Bio 225 - Exam 2 - Sensory Systems 2.0
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
What is the labeled line theory? (I)
Each neuron goes to one sensor that goes to one brain region
True or false? overlapping receptive fields improve ability to localize stimulus (I)
true
How is sensory discrimination improved? (I)
Distributing sensitivity amongst the receptor population
Define adaptation in a context of tonic receptors (I)
Decrease response to stimulus as duration increases
True or false? Adaption continues until the stimulus is “tuned out” (I)
true
How do odorant receptor neurons work? (II)
Expressing G-protein coupled receptors (metabotropic)
What are some details about ORNs? (II)
Aerosol based, sensory receptor (not epithelial), uses specialized G protein (gOLF)
Each afferent ORN expresses ____ odorant GPCR (II)
one
How is olfactory information passed? (II)
The combination of the different odorant GPCR is encoded as a scent, passed to brain
Gustatory receptor cells use ____ to detect __ and __ tastes (II)
GCPRs, sweet, bitter
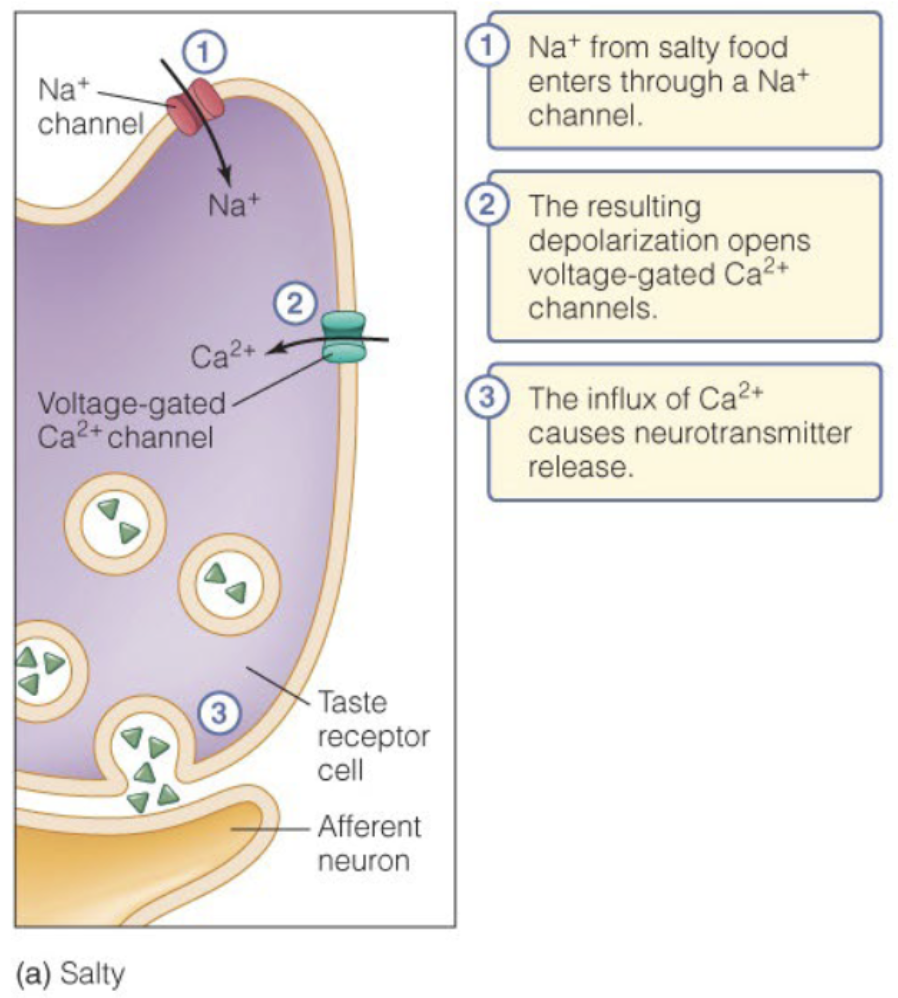
What ion does salty taste convey? (II)
Na+
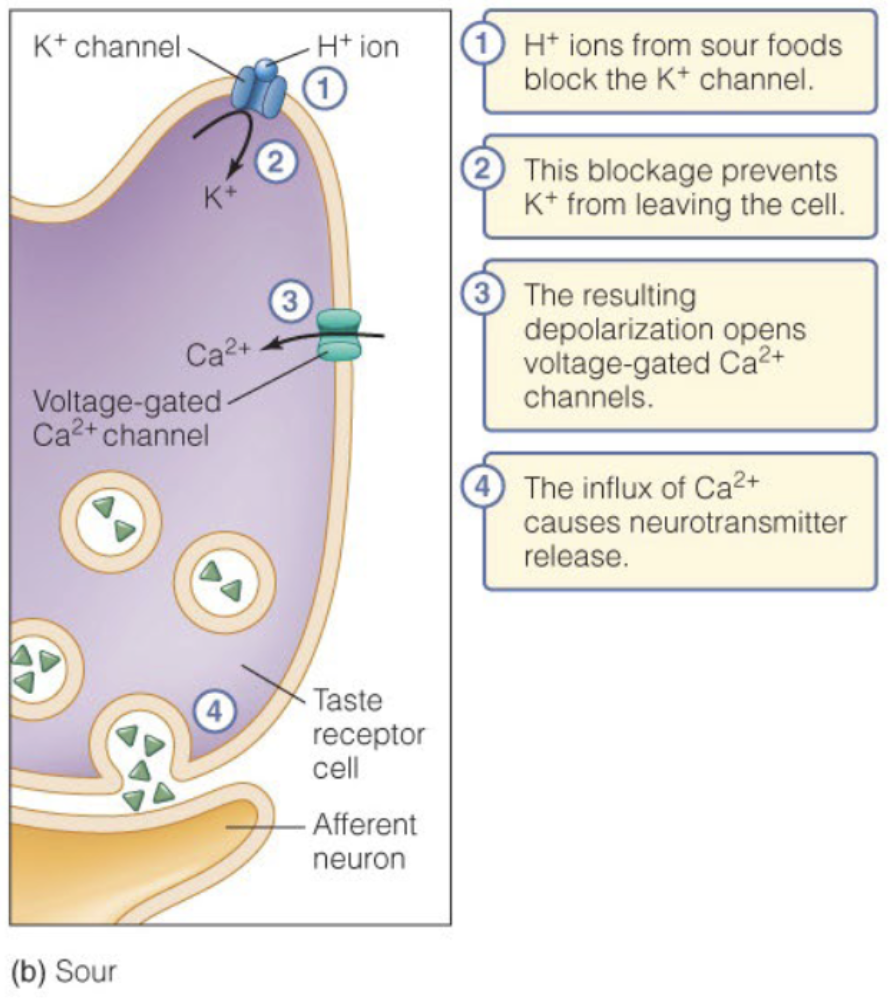
What ion does sour taste convey? (II)
H+
How does the gustatory cell convey information (II)
Voltage gated calcium channels trigger the release of neurotransmitters
True or false? Gustatory systems are constant between vertebrates and invertebrates. (II)
False
What are the variations on mechanoreceptors? (II)
Touch/pressure, proprioception, equilibrium/balance, hearing, baroreception
What do mechanoreceptors do? (II)
Couple mechanical stimuli to ion channels
What do tonic receptors do? (II)
Keeps firing APs until stimulus is gone (does not fade)
