimens to separate fluids.

Specimen suitability
Criteria ensuring specimens meet testing requirements.
Transport containers
Secure lids essential for nonblood specimen transport.
Time limit exceptions
Specific tests may have extended processing times.
Contamination prevention
Keep stoppers on tubes before centrifugation.
Hemolysis
Destruction of red blood cells affecting test results.
QNS
Quantity Not Sufficient; specimen volume inadequate for testing.
Thrombin clot activator
Substance used to enhance clotting in blood tubes.
Biohazard logo
Indicates potential infectious materials in transport.
Specimen storage
Proper conditions necessary to maintain specimen integrity.
Centrifuging serum
Separating serum from cells after blood collection.