b. Gynecology Pathology
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
a) 3D of abn mirena IUD placement
b) 2D of normal Essure microinserts
c) 3D of normal Mirena IUD placement
d) 3D of normal Essure microinserts
d) 3D of normal Essure microinserts
which is assoc w/precocious puberty
a) mucinous cystadenoma
b) serous cystadenoma
c) cystic teratoma
d) granular cell tumor
d) granular cell tumor

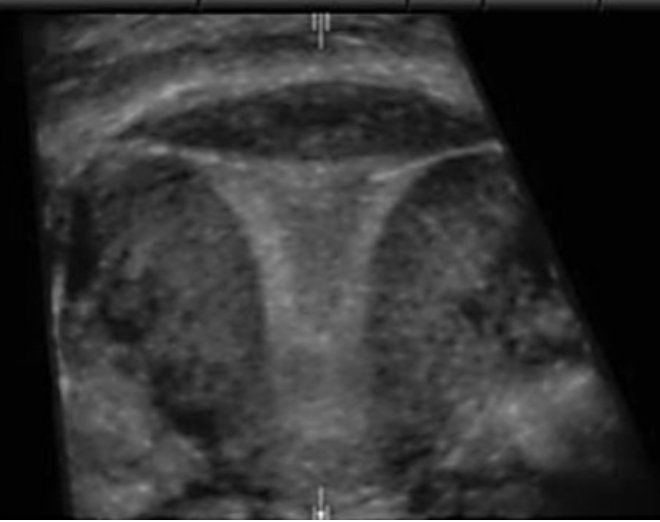
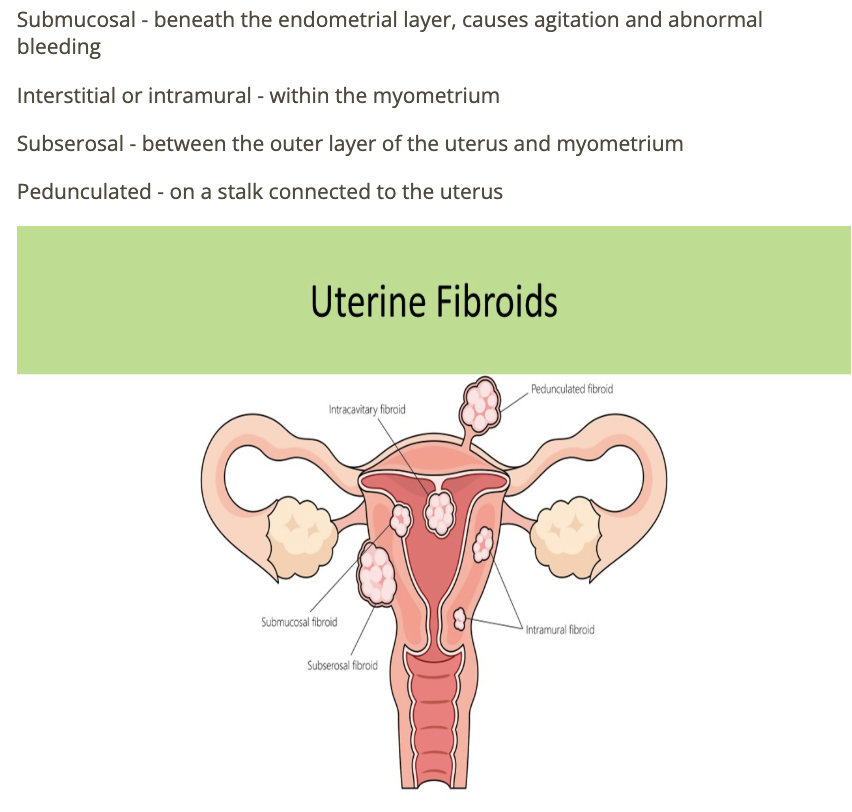
where is the fibroid in the sag uterus
a) posterior fundal
b) posterior body
c) anterior fundal
d) anterior cervix
c) anterior fundal

what is the most common uterine mass/tumor
a) leiomyoma
b) Brenner tumor
c) serous cystadenoma
d) endometrial polyp
a) leiomyoma
formation of bilateral solid ovarian neoplasm is high suspicious for
a) yolk sac tumor
b) serous cystadenoma
c) Krukenberg tumor
d) dysgerminoma
c) Krukenberg tumor
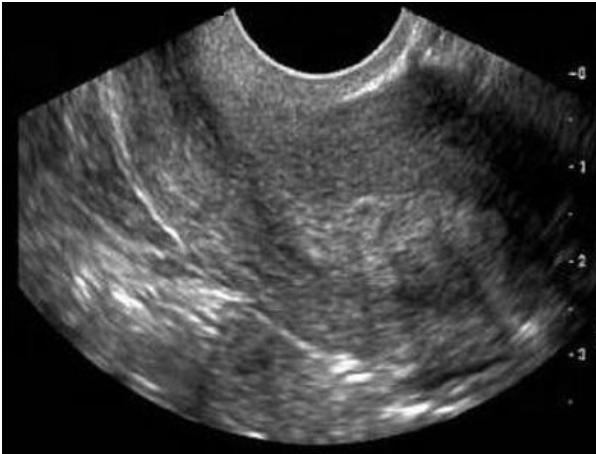
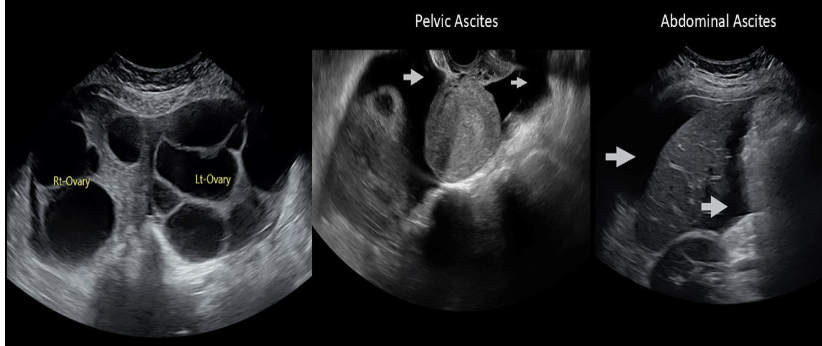
this is ascites in morison pouch
a) twin gestation
b) normal ovulation
c) ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
d) multiple large uterine fibroids
c) ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
which is related to abn testosterone production
a) menometrorrhagia
b) dyspareunia
c) dysmenorrhea
d) hirsutism
d) hirsutism
a hypoechoic mass w/benign characteristics is identified in the right ovary of a 6 yo girl. her labs show moderate levels of estrogen levels in the blood.
.
a) androblastoma
b) Brenner tumor
c) granulosa cell tumor
d) krukenberg tumor
c) granulosa cell tumor
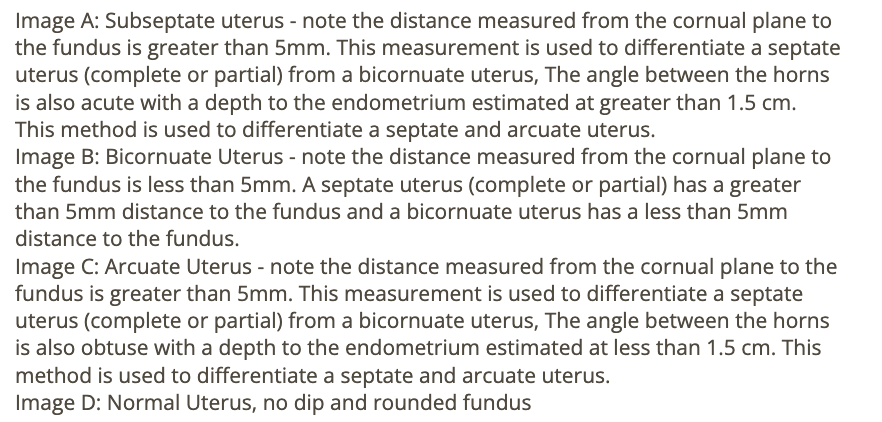
hydrosalpinx + pyosalpinx are differentiated from pelvic veins using
a) graded compression
b) color doppler
c) harmonic imaging
d) water enema
b) color doppler
what does McBurney’s point refer to
a) location of tip of endometrial canal
b) point of greatest tenderness in RLQ in a pt w/endometriosis
c) point where 2 halves of the uterus merge together during development
d) the most common location of the appendix
d) the most common location of the appendix
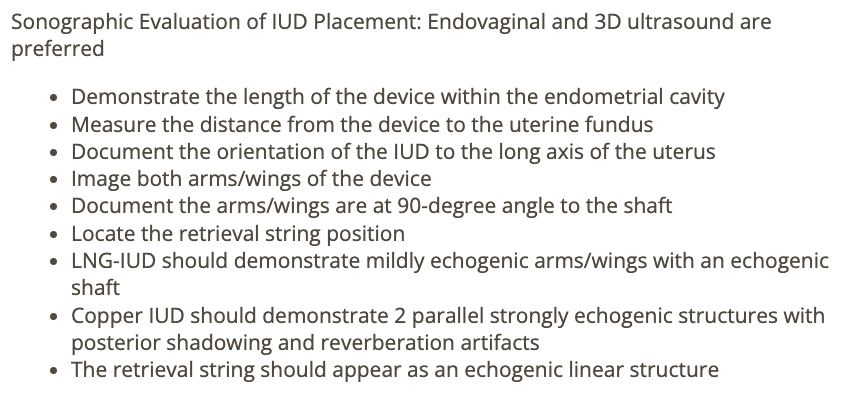
the evaluation of IUD placement in the uterine cavity includes the measurement of
a) span of wings of device
b) distance of uterine cornua on both sides
c) distance from IUD to uterine fundus
d) thickness of device
c) distance from IUD to uterine fundus
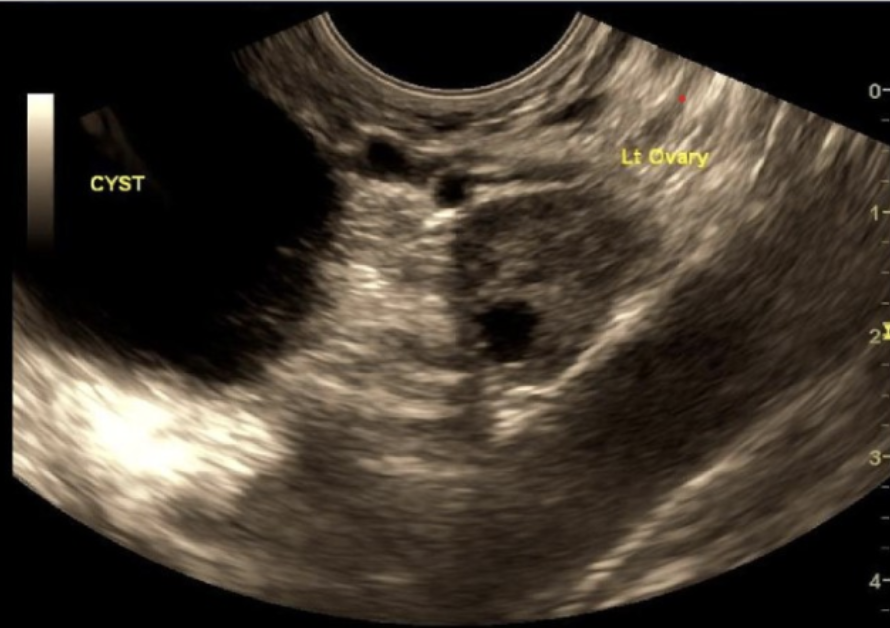
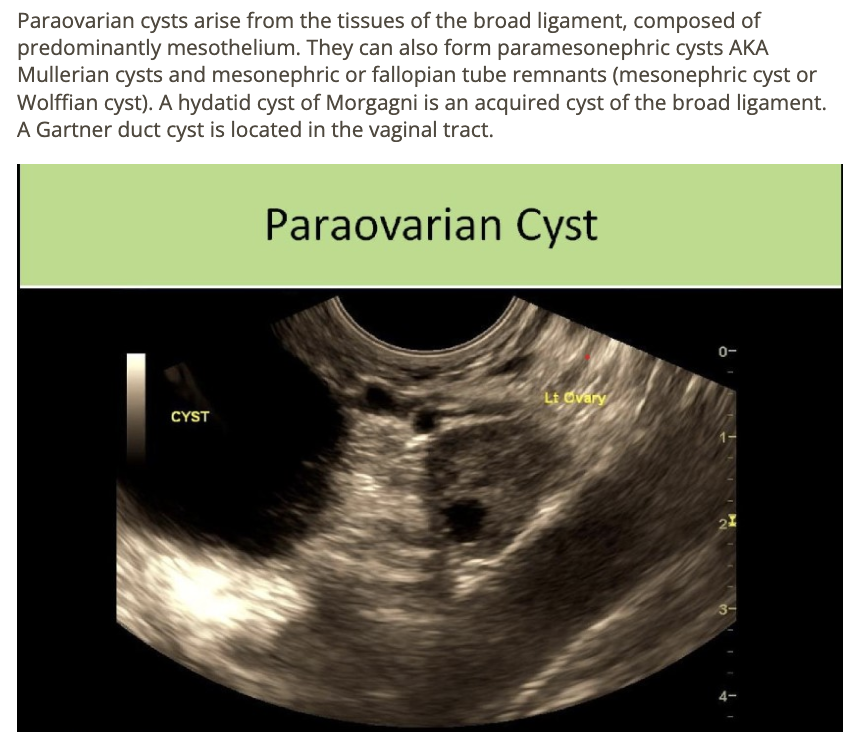
a paraovarian cyst is aka
.
a) morgagni or gartner duct cyst
b) gartner duct or mesonephric cyst
c) mesonephric cyst or nabothian cyst
d) morgagni or mesonephric cyst
d) morgagni or mesonephric cyst
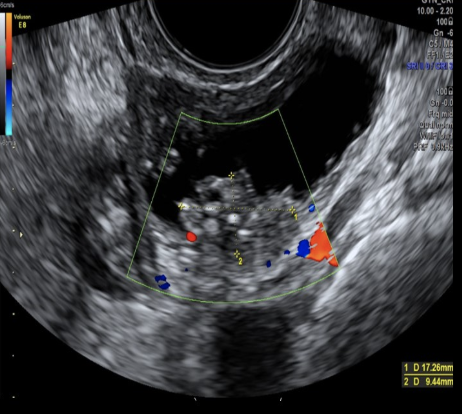
which ovarian tumor contains both epithelial + stromal componenets
a) thecoma
b) mucinous cystadenoma
c) serous cystadenoma
d) cystadenofibroma
d) cystadenofibroma

