Demography
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Population
a group of interacting individuals of a single species in a single location
population ecology
What factors affect the number of individuals of a species in a location & over time
Population descriptors
Dispersion
Size & Density
Demographics
Population Dispersion
describes the pattern of individuals in space
Random dispersion
position is not impacted by other individuals (unpredictable and rare)
Uniform dispersion
even spacing reinforced by avoidant interactions with others
Chemical inhibition
Territoriality
Clumped dispersion
individuals cluster in space
Resource distribution
Social groups
Reproductive behavior
Population Size
total number of individuals in a population across all areas
Population Density
number of individuals in a defined area; varies across the distribution if organisms are not uniformly dispersed
Ecological Census (sample plots)
study area is divided into subunits (quadrats) to count individuals
Count every individual in randomly selected areas (average population density)
Extrapolate to get total population size
Most effective for evenly spaced or sedentary organism
aerial surveys
divide land into sections, count animals in each area
total count
all animals in an area counted; sometimes impractical
sample counts
only sections of each section are counted; remaining estimated with algorithm
transect lines
perpendicular to major physical barriers i.e. waterways and mountains
Mark-Recapture
Individuals in an area are captured, marked, and recapture
Mark-Recapture Assumptions
marked & unmarked individuals have equal probability of sampling
no birth, death, immigration, emigration during resampling
Population mixes thoroughly between sample
eMark-Recapture equation
M/N = r/n
marked/population = recaps/new captures
N = Mn/r
over-estimation of mark-recap error
animals avoid second capture
under-estimation of mark-recap error
animals prefer recapture (‘trap-happy’)
Population Genetics
Individuals can be identified from genetic sequence; DNA samples can be used to build genetic profiles of each individual in a population; forensics for wildlife
useful if animals are hard to capture or identify as individuals; used to determine which individuals are reproducing
Demography
study of populations & how they change over time
demography descriptors
Age & Sex structure
Survivorship
Life History (reproduction)
Age structure
distribution of individuals at different ages in a population; may constrain growth if ratio is skewed