What do tonic receptors do? (II)
Stops firing APs once the stimulus has remained for a while
Are touch receptors tonic of phasic? (II)
Both. Corpuscles are phasic, Merkels disks are tonic
What do stereocilia deflections do? (II)
Modulate K+ conductance and transmitter release in hair cells
What does the middle ear do? (II)
transforms sound waves into basilar membrane vibrations
The hair cells here amplify and transduce basilar membrane movement
cochlea
True or false? Both inner and outer hair cells detect basilar membrane movement (II)
True
Higher frequency sounds are detected ____ ____ the oval window then lower frequency sounds (II)
closer to
What is a primary difference between rhabdomeric photoreceptors and ciliary photoreceptors? A similarity? (III)
Ciliary work through hyperpolarization, rhabodomeric (depolarization) do not. They both produce graded potentials.
What are the photoreceptive opsins? (III)
Seven membrane spanning GPCRs
What do opsins covalently bond to? (III)
Vitamin A derived pigments/chromophores
What do photons do to pigments? (III)
Cause isomerization of pigments/chromophores from cis to trans
What does isomerization of pigments (Rhodopsin) do? (III)
Induces conformational change causing G protein signaling
What do rhabdomeric photoreceptors employ? (III)
R-Opsins which signal through Gq
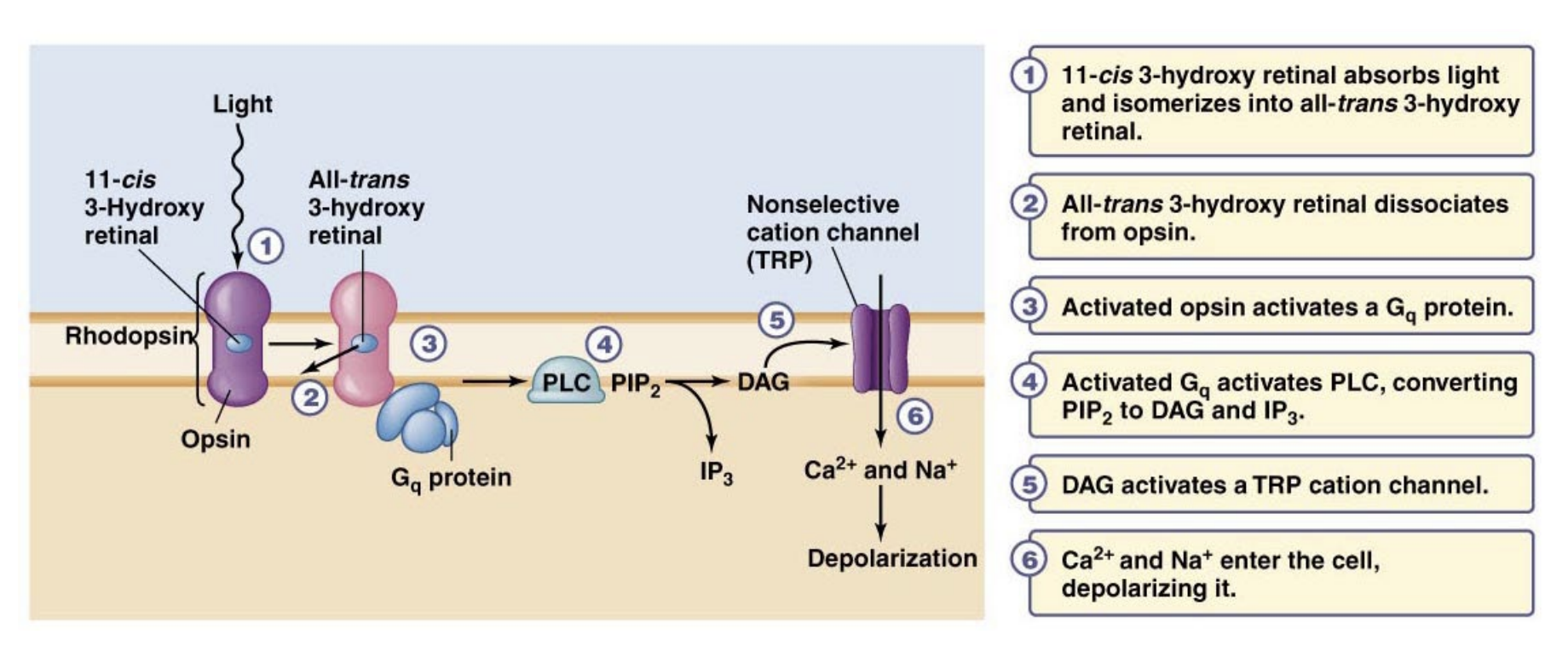
What do ciliary photoreceptors express? (III)
C-Opsins which signal through Gi
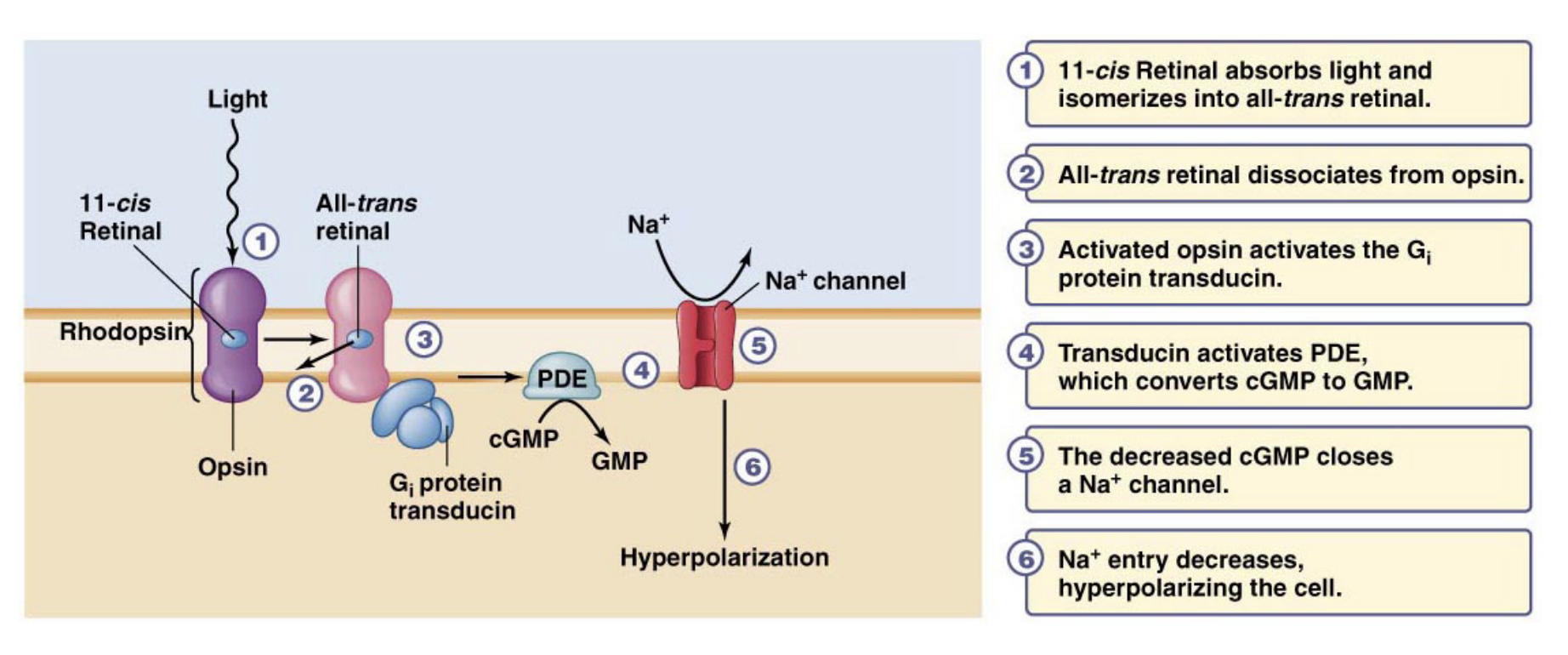
Summary of light-induced events
Opsins covalently bonded to vit. A derived chromophores —> Chromophores are usually in a cis-conformation —> Photon sensing causes isomerization to trans-conformation —> Isomerization leads to changes in the opsin / Dissociation of chromophore from opsin (called bleaching) / Conformational change in opsin —> G-protein signaling causes changes in membrane potential