a 55 yo female has pelvic pain, vaginal spotting, and enlarged uterus on clinical examination.
.
the last exam 4 months ago showed a 4 cm intramural fibroid + 6 mm endometrium. she has no hx of hormone replacement therapy, but does take tamoxifen regularly.
.
the current US exam shows 7 mm endometrium + 6 cm intramural, non-circumscribed, heterogenous, hypoechoic mass in the uterus body
.
a) leiomyosarcoma
b) leiyomyoma
c) adenocarcinoma
d) cervical carcinoma
a) leiomyosarcoma

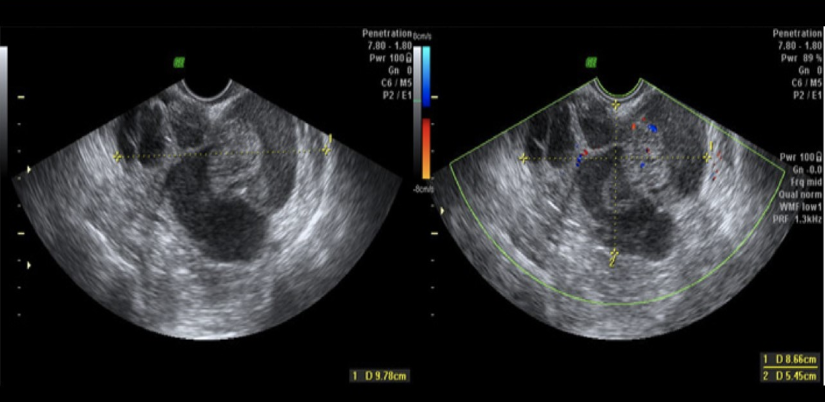
a 64 yo female has left sided pain + bloating. the exam shows a
.
4cm cystic mass w/numerous thick septations + small loculations that give it a honeycomb appearance.
.
there is also a 7 mm solid nodule on the lateral aspect of the cyst.
.
a) Brenner tumor
b) mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
c) serous cystadenocarcinoma
d) mucinous cystadenoma
b) mucinous cystadenocarcinoma

a pt has pelvic pain + abn lab testing of
high erythrocyte sedimentation rate
elevated C-reactive protein
elevated CA-125
positive Chlamydia
.
a) pelvic inflammatory disease
b) endometriosis
c) lynch syndrome
d) stein-leventhal syndrome
a) pelvic inflammatory disease
uterine / vaginal prolapse is assoc w/weakness of
a) rectus abdominis
b) levator ani
c) obturator internus
d) piriformis
b) levator ani
which symptoms is assoc w/hematometrocolpos
a) dyspareunia
b) menorrhagia
c) amenorrhea
d) menometrorrhagia
c) amenorrhea

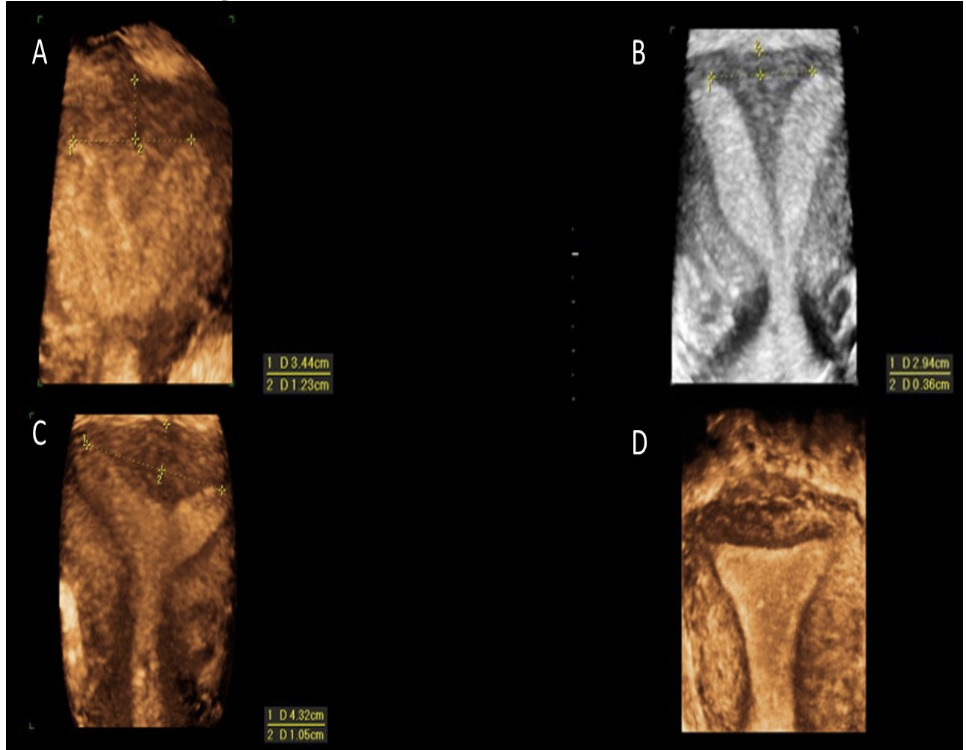
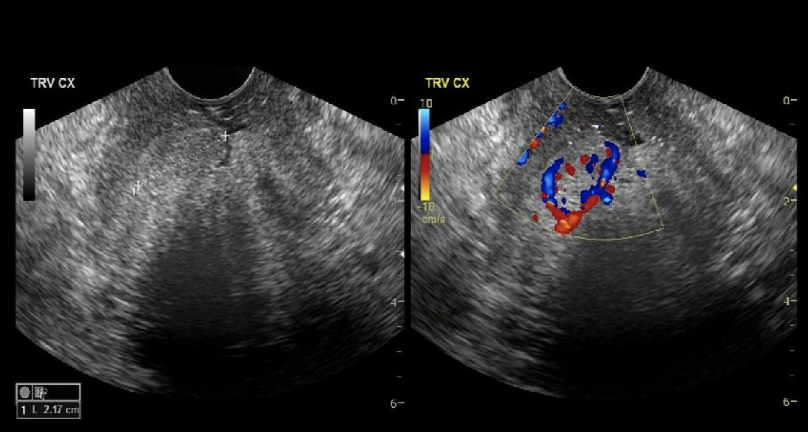
which shows arcuate uterus
a) A
b) B
c) C
d) D
c) C
chronic pelvic inflammatory disease can lead to
a) emergency hysterectomy
b) emergency salpingectomy
c) formation of cervical polyps
d) formation of uterine septum
c) formation of cervical polyps

30 yo has amenorrhea. she says her cycles slowed + stopped over the last few months. she also complains of reduced breast size. these clinical findings are for
a) teratoma
b) arrhenoblastoma
c) fibroma
d) thecoma
b) arrhenoblastoma

which is a benign tumor that can lead to fibroid enlargement + postmenopausal bleeding
a) thecoma
b) leiomyosarcoma
c) endodermal sinus tumor
d) dermoid cyst
a) thecoma
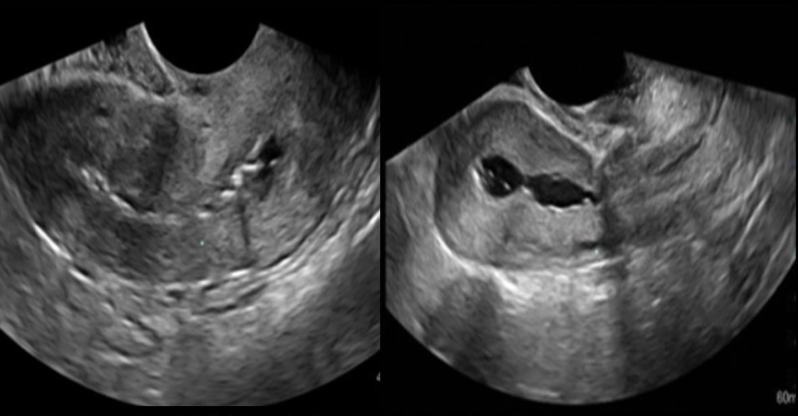
_____ syndrome refers to intrauetrine adhesion of endometrial lining caused by C-section or D&C
a) fitz hugh curtis
b) mirizzi
c) digeorge
d) asherman
d) asherman
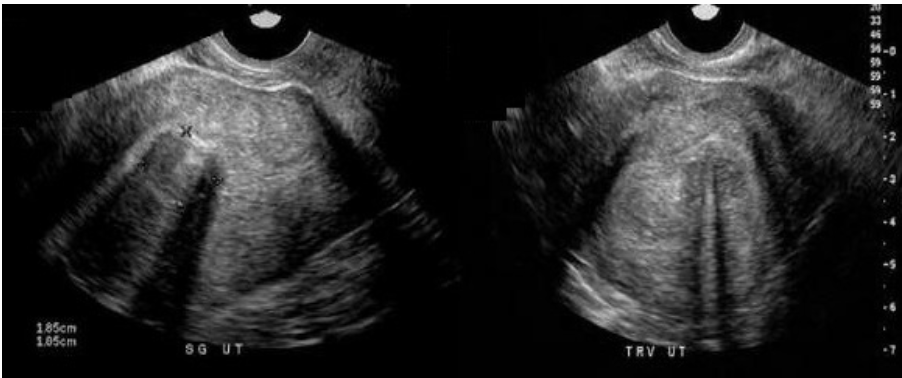
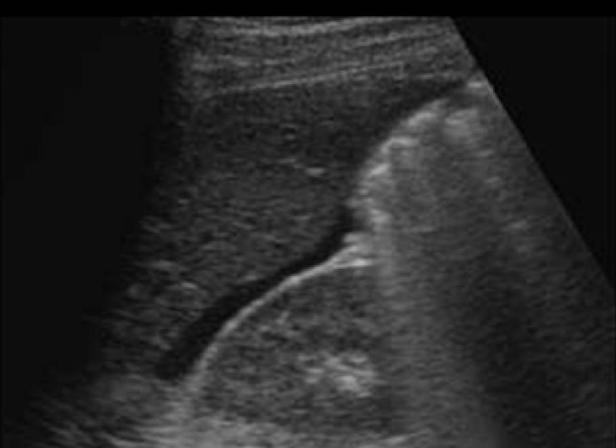
what type of fibroid is this
a) submucosal
b) subserosal
c) pedunculated
d) intramural
a) submucosal

which refers to pain assoc w/sex
.
a) menorrhagia
b) amenorrhea
c) mittelschmerz
d) dyspareunia
d) dyspareunia
a peritoneal inclusion cyst is commonly assoc w/
a) prior C-section
b) molar pregnancy
c) multiple vaginal birth
d) congenital malformation
a) prior C-section

