Organic Chemistry Midterm 1 Content
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 13, 14, 15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Nitration reagents and product
HNO3, H2SO4. Adds nitro (-NO2) group.
Sulfonation reagents and product
SO3,H2SO4. Adds sulfonic acid (-SO3H) group.
Halogenation reagents and product
Br2, Cl2, and AlX3. Adds halogen (-X) group.
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation reagents and products
Alkyl halides and AlX3. Adds alkyl group (-R) to aromatic ring.
Friedel-Crafts Acylation reagents and products
Acyl halides (C=O with attached chlorine halogen) and AlCl3. Adds acyl group (-C(O)R) to aromatic ring.
Benzylic oxidation reagents and products
1)KMnO4, H2O
2)HCl
OR
1) Na2Cr2O7 (or K2Cr2O7), H2O
2) H2SO4, heat
Turns benzylic hydrogen into carboxylic acid (C=O with OH attached).
Nitro reduction reagents and products
H2, Pd
OR
1) Fe (or Sn), HCl
2) NaOH
Converts nitro group (-NO2) to amine group (-NH2) on aromatic ring.
Wolf-Kishner reduction reagents and products
1) NH2NH2, KOH, HO(CH2)2OH
Turns ketones into alkyl groups.
Clemmonson reduction reagents and products
1) Zn(Hg), HCl
Just reduces ketones to alkyl groups.
2) NaOH
Additionally reduces nitro groups to amines.
Nitration can’t happen with:
Amines (-NH2), explosive
Halogenation cant happen with:
Amines (-NH2), alcohols (-OH), and ethers (-OR). Polyhalogenation occurs (halogens in all ortho/para positions).
Organolithium prep reactants and products
R-X + 2Li —> R-Li + LiX
Grignard prep reactants and products
R - X + Mg —> R - MgX
Organometallic reagent and what gives a primary alcohol?
Formaldehyde H2(C=O) w/ Et2O and 2)H3O+
Organometallic reagent and what gives a secondary alcohol?
Aldehyde R(C=O)H w/ Et2O and 2) H3O+
