BSF L3 pt. 1
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
The sum of all chemical reactions in a cell
Metabolism
Which pathway delivers chemical energy in the form of an ADH, NADPH, FADH2, GTP, and ATP?
Catabolic pathway
Which pathway converts, small, precursor molecules into cellular macromolecules?
Anabolic pathways
In a normal state, exercise/stress, extreme exercise/stress conditions what do red blood cells use as an energy source?
Glucose
Why do blood cells provide and only glucose?
They have no mitochondria
Why does the heart use FFA first in normal conditions?
Has to pump blood all the time; It has high energy demand; FFA has high energy (ATP) value
Why does the muscles FFA In exercise/stress and extreme exercise?
More energy is needed in those conditions and glucose and muscle is used up in 24 hours
Extreme exercise conditions what does the brain use as its energy source?
Ketones
for each molecule of glucose that passes through the preparatory phase of glycolysis, what is formed?
Two molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
In step one of glycolysis what is the enzyme involved?
Hexokinase
And one about glycolysis what is the reaction?
Glucose + ATP = G6P & ATP
Step two of lysis what is the enzyme involved?
Phosphohexose isomerase
Step two of glycolysis what is the reaction?
G6P = F6P
Step three of glycolysis what is the enzyme involved?
Phosphofructokinase-1
Instead of glycolysis, what is the reaction?
F6P = FBP
Step four of the lysis what is the enzyme involved?
Aldolase
Step four of glycolysis what is the reaction?
FBP = DHAP & G3P
In step five of glycolysis, what is the end and used?
Triose phosphate isomerase
What is the start of the payoff phase in glycolysis?
Step five
Step five of glycolysis what is the reaction?
DHAP = G3P
During the payoff phase of glycolysis ___ glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate molecules formed in the preparatory phase and the payoff phase producing what?
2; pyruvate
Each glucose yields a net gain of what?
2 ATP
In step six of glycolysis, what is the enzyme used?
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Step six of glycolysis what is the reaction?
G3P = BPG
In step of six of glycolysis oxidation and phosphorylation happens producing what?
2NADH
In step seven of glycolysis what is the enzyme used?
Phosphoglycerate kinase
Step seven of glycolysis what is the reaction?
BPG = 3PG
What is the first ATP farming reaction In glycolysis?
Step 7
In step eight of glycolysis, what is the enzyme used?
Phosphoglycerate mutate
In step eight of glycolysis, what is the reaction?
3 PG = 2 PG
In step nine of glycolysis, what is the enzyme used?
Ebola’s
Step nine of glycolysis what is the reaction?
2PG = PEP
In step 10 of lysis what is the enzyme used?
Pyruvate kinase
In step 10 of glycolysis, what is the reaction?
PEP = pyruvate
What is the second ATP forming reaction in glycolysis?
Step 10
____ ATP are produced, but ___ are put back into the cycle in preparatory phase.
4; 2
how is NADH formed in glycolysis?
GPDH oxidizes the aldehyde group of G3P to a carboxyl group and transfers the electrons to NAD to form NADH
Glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 Pi +2 ADP → 2 Pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 ATP + 2H2O
Glycolysis reaction
How is liquor made?
Pyruvate to ethanol fermentation
Why do muscles get sore after intense exercise?
Anaerobic pyruvate to lactate reduction
Under anaerobic conditions, what is pyruvate reduced to?
Lactate
When does anaerobic metabolism take place?
When there is a limited supply of oxygen, a few or no mitochondria, or greatly increased demands for ATP
What does lactic acid generated by skin act as?
Antibacterial agent
The quarry cycle is the cycling of lactate and glucose between what?
Peripheral tissues and liver
What are the sources of Acetyl-CoA
Acid, ketone body, sugar, pyruvate, amino acid, and ethanol
What does Acetyl-CoA undergo to become TCA?
Citrate synthase
Where does the pentose phosphate pathway occur?
In the cytosine
What regulates G6P partitioning?
NADPH
If NADPH is forming faster than it is being used, what happens?
It rises and inhibits the first enzyme
What does the pentose phosphate pathway achieve?
It yields reducing potential in the form of NADPH to be used in anabolic reactions requiring electrons
What does the PPP yield?
Ribose-5-phosphate
Ribose-5-phosphate is a nucleotide biosynthesis that leads to…
DNA
RNA
Various cofactors
What is glutathione?
