GRADE 11 BIOLOGY EXAM REVIEW
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Rank + Taxons (Hierarchy)
Domain = Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya.
Kingdom = Animalia (animals), Plantae (plants), Fungi, Protista, and Bacteria.
Phylum = Chordata, Arthropoda, Mollusca.
Class = Mammalia (mammals), Aves (birds), Reptilia (reptiles).
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Relationships Between Species Based on Scientific Names
Binomial Nomenclature:
Developed by Carl Linnaeus = uses 2 Latin names to uniquely identify each species.
Genus Name = first part of the name is the genus, which is always capitalized.
Species Name = second part is the species, which is not capitalized.
Taxonomy and Classification:
Hierarchical Structure = classified into a hierarchy of taxonomic ranks: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species.
Domains = broadest category (e.g., Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya).
Species = most specific category; a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring.
Phylogenetic Relationships:
Phylogenetics = evolutionary relationships among species.
Phylogenetic Trees = diagrams depict the evolutionary history and relationships of species based on common ancestry.
Clades = groups of organisms that include a common ancestor and all its descendants.
Bacteria vs. Virus
Bacteria = single-celled, prokaryotic organisms that have a cell wall, cell membrane, and can reproduce independently through binary fission.
Viruses = non-living entities that lack cellular structure and can only reproduce by infecting a host cell and using the host's cellular machinery
Eukaryotes vs. Prokaryotes
Eukaryotic Cells = a larger, complex type of cell that does have a membrane-bound nucleus.
Prokaryotic Cells = a smaller, simple type of cell that does not have a membrane-bound nucleus.
Domains + Animal Kingdom Characteristics
Bacteria:
Kingdom Bacteria = prokaryotic, unicellular, peptidoglycan, auto+heterotrophs, asexual.
Ex. Staphylococcus
Archaea:
Kingdom Archaea = prokaryotic, unicellular, not peptidoglycan + sometimes no cell wall, auto+heterotrophs, asexual.
Ex. Sulfolobus archaea
Eukarya:
Kingdom Protista = eukaryotic, uni+multicellular, sometimes cellulose + no cell wall, auto+heterotrophs, asexual+sexual.
Ex. Amoeba
Kingdom Plantae = eukaryotic, multicellular, cellulose, autotroph, sexual.
Ex. Maple Tree
Kingdom Fungi = eukaryotic, mostly multicellular, chitin, heterotrophs, sexual.
Ex. Mushroom
Kingdom Animalia = eukaryotic, multicellular, no cell wall, heterotrophs, sexual.
Ex. Rabbit
Groups of Protists Characteristics
Animal-Like = heterotrophs, some are parasites
Cercozoans = has pseudopods. Ex. Amoebas
Ciliates = has hairlike layer(cillia). Ex. Paramecia
Flagellates = has 1+ flagella. Ex. Species living in animal’s digestive tract.
Sporozoans = Ex. Parasites of animals.
Plant-Like = autotrophs, without light → heterotrophs, some live as symbionts with other organisms. Ex. red, green + brown seaweed.
Diatoms = free-floating aquatic organisms. Ex. phytoplankton
Dinoflagellates = 2 flagella at right angles to each other. Ex. Gonyaulax Catenella → “red tide”
Euglenoids = have chloroplasts + flagella + plant and animal like characteristics. Ex. Euglena.
Fungus-Like = autotrophs, some water moulds are parasites, produce spores, wet surfaces. Ex. moulds
3 Types of Evidence of Relationships
Anatomical = study of the structure + form, including internal systems. (Ex. Modern Birds and Dinosaurs + their bones).
Physiological = study of the physical + chemical functions including internal processes. (Ex. The difference of insulin in a guinea pig vs. other rodents led to them being reclassified from “rodents” to their own taxon”).
DNA = genes made of long chains of molecules called nucleotides. Determines the sequence of nucleotides of specific genes and can compare between species.
Punnett Squares
Punnett Squares = grid used to show all possible genotypes + phenotypes of offspring from genetic cross.
