THE DESIGN AGENDA (an approach to the sequence of house design issues)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Making connections
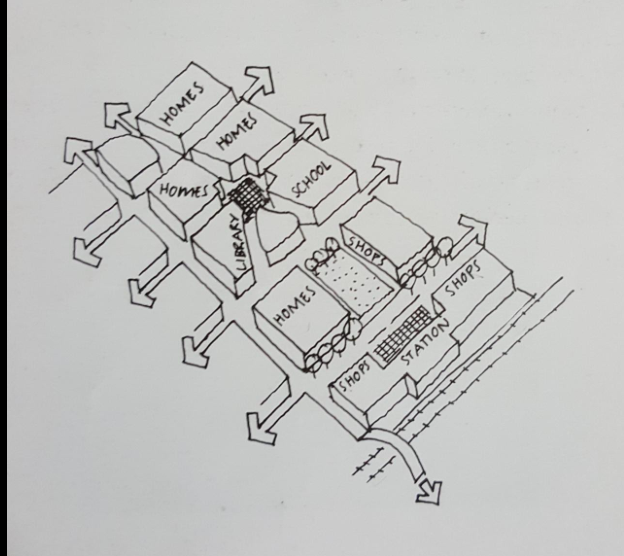
Grids facilitate connections. They do not have to be
orthogonal and rigid and can take on many forms and
shapes. The key is that grids provide permeable
movement networks
Making connections
Permeable or connected movement networks (streets,
paths and public spaces) provide choices for pedestrian
routes. Maximizing choice encourages people to walk or
cycle
Making connections
Providing green areas and corridors
important elements in place-
making: they enhance the legibility of a place and
increase the variety of users in a place
Providing green areas and corridors
an be for biotic
support and public amenity – these can be part of
the public or private realm, and some can be
specifically for biotic support only
Providing green areas and corridors

Treating the street as a place
With permeable movement networks and the
focus on choice and pedestrian activity, it is
important to minimize car dominance and make
streets into safe and attractive places to be
Laying out the built form
Permeable movement networks are not effective
and safe unless they are complemented by a
building form that defines the routes and spaces
Laying out the built form
By orientating “active” fronts to streets and
public spaces, and inactive “backs” to the
private realm, activity is encouraged in the streets
and public spaces, and security and privacy is
maintained in “back” spaces or courts
Absorbing diversity
The flexibility of the perimeter block form can absorb
different residential building types from apartment
buildings to terraced houses, as well as other uses
Absorbing diversity
Perimeter blocks also facilitate the integration of
different housing tenures, without having to create
completely separate buildings, which then often have
problems with the use and management of the
spaces between the buildings. With a terraced and
perimeter block form, buildings can still have
separate accesses from the street, each with their
own entrance
Absorbing diversity
The flexibility of the terrace form and the perimeter
block also encourages a variety of architectural
treatments and a range of expressions
Absorbing Diversity: Different building types a
efining public and private space
Built form should mediate between public and private
space
•This gives residents the opportunity to choose between
activity and privacy
Creating a relationship between buildings and spaces
Buildings can affect the quality of public spaces in two
ways: the way the uses interface with the space; and
how volume and mass frames or encloses the space.
These are all important considerations for the legibility
of streets and spaces
Creating a relationship between buildings and spaces
Building fronts should always face the public
realm, whether it is a street, public walkway,
park or square
Arranging the building mass
often a factor of required
densities for housing projects. High density
need not be negative, and if the building mass
is sensitively and appropriately arranged, the
places created can be very positive
Optimizing solar potential and good aspect
Sensitive orientation of buildings are more energy
efficient through passive solar gain, daylight, photovoltaic
modules and solar panels
Managing and integrating parking
Ideally, with parking in the streets, pedestrian safety
should not be compromised relying on good layout and
street landscaping and still keeping good activity in the
street
Managing and integrating parking
Decking over parking between buildings inside a block
can be a very positive move – parking requirements are
met, the cars do not dominate, and an amenity space for
the residents can be created on the deck. It is important to
maintain activity on the ground floor of the building
especially when it faces the public realm
Providing frequent and convenient access
Entrances to buildings should be from the street (public
realm) and as frequent as possible with buildings narrow
and closer together in a terrace form
Mixing uses/recycling/building in flexibility
key dimension of
sustainable high density urban housing, providing
facilities and amenities for residents and a varied and
active public neighbourhood
Providing spaces around the home
orm important interfaces
between inside and outside, private and public space.
These interface spaces can also be used as private
screens
Meeting the ground – thresholds and interface
Interfaces between the buildings and spaces
control the privacy of homes and safety in the
spaces beside. Where the buildings are high
enough
Meeting the ground – thresholds and interface
Where buildings are only two or three storeys
high (usually houses) and the streets are not of
the narrow mews type, other mechanisms must
be used to protect privacy, while enhancing
surveillance of the street.