Missed Practice Exam Concepts/Terms
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Self-Awareness
Key area of EI:
The ability to conduct a realistic self assessment. it includes understanding ones own emotions, goals, motivations, strengths, and weaknesses.
Self-Management or Self-Regulation
Key area of EI:
The ability to control and redirect disruptive feelings and impulses.
ability to think before acting and to suspend snap judgments and impulsive decisions.
Social Awareness
Key area of EI:
Convey empathy and understanding and considering other people's feelings.
includes the ability to read nonverbal cues and body language.
Social Skill
Key area of EI:
The culmination of the other dimensions of emotional intelligence. It is concerned with managing groups of people (such as project teams), building social networks, finding common ground with various stakeholders, and building rapport.
Emotional Intelligence (EI)
An important attribute for project managers, this is the capability to understand and manage not only one's own emotions, but also the emotions of others. Multiple models exist, but all models for this concept focus on four key areas.
Iterative Life Cycle
A subcategory of the adaptive lifecycle in which development occurs through continuous refinement over the life of the project.
Development during this life cycle focuses on initial, simplified implementation, followed by future progressive elaboration that adds to the features until the final deliverable is complete.
Nothing is delivered partially. All cumulative iterations are delivered in one go.
Incremental Lifecycle
A subcategory of the adaptive lifecycle in which development occurs in small segments, gradually forming the end deliverable through these same segments
During this life cycle, focus is on releasing fully functional features successively until the final deliverable is complete.
Adaptive lifecycle
This lifecycle allows a project to be less constrained because developing requirements early is avoided
allows modifications as the deliverables are finally reviewed
often makes the end product very different from what might have been articulated at the start of the project.
Predictive Life Cycle
This lifecycle is associated with clear phases.
constrained to develop requirements early
stay with the original requirements and design plans that were created at the start of the project
Hybrid Lifecycle
A project lifecycle that contains elements of both predictive and adaptive approaches
Each is used to achieve greater overall effectiveness that could be achieved by using either approach alone.
Practical when compliance requirements demanded that certain aspects of the deliverable be implemented in a very predictable way, but the court of the solution may need to be determined entirely through iteration and simulated.
Schedule Compression
A means of improving the duration of a project.
Common techniques include fast tracking and crashing.
Crashing
A means of schedule compression.
Shorten the schedule duration for the least incremental cost by adding resources in key activities along the critical path.
Fast tracking
A means of schedule compression.
Activities or phases normally done in sequence are performed in parallel for at least a portion of their duration.
Mandatory dependency
A consideration in schedule compression.
A relationship that is contractually required or inherent in the nature of the work.
Usually cannot be modified.
Discretionary dependency
A consideration in schedule compression.
A relationship that is based on best practices or project preferences.
May be modifiable.
External dependency
A consideration in schedule compression.
A relationship between project activities, and non-project activities.
This type of dependency usually cannot be modified.
Internal dependency
A consideration in schedule compression.
A relationship between one or more project activities.
May be modifiable.
Risk
An uncertain event or condition that, if it occurs, has a positive or negative effect on one or more of the project objectives.
Negative risks are called threats.
Positive risks are called opportunities.
Issue
A question, current condition, or situation that may have an impact on a project, and that therefore requires some sort of research and resolution.
Also a risk that has materialized.
Constraint
A project boundary or limit on time, cost, scope, or quality.
Assumption
Presumed context about a project or its requirements that creates a special condition around which the project must be planned and executed.
Risk/Threat avoidance
When the project team acts to eliminate a threat or to protect a project from the impact of a threat.
Examples include realizing that there is not enough time to implement an app for both android and iOS operating systems so changing the scope to implement for only one software.
Threat Transfer
Involves shifting ownership of a threat to another party to manage the risk or bear the impact if the threat occurs.
Examples include sourcing an external vendor to build out certain elements of a project or product.
threat mitigation
Action is taken to reduce the probability of the occurrence or impact of a threat. Doing this early is often more effective than attempts to repair the damaged after a threat has occurred.
Examples include sending a training resource to team members to prevent risks materializing into threats due to inexperience
Threat Acceptance
Acknowledging the existence of a threat, but no proactive action is taken or planned.
Examples include deciding that not offering an app on android software does not pose a sufficient concern to project success.
Definition of Done
Checklist of all the criteria required to be met so that a deliverable can be considered ready for customer use.
Can be applied to one or multiple deliverables
Example: code is peer reviewed, tested, documented, and deployed to staging.
“What must be true for any work to be considered complete”
Acceptance Criteria
Define the conditions that must be met for a particular user story to be considered complete
Written from a users perspective to ensure functionality meets their needs.
Example: the system must allow users to reset their password via email.