Autosomal vs. Sex-Linked
Autosomal Inheritance = traits governed by genes located on the autosomes (non-sex chromosomes).
Ex. Cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington's disease.
Sex-Linked Inheritance = traits governed by genes located on the sex chromosomes (X+Y chromosomes).
Ex. Hemophilia, red-green color blindness, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy, infertility.
Disorders + Syndromes
Non-disjunction = when chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis → 1 daughter cell has an extra chromosome while the other is lacking a chromosome.
Genetic Disorders:
Down Syndrome = a random error in cell division that results in the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21.
Turner Syndrome = one of two of the X chromosomes is missing, either partially or completely.
Klinefelter Syndrome = extra X chromosome occurs as a result of either the mother's egg or the father's sperm having the extra X chromosome.
Types of Mutations
Deletion = A section of a chromosome is lost.
Duplication = A section of a chromosome is duplicated.
Inversion = A section of a chromosome is reversed.
Translocation = A section of one chromosome is transferred to another chromosome.
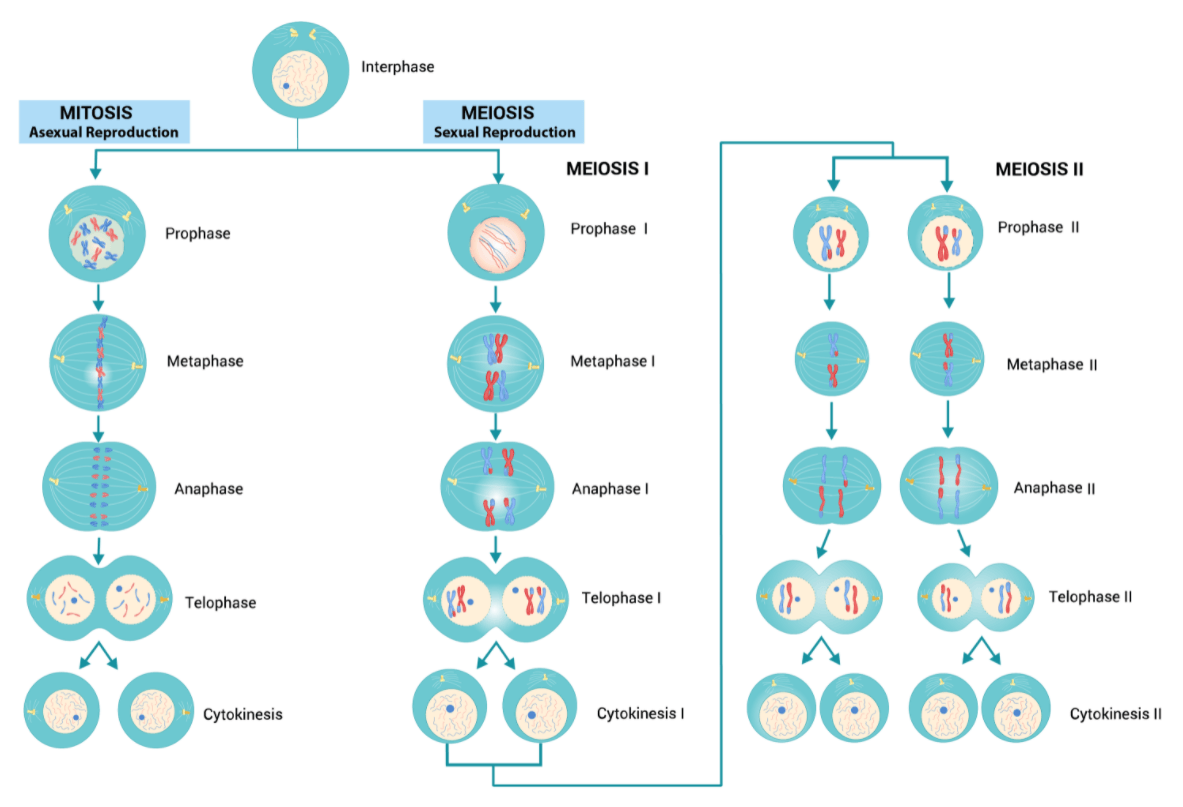
Mitosis vs. Meiosis: What are The Phases + What is Happening in Each Phase?