Sex structure
ratio of males to females in a population; may constrain growth if ratio is skewed (Female biased ratios typically increase birth rates, male-biased decrease with limits)
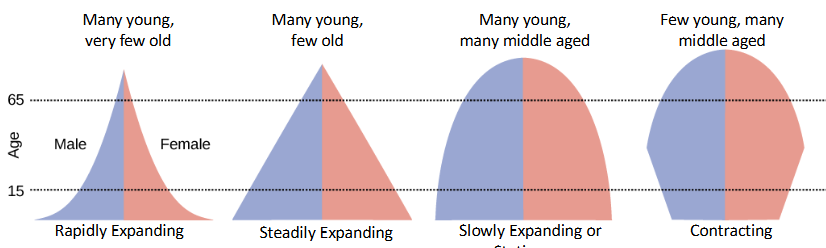
population pyramid
compares age and sex structures
cohort
age group
life tables
summarize mortality, survival, & reproduction in a population by age-group; also tracks disease outbreaks & interventions
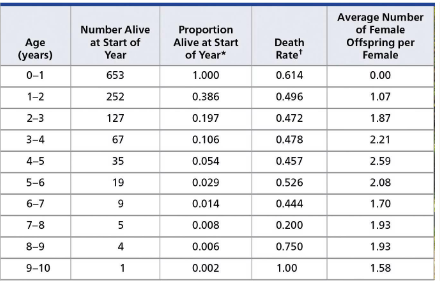
static / time-specific
records information about a population at a single time point
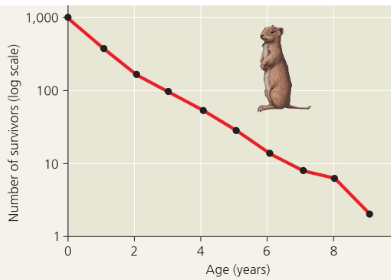
Survivorship curves
summarize life table data: deaths over time
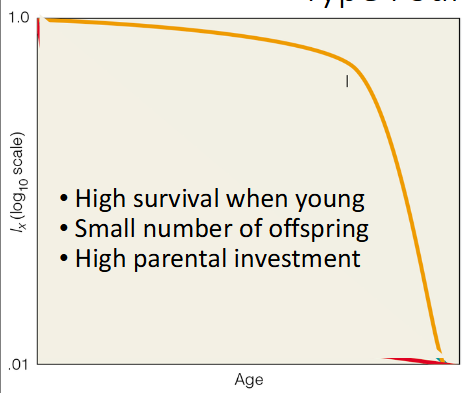
Type I Survival
low death rates during early & middle life; steep increase in deaths in older age groups
Type II Survival
constant death rate over entire lifespan
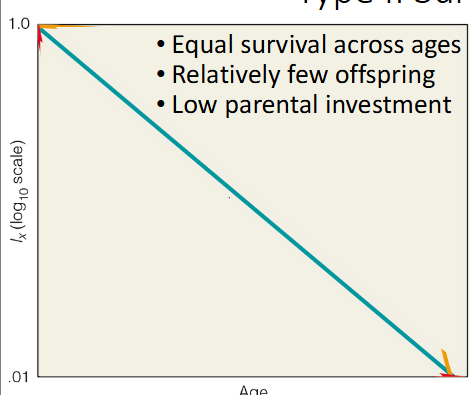
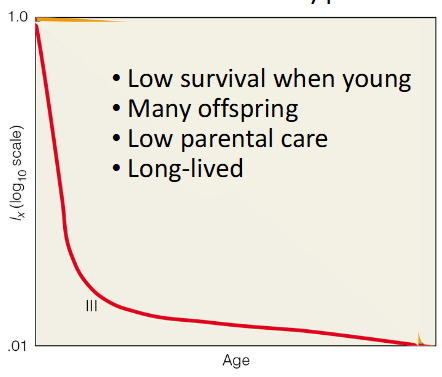
Type III Survival
very high death rates for young; low death rates for those that survive early life
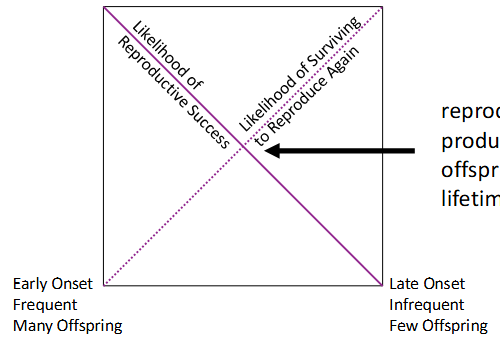
Reproductive onset
when reproduction begins
Early reproduction lowers risk of dying without producing offspring… but at expense of growth & health
Later reproduction produces more or larger offspring that are more likely to survive… but there’s a risk of not surviving to reproduce at all
Reproductive frequency
how often to reproduce; semelparous vs. iteroparous
Reproductive output
how many offspring each time; reflects parental investment
Good chance of survival? Make less offspring & help them survive
Low chance of offspring survival? Make more offspring & wish them luck!
fecundity
organism’s reproductive capacity; determined by tradeoffs and natural selection
semelparity
“fuck and die”; one reproductive event in life history followed by death
iteroparity
multiple reproductive events (possible) before death
K-selected species
tend to live longer, be larger, have feeer offspring at a time; spend more time raising children, longer childhood
population flatlines at carrying capacity
r-selected species
tend to live shorter, be small, have more offspring at a time; spend less time raising children, short childhood (if at all)
population grows exponentially dependent on biotic potential
biotic potential (r)
how quickly a species can reproduce and what percentage of that offspring makes it to maturity in a given environment
carrying capacity
maximum population size of a biological species that can be sustained by that specific environment