Organometallic reagent and what gives a tertiary alcohol?
Ketone R2(C=O) w/ Et2O and 2)H3O+
CH3MgBr, Et2O, 2) H3O+ with alcohol gives what?
Deprotonated alcohol + CH4. Essentially no net rxn for alcohol compound of interest.
What reagent can be used instead of an organometallic one?
Sodium acetylide. (R-CN-H) + NaNH2 = Acetylide ion (R-CN:-)
Organometallic reagent w/ ethylene oxide and H3O+
Forms primary alcohol w/ 2 carbons as substituent.
What double bonds does H2, Pd reduce? What reaction is this?
Nitro reduction. Turns both C=O AND C=C (except aromatics) into single bonds. Turns C=O into C - OH
What bonds does NaBH4 , MeOH reduce?
Reduces aldehydes to primary alcohols, and ketones into secondary alcohols.
Mechanism for NaBH4, MeOH with a ketone
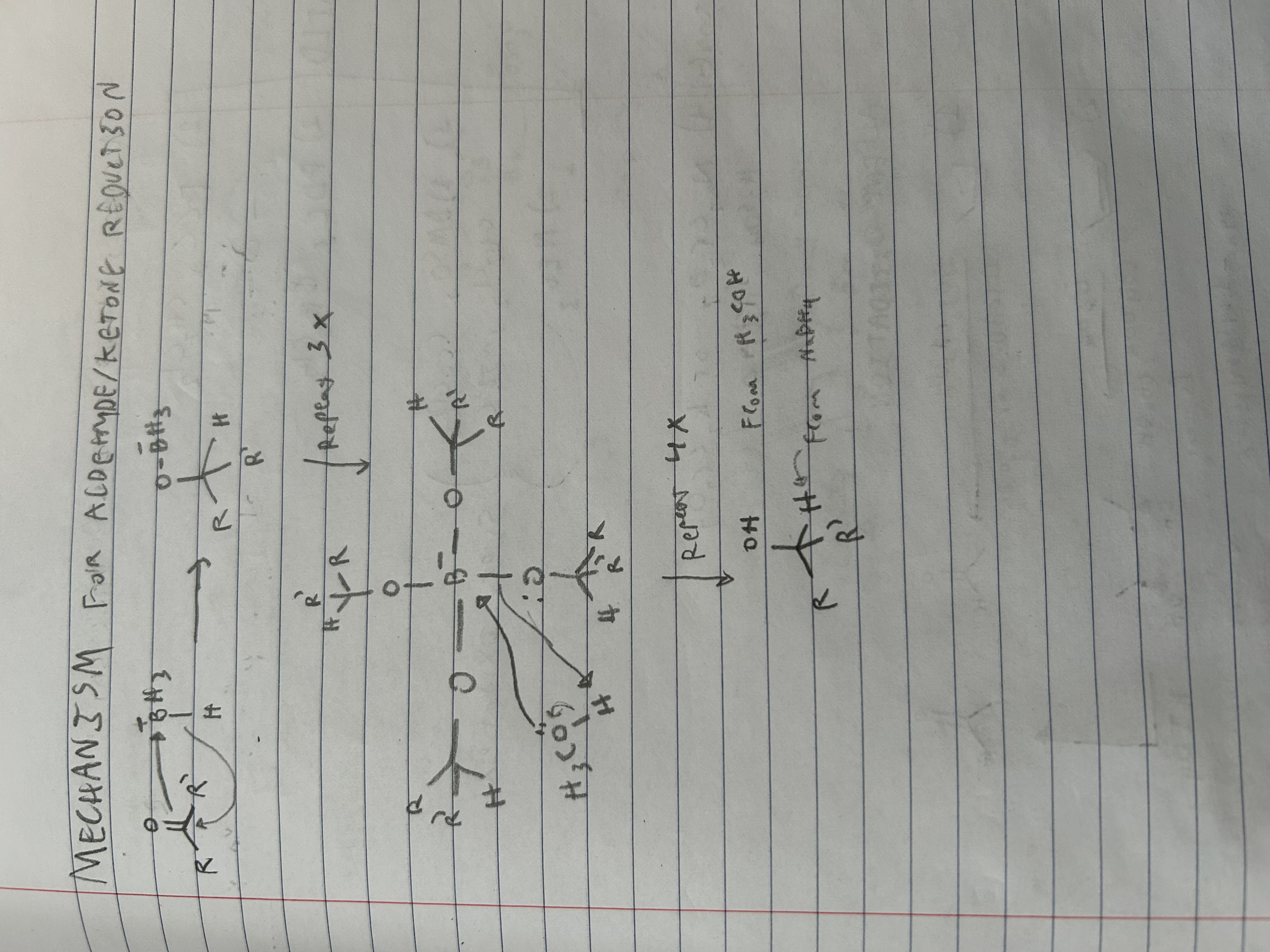
What bonds does 1) LiAlH4, Et2O 2) H3O+ reduce?
Aldehydes to primary alcohols, ketones to secondary alcohols, CARBOXYLIC ACID TO PRIMARY ALCOHOL! R(C=O)OH → R-COH
How can tertiary alcohol be reduced/oxidized?
It can’t, you need an H-C bond at the alpha position for oxidation. Reduction is ridiculous, you’d need a double bond and 3 substituents, which is not possible.
What does PCC, CH2Cl2 do?
Oxidizes primary and secondary alcohols into aldehydes and ketones respectively.
What does PDC, CH2Cl2 do?
Oxidizes primary and secondary alcohols into aldehydes and ketones respectively.
Swern oxidation. 1)DMSO, (COCl)2, CH2Cl2 ~78°C 2)NEt2
Oxidizes primary and secondary alcohols into aldehydes and ketones respectively.
Na2Cr2O7, H2SO4, H2O, heat.
Can use Kr2Cr2O7 as well.
Benzylic oxidation! Turns primary alcohols into CARBOXYLIC ACIDS. Turns secondary alcohols into ketones.
1) O3, CH3OH
2) (CH3)2S (or H2O, Zn)
Ozonolysis to split C=C into two C=O bonds.