Mitosis = 1 set of division phases + produce 2 diploid daughter cells that are identical. (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase).
Meiosis = 2 sets of division + produce 4 haploid daughter cells that are NOT identical. (prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I → prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II).
Mitosis Process
Interphase = cell grows w normal functions
G1 - major growth + synthesizing many new molecules.
S - DNA copied → o.g chromosome + copied are attached by centromere → sister chromatids → DNA exists into chromatin (thread-like structure).
G2 - synthesize more molecules + organelles replicate.
Prophase = chromosomes short, thick, + visible → centrioles move to opposite ends of cell → create spindle fibre that attach to chromosomes @ centromere + organize the movement of chromosomes → nuclear membrane + nucleolus disappear.
Metaphase = spindle fibres align each chromosome into middle of cell.
Anaphase = Centromere divides → split sister chromatids to opposite poles of cell.
Telophase = chromosomes uncoil into chromatin → spindle fibre dissolves → nuclear membrane reforms around chromosomes → result 2 daughter nuclei.
Cytokinesis = cell divides cytoplasm into 2 new diploid daughter cells. * Follows mitosis NOT part of it!!
Meiosis Process
Meiosis I:
Interphase = *Same as mitosis
Prophase I = nuclear membrane dissolves → sister chromatids attached by centromere to form chromosome → centrioles move to poles → spindle fibres form → homologous chromosomes join together (tetrad) = bundle of 4 chromosomes, 2 from each parent, (process = synapsis) → synapsis has sister chromatids INTERTWINING + cross over.
Metaphase I = tetrads move to centre of cell + align centromeres across middle → independent assortment (tetrads align independently of each other) → spindle fibres attach to centromeres of sister chromatids.
Anaphase I = spindle fibres contract + pull apart tetrad so the H.C move to opposite poles of cell. *Centromere does NOT split, it holds chromosome together.
Telophase I + Cytokinesis = nuclear membrane reforms around nucleus + cytoplasm divided → creating 2 NON-IDENTICAL cells → each daughter nucleus receives 1 of each original o.g chromosome (daughter cell is haploid) → *immediately goes into “Meiosis II” b/c no second round of interphase.
Meiosis II: *similar to “Meiosis I, but process occurs in 2 cells @ same time → resulting in 4 non-identical haploid cells.
Prophase II = nuclear membrane dissolves → chromosomes are more visible + still attached to their copy by centromere → centrioles move towards the poles of cell.
Metaphase II = chromosomes(existing as sister chromatids) line up in the middle → spindle fibres emerge from centrioles + attach to the centromere of each chromosome pair.
Anaphase II = spindle fibres contract + break centromere + pull apart sister chromatids → one copy of pair goes to one pole while the other half goes to opposite pole.
Telophase II = nuclear membrane reforms around chromosomes that have been pulled to each pole + 2 new nuclei form in each cell → cell membrane pinches inward at equator.
Cytokinesis = *same as “Meiosis I” cytokinesis, + end product of 4 non-identical haploid cells.
Blood Types
Type A = IAIA , IAi
Type B = IBIB, IBi
Type AB = IAIB
Type O = ii
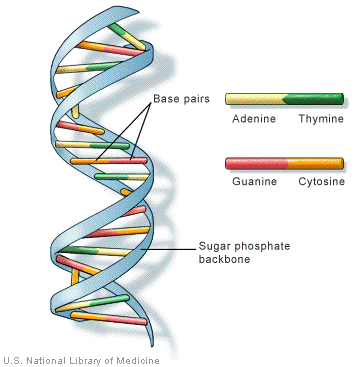
DNA Structure
Double Helix = resembles a twisted ladder.
Sugar-Phosphate Backbone = forms the sides of the ladder + nitrogenous bases form rungs.
