Internet and Cyber Security
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts relating to the internet, web technologies, and cyber security.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is the difference between the internet and the World Wide Web?
The internet is a collection of interconnected networks and devices, while the World Wide Web is a collection of multimedia web pages accessible via web browsers.
What does URL stand for and what is its purpose?
URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator, and it specifies the location of web pages.
What are HTTP and HTTPS?
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is used for transmitting data over the internet, while HTTPS is the secure version that uses encryption for secure data transmission.
What are cookies in the context of web browsing?
Cookies are small files stored on a user's computer that store information about user preferences and browsing activity.
What is the difference between session cookies and persistent cookies?
Session cookies are temporary and only exist while the browser is open; persistent cookies remain on the user’s computer until they expire or are deleted.
What is phishing?
Phishing involves cybercriminals sending legitimate-looking emails to trick users into providing personal information or clicking malicious links.
What is a DDoS attack?
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack overwhelms a target server or network with excessive traffic, preventing legitimate users from accessing services.
What is the role of a firewall?
A firewall filters incoming and outgoing traffic to protect a computer or network from unauthorized access and security threats.
What is blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized database that securely stores transaction data across multiple computers, ensuring data integrity.
What does SSL stand for and why is it important?
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer; it's important because it encrypts data transmitted between a user's browser and a web server, ensuring secure communication.
What is malware?
Malware refers to malicious software designed to harm, exploit, or otherwise compromise the integrity of a computer system.
What is strong password criteria?
A strong password should contain at least one capital letter, one numerical value, and one special character, making it hard to guess.
What is the purpose of anti-virus software?
Anti-virus software detects and removes malicious software (malware) from a user's computer.
What is two-step verification?
Two-step verification is an authentication process that requires two forms of identification before granting access to an account.
What is the purpose of a proxy server?
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between a user's computer and a web server, providing privacy and an extra layer of security.
What are the types of malware?
Types of malware include viruses, worms, Trojan horses, spyware, adware, and ransomware.
What is a virus?
A virus is a type of malware that attaches itself to clean files and spreads throughout a computer system.
What is a worm?
A worm is a standalone malware that replicates itself in order to spread to other computers.
What is a Trojan horse?
A Trojan horse is malware that disguises itself as legitimate software to deceive users.
What is spyware?
Spyware is malware that secretly monitors user activity and collects personal information.
What is adware?
Adware is a type of malware that automatically displays or downloads advertisements.
What is ransomware?
Ransomware is malware that encrypts a user's files and demands payment for the decryption key.
What is a brute-force attack?
A brute-force attack is a trial-and-error method used to decode passwords or encryption keys.
What is data interception?
Data interception is the unauthorized capturing of data during transmission between devices.
What is hacking?
Hacking refers to the unauthorized access and manipulation of computer systems or networks.
What is pharming?
Pharming is a cyber attack that redirects users from legitimate websites to fraudulent ones.
What is social engineering?
Social engineering involves manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information.
How does access levels enhance data security?
Access levels restrict user permissions to sensitive data and systems based on roles.
What is anti-malware?
Anti-malware is software designed to detect, prevent, and remove malicious software.
What are authentication methods?
Authentication methods include username/password, biometrics, and two-step verification to validate user identity.
Why are automated software updates important?
Automated software updates ensure that security patches are applied promptly to prevent vulnerabilities.
What role do firewalls play in data security?
Firewalls act as barriers between trusted and untrusted networks to control incoming and outgoing traffic.
What is the purpose of checking URLs?
Checking URLs helps to prevent access to phishing sites and ensures legitimate website navigation.
What is SSL and why is it important?
The Secure Socket Layer (SSL) security protocol encrypts data transmitted over the internet to protect it from interception.
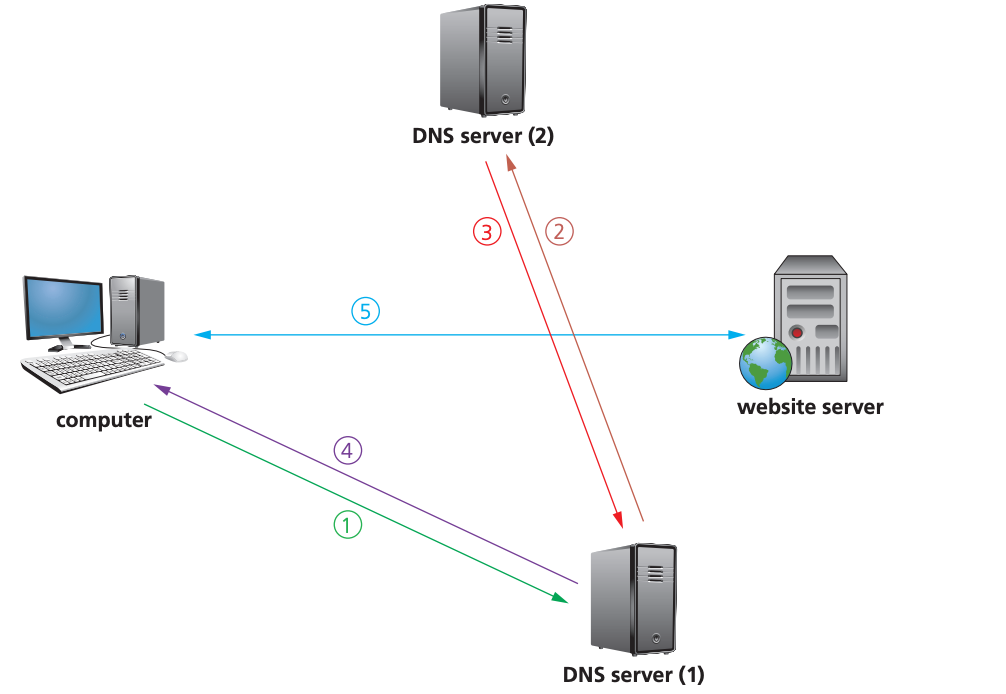
How DNS is used to locate and retrieve a web page
The user opens their browser and types in the URL and the browser asks the DNS server for the IP address of the website.
In this case, let’s assume the DNS server can’t find in its database or its cache, so it sends out a request to a DNS server
The DNS server finds the URL and can map it to IP address; this IP address is sent back to the DNS server which now puts this IP address and associated URL into its cache/database.
This IP address is then sent back to the user’s computer.
The computer now sets up a communication with the website server and the required pages are downloaded. HTML files are sent from the website server to the computer.
The browser interprets the HTML, which is used to structure content, and then displays the information on the user’s computer.