Endocrinology: Testosterone Physiology and Pharmacology (Sharma)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What is the plasma concentration of testosterone in men?
0.6 mcg/dl
Where is testosterone synthesized in men?
95% in the Leydig cells of the testes and 5% in the adrenal cortex
What is the plasma concentration of testosterone in women?
0.03 mcg/dl
Where is testosterone synthesized in women?
In equal amounts by the corpus luteum and adrenal cortex
What is testosterone required for in women?
Normal libido
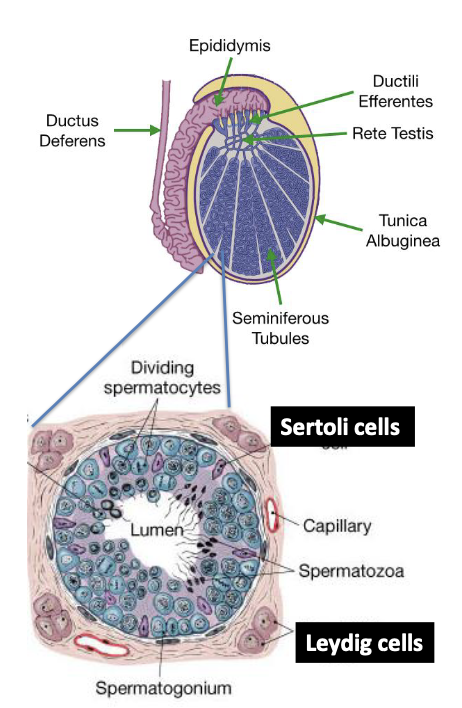
What occurs in the seminiferous tubules of the testes?
Spermatogenesis (sperm production)
What types of cells are found in the seminiferous tubules?
Primary spermatogonia and Sertoli cells
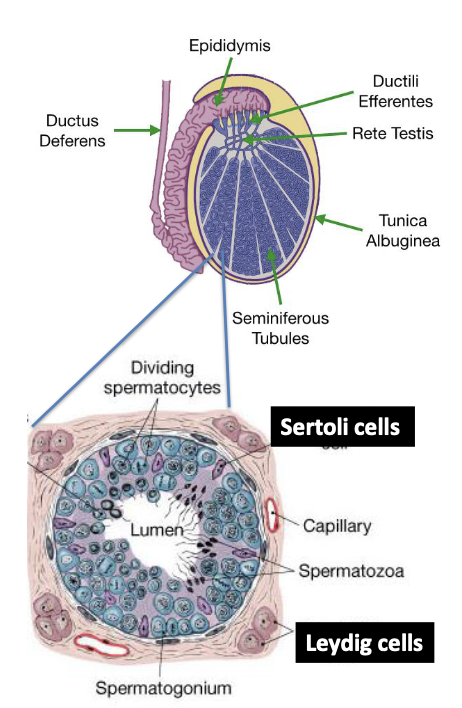
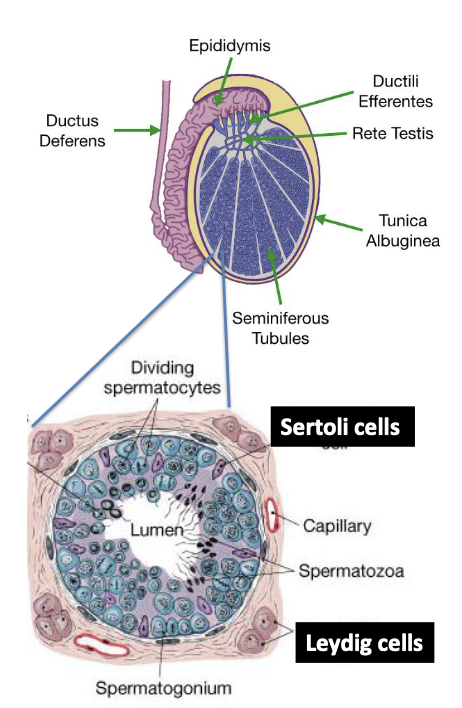
What do Sertoli cells synthesize?
Androgen-binding protein
What cells surround the seminiferous tubules?