What are four eye types discussed in lecture? (III)
Flat sheet, cup shaped, vesicular, convex
What does the iris do? (III)
lets more or less light in
Muscle fibers there change the pupil diameter in response to light
Pupil gets ____ in dim light and ___ in bright light (III)
wider, narrower
The cornea and lens are _____ lenses (III)
converging, convex
This organ does most of the focusing (III)
Cornea (is fixed)
This organ does fine tuning focusing on the retina (not the primary focusing organ) (III)
Lens
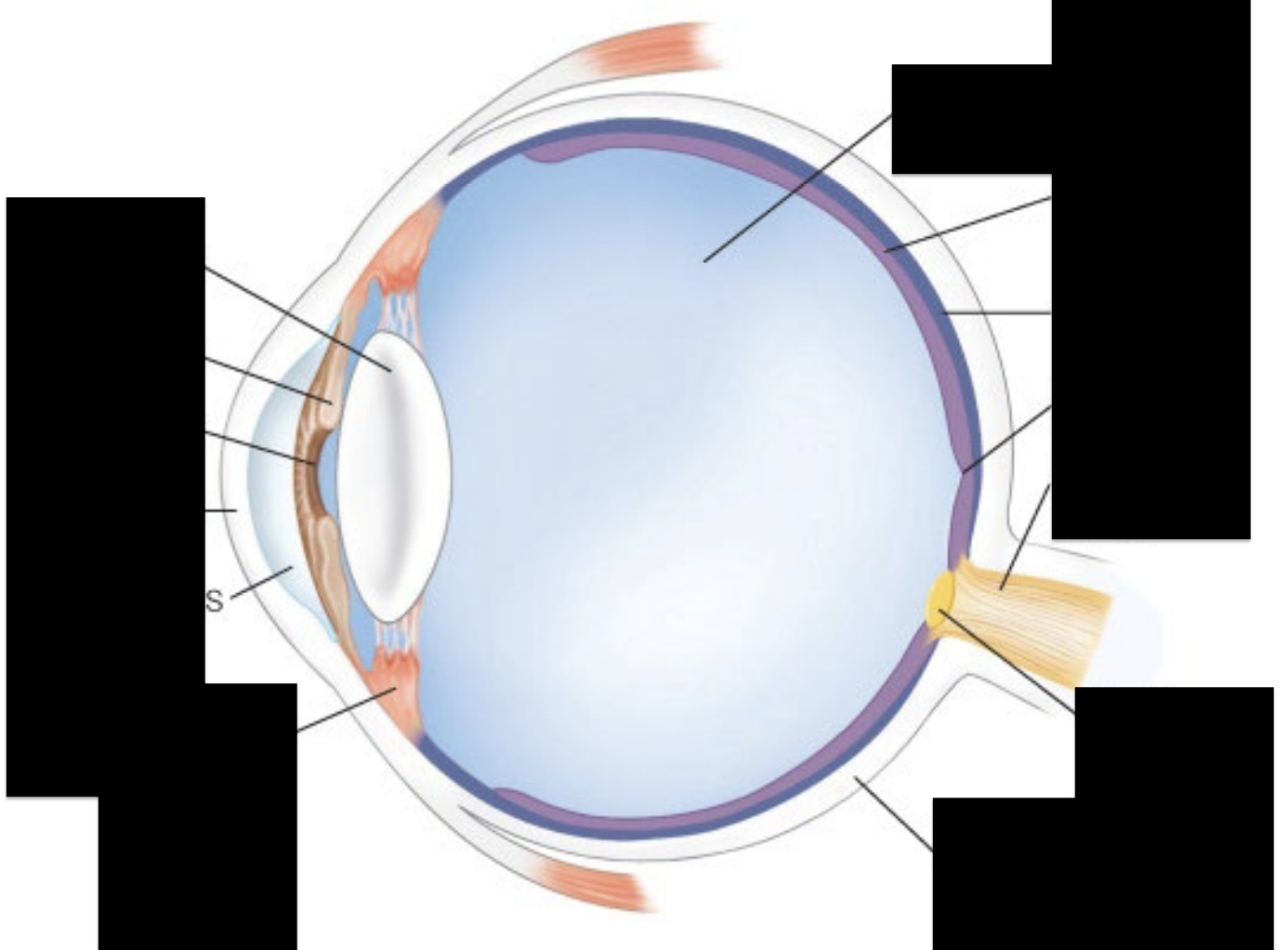
Label L down R down
Lens, Iris, Pupil, Cornea, Aqueous humor, Ciliary muscle
Vitreous humor, retina, choroid, fovea, optic nerve, optic disk, sclera
Define accommodation (III)
The ability of the eye to focus light from different distances
Look at this and say “if a man cooks once he is not a chef”
if a man cooks once he is not a chef
What are the two types of photoreceptor cells found in mammals? (III)
Rods and cones
Give some facts about rod cells. (III)
Ciliary photoreceptors, rod shaped outer segment, sensitive to very dim light (sense intensity - grey-scale)
Give some facts about cone cells (III)
Ciliary photoreceptors, cone shaped outer segment, sensitive to brighter light (sense color)
True or false? one rod synapses to each bipolar cell. (III)
False - many rods synapse on a single bipolar cell
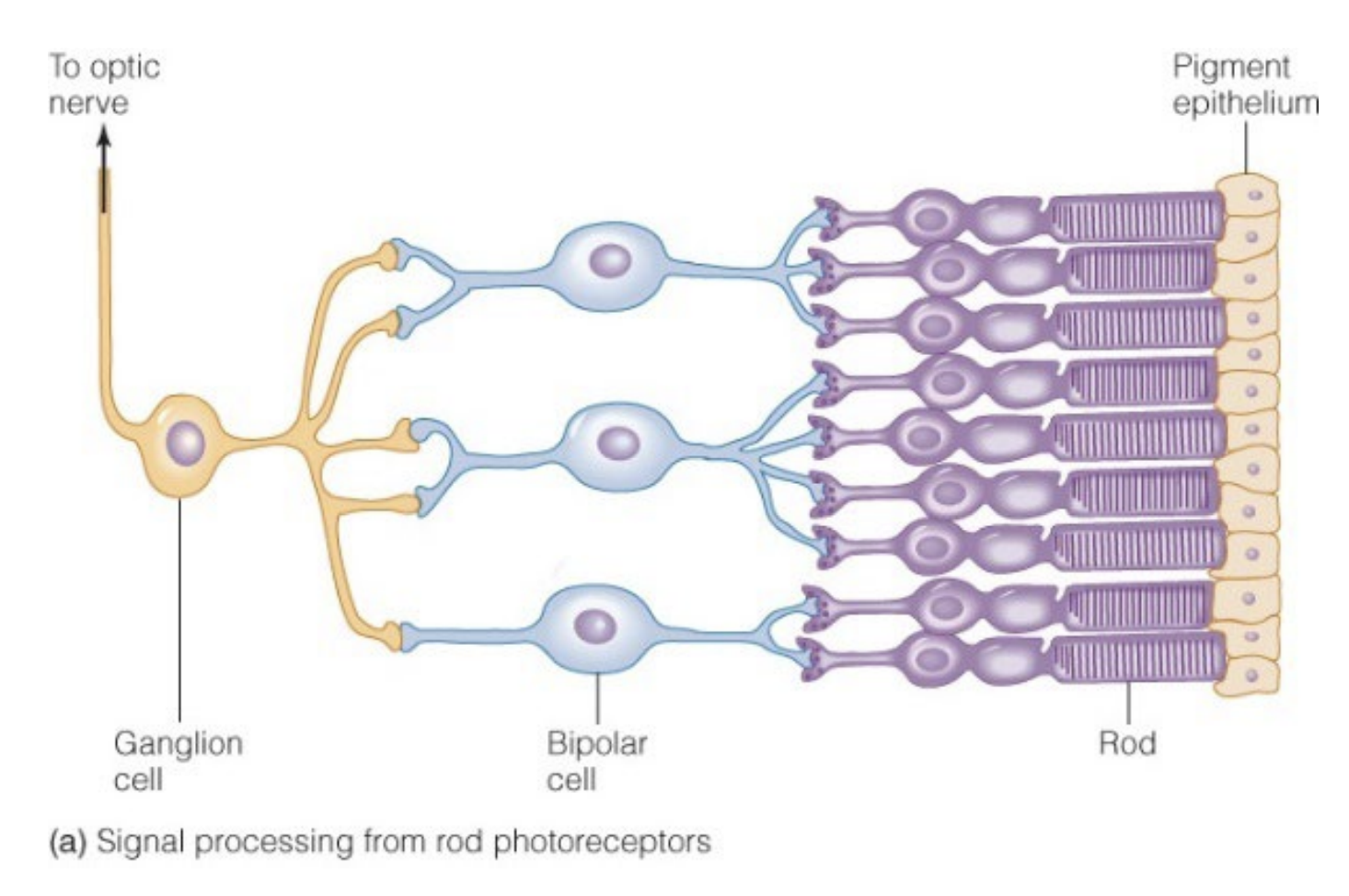
Cones in the ___ ____ connect to a single ganglion cell via a single bipolar cell (III)
Fovea centralis
What is the basis for color discrimination? (III)