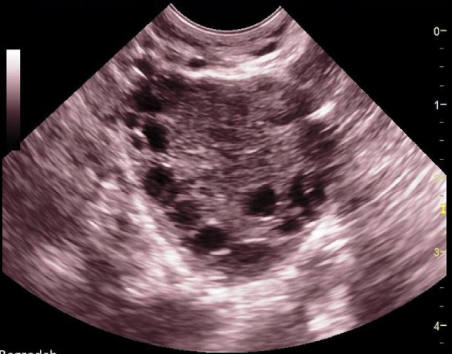
pt has amenorrhea + hirsutism. if the right ovary has the same appearance,
a) normal ovary w/multiple follicles
b) partial ovarian torsion
c) ovarian hyperstimulation
d) possible stein-leventhal syndrome
d) possible stein-leventhal syndrome
ovarian malignancy
a) 2nd leading cause of cancer death in women
b) will cause decreased serum levels of CA-125
c) is most commonly diagnosed at stage 3 or greater
d) requires monthly screening protocol for those w/family hx
c) is most commonly diagnosed at stage 3 or greater

which is a contraindication for IUD placement
a) active pelvic inflammatory disease
b) endometrial hyperplasia
c) fibroid uterus
d) adenomyosis
a) active pelvic inflammatory disease

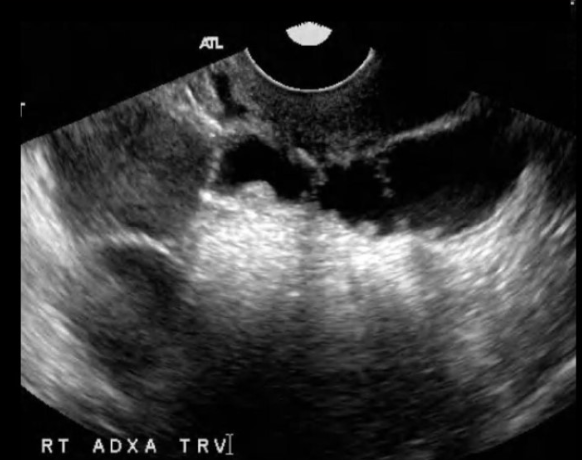
which is a common sono sign of chronic PID
a) endometritis
b) beads on a string sign
c) cogwheel sign
d) tubular, thick-walled, hypervascular adnexal structure
b) beads on a string sign

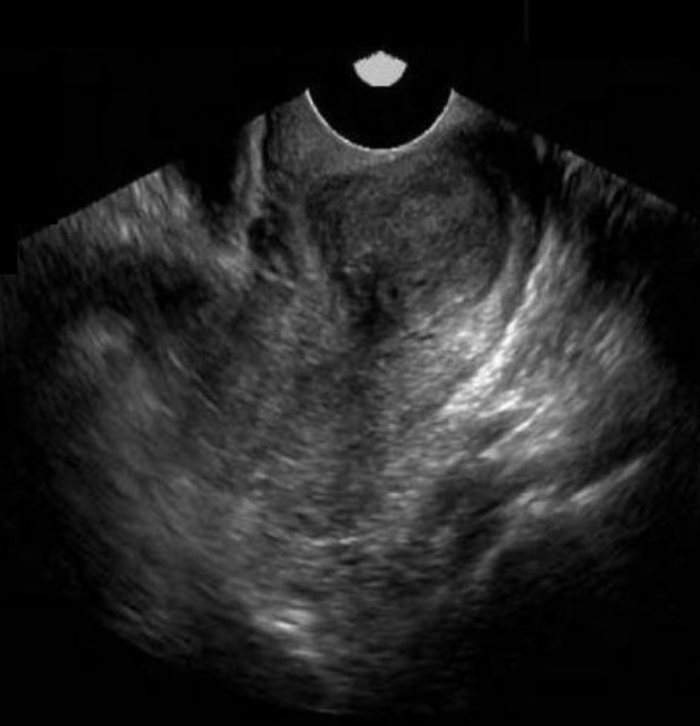
30 yo has pelvic pressure + dyspareunia. she has partial hysterectomy 1 year ago.
a) large chronic hematoma remaining in the cervix
b) solid mass in cervix, most likely carcinoma
c) large complicated nabothian cyst
d) fibroid formation in the remaining uterine tissue left behind unintentionally
b) solid mass in cervix, most likely carcinoma
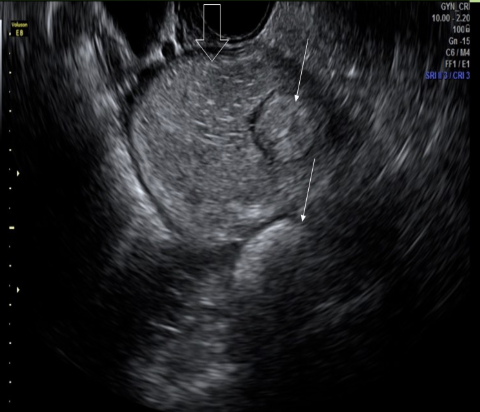
an ovarian mass w/dot-dash pattern internally is most likely
a) mucinous adenoma
b) dysgerminoma
c) teratoma
d) mucinous adenocarcinoma
c) teratoma

t-shaped uterus is most commonly assoc w/
a) maternal exposure to DES
b) personal hx of smoking
c) personal exposure to DES
d) maternal alcohol abuse
a) maternal exposure to DES
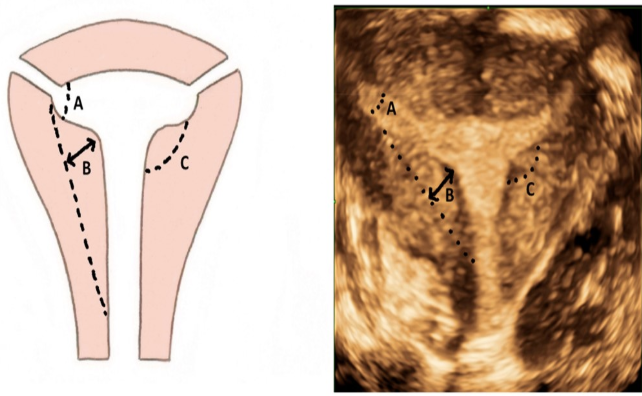
which is an expected finding with metritis
a) leukocytosis
b) high HCG serum levels
c) anemia
d) leukopenia
a) leukocytosis

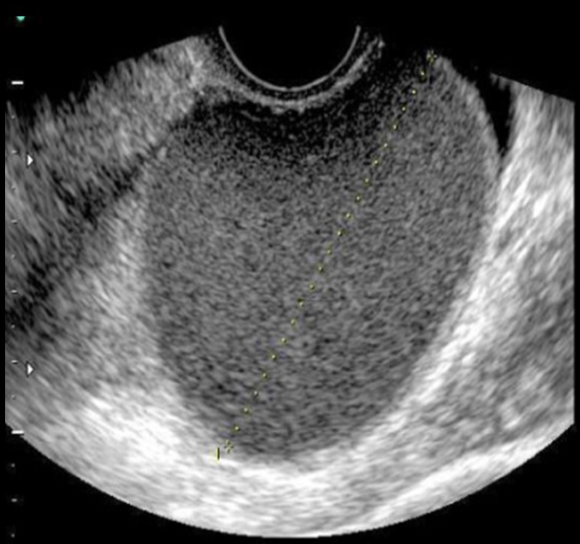
a 20 yo has dysmenorrhea + menorrhagia. she says her menstrual cycle occurs every 28 days + LMP was 21 days ago.
a) hematometrocolpos
b) endometrioma
c) andeocarcinoma
d) pyosalpinx
b) endometrioma

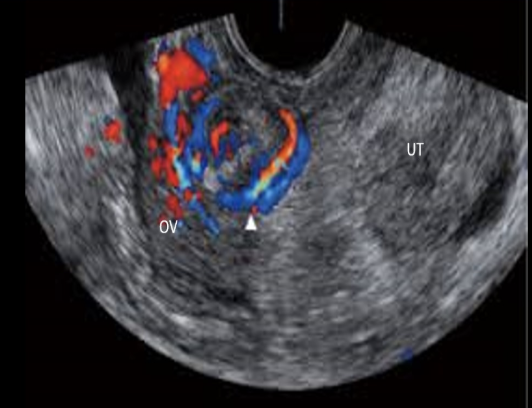
the whirlpool sign shows with
a) ectopic pregnancy
b) molar pregnancy
c) ovarian torison
d) hydrosalpinx
c) ovarian torsion
____ is the most common adnexal mass
a) fibroid
b) dermoid
c) serous cystadenocarcinoma
d) ovarian cyst
d) ovarian cyst

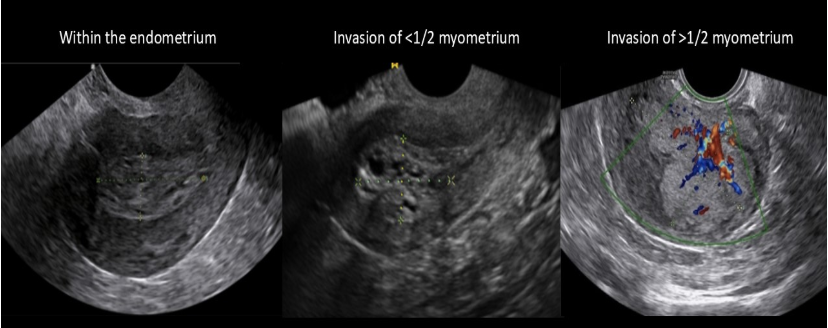
in stage 1 endometrial cancer, the cancer has invaded the
a) pelvic lymph nodes
b) ovaries
c) myometrium in UT body
d) cervix
c) myometrium in UT body

____ occurs when the IUD penetrates the myometrial layer but not the serosal layer.
.
When the IUD penetrates both layers of the uterine wall, the complication is called ____
.
a) perforation, expulsion
b) embedment, perforation
c) displacement, expulsion
d) expulsion, perforation
b) embedment, perforation