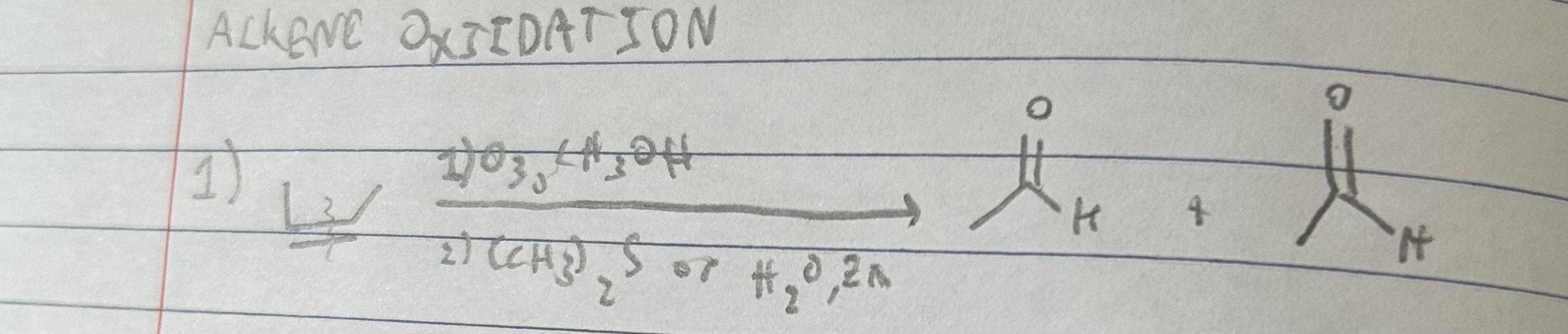
1)OsO4, tBuOOH, tBuOH
2)HIO4
Vicinal diol into split aldehydes (be wary of other substituents).

Ether synthesis from ethanol reactants and mechanism