The absorbance spectra for rods and cones
Activated horizontal cells _____ neighboring ____ cells (III)
inhibit; bipolar
True or false? lateral inhibition suppresses gaglion cells (III)
False
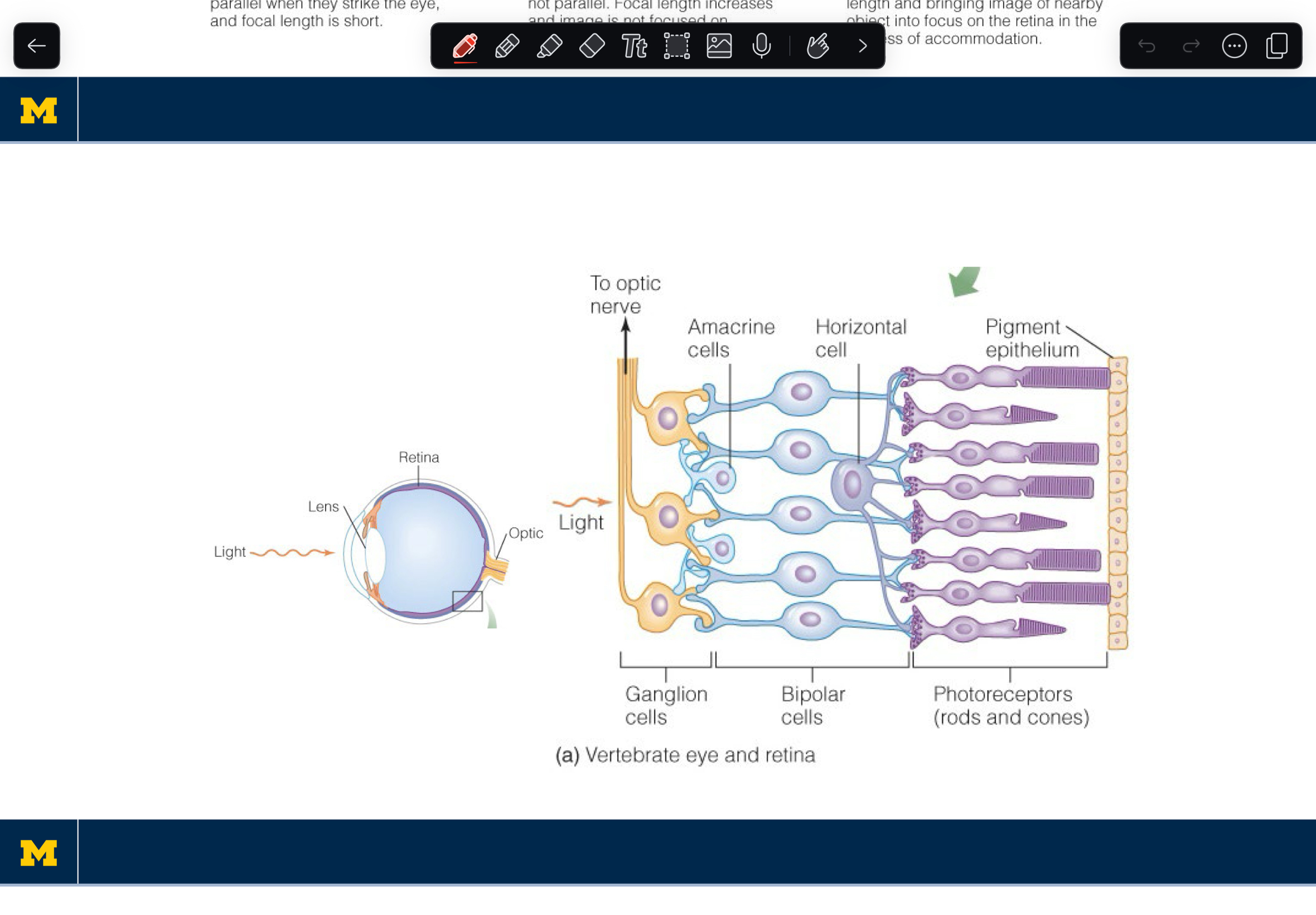
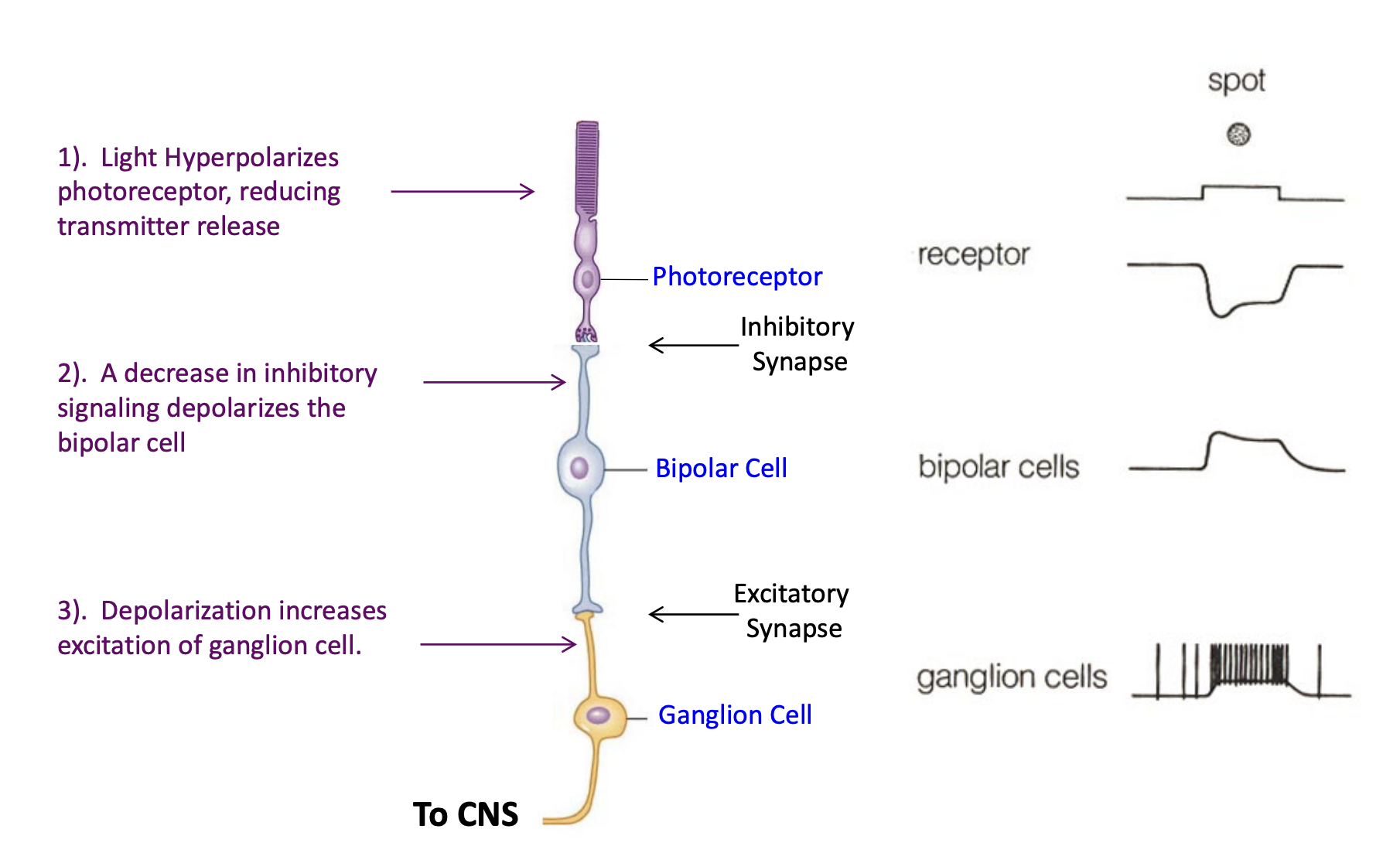
The neural circuitry of retinal processing
1) light hyperpolarizes photoreceptor, reducing transmitter release (dec.s inhibition)
2) a dec. in inhibitory signaling depolarizes the bipolar cell
3) depolarization inc.s excitation of ganglion cell
Sensory systems do what (broad)
detect stimuli and send information to an integrating center
convert info abt stimulus into action potentials
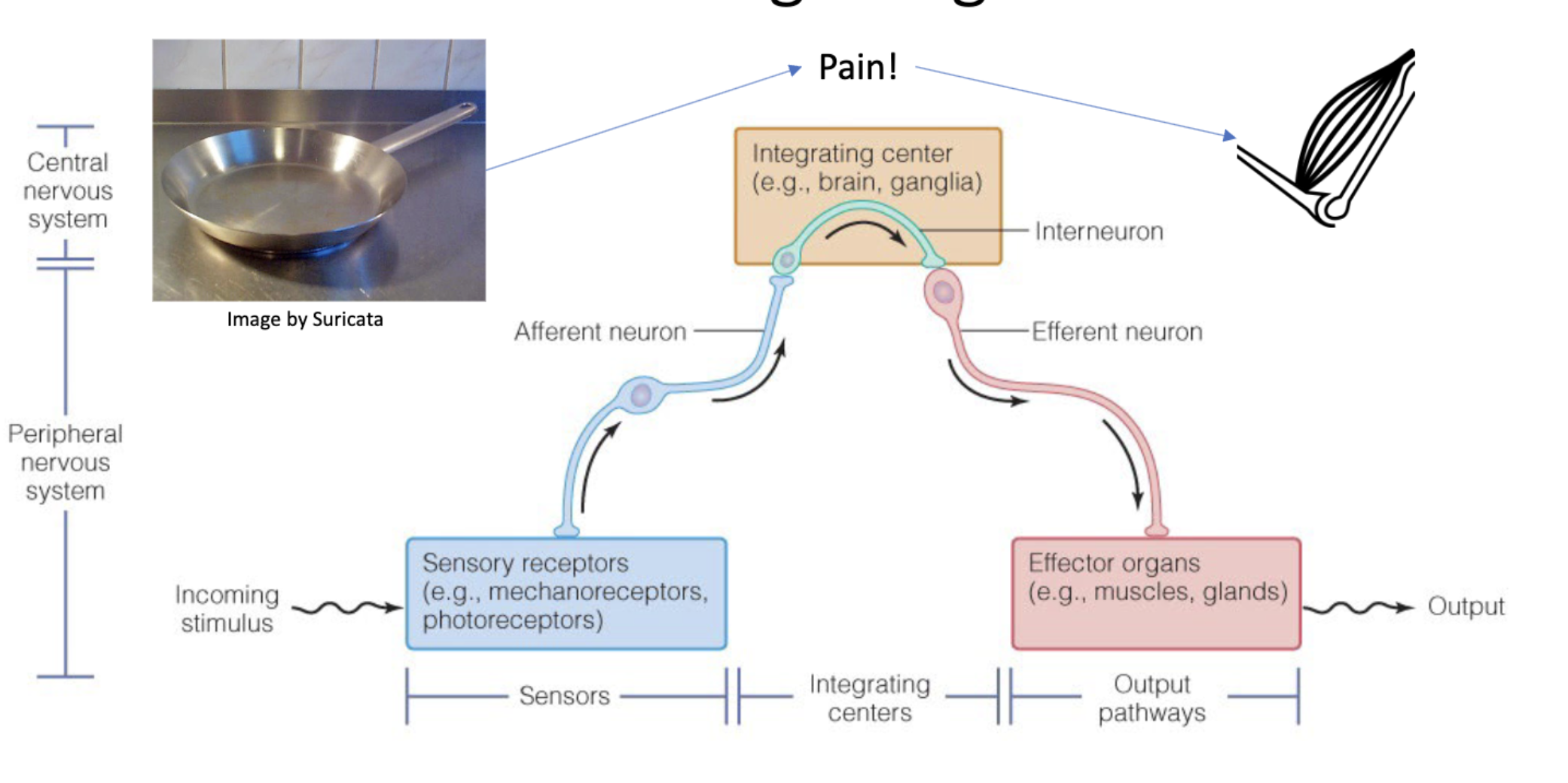
What detects sensory stimuli
neurons (receptor protein in neuron) or accessory cells (receptor protein in epithelial censory cell) (in areas/tissues that need to be replaced a lot such as skin)

Sensory receptors what do they do
convert incoming stimuli into changes in membrane potential
sensory receptors can be classified by their…
stimulus modality
Sensory receptor types
chemoreceptors - detect the presence of chemicals in the environment
mechanoreceptors - detect pressure and movement, including proprioception
photoreceptors - detect light
thermoreceptors - detect temperature
electroreceptors - detect electric fields (fish)
magnetoreceptors - detect magnetic fields (birds)
sensory receptors encode 4 important features
stimulus modality, location, intensity, and duration
labeled line theory
separate and dedicated sensory pathways encode different stimulus modalities (ex: taste, smell, and touch)
A _____ _____ neuron is associated with one type of ______ (label line theory)
particular afferent; receptor
