Plant tissue, Photosynthesis, Plant diseases
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Epidermal tissue
Secretes a waxy substance
waterproofs and protects the surface of the plant
Palisade Mesophyll
contains lots of chloroplasts
allows for photosynthesis to take place
spongy mesophyll
contains big spaces
large surface area for diffusion of gases
stomata / guard cells
stomata is opened and closed by guard cells
allows for diffusion of gases and water loss to take place
meristem tissue
stem cells that can differentiate
found on tips of roots and shoots which help their growth
What are xylem and phloem?
Transport tissues in a plant
How does temperature affect transpiration?
Higher temperatures increase the rate
What is the structure and function of xylem tissue?
Made of dead cells connected end to end
One-way system for water transport
Contains a central space called lumen
Transports water from roots to leaves
What is the role of xylem in plants?
Transports water and minerals from soil to leaves
Water travels up the lumen by transpiration
Supports photosynthesis
What are xylem walls made of?
Lignin (which helps it handle pressure changes)
What is transpiration in plants?
Movement of water from roots to leaves
Water evaporates at the leaf surface
Flow of water is known as transpiration stream
How light affects transpiration
bright light increases rate
stomata opens wider to allow more CO2 into the leaf for photosynthesis
How temperature affects transpiration
faster in higher temperatures
evaporation and diffusion are easier in higher temperatures
How wind affects transpiration
faster in windy conditions
water vapour near stomata is removed quickly speeding up diffusion of water vapour out of leaf
How humidity affects transpiration
slower in humid conditions
diffusion of water vapour out of leaf slows down if surrounded by moist air
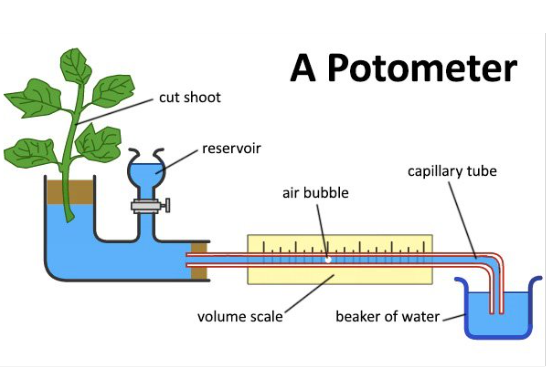
Potometer
used to measure transpiration
water loss from apparatus is via transpiration
as water moves up the plant the bubble moves along the scale giving a measure of water absorbed by the plant over time → transpiration rate
What is the function of phloem tissue in plants?
Carries food made by photosynthesis from leaves to the rest of the plant
Moves sugars through translocation
translocation
the process of movement of dissolved sugars
can move sugars up and down the plant
What is the composition of phloem?
cell walls made of cellulose
cells are arranged end to end
cell wall has holes called sieves which allows cytoplasm from one cell to extend to the other cell
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
Photosynthesis
process of making glucose
light energy from sun is converted to chemical energy in glucose
endothermic
takes place in chloroplasts because chlorophyll pigment absorbs light
What role do stomata play in photosynthesis?
They allow carbon dioxide to enter
What is the role of glucose in plants?
It is used to make cellulose
What do plants store for long-term energy?
Starch
What are the limiting factors of photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide concentration
Light intensity
Temperature
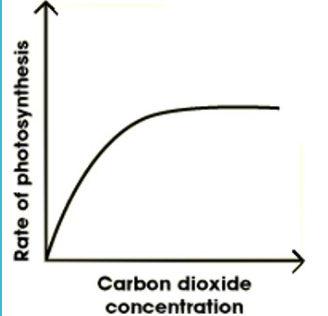
Carbon Dioxide concentration
•The rate of photosynthesis increases steadily initially as the concentration of CO2 increases.
• After a while, the rate of photosynthesis does not increase, even though there is an increase in the concentration of CO2
•The graph plateaus as raising CO2 will no longer have an effect on photosynthesis and therefore it is no longer a limiting factor.