Molecule of DNA = millions of nucleotides → pentose sugar, nitrogenous base, + phosphate group.
Pentose Sugar = 5 carbon sugars
Nucleotides = 4 nitrogenous bases → adenine, guanine, cytosine, + uracil/thymine.
DNA = AGCT
RNA = AGCU
Base Pairs = A+T, C+G, *RNA→ A+U
What is Karyotype?
Karyotype = photograph of pairs of homologous chromosomes in a cell.
3 Animal Systems
Digestive, Circulatory, + Respiratory Systems
Structures + Functions of Each System
Digestive System:
Mouth = Ingestion, mechanical digestion (chewing), chemical digestion (salivary enzymes in glands).
Pharynx = Passageway for food from mouth to esophagus.
Esophagus = Transports bolus to stomach via peristalsis.
Stomach = Mechanical digestion (churning), chemical digestion (gastric juices), temporary food storage.
Small Intestine:
Duodenum: Chemical digestion with bile and pancreatic enzymes.
Jejunum: Nutrient absorption.
Ileum: Absorbs remaining nutrients, vitamin B12, and bile salts.
Large Intestine = Absorbs water and electrolytes, forms and stores feces.
Rectum = Stores feces until defecation.
Anus = Expels feces from the body.
Circulatory System:
Superior Vena Cava = large vein responsible for returning deoxygenated blood collected from body, to the right atrium.
Aorta = artery carrying blood directly from heart to other arteries.
Pulmonary Trunk = transports deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygen.
Left Pulmonary Arteries = large blood vessel carrying blood from the heart to left lung.
Left Pulmonary Veins = blood vessel carrying blood from left lung to the heart.
Left Atrium = 1 of the 4 chambers of the heart… receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs → empties the blood into the left ventricle.
Bicuspid Valve = valve in heart between left atrium + left ventricle.
Aortic Semilunar Valve = between the left ventricle and aorta to ensure oxygen-rich blood doesn’t flow back into the left ventricle.
Left Ventricle = 1 of the 4 chambers of the heart… pumps oxygen-rich blood out to the body.
Septum = dividing membrane, especially between bodily spaces or masses of soft tissue.
Pulmonary Semilunar Valve = separates the right ventricle from the pulmonary trunk.
Inferior Vena Cava = large vein that returns blood from legs + abdomen, to the heart.
Right Ventricle = 1 of the 4 chambers of the heart… pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs.
Tricuspid Valve = valve in heart between right atrium + right ventricle.
Right Atrium = 1 of the 4 chambers of the heart… receives oxygen-poor blood from the body → empties the blood into the right ventricle.
Right Pulmonary Veins = blood vessel carrying blood from right lung to the heart.
Right Pulmonary Arteries = large blood vessel carrying blood from the heart to right lung.
Respiratory System:
Nose
Nasal Cavity = air that is inhaled is warmed, moistened, and cleansed of bacteria.
Mouth
Pharynx = passageway connecting mouth + nasal cavity to the larynx + esophagus.
Epiglottis = prevents food from entering the trachea by closing the glottis.
Larynx = between glottis and trachea contains vocal chords.
Trachea = tube that carries air from nasal/mouth to the bronchi and then lungs.
Pleural Membrane = sac surrounding each lung + covering it.
Intercostal Muscle = muscles attached to rib cage assisting breathing by elasticity.
Lung
Bronchi = passageway that branches from trachea to lungs.
Bronchiole = passageway branching from bronchi inside lung into smaller + thin-walled tubes.
Alveoli = found at end of each bronchiole, where the exchange of respiratory gases occurs.
Rib
Diaphragm = sheet of muscle that separate thoracic cavity from abdominal cavity.
Blood Vessels
Arteries = carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart (except for the pulmonary artery) → thick, muscular walls to withstand high pressure.
Structure = innermost layer (endothelium), the middle layer (smooth muscle and elastic tissue), and the outer layer (connective tissue) → elasticity helps maintain blood pressure + flow.
Veins = carry oxygen-poor blood back to the heart (except for the pulmonary vein) → thinner walls + valves to prevent backflow.