Leydig (interstitial) cells
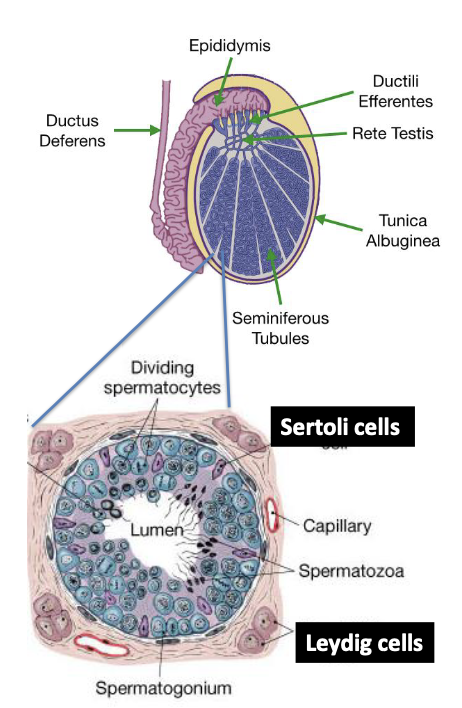
What hormone does the hypothalamus release to regulate testosterone secretion?
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
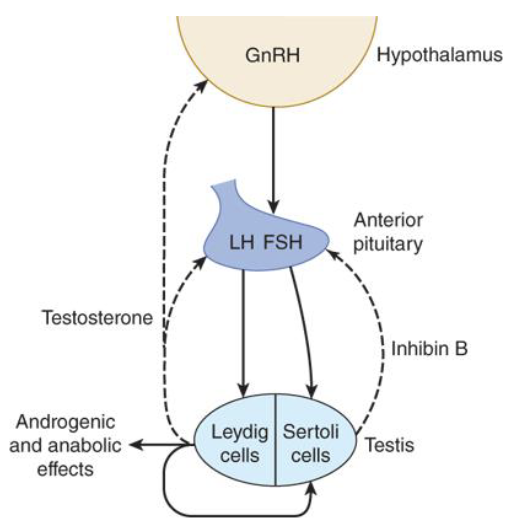
How does GnRH affect the anterior pituitary?
It causes the release of FSH and LH
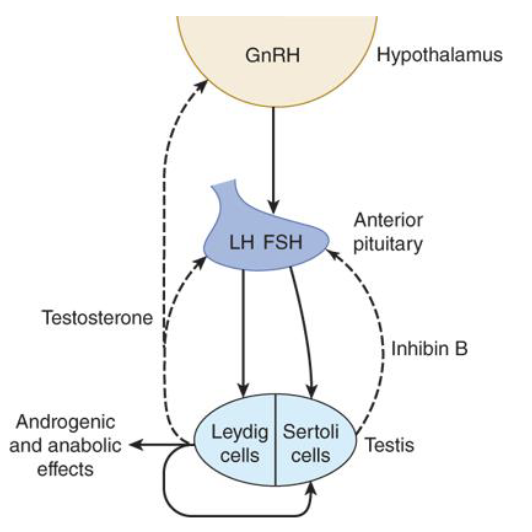
What does FSH do in the seminiferous tubules?
It causes Sertoli cells to synthesize androgen-binding protein (ABP) and aids in sperm maturation
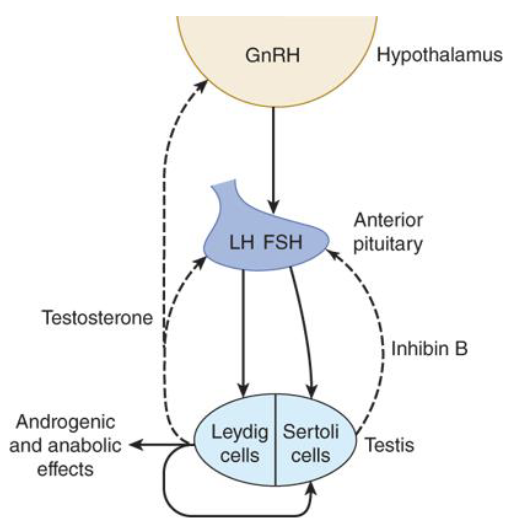
What is the role of LH in testosterone secretion?