“What does this feature need to do?”
Product Owner Roles and Responsibilities
Maximize value of the product resulting from the work being done by a project team.
Handles changes and change requests to product backlog.
Serves as liaison to customer
Business Analyst Roles and Responsibilities
Ensures business needs are clearly understood
Interface between business stakeholders and technical teams
Interprets and enhances information with domain knowledge
Project Portfolio
A collection of programs and other work that are grouped together to facilitate effective management to meet strategic business objectives.
Emphasis on building, sustaining, and advancing the organization.
Program
Related projects and activities that are managed in a coordinated manner to obtain benefits not available for managing them individually.
Project Manager Roles and Responsibilities
After receiving authority from charter,
Maintain schedule
Update logs and registers
Submit change requests
Actions taken during the Initiating phase of a Predictive Development Approach
Actions:
Develop Charter
High level requirements
Preliminary scope
Authority granted to project manager
Identify Stakeholders
Actions taken during the Planning phase of a Predictive Development Approach
Actions:
Fully define scope and requirements
Create work breakdown structure.
Define and sequence activities.
Develop schedule.
Estimate costs
Actions taken during the Executing phase of a Predictive Development Approach
Actions:
Acquire resources.
Develop and manage team.
Conduct communications and procurement.
Actions taken during the Monitoring and Controlling phase of a Predictive Development Approach
Actions:
Control costs and schedule.
Monitor risks.
Control and validate scope.
Perform change control processes
Actions taken during the Closing phase of a Predictive Development Approach
Actions
Deliver product or project deliverables.
Perform handoff activities where needed.
Ensure deliverables are accepted.
Conduct lessons learned meetings.
What is the NPV (Net Present Value) and what does it signify?
Reasons:
Provides insight into whether an investment will provide value.
The higher this is, the greater the value an option is expected to provide
What is the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) and what does it signify?
Incorporates the interest rate into net present value of all cash flows.
The higher this is, the higher the return on investment will be
What is the Payback Period (PBP) and what does it signify?
Quantifies time needed to recover an investment.
The longer this is, the greater the risk will be.
What is the Return on Investment (ROI) and what does it signify?
Compares total benefits to total cost
Shows the percentage return on an initial investment.
A Negative value is bad, a positive value is good, and a high positive value is best
What is a vision statement? What does it do?
This describes outcome, not process.
This motivates the team by painting a compelling picture of the future.
This is clear and concise and supports broader business objectives
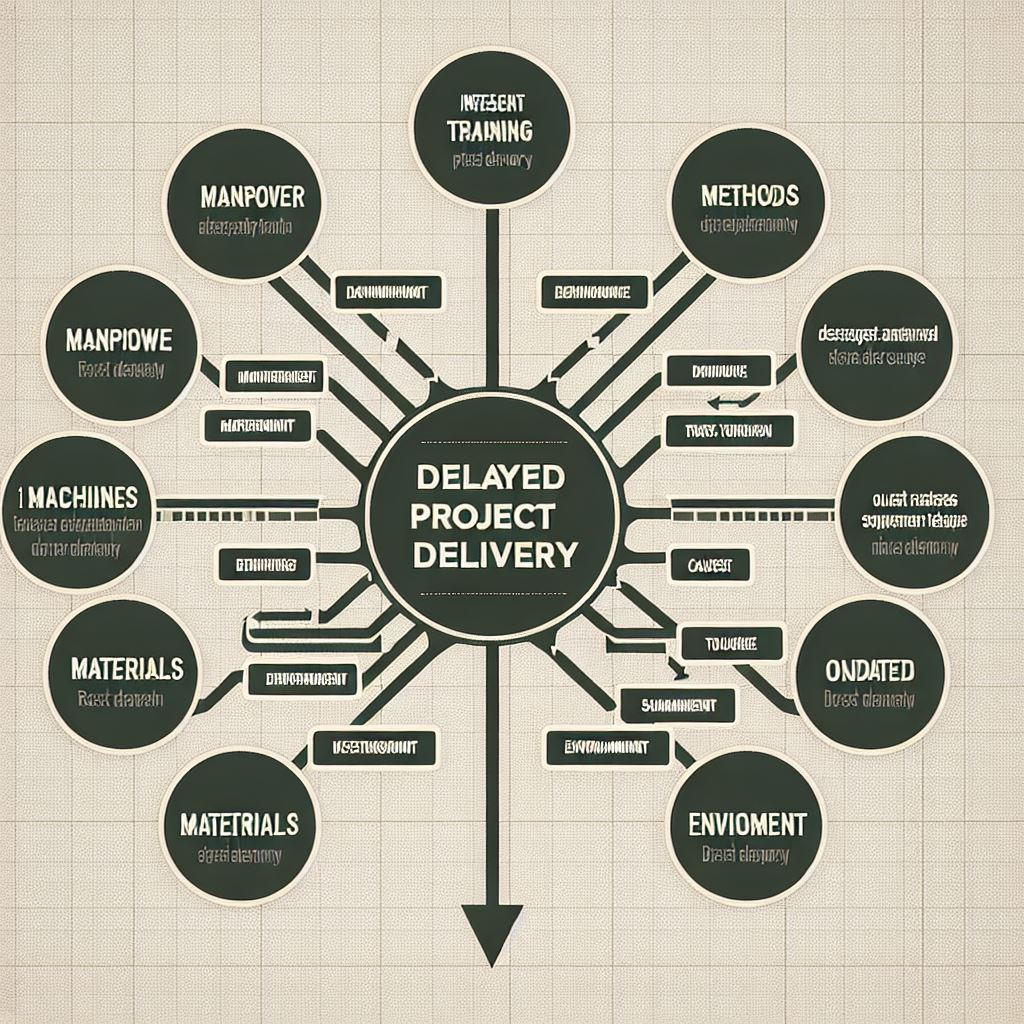
What is an Ishikawa/Fishbone/Cause-And-Effect diagram and how is it used?