Primary alcohols only.
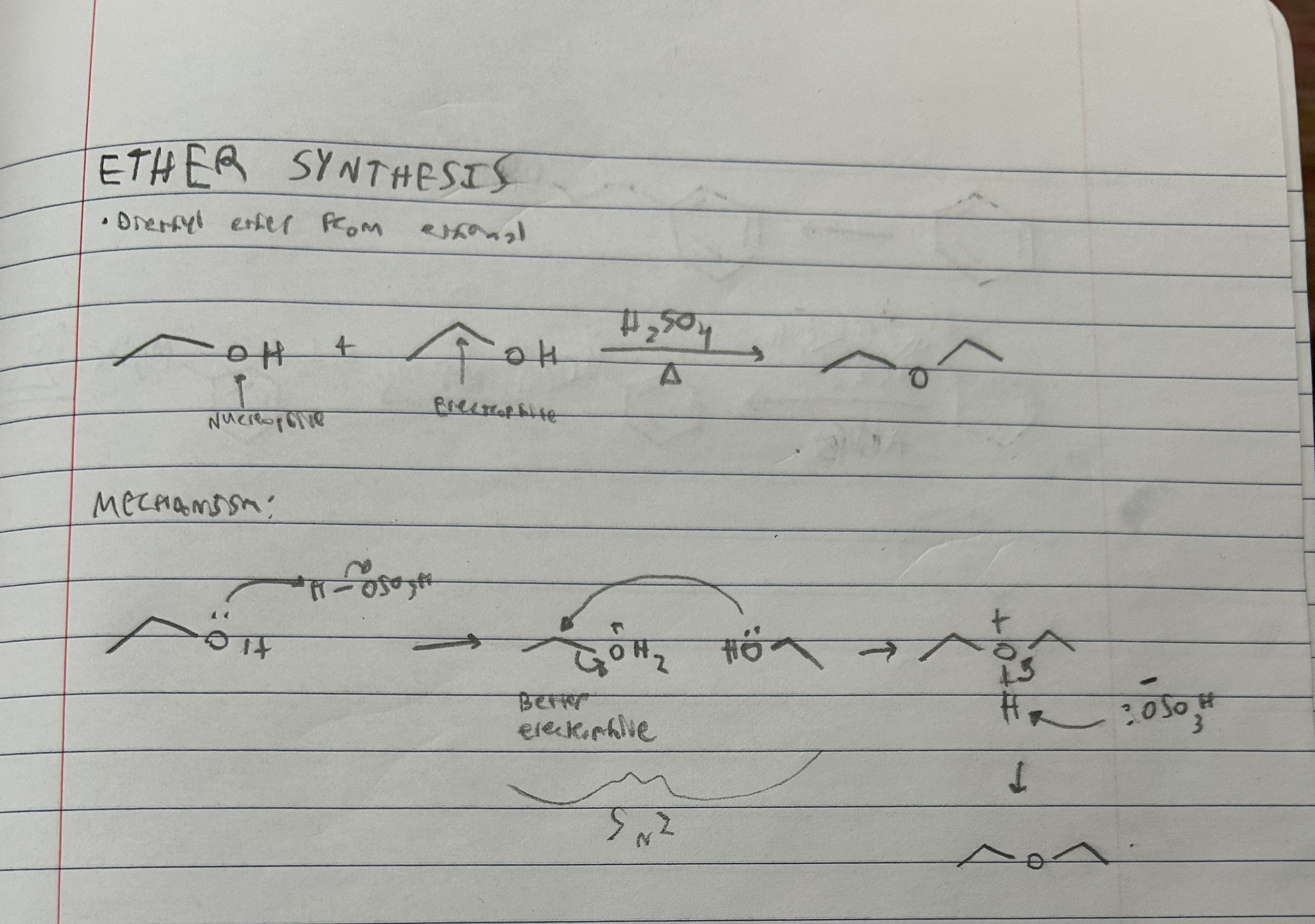
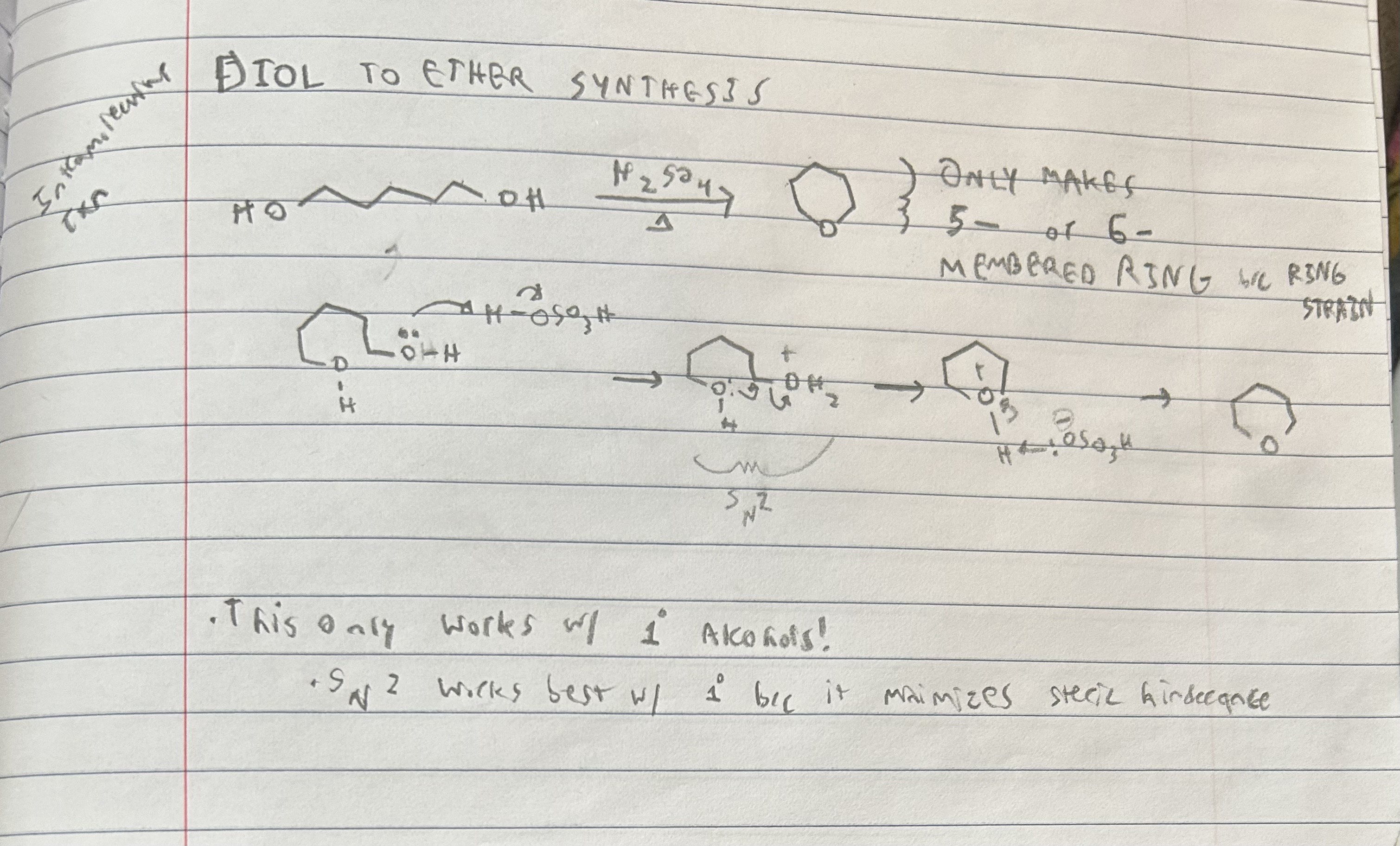
Diol to ether synthesis reactants and products
Must for a 5-6 membered ring. Primary alcohols.