_____ and granulosa cell tumors are benign ovarian neoplasms that secrete estrogen
a) sertoli leydig cell tumors
b) fibromas
c) thecomas
d) mucinous cystadenomas
c) thecomas
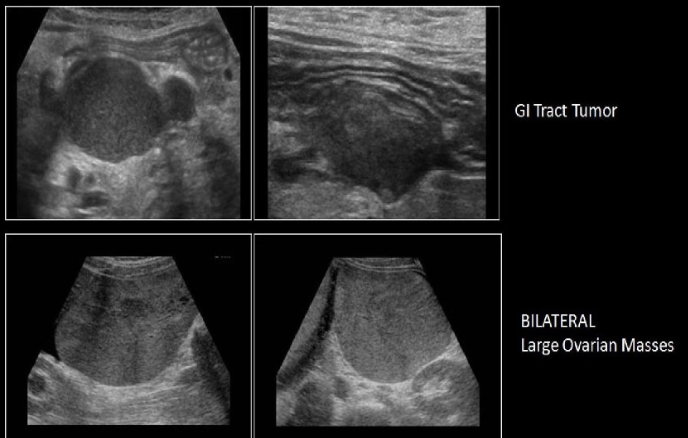
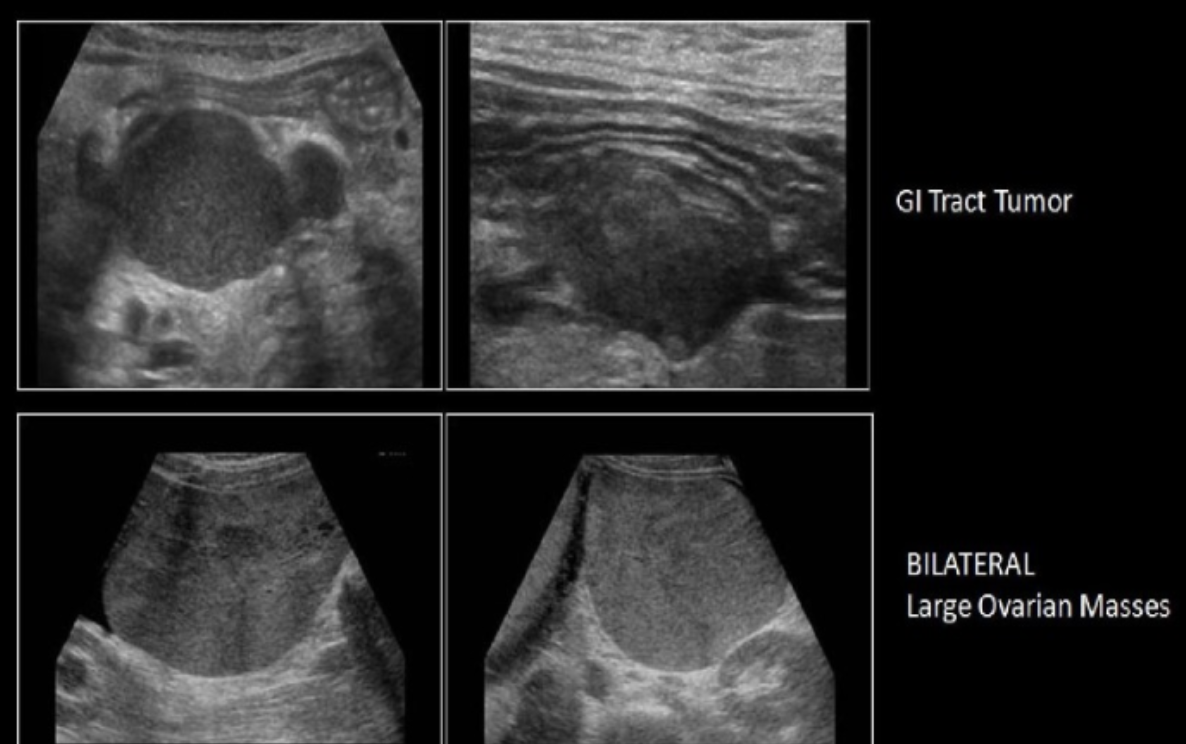
pt has pain + bloating. she has hx of GI tract carcinoma. which is the most likely sono finding in pelvis
a) lymphadenopathy + bilateral ovarian cyst formation
b) krukenberg tumor or ovary + peritoneal cysts
c) lymphadenopathy + krukenberg tumor of ovary
d) lymphadenpathy + brenner tumor of ovary
c) lymphadenopathy + krukenberg tumor of ovary
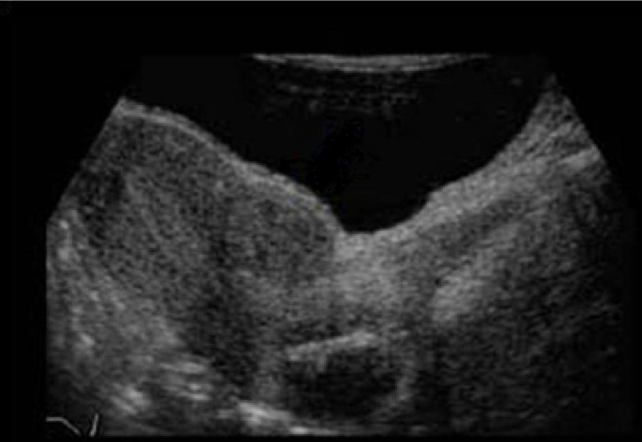
pt has irregular bleeding + pelvic pain for the last 2 months
a) multiple fibroids in uterus body + cervix
b) subserosal fibroid w/IUD in uterine cervix
c) submucosal fibroid
d) tampon in cervix
b) subserosal fibroid w/IUD in uterine cervix
spotting between cycles + infertility are common symptoms of
a) garter duct cyst
b) hematometra
c) endometrial polyp
d) endometriosis
c) endometrial polyp
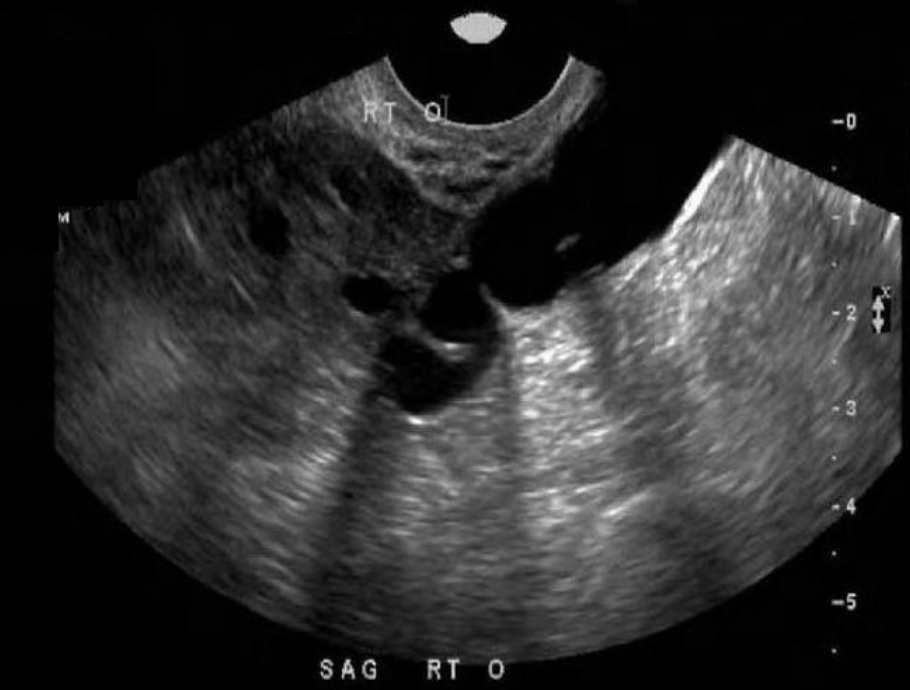
26 yo w/pelvic pain + discharge for 3 weeks, LMP 3.5 weeks ago, G1, P2. lab shows leukocytosis
a) dilated pelvic veins next to ovary, can be complication for mothers of multiple births
b) dilated fallopian tube w/internal debris + nodularity consistent w/carcinoma formation
c) dilated, anechoic fallopian tube medial to the ovary, aka hydrosalpinx, consistent w/probable PID
d) dilated fallopian tube due to the presence of interstitial ectopic pregnancy
c) dilated, anechoic fallopian tube medial to the ovary, aka hydrosalpinx, consistent w/probable PID
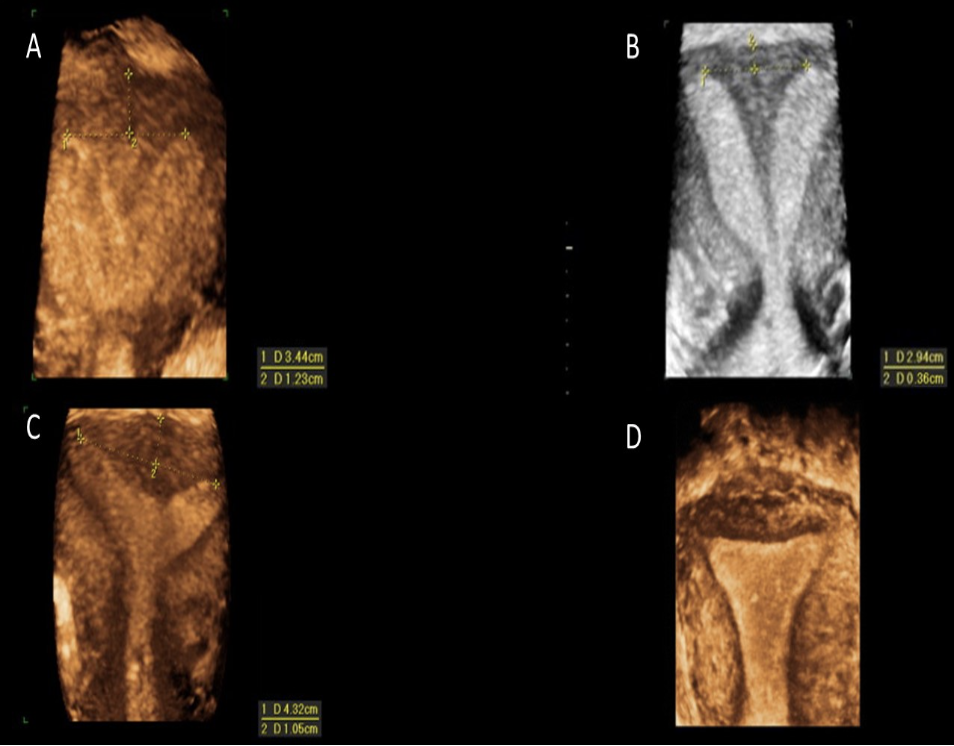
which is a subseptate uterus
a) A
b) B
c) C
d) D
a) A
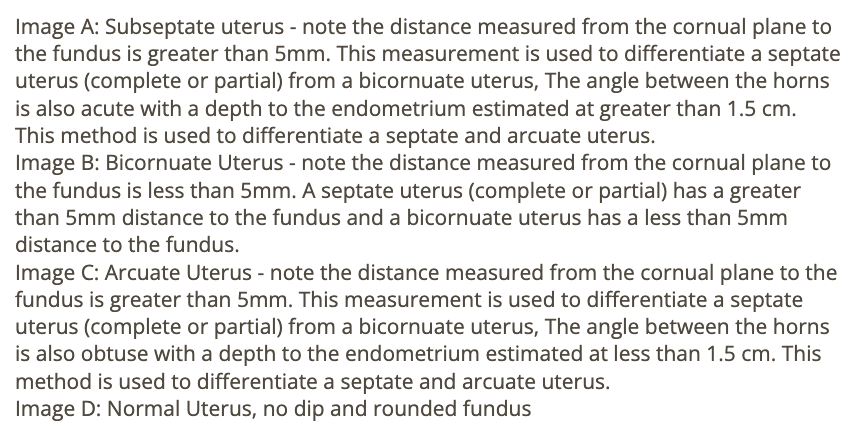
which maternal abn can be caused by a large fibroid uterus
a) systemic HTN
b) hydronephrosis
c) gestational diabetes
d) pulmonary vein dilation
b) hydronephrosis
which can cause fibroid enlargement or endometrial thickening in a postmenopausal pt
a) ovarian thecoma
b) cessation of estrogen replacement therapy
c) ovarian theca lutein cyst
d) cessation of tamoxifen treatment
a) ovarian thecoma
endometrial polyps most commonly form in the endometrial canal near the
.
a) uterine isthmus
b) cervix
c) uterine fundus
d) vaginal canal
c) uterine fundus
a ___ is a type of germ cell malignancy of the ovary
.
a _____ is an epithelial-stromal malignancy of the ovary
a) dysgerminoma, serous cystadenocarcinoma
b) mucinous cystadenocarcinoma, serous cystadenocarcinoma
c) serous cystadenocarcinoma, mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
d) endometroid tumor, dysgerminoma
a) dysgerminoma, serous cystadenocarcinoma