Each afferent neuron follows a particular ____ for ______
pathway; integration
Polymodal receptors
are sensitive to multiple sensory modalities
Polymodal nocireceptors tranduce _____, ____, and _____ cues into ____ that are sensed as _____
thermal; mechanical; chemical; signals; pain
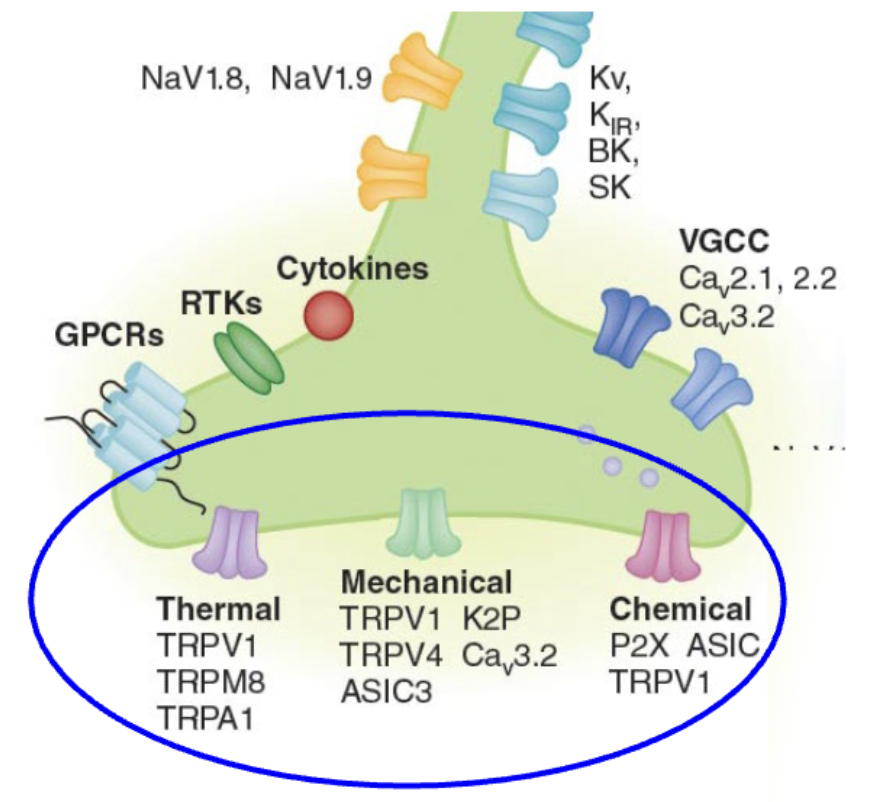
_____ of action potentials likely encodes ______ information from some polymodal receptors
pattern; modality
Types of receptive fields
large receptive fields and small receptive fields
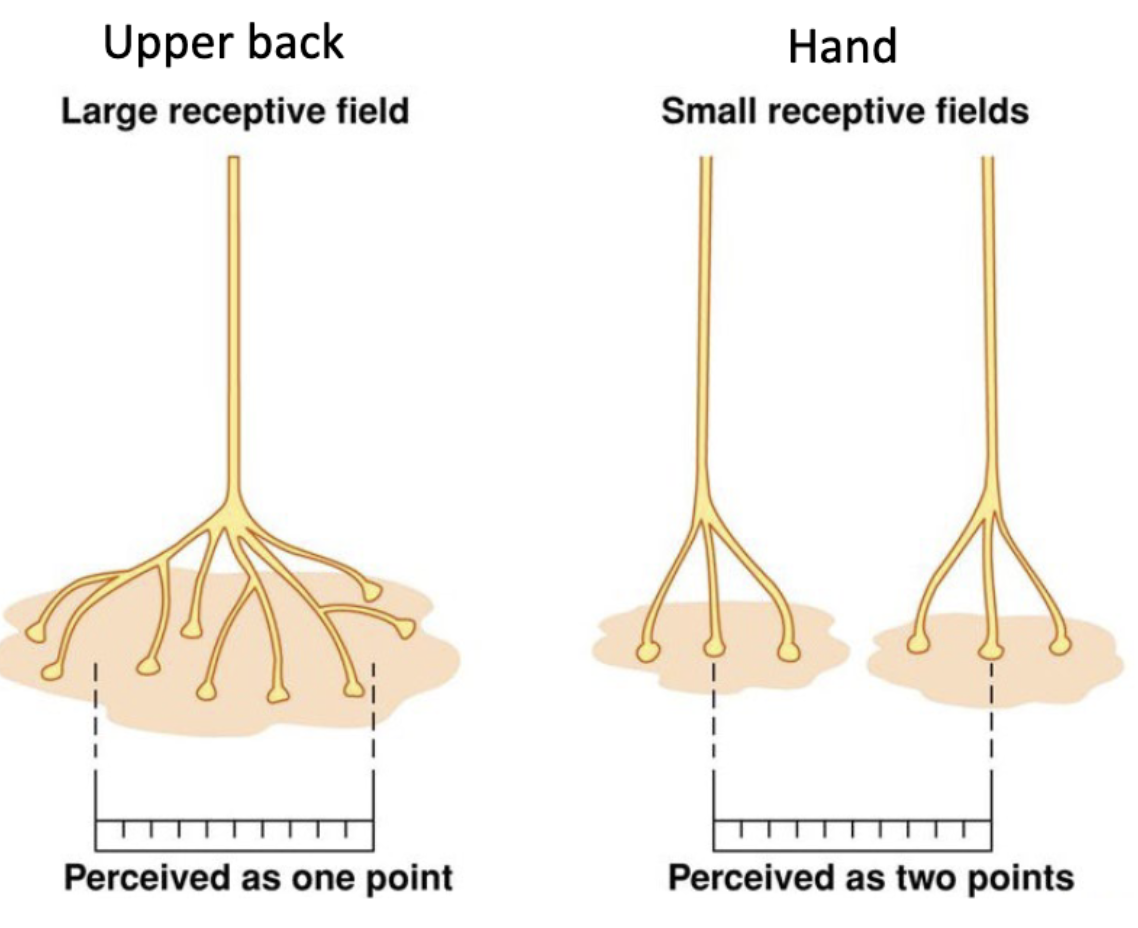
Overlapping receptive fields do what
improve ability to localize stimulus
Lateral inhibition function
improves acuity (defining exactly where touch is)

Action potential frequency encodes
stimulus strength
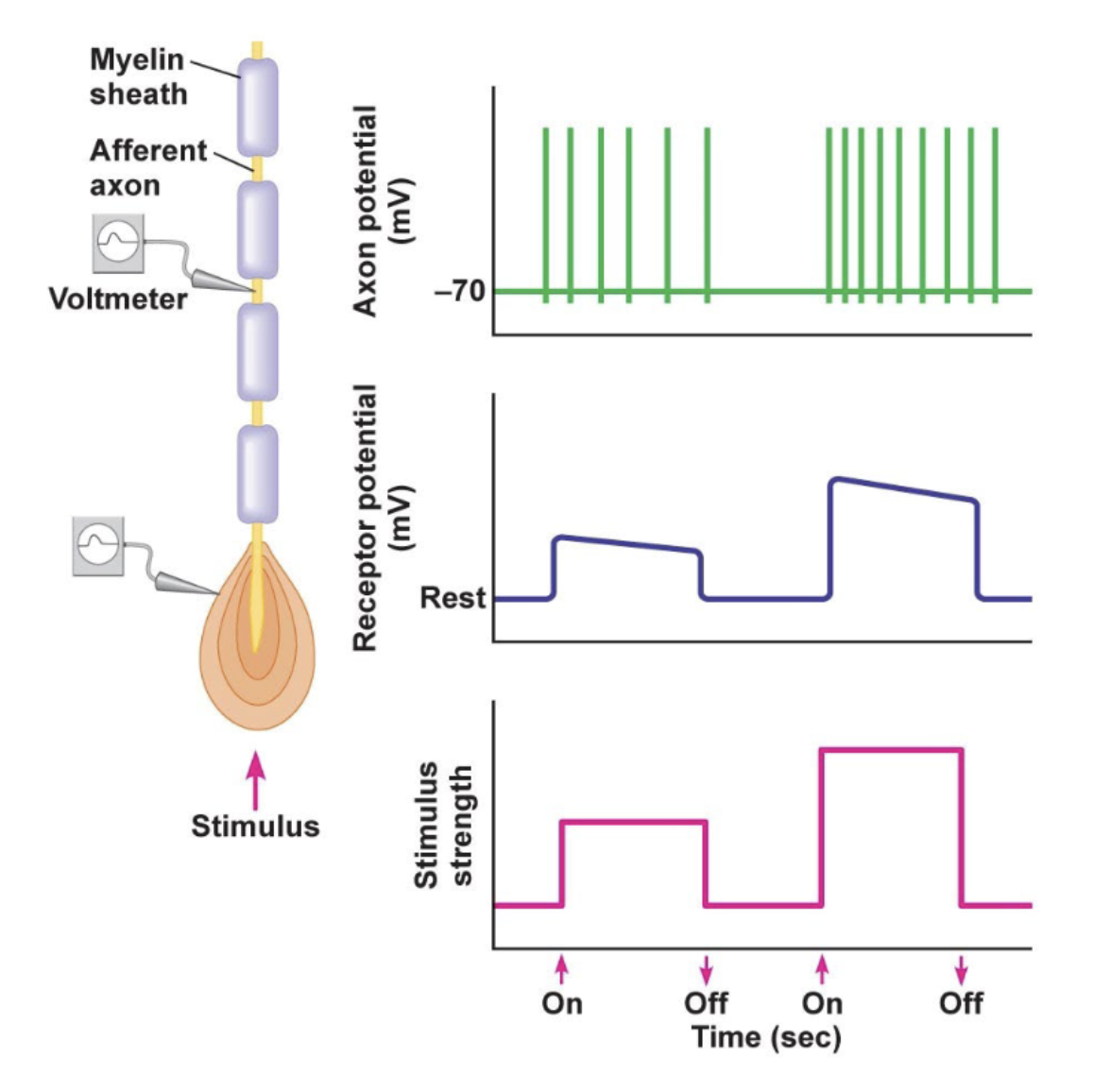
Receptor potential
a graded potential w/in the receptor
Sensory receptors encode a _____ range of stimulus ______
limited; intensities
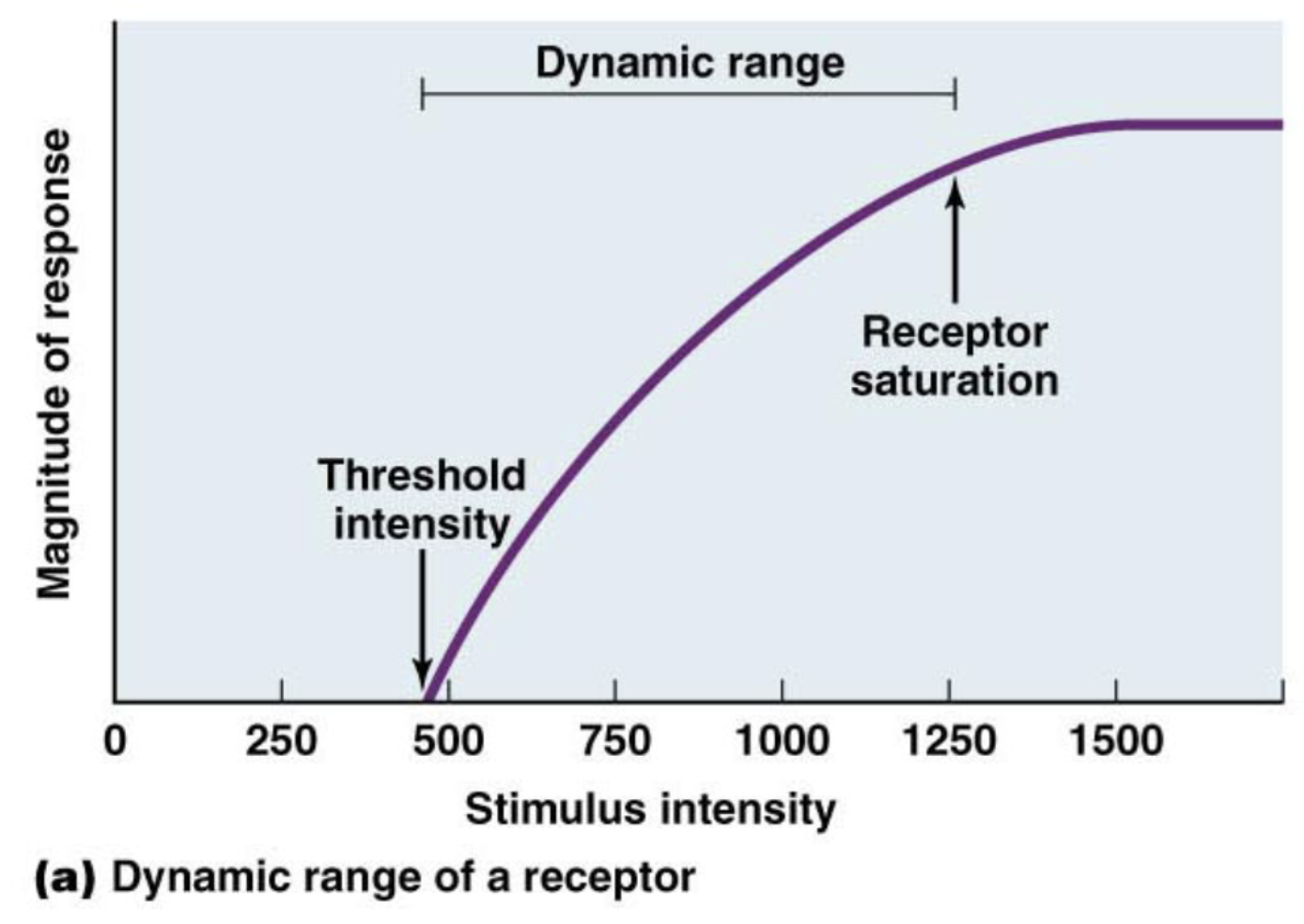
Dynamic range
at what point does a receptor start sensing something and at what point does it reach saturation
Sensory discrimination improves by
distributing sensitivity amongst the receptor population
graph shows good sensitivity and large dynamic range
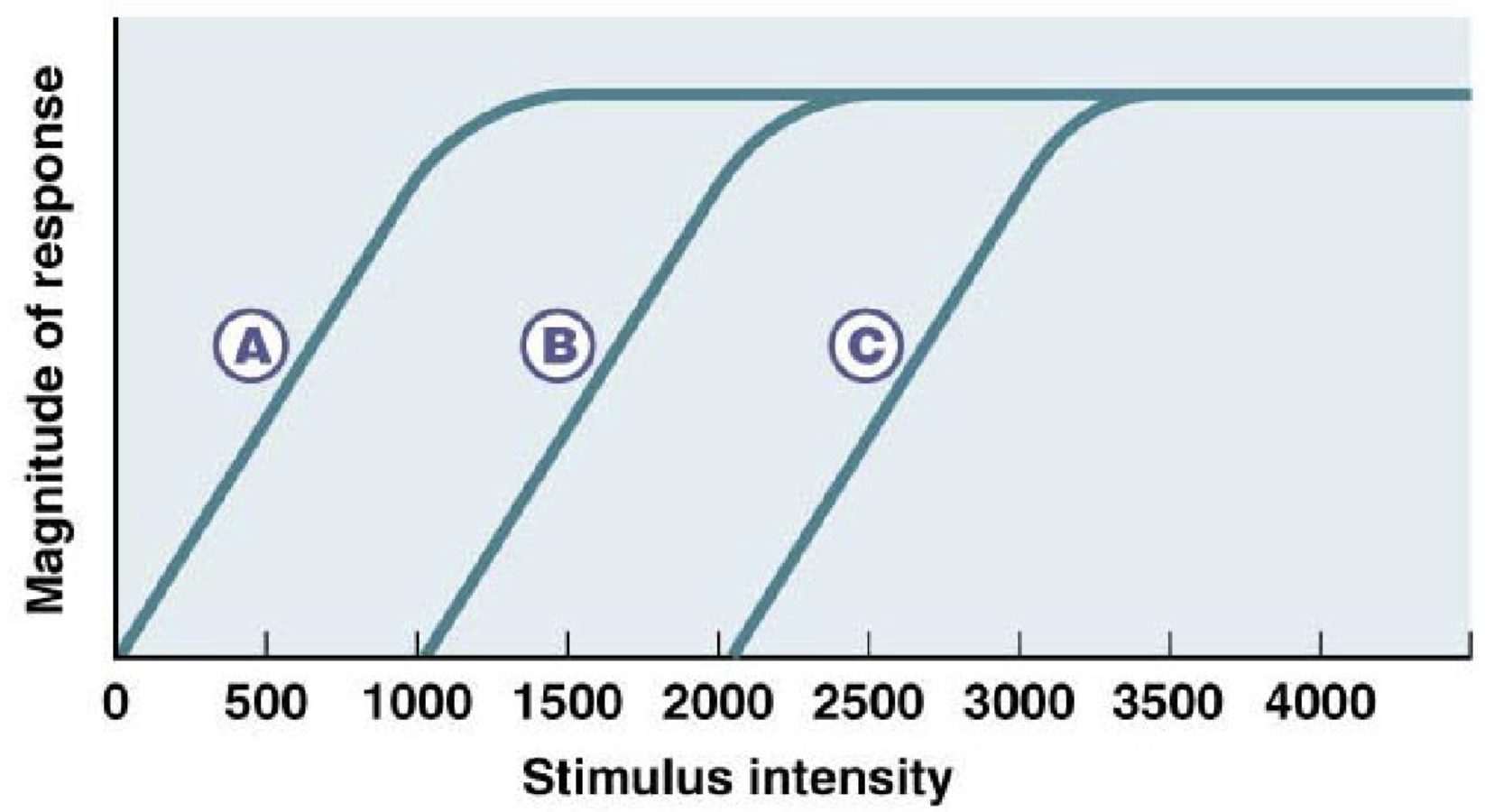
_______ _____ ___ __________ allows for a compromise b/w dynamic range and discriminaiton
logarithmic encoding of intensity
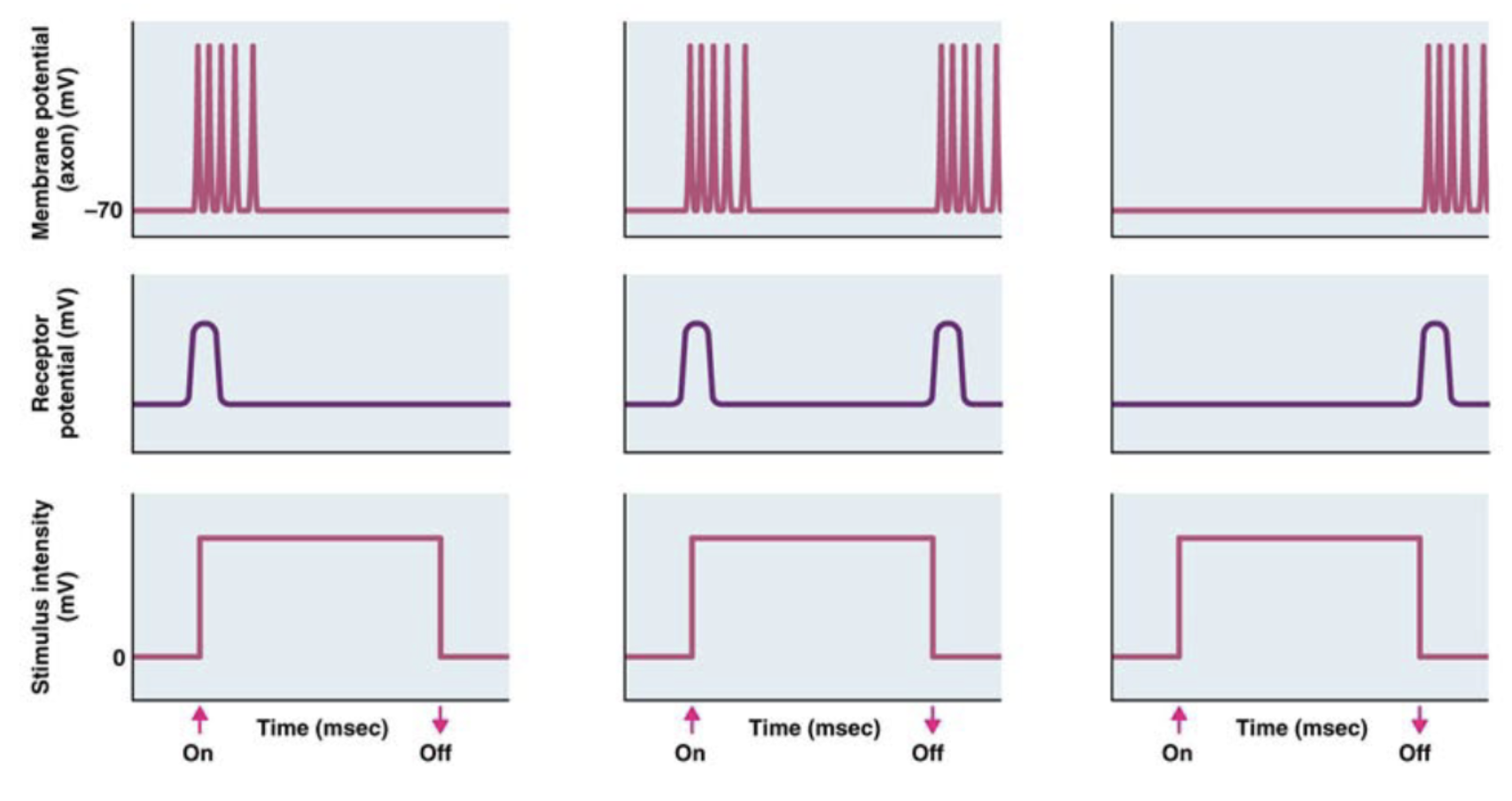
Tonic receptors
can encode stimulus duration

Phasic receptors
encode changes in stimulus
can do so in several ways
Types of chemoreceptors
exteroceptors:
interoceptors:
Exteroceptors
external to body (could be in the mouth/nasal passages)
olfaction
gustation
nocioception
?pheromones?