Structure = similar layers to arteries but with thinner middle layer + larger lumen → presence of valves assists in returning blood to heart against gravity.
Capillaries = small, thin-walled vessels where the exchange of gases, nutrients, + waste products occurs between blood + tissues.
Structure = single layer of cells to facilitate the exchange of materials between blood + tissues.
Flow of Each System: How Does Each System Work + What is The Flow?
Digestive System:
Ingestion = taking in or eating of food.
Digestion = breakdown of food ny mechanical and chemical processes into molecule small enough for cells of the body to absorb.
Absorption = transport of product of digestion from the digestive system ino circulatory system, which distributes to rest of body.
Elimination = removal of undigested solid waste matter from the body.
Circulatory System:
Heart = pumps oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle to the aorta and throughout the body.
Arteries = blood travels through arteries to various tissues.
Capillaries = nutrients + oxygen are exchanged with tissues, and waste products are collected.
Veins = ocygen-poor blood returns to the heart through veins.
Lungs = blood is pumped from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygen via the pulmonary artery.
Back to Heart = oxygen-rich blood returns to the left atrium via the pulmonary veins.
Respiratory System:
Inhalation = air enters body through nose or mouth → passes through the pharynx, larynx, + trachea.
Bronchi = air moves into bronchi → branch into smaller bronchioles within the lungs.
Alveoli = air reaches alveoli where gas exchange occurs → oxygen diffuses into blood, + carbon dioxide diffuses out of blood.
Exhalation = carbon dioxide-rich air is expelled from lungs through the bronchioles, bronchi, trachea, larynx, + pharynx → exits through the nose or mouth.
Enzymes
Carbohydrase = produced in the salivary glands + functions in the mouth.
Lipase = produced in the pancreas + functions in the small intestine.
Protease = produced by stomach glands + functions in the stomach.
Nuclease = produced in the pancreas + functions in the small intestine.
Blood: What are The Components + Functions?
Red Blood Cells (RBCs) = transport oxygen from lungs to rest of the body + return carbon dioxide from the body to lungs to be exhaled.
White Blood Cells (WBCs) = protect body against infection by identifying + destroying pathogens such as bacteria.
Platelets = Assist in blood clotting, preventing excessive bleeding when blood vessels are injured.
Plasma = 55%
Red Blood Cells = 44%
White Blood Cells + Platelets = 1%
Lung Capacity
Tidal Volume (TV) = V of air inhaled + exhaled during NORMAL breathing.
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) = V of air that can be inhaled BEYOND regular tidal.
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV) = V of air that can be exhaled BEYOND regular tidal.
Residual Volume (RV) = V of air REMAINING in lungs AFTER complete exhale.
Vital Capacity (VC) = total MAX V of air moved in + out of lungs in 1 BREATH. *VC = TV + IRV + ERV
Total Lung Capacity (TLC) = total volume of the lungs when fully inflated. *the sum of VC and RV.
Plant Tissues
Meristematic Tissue = occurs plant growth; + cells are undifferentiated, actively dividing, and develop into various specialized tissues.
Apical meristems = found at tips of roots + shoots; responsible for primary growth.
Lateral meristems = vascular cambium and cork cambium; responsible for secondary growth.
Dermal Tissue = forms outer protective covering layer; helps prevent water loss; + protect against injury and pathogens.
Epidermis = single layer of cells + often has a waxy cuticle.
Periderm = replacing epidermis with a tougher layer.
Ground Tissue = involved in functions such as photosynthesis, storage, and support.
Parenchyma; Collenchyma; + Sclerenchyma.
Vascular Tissue = transport of water, nutrients, + food throughout the plant.
Xylem = transports water + dissolved minerals from roots to shoots.
Phloem = transports sugars + other organic minerals downward from the leaves.
Reproductive Strategies of Plants
Sexual Reproduction in SEEDLESS Plants = depend on diffusion + osmosis → wet environments, swimming sperm, independent gametophyte plant, unprotected zygote/embryo/gametophyte.