asymptomatic 50 yo has hx of lynch syndrome. what findings would be assoc w/genetic syndrome
.
a) malignant ovarian mass
b) uterine prolapse
c) structral defects of the uterus
d) multiple large leiomyomas
a) malignant ovarian mass

which about polycystic ovarian disease (PCOD) is correct
a) PCOD has related infertility issues
b) PCOD symptoms - tachycardia, weight loss, HTN
c) PCOD is sono identified as numerous large follicles in ovary
d) PCOD is part of Meig syndrome
a) PCOD has related infertility issues

pt LMP was 7 weeks ago. her chart shows she’s been treated 3x for PID over last 4 years. the pt has an increased risk of
a) spontaneous abortion due to fibrosis of uterine cavity from PID
b) ectopic pregnancy due to possible tubal adhesions from PID
c) molar pregnancy due to possible fibrosis of tubes + uterine cavity from PID
d) conjoined twins due to possible adhesions in uterus from PID
b) ectopic pregnancy due to possible tubal adhesions from PID
a negative uterine sliding sign is most suggestive of
. normal sliding = rectum motion
a) extrapelvic endometriosis
b) pelvic inflammatory disease
c) normal anatomy
d) bicornuate uterus
a) extrapelvic endometriosis

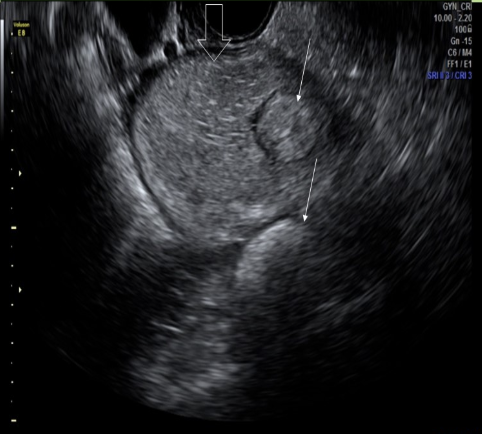
a rokitansky nodule is commonly identified with what type of pelvic mass
.aka dermoid plug
.
a) cystic teratoma
b) serous cystadenoma
c) mucinous cystadenoma
d) focal adenomyosis
a) cystic teratoma

a hypoechoic mass w/benign characteristics is identified in the right ovary. her labs show moderate levels of estrogen in the blood. these finding
a) androblastoma
b) krukenberg tumor
c) granulosa cell tumor
d) brenner tumor
c) granulosa cell tumor
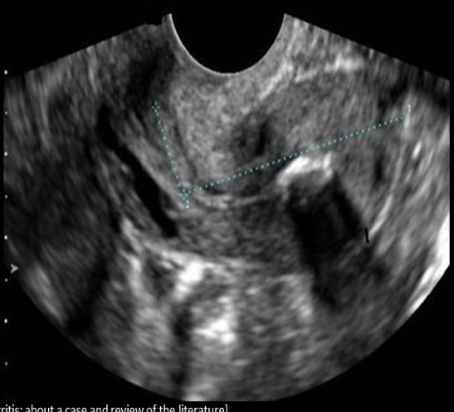
what is the 1st stage of PID identified sonographically
a) endometritis
b) tubo-ovarian abscess
c) hydrosalpinx
d) pyosalpinx
a) endometritis

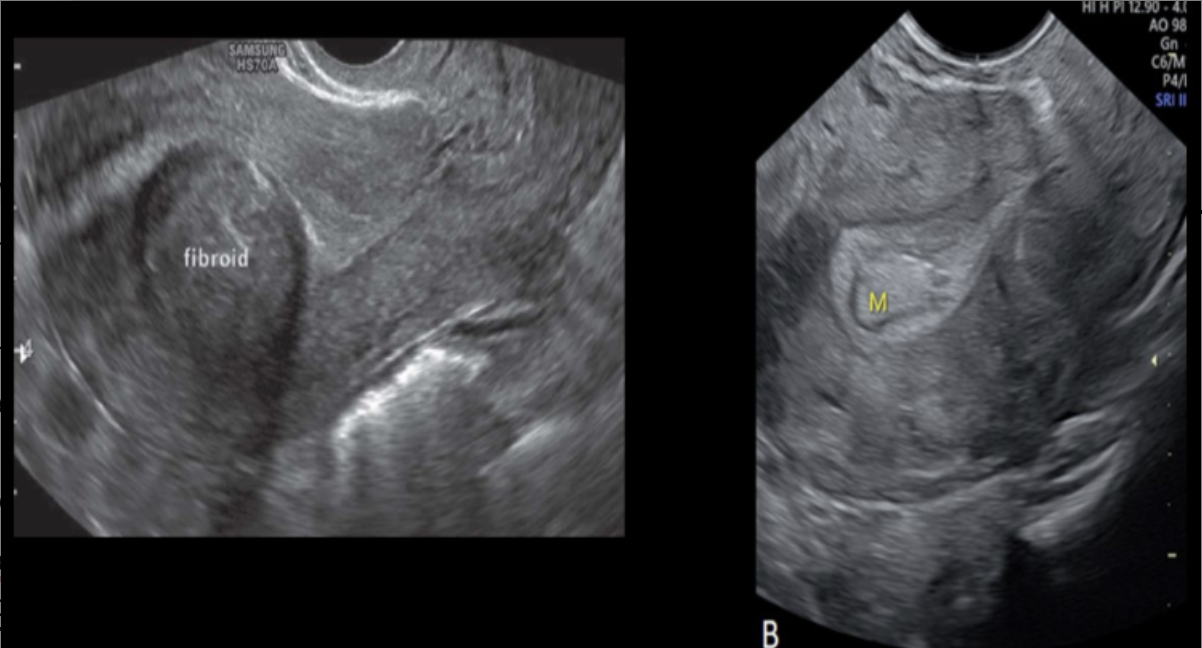
which is true about differentiation of submucosal fibroid from an endometrial polyp
.
a) fibroids always form within the tissue while polyps always form a thin stalk
b) fibroids are normally more hypoechoic while polyps tend to be more hyperechoic
c) multiple fibroids usually form while polyps usually are solitary in formation
d) hysterosalpingography can be used to effectively differentiate a fibroid from a polyp in nearly all pts
b) fibroids are normally more hypoechoic while polyps tend to be more hyperechoic
____ fibroids can distort the uterine contour while ____ fibroids can irritate the endometrial lining causing increased bleeding
a) submucosal, subserosal
b) submucosal, pedunculated
c) interstitial, pedunculated
d) subserosal, submucosal
d) subserosal, submucosal
all can cause an echogenic endometrium except
a) normal secretory phase
b) endometritis
c) cyst formation
d) IUD
c) cyst formation
cervical carcinoma is ___ while endometrial carcinoma is ____
a) most common in premenopausal women, most common in postmenopausal women
b) treated by surgical removal, treated by dilation + evacuation
c) treated by uterine artery ablation, treated by endometrial ablation
d) most common un postmenopausal women, most common in premenopausal women
a) most common in premenopausal women, most common in postmenopausal women

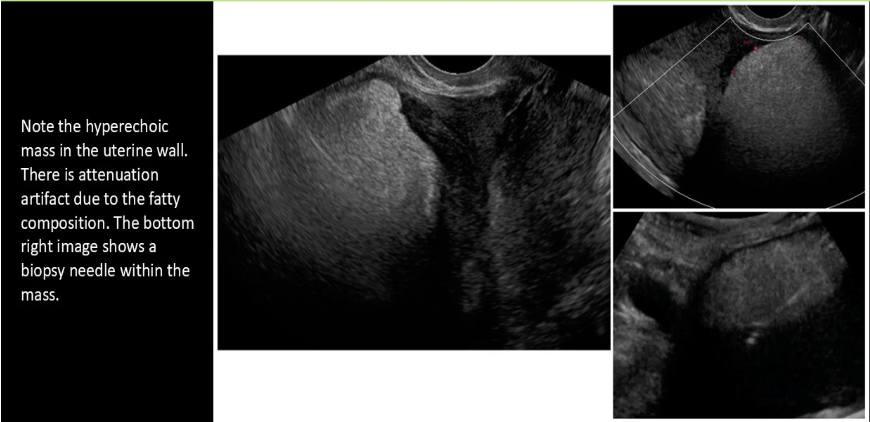
a lipoleiomyoma will be hyperechoic to the myometrium due to increased levels of
a) striated muscle tissues
b) fatty tissue
c) connective tissue
d) ectodermal tissue
b) fatty tissue

which is most likely the symptom of endometriosis
a) menometrorrhagia
b) hypomenorrhea
c) menorrhagia
d) amenorrhea
c) menorrhagia