A tripeptide composed of glutamate, cystine, and Glycerine
Why is glutathione important?
Reduced glutathione (GSH) maintains the normal reduced state of the cell
How does reduced glutathione (GSH) protect the cell?
By destroying hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl free radicals
What can be fatal in cases of high oxidative stress?
G6P dehydrogenase deficiency
What is required for the regeneration of GSH from its oxidized form (GSSG)?
NADPH
What does reduced glutathione Detoxify?
Reactive oxygen species (ROS)
Individuals with reduced GSH are subject to ___
Hemolysis
What is black urine an indicate of?
Reduced GSH; hemolysis
What do individuals with a G6PD deficiency not produce enough to cope with ROS
GSH
The cytosolic NADH generated via glycolysis transfers its equivalents to mitochondrial NAD+ via _____________
shuttle systems across the inner mitochondrial membrane
How does the pyruvate generated during glycolysis enter the mitochondria and be oxidized completely by CO2?
By pyruvate dehydrogenase and the TCA cycle
Why is glycolysis regulated?
To ensure that ATP homeostasis is maintained
Under anaerobic conditions, how is glycolysis continued?
Pyruvate is reduced to lactate by NADH, thereby regenerating the NAD required for glycolysis
On oxygen supply is not limited, what is oxidized to Acetyl-CoA?
Pyruvate
Acetyl-CoA + 3NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2 H2O → 2CO2 + 3NADH + FADH2 + GTP + CoA + 3H+
The TCA cycle
What is generated in the TCA cycle?
3 NADH, 1 GTP/ATP, 1 FADH2, 2 CO2
Where does the TCA cycle occur?
Mitochondrial matrix and the cytosol for prokaryotes
What is step one in the TCA cycle?
Acetyl-CoA = citrate
What is step two in the TCA cycle?
Citrate = isocitrate
What is the net oxidation of the TCA cycle?
2 carbons = CO2
Citrate undergoes rearrangements that produce 2 CO2 and 2 NADH.
Where do the electrons transfer from the energy captured in the TCA cycle?
NADH and FADH2
What is step three in the TCA cycle?
Isocitrate = alpha-Ketoglutarate
What is step four in the TCA cycle?
alpha-Ketoglutarate = Succinyl-CoA
What is step five in the TCA cycle?
Succinyl- CoA = Succinate
What is step six in the TCA cycle?
Succinate = Fumarate
What is step seven in the TCA cycle?
Fumarate= Malate
What is step eight in the TCA cycle?
Malate = Oxaloacetate
Describe the TCA cycle
1. Acetyl-CoA joins oxaloacetate (four-carbon) to form citrate (six-carbon).
2. Citrate undergoes rearrangements that produce 2 CO2 and 2 NADH.
3. After the loss of two CO2, the resulting four-carbon molecule produces 1 GTP through substrate-level phosphorylation.
4. The molecule will now transfer electrons to 1 FAD, which is reduced into 1 FADH2.
5. Lastly, the molecule is converted back into oxaloacetate and also gives electrons to produce 1 NADH.
6. Two acetyl-CoA molecules produce 4 CO2 + 6 NADH + 2 FADH2 + 2 GTP
What steps in the TCA cycle is NADH/H+ produced?
3, 4, and 8
What step in the TCA cycle is GTP/ATP produced?
5
What step in the TCA cycle is CO2 produced?
3 and 4
What step in the TCA cycle is FADH2 produced?
6
In the liver, TCA cycle intermediates are continuously withdrawn into the pathways of…
fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, gluconeogenesis, and heme synthesis
In the brain, α-ketoglutarate is converted to _______ and _______ both of which are neurotransmitters.
glutamate and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
Refers to the removal of intermediate from the metabolic cycle
Cataplerosis
Refers to the pathways which replenish the intermediate of the TCA cycle
Anaplerosis
What is a major annaplerotic enzyme?
Pyruvate carvoxylase
What also forms TCA cycle intermediate?
Amino acid degradation
Refers to cellular energy transformations
Bioenergetics
How is the electrochemical proton gradient created?