Non-Vascular = dominant gametophyte plant.
Vascular = dominant sporophyte plant.
Sexual Reproduction in SEED Plants = depend on pollination → dry environments, non-motile sperm, dominant sporophytes, dependent gametophyte, protected zygote embryo.
Gymnosperms = unprotected seeds on surface of structure; wind pollination; single fertilization.
Angiosperms = protected seeds within ovary wall; wind/insect/animal pollination; double fertilization.
Asexual Reproduction in Natural Vegetative Propagation:
growth from roots, stems, or leaves.
Asexual Reproduction in Artificial Propagation:
dividing, grafting, cuttings, layering, tissue culturing
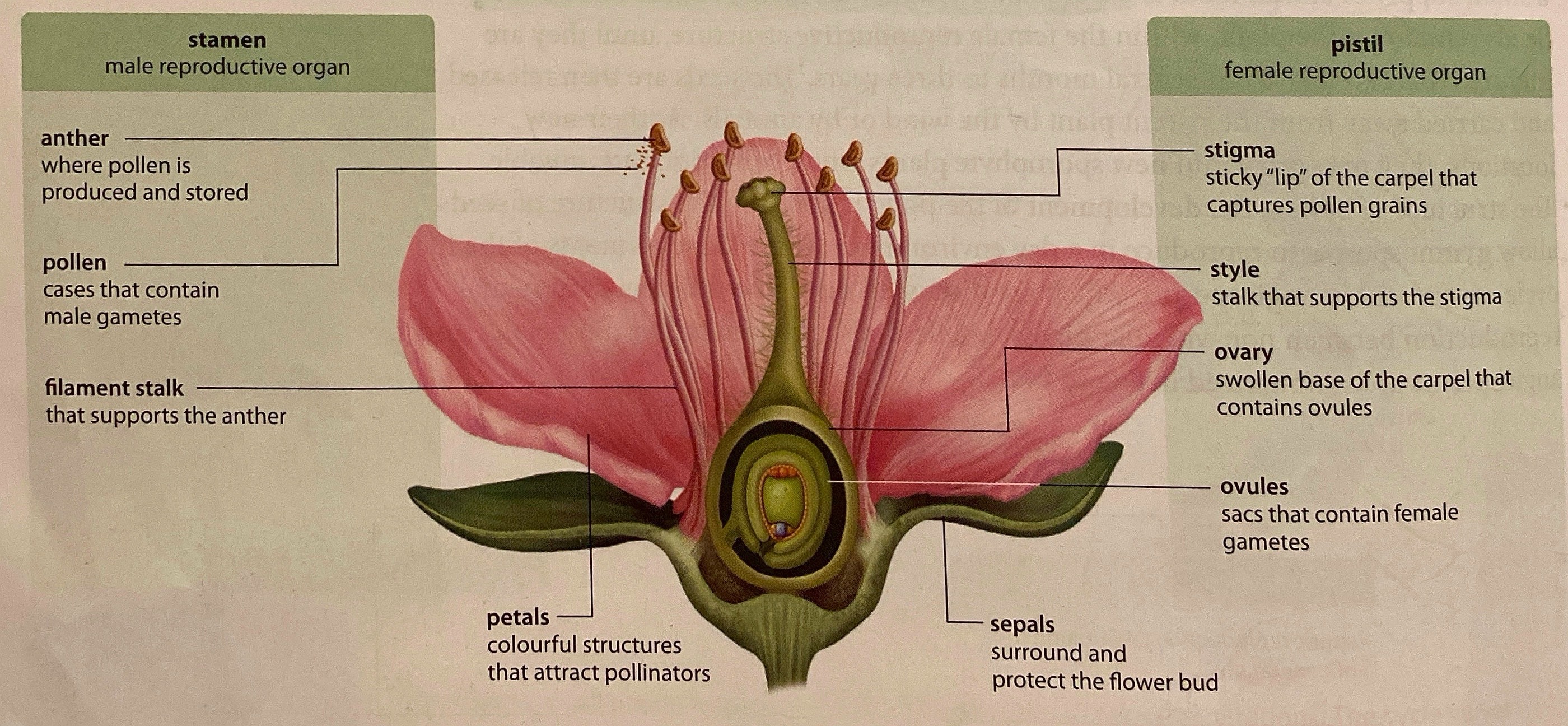
Parts of a Flower
Male Reproductive Parts (Stamen):
Anther = pollen is produced + stored.