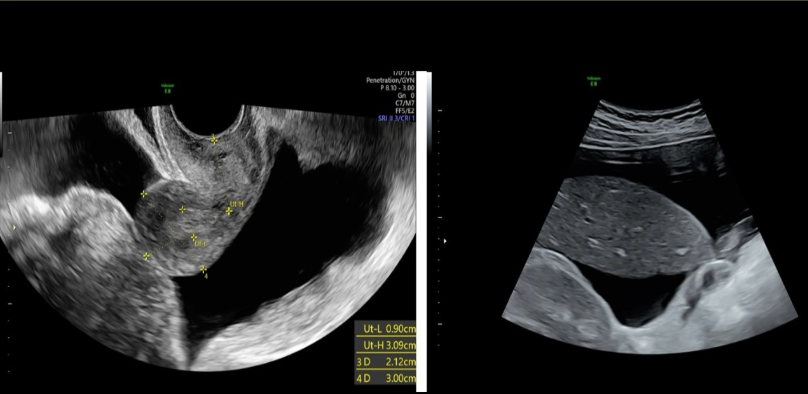
which ovarian tumor is commonly a part of Meigs syndrome
a) fibroma
b) cystadenoma
c) teratoma
d) androblastoma
a) fibroma
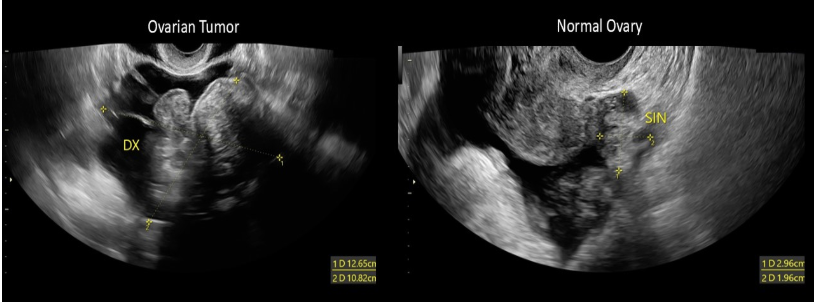
ascites is a complication of ___ while pseudomyxoma peritonei is a complication of ___
a) serous cystadenocarcinoma, arrhenoblastoma
b) serous cystadenocarcinoma, mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
c) thecoma, fibroma
d) endometriosis
b) serous cystadenocarcinoma, mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
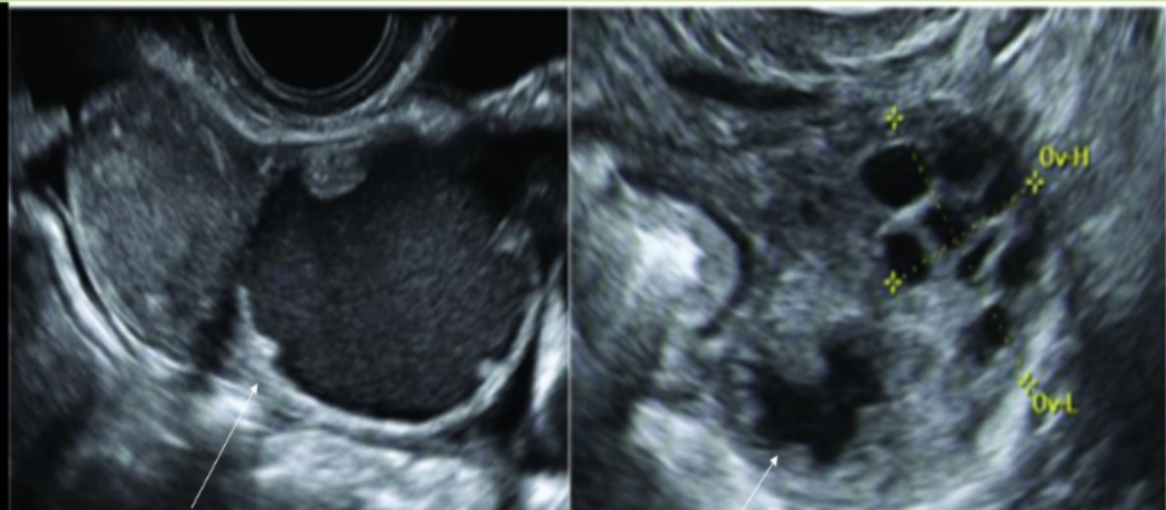
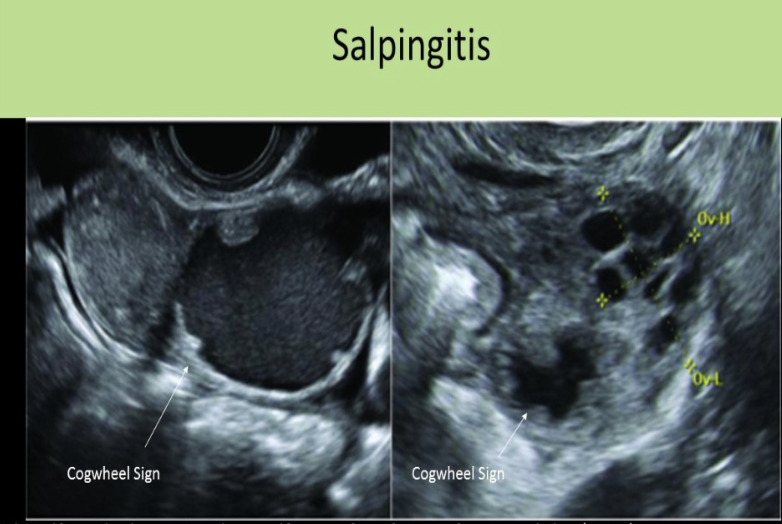
which is a common sono sign of acute PID
a) <5mm wall thickness of fallopian tube
b) thin walled, anechoic avascular adnexal structure
c) cogwheel sign
d) beads on a string sign
c) cogwheel sign
acute ovarian torsion is
a) considered a critical finding that needs immediate intervention
b) an atrophied ovary w/no blood flow detected by color doppler
c) most common in postmenopausal pts
d) assoc w/large, pedunculated leiomyomas
a) considered a critical finding that needs immediate intervention

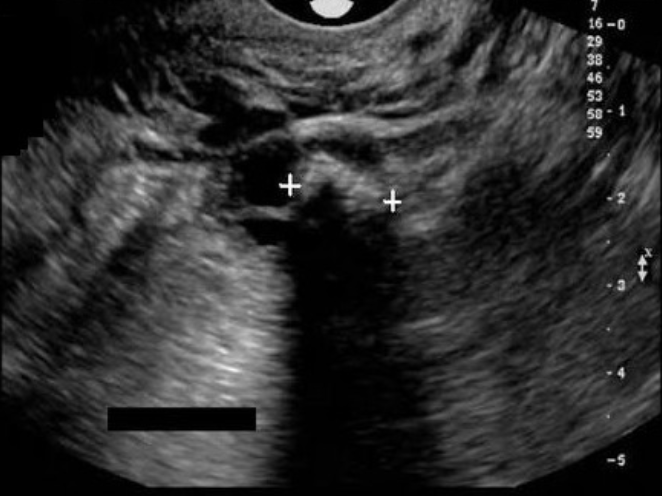
26 yo female has pelvic pain + prior left oophorectomy due to cyst formation. the calipers are measuring a large echogenic mass with
a) dirty shadowing, most likely large fecalith in bowel
b) dirty shadowing, most likely an obstruction in the bowel
c) posterior shadowing, most likely a dermoid cyst
d) posterior shadowing, most likely a chocolate cyst
c) posterior shadowing, most likely a dermoid cyst
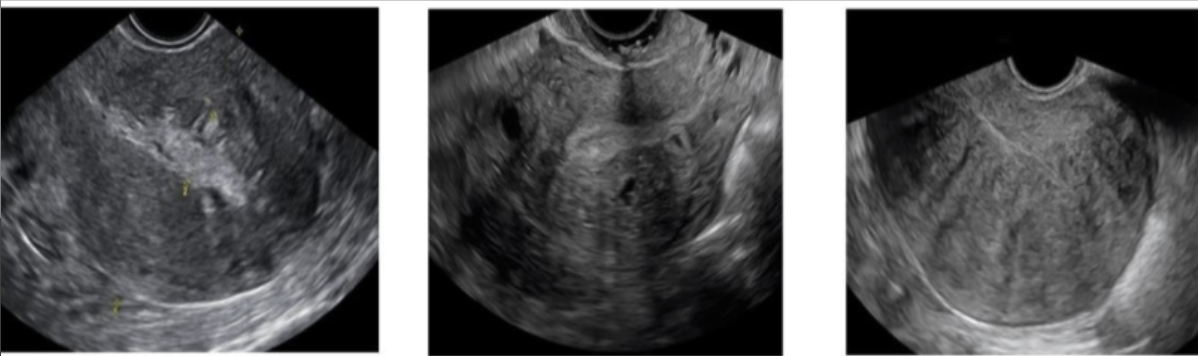
which uterine abn is described as causing a swiss cheese appearance of uterus on US
a) placenta accreta
b) chorioangioma
c) choriocarcioma
d) adenomyosis
d) adenomyosis
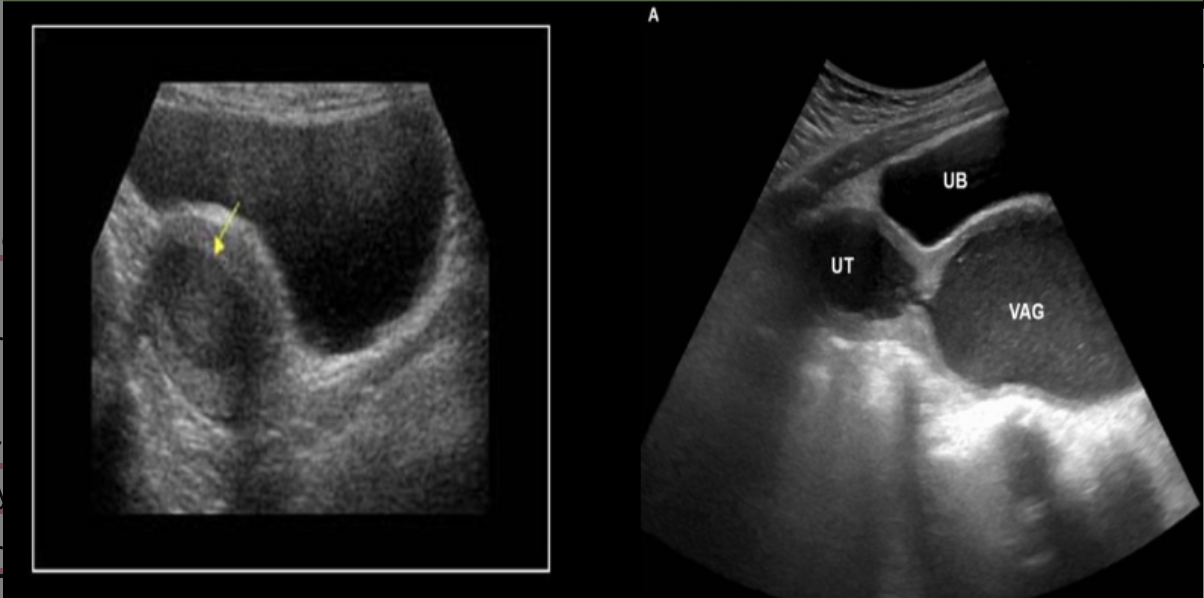
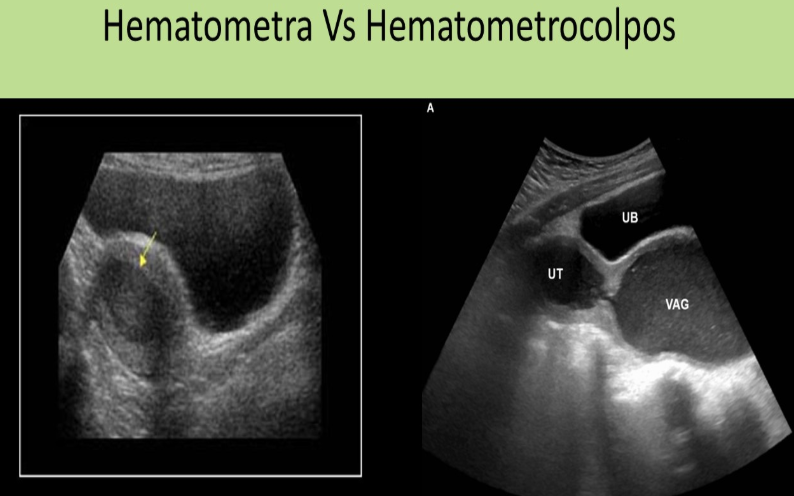
hematometra refers to
.
hematometrocolpos refers to
.
a) pus dilating uterine cavity, blood + pus dilating uterine cavity
b) blood dilating uterine cavity, blood dilating uterine cavity, cervix, and vagina
c) blood dilating uterine cavity, cervix, and vagina, blood dilating uterine cavity
d) blood dilating uterine cavity, pus dilating uterine cavity
b) blood dilating uterine cavity, blood dilating uterine cavity, cervix, and vagina
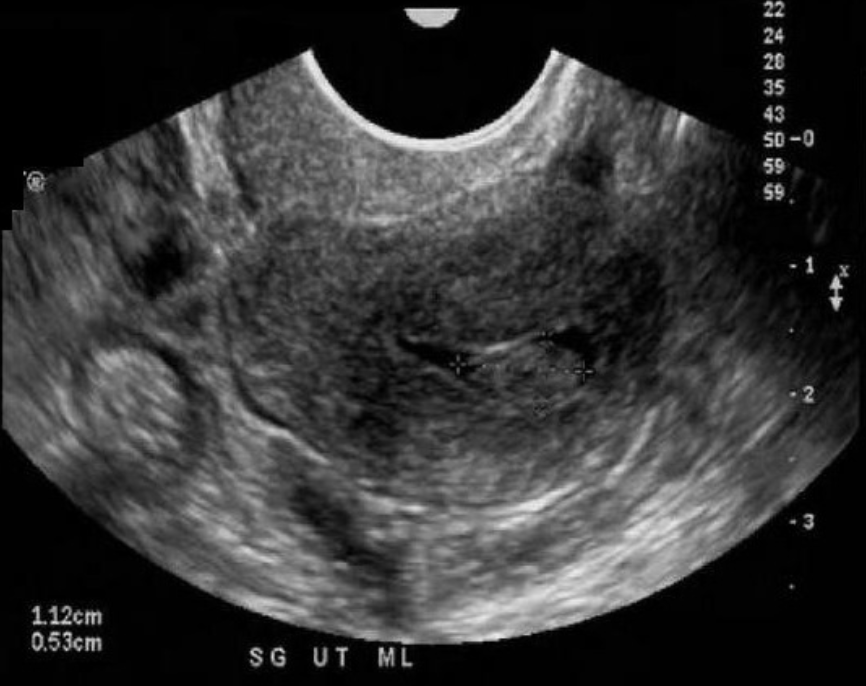
a) a fibroid forming in endometrial canal
b) mass of ectopic endometrium surrounded by a small amount of fluid in the endometrial canal due to endometriosis
c) a blighted ovum w/fetal pole + diminishing GS
d) an endometrial polyp + small amount of fluid in the endometrial canal
d) an endometrial polyp + small amount of fluid in the endometrial canal
primary amenorrhea refers to
a) amenorrhea caused by a foreign object in the vagina
b) onset of menarche before age 8
c) amenorrhea caused by a vaginal mass
d) absence of menarche after age 15
d) absence of menarche after age 15
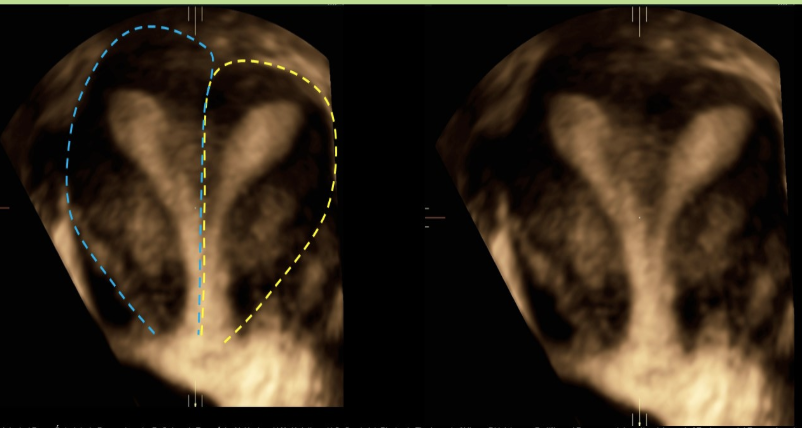
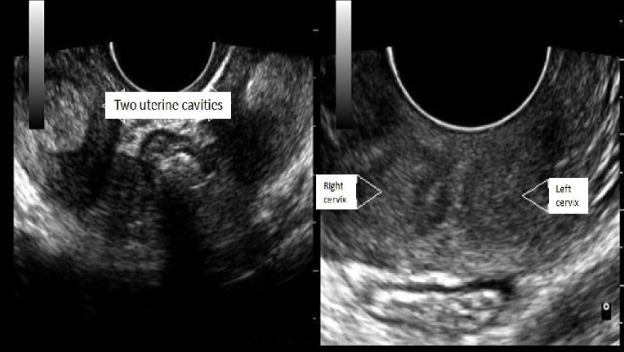
a pt has suspected uterine didelphys. if the exam is positive for the anomaly, what do you expect to find
a) a right + left uterine body w/single cervix + vaginal canal
b) a right + left uterine body, cervix, and vaginal canal
c) single uterine body connected to 2 cervixes + 2 vaginal canals
d) a right + left uterine body and cervix that are both connected a single vaginal canal
b) a right + left uterine body, cervix, and vaginal canal
the most common complication of a germ cell tumor of the ovary is
a) rupture
b) infertility
c) torsion
d) adhesions
c) torsion