By active transport of protons across the membrane from complex one and complex five, chemically removing protons from the matrix and releasing protons into the intermembrane space
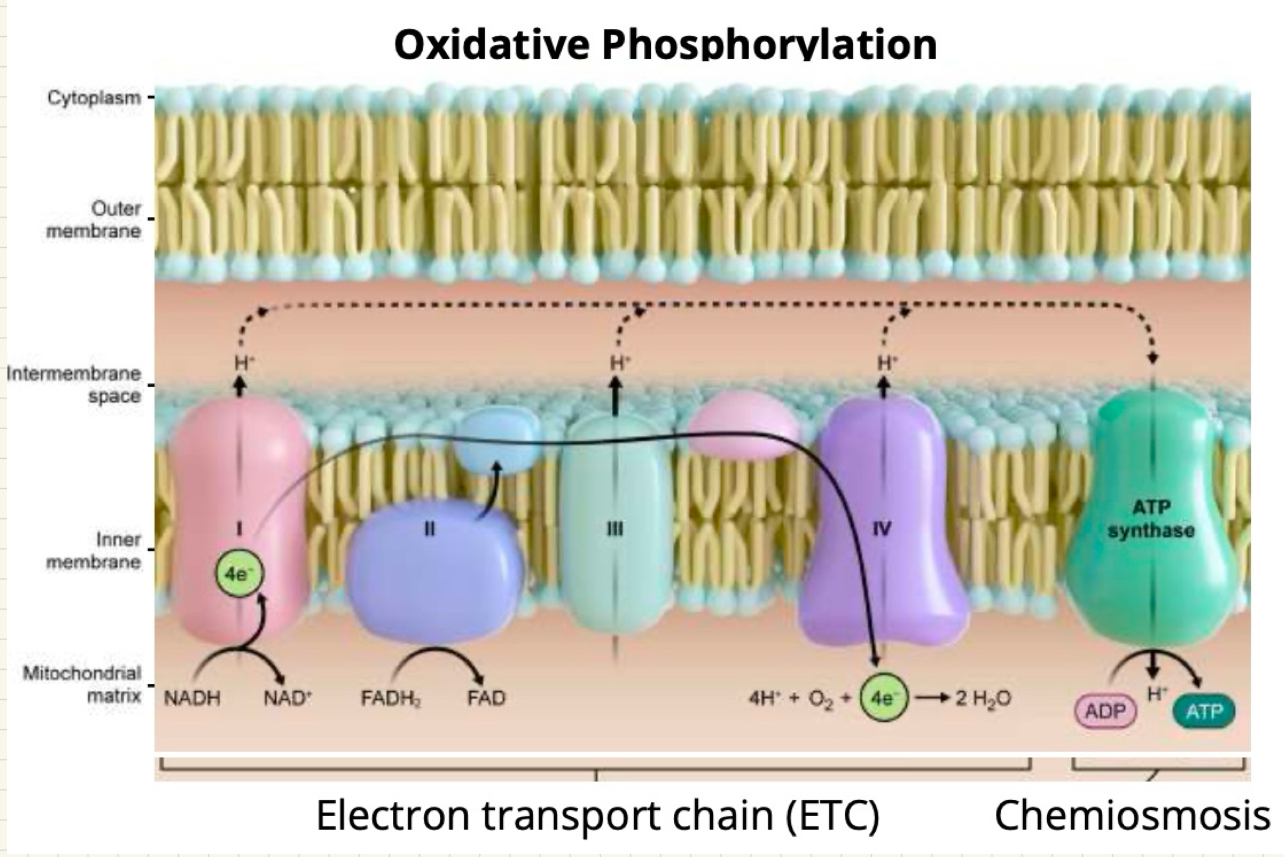
What does the electrochemical potential gradient create?
Proton motif force (PMF)
What is proton motif force (PMF)?
The energy that pushes the protons to re-enter the matrix to equilibrate on both sides of the membrane
Why can’t electron flow occur faster than protons are used for ATP synthesis or return to the matrix by uncoupling?
Because electron flow requires proton pumping
What happens as ADP levels increase?
proton influx increases (through ATPase)
Electrochemical gradient decreases
Proton dumping electron transfer are increased to maintain electrochemical gradient
Oxygen consumption increase
Why do we need ATP?
Mechanical work and transport work
how do we convert the chemical energy of ATP to mechanical work?
Muscle contraction
What requires ATP to transport molecules or ions against the concentration gradient?
Active transport
What has high energy phosphate bonds?
ATP