Light intensity
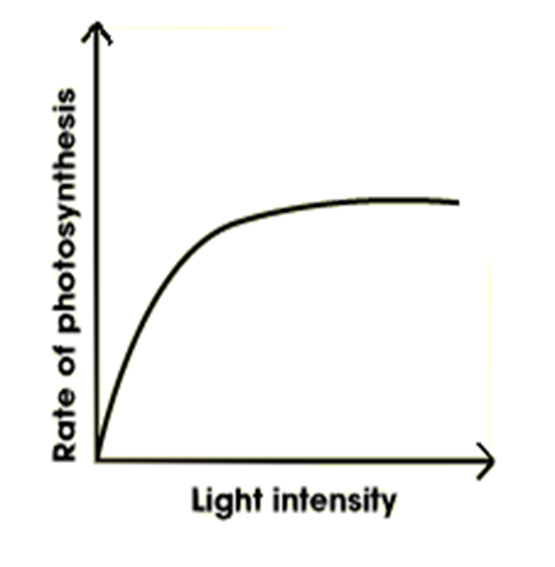
•The rate of photosynthesis increases steadily initially as the intensity of light increases.
• After a while, the rate of photosynthesis does not increase, even though there is an increase in the intensity of light.
•The graph plateaus as raising light intensity will no longer have an effect on photosynthesis and therefore it is no longer a limiting factor.

Temperature
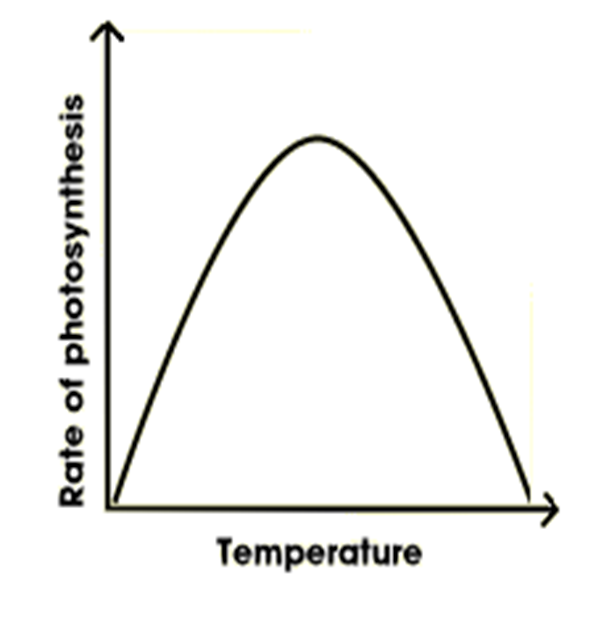
The rate of photosynthesis increases steadily as temperature increases.
Enzymes have increased kinetic energy and more successful collisions occur
The highest rate of photosynthesis is achieved at the optimum temperature.
At higher temperatures, there is denaturing of the enzymes, which leads to a decrease in the rate of photosynthesis.
How CO2 is used as a limiting factor
•Burning of propane produces carbon dioxide in greenhouse
How light is used as a limiting factor
•Sunlight gets in through glass
•Light switched on at night
How temperature is used a s a limiting factor
•Greenhouse trap heat energy from sunlight
•Heating and cooling systems keep greenhouses at optimum temperature
•Air circulation system keeps heat evenly distributed
Deficiency disease
Lack of nitrates = not enough protein in plants = reduced growth in plants = stunted growth
Lack of magnesium ions = not enough chlorophyll made in plants = reduced photosynthesis = chlorosis. Plants would look yellow
Diseases caused by pathogens and pests
Aphids found on plants can cause huge damage
TMV caused by viruses
Rose black spot caused by fungi
How to detect plant disease
1.Stunted growth
2.Spots on leaves
3.Patches of decay
4.Abnormal growths (lumps)
5.Discolouration
6.Malformed stems or leaves
7.Presence of pests
Physical plant defences
Thick waxy cuticle which acts as a barrier to pathogens
Cell wall made out of cellulose which is tough and difficult for pathogens to enter
Dead cells layers on their stem/bark which acts as a barrier to pathogens
Chemical plant defences
Anti-bacterial chemicals which can kill bacteria
Poisons produced to deter herbivores (plant eaters)
Mechanical plant defences
Thorns and hairs – deters animals
Leaves that droop or curl when touched
Mimics animals
Passion flower has bright yellow spots which looks like butterfly eggs; this stops other butterflies from laying their eggs there
Describe two ways the gardener could identify a plant disease.
compare symptom with gardening manual
use monocional antibodies test