which ovarian tumors most commonly occurs in the postmenopausal woman
.
a) teratoma
b) serous cystadenoma
c) granulosa cell tumor
d) sertoli leydig cell tumor
c) granulosa cell tumor

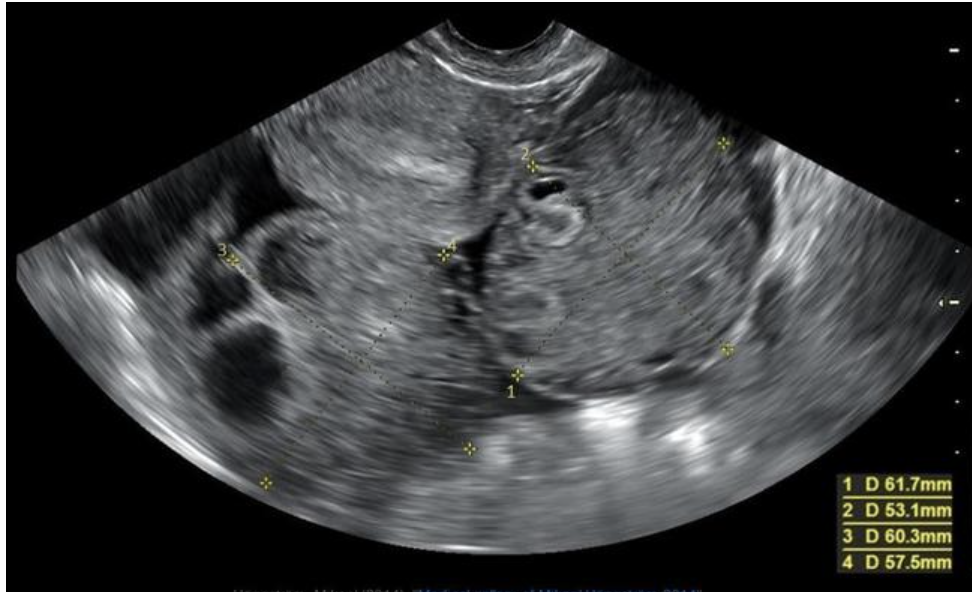
a 27 yo complains of pelvic fullness
a) ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
b) ovarian lymphoma
c) bilateral endometriomas
d) Krukenberg tumor
a) ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome

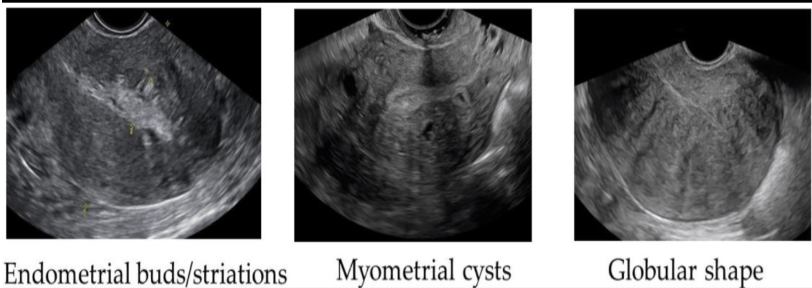
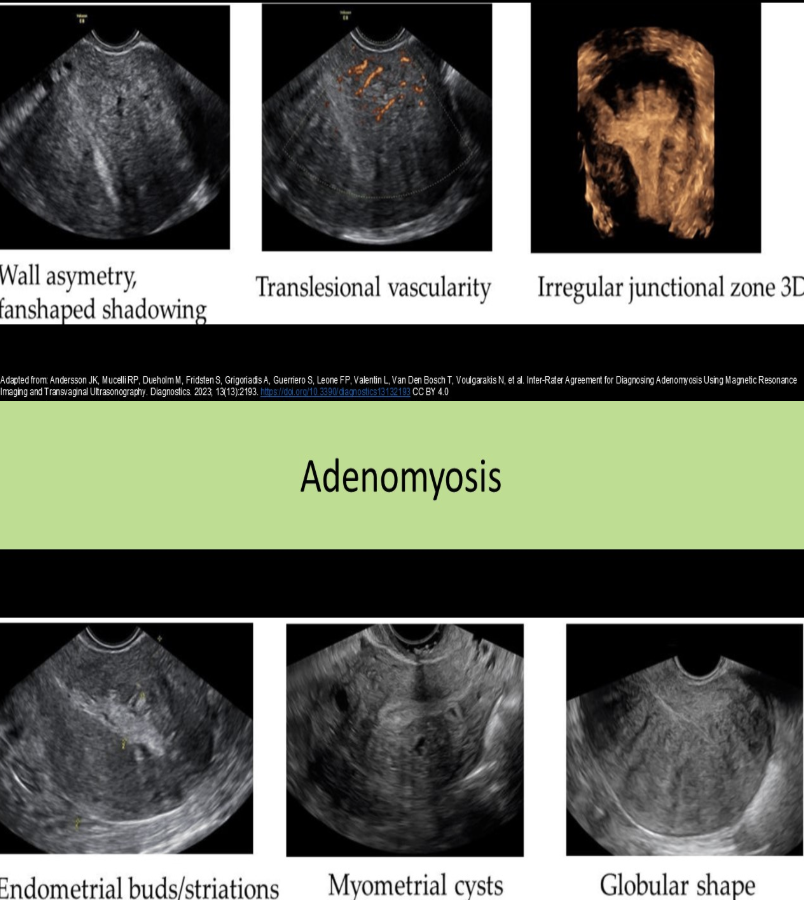
the uteus is enlarged + shows multiple myometrial cysts <6 mm in size + several subendometrial echogenic nodules. what is the most likely cause
a) endometrial atrophy
b) adenomyosis
c) endometrial carcinoma
d) endometrial abscess
b) adenomyosis

a 35 yo has post-coidal bleeding, low back pain, and watery vaginal discharge. labs are normal. she had a partial hysterectomy at age 30 due to complications from multiple fibroids. these clinical findings are most suggestive of
a) PID
b) cervical cancer
c) endometrial carcinoma
d) choriocarcinoma
b) cervical cancer

which is a common cause of abn uterine bleeding
a) leiomyomas
b) HRT
c) PCOS
d) oral contraceptives
a) leiomyomas

which is related to an increased risk of developing ovarian or endometrial cancer
a) multiparity
b) human papilloma virus vaccine
c) early menopause
d) lynch syndrome
d) lynch syndrome

what is the greatest risk factor for cervical carcinoma
a) early onset of sex
b) multiple sex partners
c) HPV vaccine
d) smoking
c) HPV vaccine
which is not an expected finding w/ fits hugh curtis syndrome
a) inflammation of glisson capsule
b) krukenberg tumor
c) PID
d) peritonitis
b) krukenberg tumor

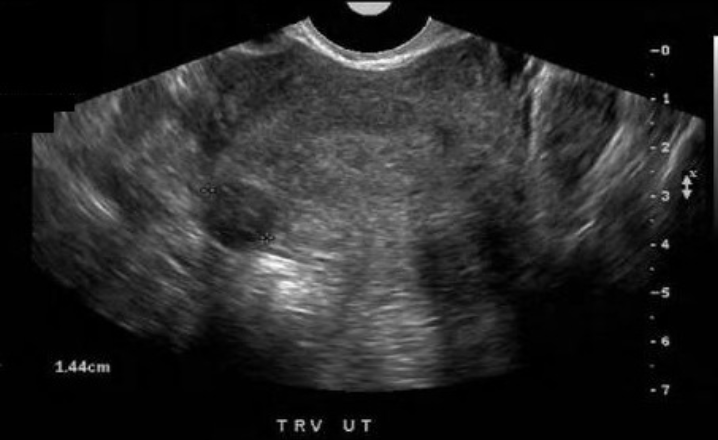
what type of fibroid is this
a) pedunculated
b) subserosal
c) submucosal
d) intramural
b) subserosal
Endometrial hyperplasia in a pre-menopausal female is dx when the endometrial thickness in the secretory phase exceeds
a) 12 mm
b) 10 mm
c) 14 mm
d) 18 mm
d) 18 mm

all are assoc w/small amount of fluid in the endometrial canal of a 62 yo female except
a) endometrial hyperplasia
b) ectopic pregnancy
c) cervical stenosis
d) endometrial atrophy
b) ectopic pregnancy
what is the most common cause for PID
a) chlamydia
b) tuberculosis
c) bladder infection
d) poor hygiene
a) chlamydia
which is the most commonly occurring germ cell tumor of the ovary
a) malignant dysgerminoma
b) yolk sac tumor
c) embryonal cell carcinoma
d) benign cystic teratoma
d) benign cystic teratoma
which describes the US appearance of a copper IUD
a) 2 parallel strongly echogenic structures w/posterior shadowing + reverberations
b) circular echogenic structure located centrally in the fundal area
c) t-shaped anechoic area in the endometrial cavity
d) linear echogenicity w/each of the proximal fallopian tubes
a) 2 parallel strongly echogenic structures w/posterior shadowing + reverberations