Interoceptors
internal to body
blood pH
Chemosensors in stomach
BP sensors
Odorant receptors neurons - receptor type and mechanism
express G-protein coupled receptors
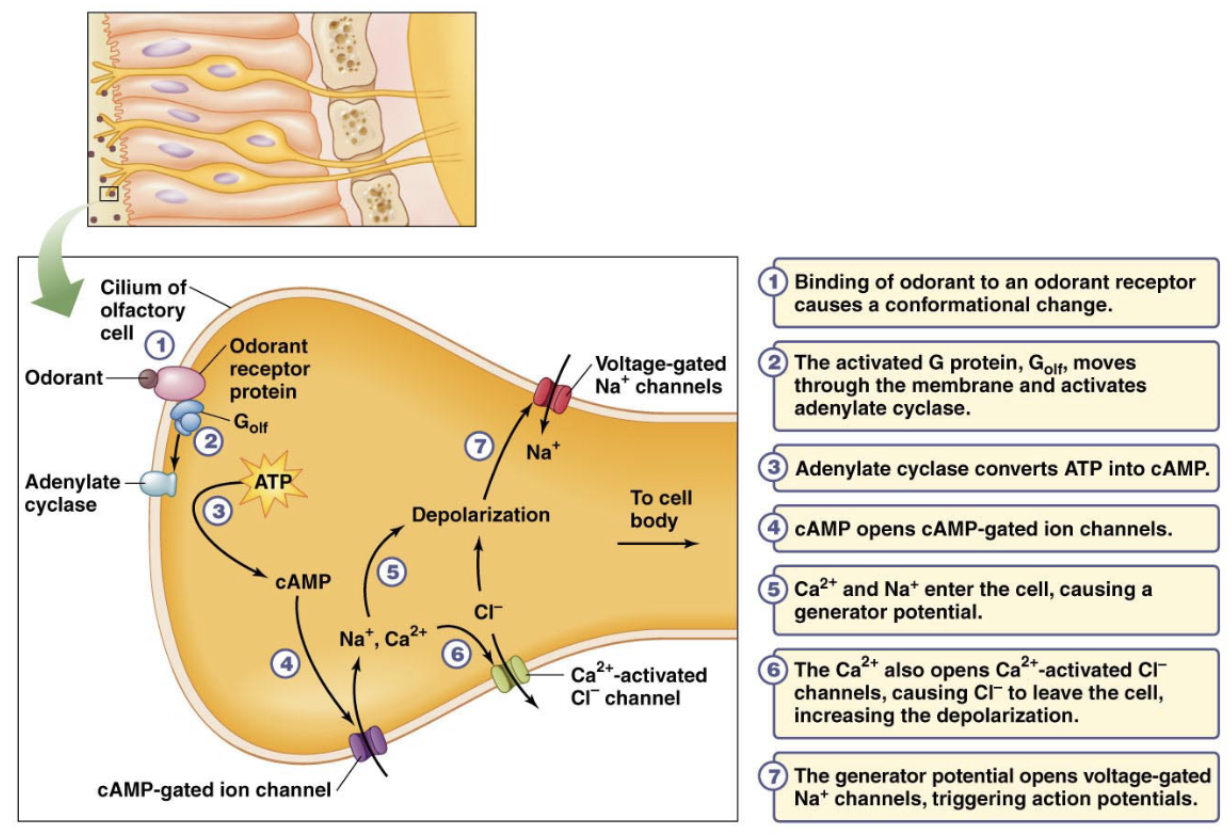
Each afferent ORN expresses a
single odorant receptor
Combinatorial code for odors
odorant molecules binds G-protein receptor (can bind multiple different receptor types) —> tiggers combination of ORNs —> transmitted to brain for processing (diff. combinations = different smells)
Afferent ORNs w/ same GPCR connect to
the same region of the olfactory bulb (glomerulus) - the brain reads these combinations as distinct patterns of activation in the olfactory bulbs - this is the combinatorial code for odors
5 tastes
sweet, bitter, salty, sour, umami
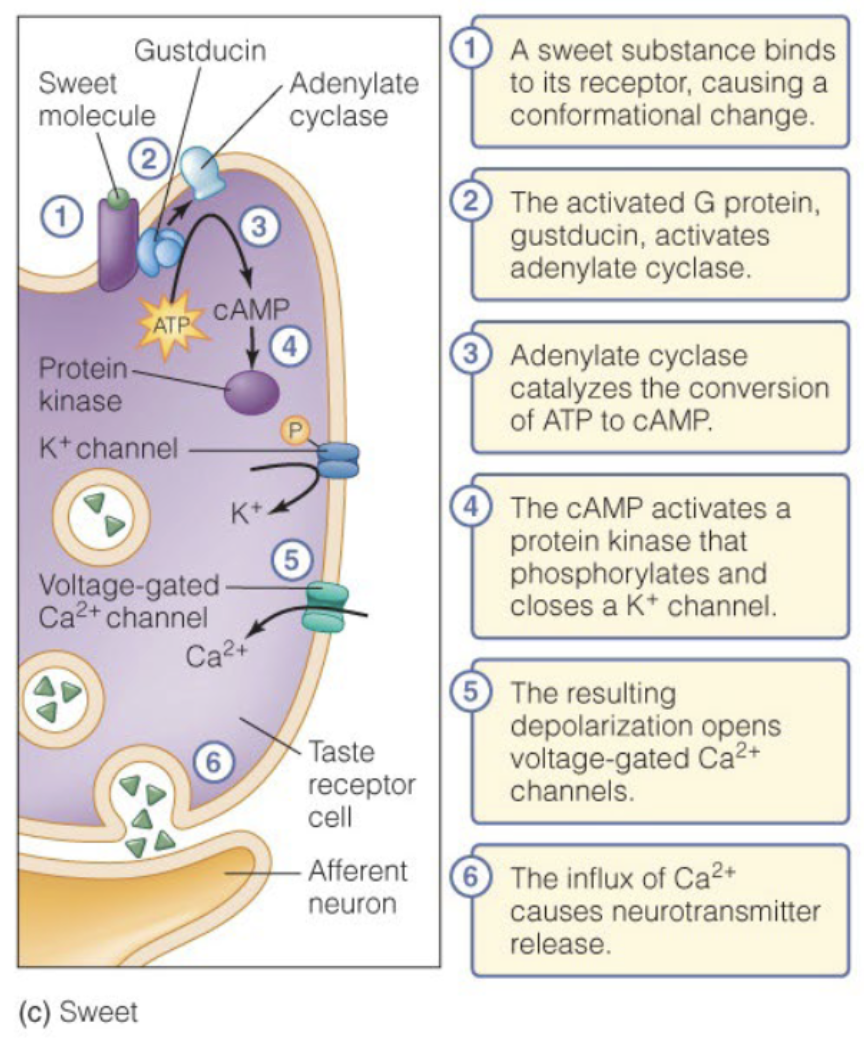
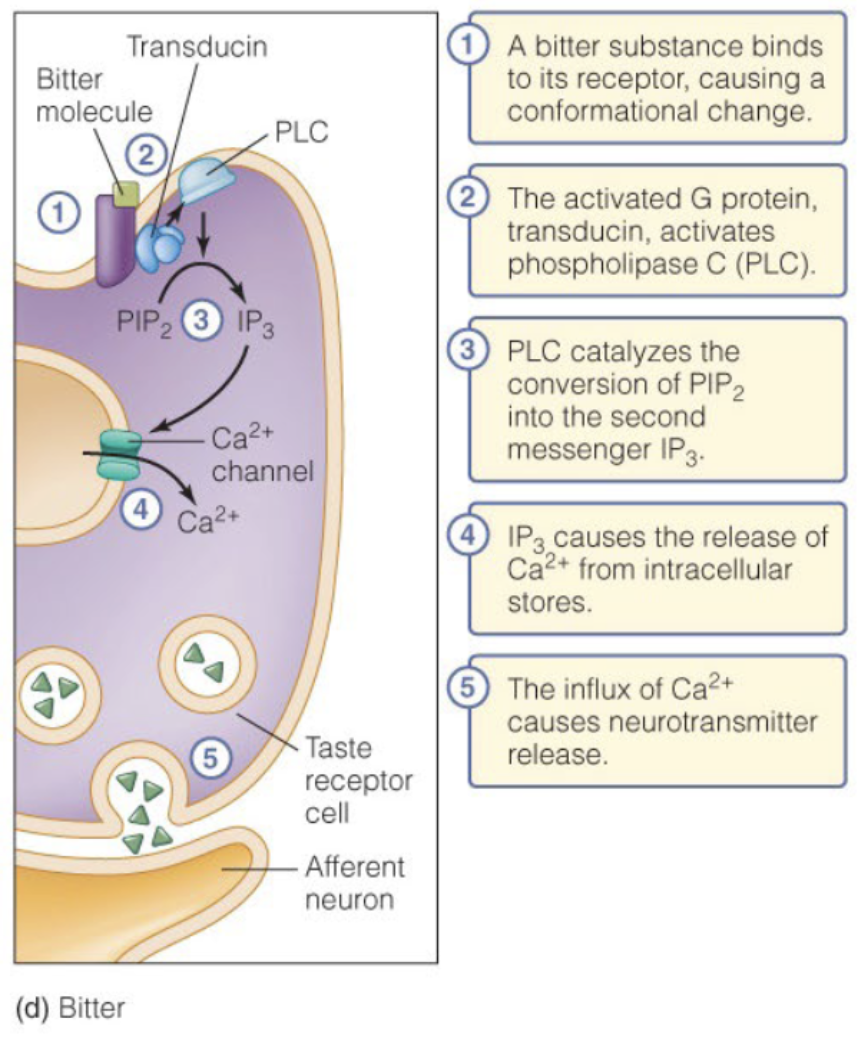
Gustatory receptors use
GPCRs to detect sweet and bitter tastes
Sweet Sensory Pathway
Bitter Sensory Pathway
Sour Sensory Pathway
Salty Sensory Pathway
Variations on mechanoreception
touch/pressure
proprioception
equilibrium/balance
hearing
baroreception (BP sensing)
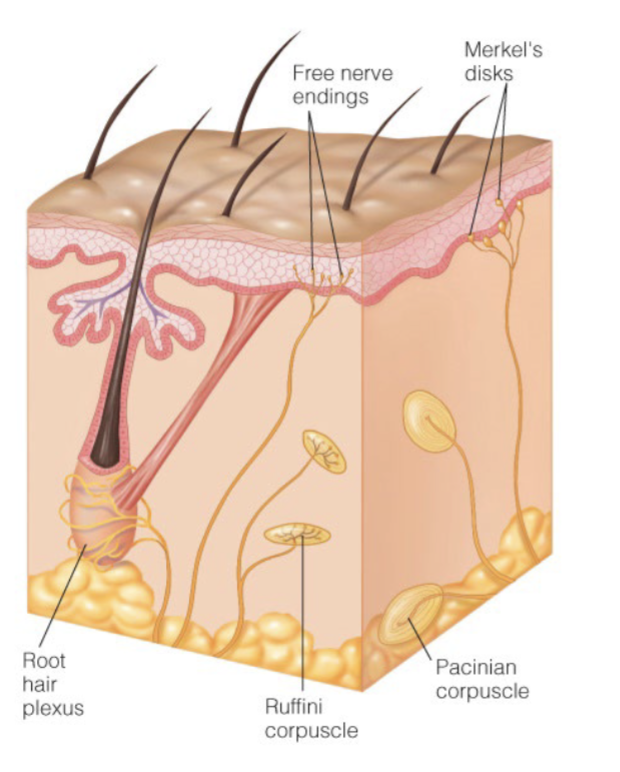
