Muscle Tissues
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
muscle tissue
A group of muscle cells or fibers composed of organelles and inclusions like any other cells
Sarcolemma, sarcoplasm, flesh
In muscles tissue, _____ is the name of the cell membrane and the cytoplasm is called ______. The prefix “sarco” means _____
actin and myosin
In the muscle tissue, the ____ and ____ that comprise the myofilaments enable the muscle to perform the property of its sarcoplasm i.e. contractility responsible for locomotion/movement of the body.
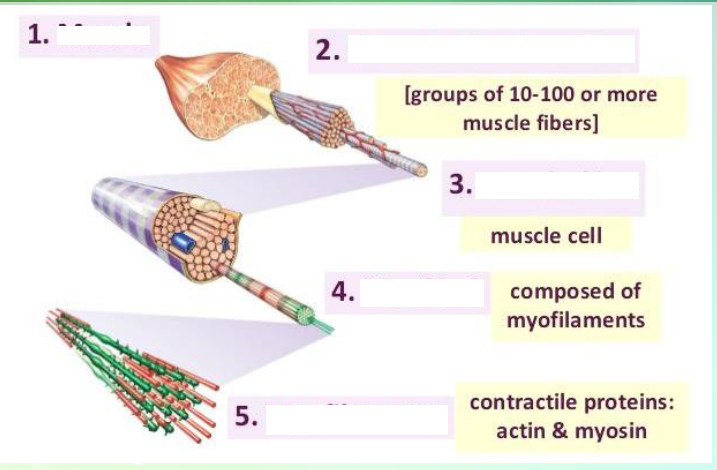
muscle
muscle fiber bundles
Muscle fiber
myofibril
myofilaments
Identify the structures
left to right
Triad
sarcoplasmic reticulum
T tubules
myofibrils
sarcoplasm
sarcolemma
terminal cisterna
identify the pointed structures
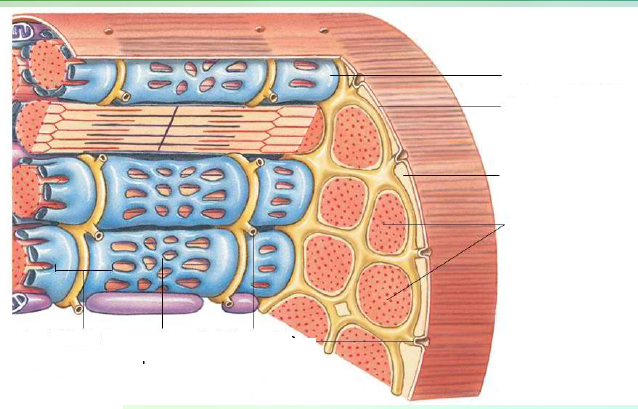
smooth/ non-striated /involuntary muscle
skeletal/ striated / voluntary muscle
cardiac/ striated/ involuntary muscle
What are the types of muscle tissue?
cells are elongated and spindle-shaped cells with tapered ends
nucleus is also elongated, centrally located
Describe the cell shape and nucleus of the smooth muscles
tightly packed
The muscle fibers of smooth muscle are _____ to form sheet.
longitudinal section
In ______, fibers of smooth muscle forms sheet that ae arranged in staggered fashion.
staggered
In smooth muscle, the middle portion of the fiber is adjacent to the tapered end of other fiber making the nuclei appear _____.
long, cylindrical, blunt, peripherally
In skeletal muscle, the fiber is ____ and _____ with ____ ends. Many of its nuclei are located _____.
cross-striations, sarcoplasm
Skeletal muscle’s special feature is __________ of the ______ oriented perpendicular to the long axis of the fiber
dark or A band, light or I band
The striations in skeletal muscles are the alternating ______ and ______
I band contains the fine/thin actin filaments
A band contains the thick myosin filament and overlapping ends of actin, that makes A band dark
Describe the I and A band
sliding of actin into the interstices of the myosin, Z lines, middle of the sarcomere
In skeletal muscle, the contraction of the sarcomere is the result of _________, where they are interdigitated, pulling the _____ until at full contraction. The free ends of actin meet in the ________.
H band
A contracted sarcomere has no _____.