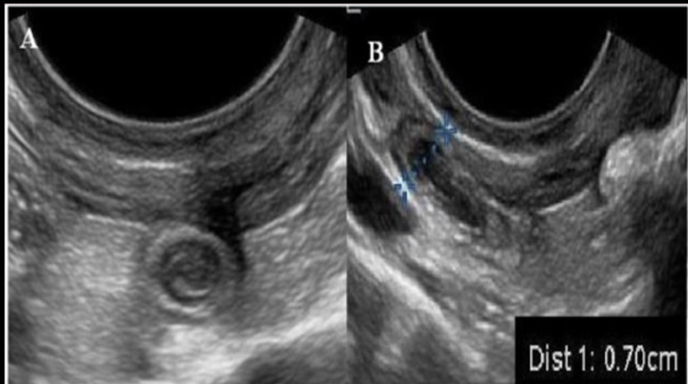
a pt has moderate RLQ + low grade fever. a US exam of area shows 7mm thick aperistaltic tube that is noncompressible
a) peritoneal inclusion cyst
b) intussusception
c) pelvic congestion
d) appendicitis
d) appendicitis
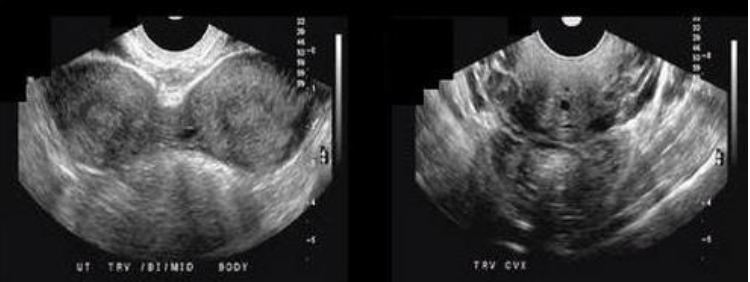
which congenital abn is this
a) uterine subseptus
b) uterine bicornis bicollis
c) uterine arcuatus
d) uterine bicornis unicollis
d) uterine bicornis unicollis

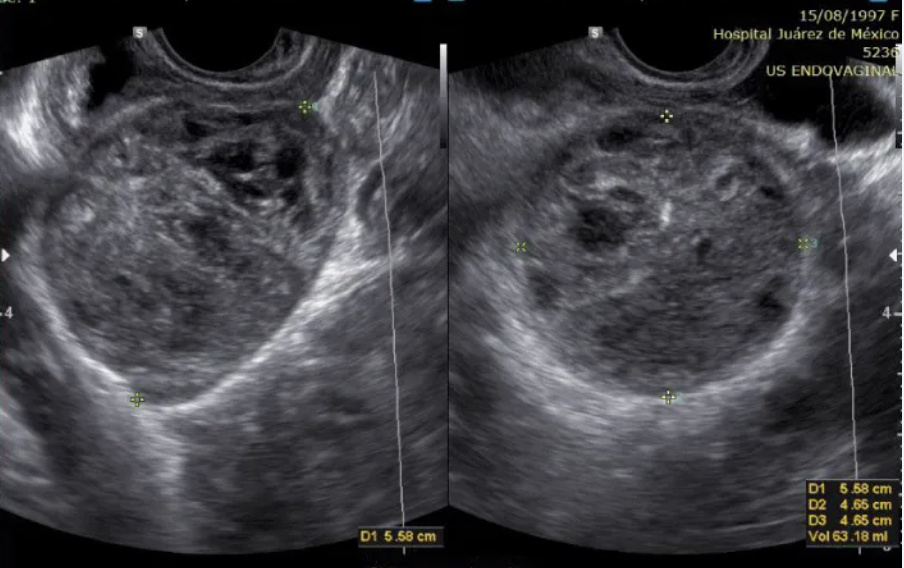
a 19 yo has intermittent pelvic pain on the left side + abn menstrual cycles.
.
she has no recent sexual activity, but her LMP was 10 weeks ago. she has a recent positive home pregnancy test.
.
the US shows a solid mass w/cystic degeneration on the left ovary
.
a) mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
b) serous cystadenocarcinoma
c) krukenberg tumor
d) choriocarcinoma
d) choriocarcinoma

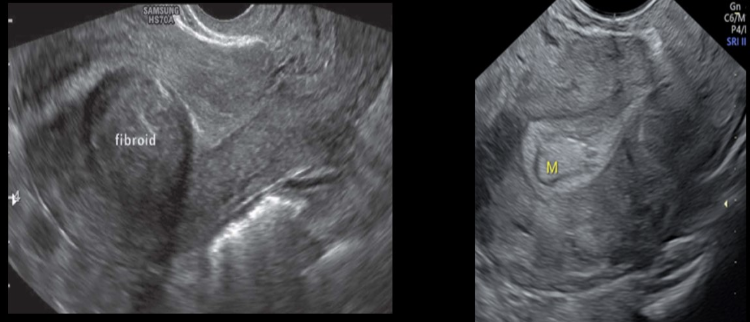
an endometrial polyp is described as
a) focal endometrial hypertrophy
b) stage 1 of endometrial adenocarcinoma
c) malignant overgrowth of the endometrial tissue
d) stage 1 of PID
a) focal endometrial hypertrophy
asymmetric ovarian volumes in a postmenopausal woman are most suggestive of
a) ovarian lymphoma
b) ovarian malignancy
c) krukenberg tumors
d) PCOS
b) ovarian malignancy

which type of fibroid disturbs/distorts the endometrial layer + causes the most abn uterine bleeding of all types of fibroids
a) submucosal
b) intramural
c) subserosal
d) interstitial
a) submucosal
which is most common gynecological cancer
a) serous adenocarcinoma of ovary
b) leiomyosarcoma
c) endometrial carcinoma
d) mucinous adenocarcinoma of ovary
c) endometrial carcinoma
which patients have the highest risk of developing pyometra
a) 40 yo w/fibroids
b) 24 yo w/IUD
c) 70 yo w/uterine adenocarcinoma
d) 15 yo w/imperforate hymen
c) 70 yo w/uterine adenocarcinoma

which is the least likely to cause PID
a) tuberculosis
b) lithium exposure
c) rupture appendix
d) TORCH infections
b) lithium exposure

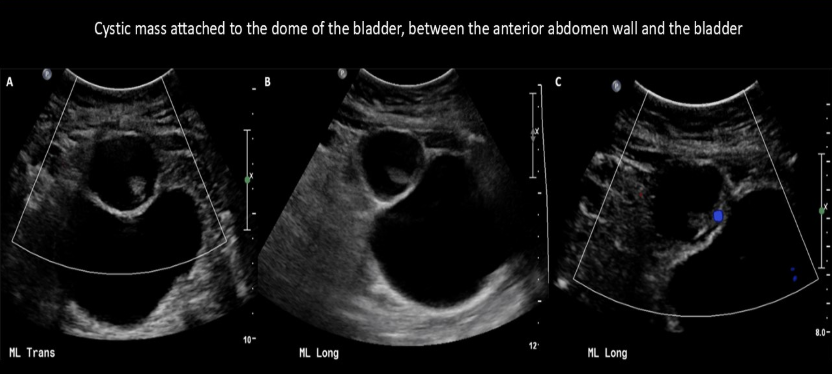
incomplete resolution of which embryonic structure can cause a cystic formation between the abd wall + anterior bladder wall
a) ectoderm
b) umbilical vein
c) urachus
d) ductus venosus
c) urachus

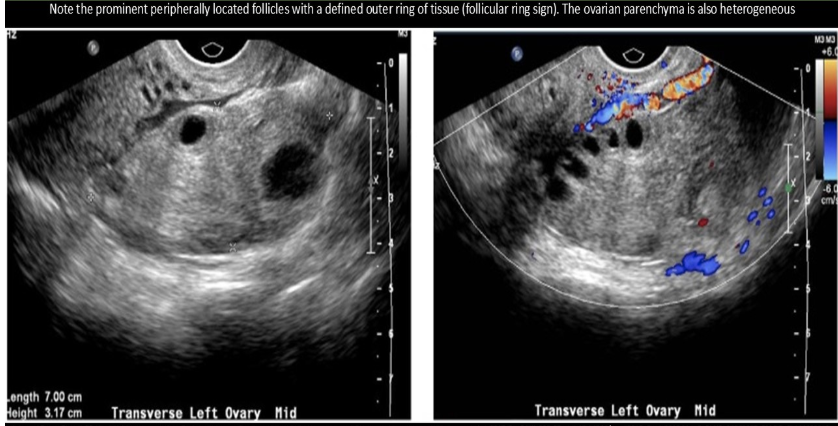
the follicular ring sign is assoc w/
a) ectopic pregnancy
b) OHS
c) ovarian torsion
d) normal intrauterine pregnancy
c) ovarian torsion

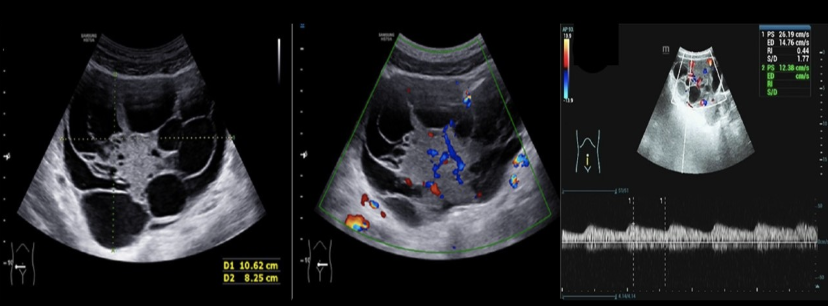
which ovarian tumor causes serum levels of AFP to rise
a) mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
b) yolk sac tumor
c) dysgerminoma
d) krukenberg tumor
b) yolk sac tumor

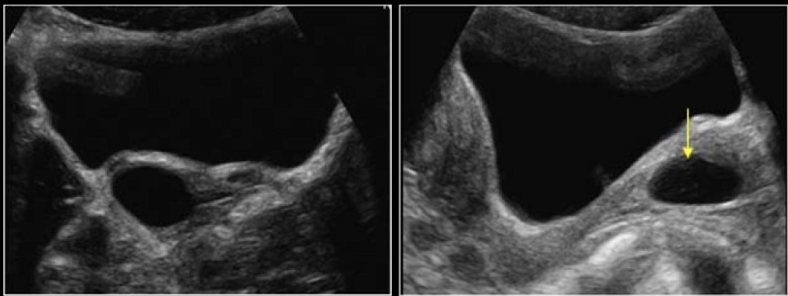
a pt has palpable, pliable, rounded, mobile mass in vaginal canal
a) gartner cyst
b) fibroid
c) brenner cyst
d) nabothian cyst
a) gartner cyst