What kind of receptors are widely disperesed in the skin
touch receptors
combination of tonic (Merkel’s disks - for light and fine touch) and phasic (Ruffini corpuscle - sense deep touch - have large receptive fields that don’t overlap as much) receptors which allows for detection of both transient and sustained stimuli
Proprioceptors monitor
the position of the body in space - knowing where you are in space
vertigo: not knowing where you are in space
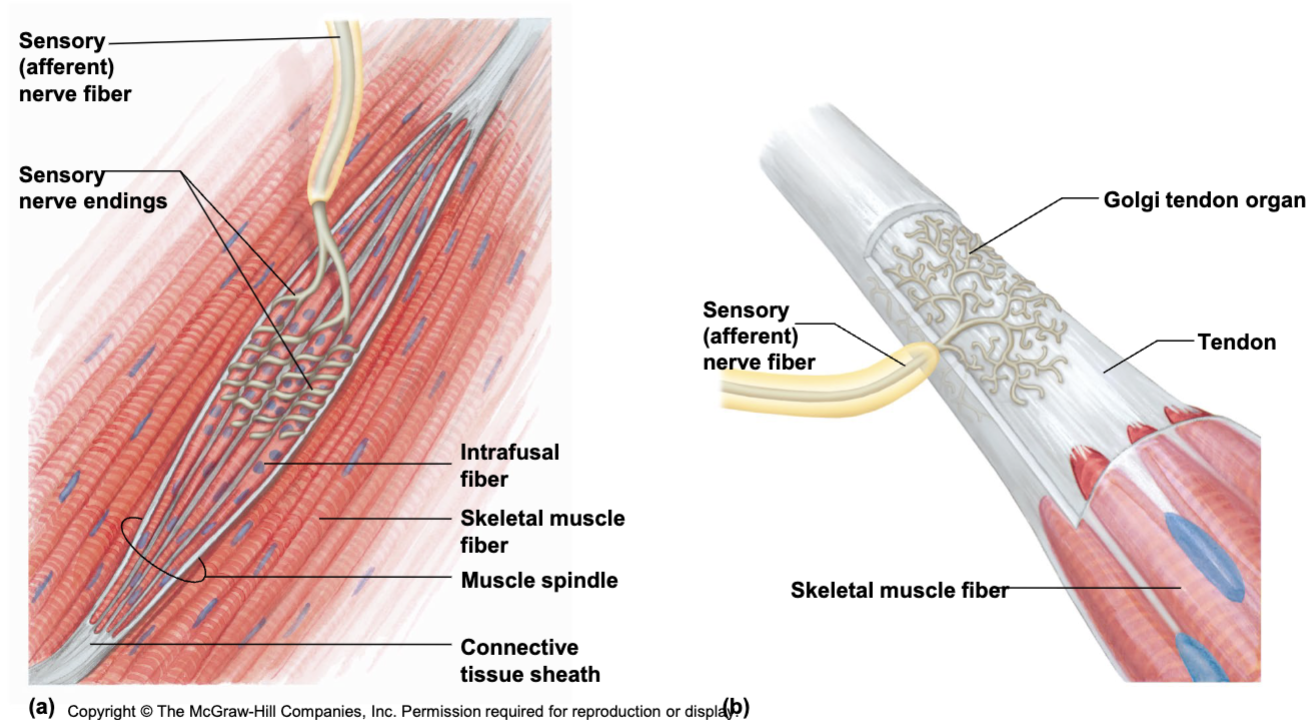
Muscle spindle fiber
senses stretch - causes contraction - incresaes contractile force
ex: stretching before box jump by bouncing/loading
lack of causes muscle discordination
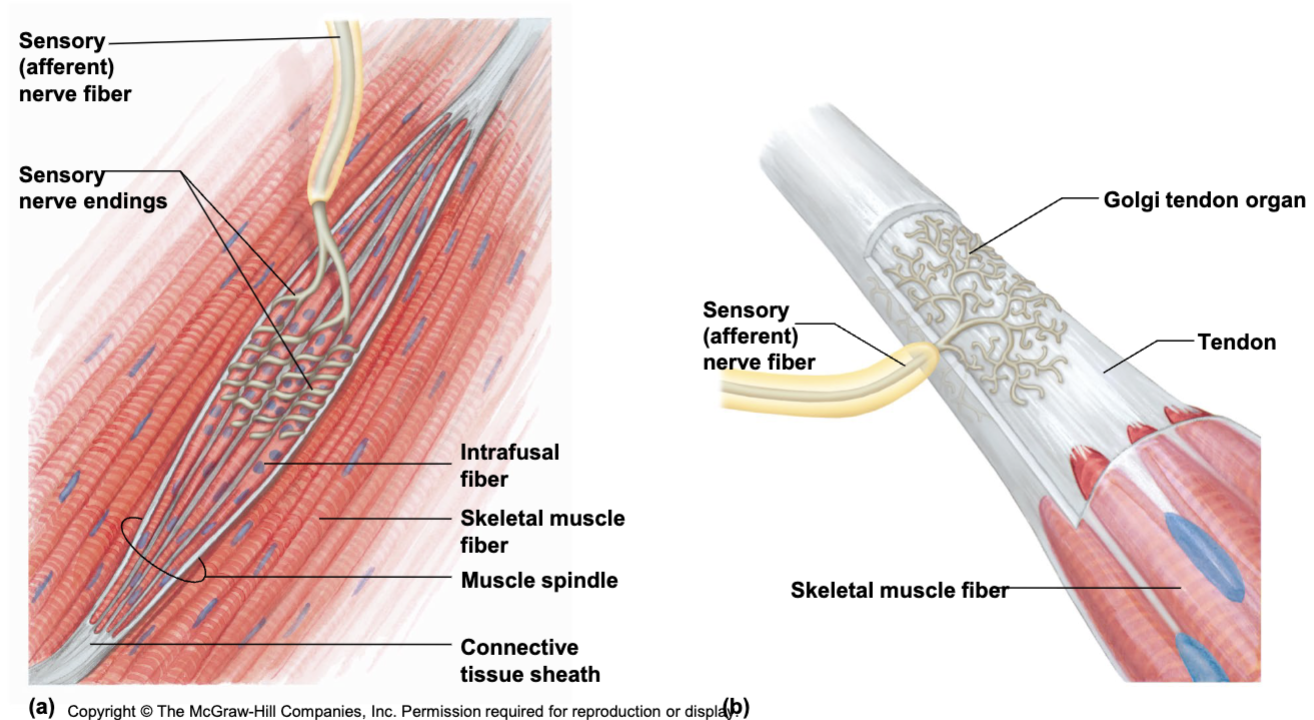
Golgi tendon organ
senses overstretching of muscle - cause muscle relaxation
protection mechanism
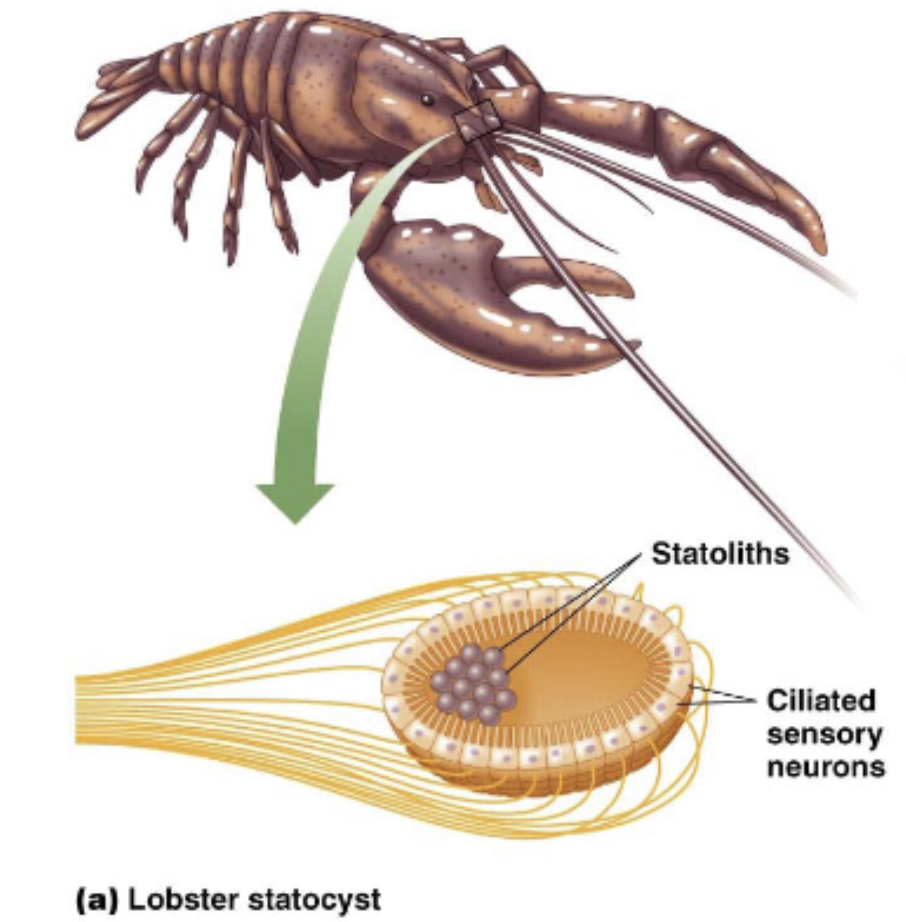
Invertebrate ______ employ _____ for equilibrium
statocysts; mechanoreceptors
ciliated sensory neurons: the mechanoreceptors
helps signal which direction the lobster is moving in/oriented
The ____ cell is the _______ responsible for hearing and ______ in vertebrates
hair; mechanoreceptor; balance
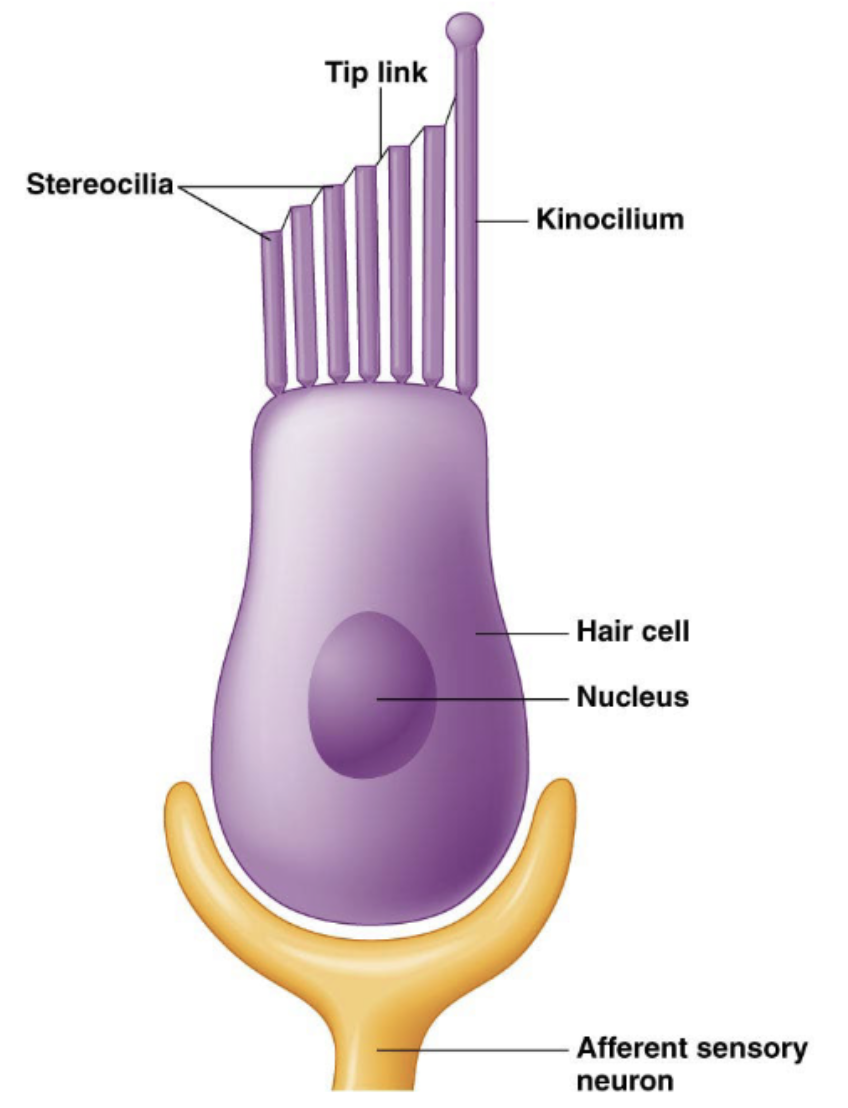