Pollen = cases containing male gametes.
Filament Stalk = supports the anther.
Female Reproductive Parts (Pistil):
Stigma = sticky lip of carpel; grab pollen grains.
Style = stalks supporting the stigma.
Ovary = swollen base of carpel, contains ovules.
Ovules = sacs containing female gametes.
Other:
Petals = colourful structures, attract pollinators.
Sepals = surround + protect flower bud.
Evolutionary Theories and Scientists
George-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon (1707-1788)
Common Ancestry and Variation = suggested species could change over time + shared common ancestors → noted the similarities between humans + apes, and suggests that environmental influences lead to changes in species.
Georges Cuvier (1769-1832)
Extinction and Catastrophism = suggested that Earth's history was shaped by sudden, violent events (catastrophes) → caused extinction of species →… used fossils to show many species that once existed, no longer do.
Charles Lyell (1797-1875) + James Hutton (1726-1797)
Gradualism = Hutton suggested Earth's geological features were result of slow, continuous processes → Lyell expanded this with his theory of uniformitarianism → suggests same geological processes seen today have been occurring throughout Earth's history → concept of gradual change over time.
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829)
Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics = suggested that organisms could pass on traits acquired during their lifetime to their offspring. Ex. giraffes' long necks evolved from ancestors stretch necks to reach leaves.
Use and Disuse = theorized that body parts used extensively would become stronger + more developed, while those not used would deteriorate over time.
Charles Darwin (1809-1882)
Natural Selection = suggests individuals with traits better suited to environment are more likely to survive + reproduce → passing advantageous traits to next generation → Over time, leads to evolution of species.
Descent with Modification = suggested that all species are related through common ancestry + change over time due to natural selection.
Thomas Malthus (1766-1834)
Population Growth = proposed populations grow larger while food supply grows smaller → leads to a struggle for existence where ONLY the fittest survive → concept helped Darwin + Wallace understand the competition aspect of natural selection.
Alfred Russel Wallace (1823-1913)
Natural Selection = *similar to Darwin → Wallace suggests that species evolve through natural selection → collected extensive data during travels in Malay Archipelago → supporting idea that geographical distribution of species provided evidence of evolution.
Gregor Mendel (1822-1884)
Laws of Inheritance = discovered traits are inherited in genes + formulated laws of segregation/independent assortment → clarified mechanism of inheritance… which later connected with Darwin's theory of natural selection to form our modern theory of evolutionary biology.
Pre-Zygotic vs. Post-Zygotic Mechanisms
Pre-Zygotic = barrier either impedes mating between species or fertilization of eggs if individuals from different species attempt to mate.
Post-Zygotic = barrier preventing hybrid zygotes from developing into viable, fertile individuals.
Homologous vs. Analogous Structures
Homologous = structures having similar structural elements + origin BUT different functions.
Analogous = structures that do NOT have common evolutionary origin BUT similar functions.
Evidence for Evolution
Biogeography = species geographically isolated (islands) often evolve unique traits. Ex. finches of Galápagos Islands evolved distinct beak shapes due to feeding habits.
Fossil Record:
Transitional Fossils = show intermediate states between ancestors and descendants (Ex. Archaeopteryx).
Vestigial Structures = non-functional parts that were functional in ancestors (Ex. human appendix).
Anatomy:
Homologous Structures = body parts of organisms with different functions but similar structure/origin.
Analogous Structures = body part of organisms with similar function but different structure/origin.
Embryology = similar embryonic stages in different species suggest common origins
DNA = show relatedness between organisms when no other method to prove of a common ancestor.