Relaxed muscle
Partially contracted muscle
maximally contracted muscle
identify
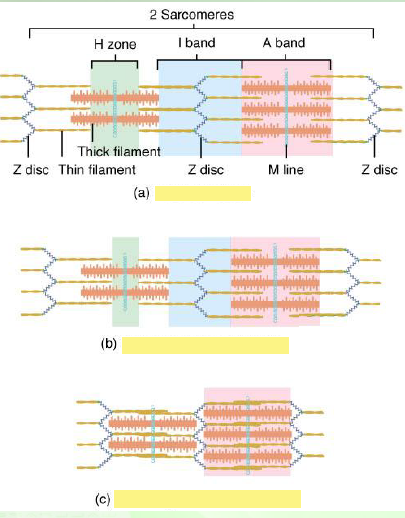
overextend, slide away, H band, A band
In a stretched sarcomere, the actin filaments ______ and _______ from the myosin, resulting to a wide ________ almost obliterating the _______
middle, ends
In relaxed or contracted sarcomere, myofilaments are longitudinal arrangement in the ______, extending to but not reaching the ____ of sarcomere.
Z line, middle of each adjacent sarcomere, H band
Actin filaments extend from the ______ toward the _______ in between the myosin filaments where they terminate in free ends before reaching the _______
fields of cohnheim
Skeletal muscle under the light microscope, group of myofilaments appear clumps of acidophilic dots called _______
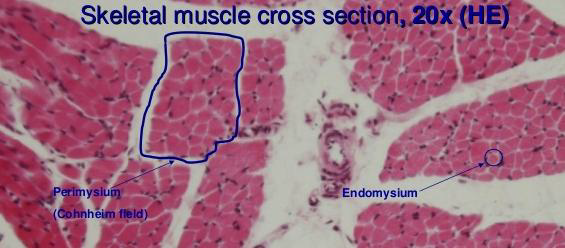
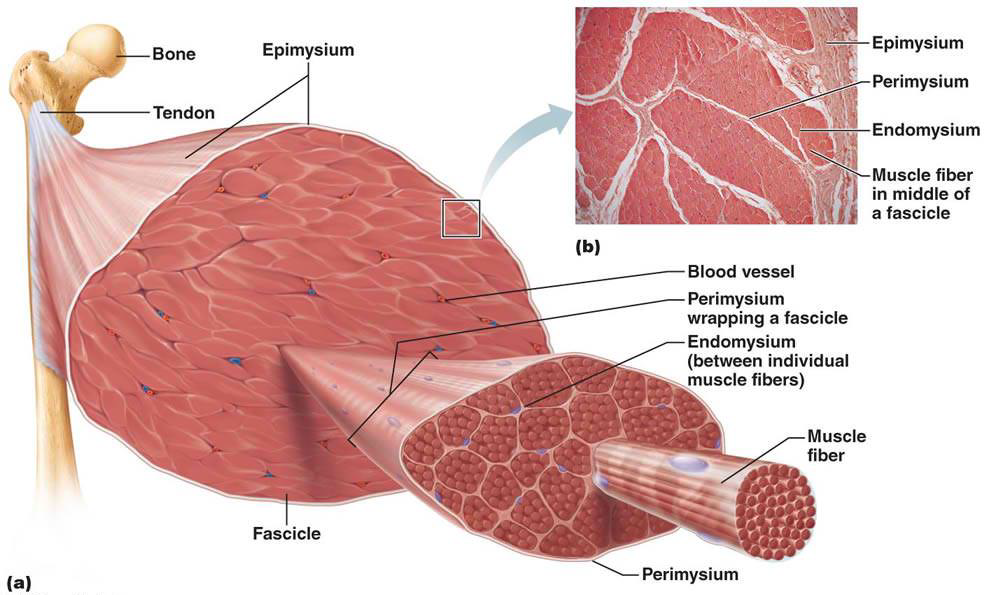
refer to this pic for the answers
identify the pointed structures
low
high
many
white
yes
fast
prolonged
high
low
few
red
no
slow
short
Type I Slow Twitch | Type II Fast Twitch | |
|---|---|---|
Myosin ATPase | 1 | 8 |
Energy Utilization | 9 | 2 |
Mitochondria | 3 | 10 |
Color | 11 | 4 |
Myoglobin | 5 | 12 |
Contraction rate | 13 | 6 |
Duration | 7 | 14 |
fill up the table
ordinary cardiac muscle
special cardiac muscle fiber or Purkinje fiber
2 types of cardiac muscles
cross-striations, smooth muscle, center
Ordinary cardiac muscle has _______ but functions like ______. Many of their nuclei are located at the ______ of elongated branched fiber.
vascular, intercalated disc
Ordinary cardiac muscles are highly _________ and have ______, running transversely on the longitudinal axis of the fibers.
the point of end to end contact of the muscle fibers
what does the intercalated disc indicates?
fiber-impulse conducting cells, A-V node to IV septum
Special cardiac are _______ located from _____ to ______
Smooth muscle - regeneration is limited, healing is through connective tissue formation
Skeletal muscle - regeneration is limited, healing is through scar tissue formation
Cardiac muscle - do not regenerate, healing is through scar formation
Provide the Regeneration and Repair characteristics of the 3 types of muscles