This tool is used to systematically identify and analyze the origins of a specific problem or effect.
Commonly used for:
Root cause analysis
Process improvement
Brainstorming sessions
Quality control
What are key components of an Agile PM team?
Key Components of this team type include:
Self organizing
Self-directing
Working collaboratively and among themselves to determine who is best for any given task
What are key characteristics of a Product Backlog?
Key characteristics of this Agile tool include:
Maintained by product owner
Continuously evolving
contains all work, features, technical tasks associated with product lifecycle at all levels of detail (high-level to granular)
What are key characteristics of a release plan?
Key characteristics of this Agile tool include:
outlines what items will be delivered from the backlog and when
Focuses on a specific timeframe or milestone
includes high-priority items from backlog only
What is the Risk Appetite? Who is responsible for providing it in a Project Management Environment?
The level of uncertainty or risk your stakeholders are willing to accept.
What is the Risk Threshold? How is it applied to Risk Appetites and Risk Levels?
The measure of acceptable variation around an objective reflecting the risk appetite.
If a risk has a potential impact of $2,000,000, and this concept equals 10%, the risk level would have an acceptable variation of $1.8m to $2.2m
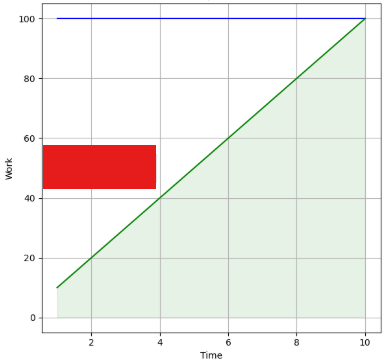
This chart tracks the completed work over time
The definition for Burnup chart.
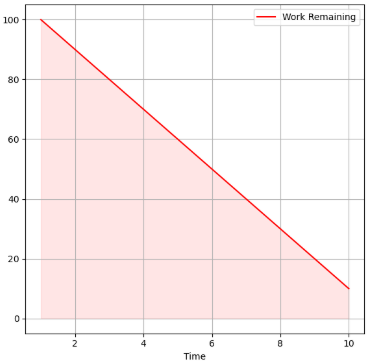
This chart tracks the work remaining over time
The definition for Burndown chart.
What are the best times to use formal verbal communication?
This communication style would be best used for:
Product demos
Kickoffs
Status updates
What are the best times to use formal written communication?
This communication style would be best used for:
Providing progress reports and other artifacts
Distributing the project charter, project plan.
Informing stakeholders of quality evaluation outcomes
Last Responsible Moment
The latest point in time at which a decision can be made without negatively impacting the outcome of a project.
What is a Schedule Management Plan? What is put there?
a component of the project management plan
developed at the beginning of a project’s lifecycle
outlines how a schedule will be developed.
Includes:
What is a schedule baseline?
The approved version of a project schedule
serves as benchmark against which actual performance is measured
What is typically included in a schedule baseline?
This typically includes:
finalized start and end dates
milestones
deadlines
the critical path
resource assignments
What is typically included in a Schedule Management Plan?
This typically includes:
accuracy of the schedule
reporting formats
model(s) used
tools/software used
expected cadence of schedule updates
Guidelines for managing changes
What are the components and considerations of a RACI Diagram?
Components:
Responsible
Accountable
Consulted
Informed
Considerations:
“Responsible” can also be “accountable”
Ensure there is only one person assigned to “Accountable” so there is no confusion over authority.