Hair cells general
are bathed in endolymph
maintain high external K+ relative to internal K+
hair cell is and main components
is an epithelial cell
kinocilium and stererocilia
tip links
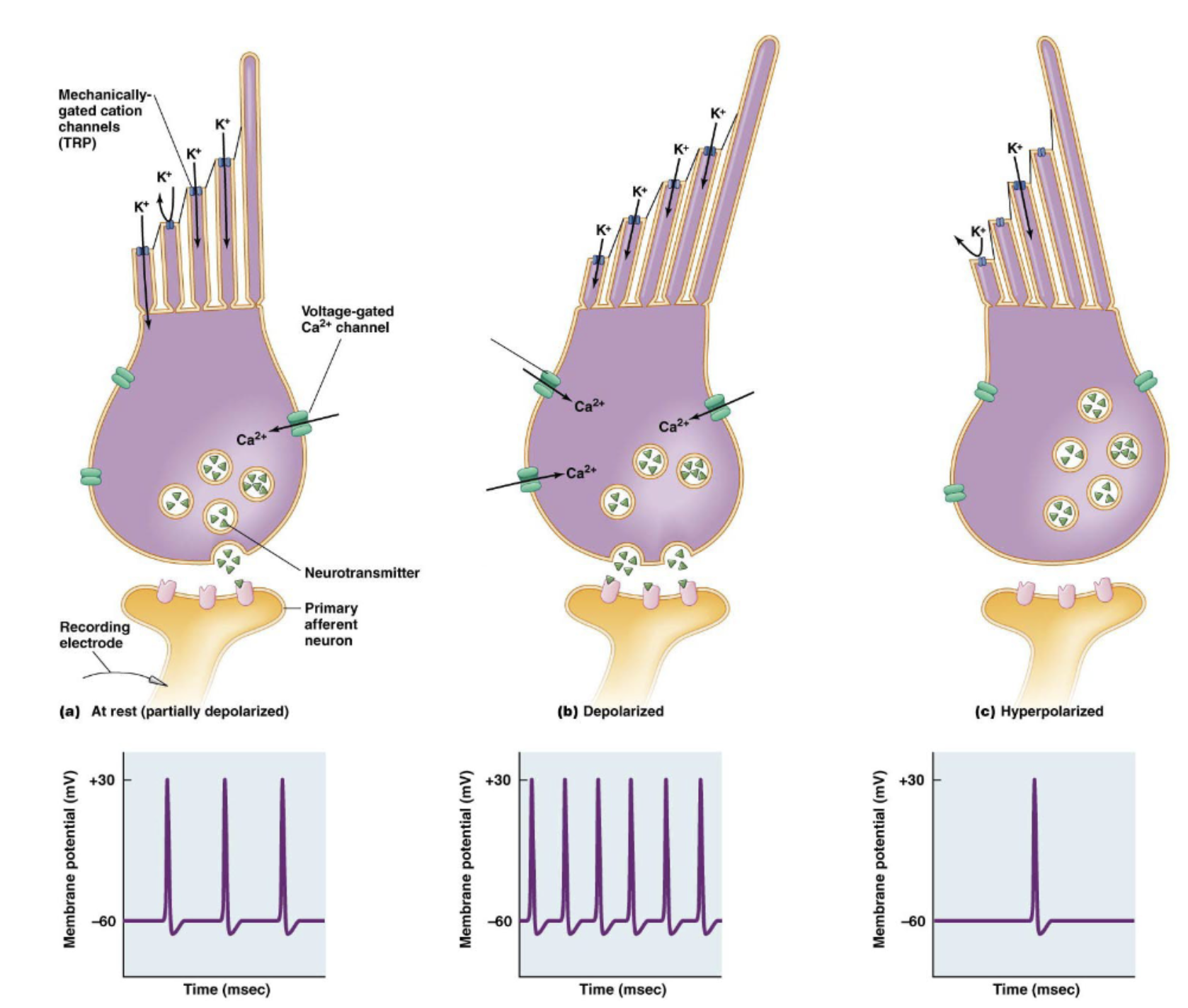
mechanically-gated K+ (cation) channels (TRP) at stereocilia tips
voltage-gated Ca2+ channels at body of epithelial cells
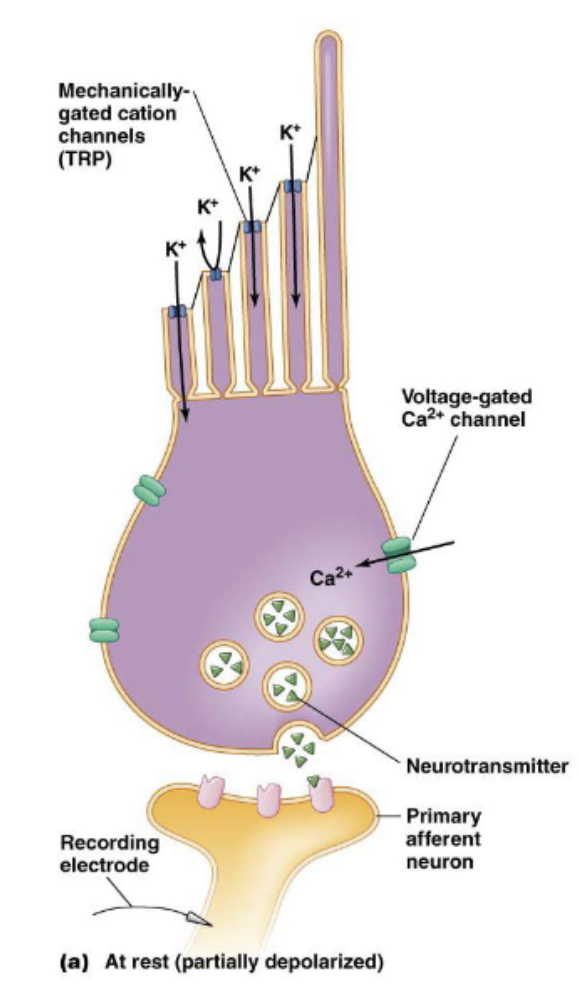
Hair cells maintain ______ ____ on to _____ ____, even in the absence of ______
transmitter release; afferent neuron; delfection
____ deflections modulate K+ conductance and _______ _____ in hair cells
sterocilia; transmitter release
movement to left - cilia move right: depolarization —> higher frequency of APs
movement to right - cilia move left: hyperpolarization —> lower frequency of APs
Where are the mechanreceptors necessary for hearing and balance located
inner ear - vestibular apparatus which includes utricle, saccule, and semicircular canals
Hair cells in _____ and _____ detect movements of _______ _____
utricle; saccule; otolithic membranes
x+y movement (front/back and up/down)
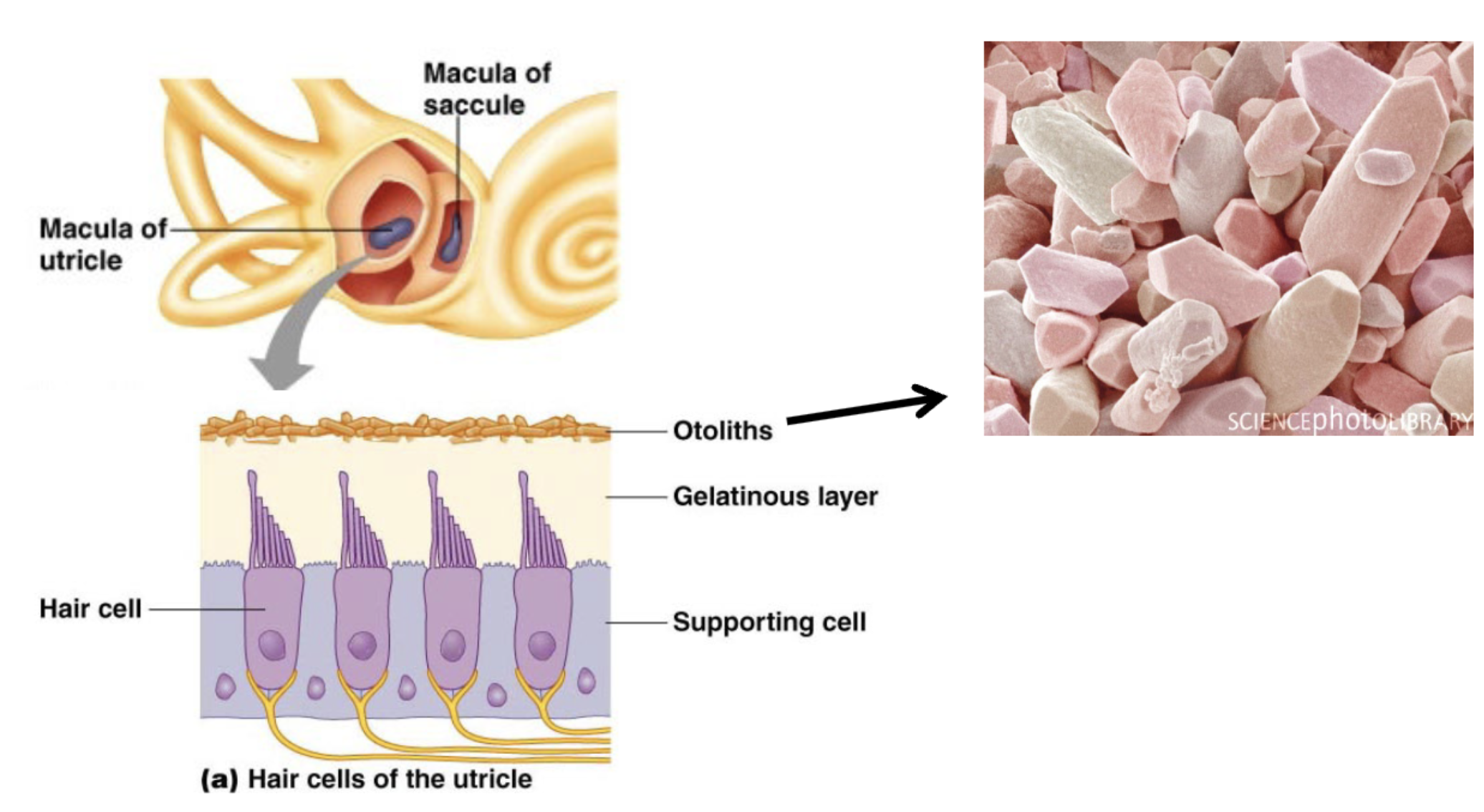
Macula of utricle
recognizes veritcal movement