LH stimulates Leydig cells to synthesize and release testosterone
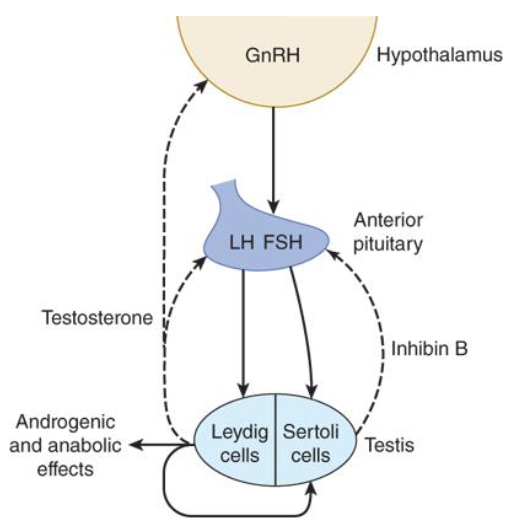
How does circulating testosterone affect the hypothalamus?
It decreases GnRH release (negative feedback)
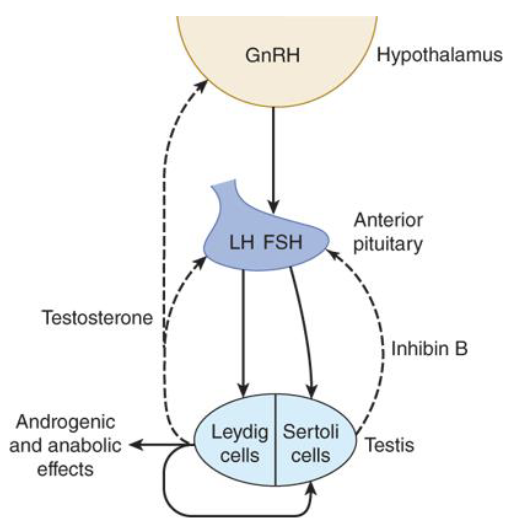
How does circulating testosterone affect the anterior pituitary?
It decreases LH release (negative feedback)
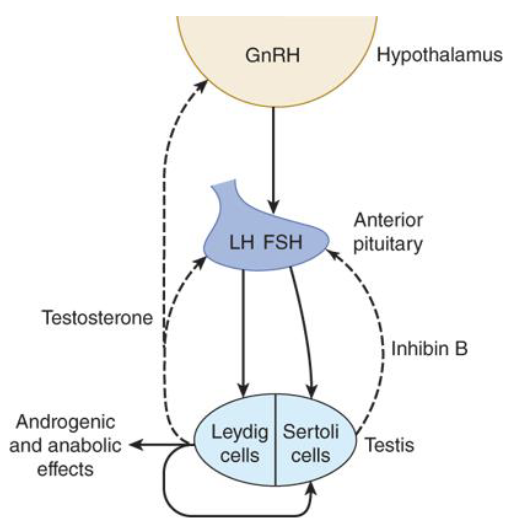
What happens when high amounts of therapeutic testosterone are administered?
It suppresses GnRH and LH, which lowers testicular testosterone and impairs spermatogenesis
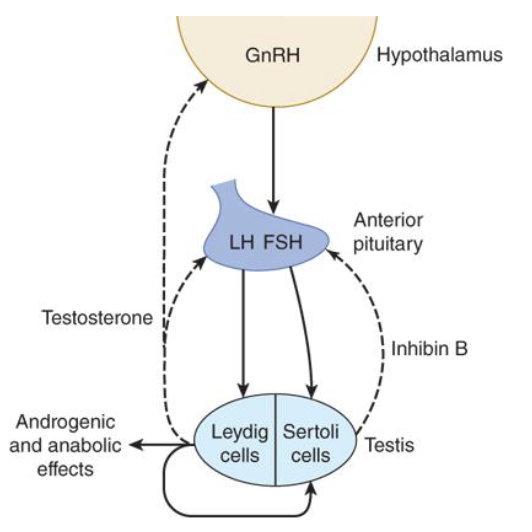
What are testosterone levels in men during puberty to their 30s?
500-770 ng/dl
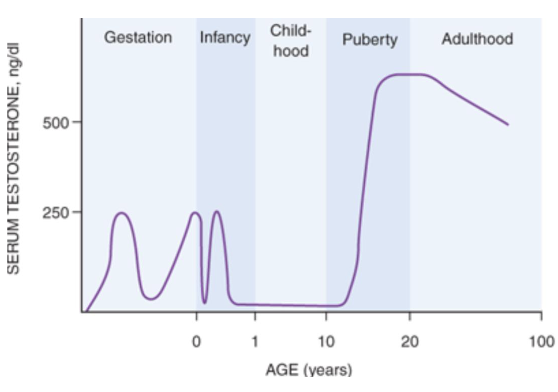
When does testosterone start to decline in men?
In the mid-40s
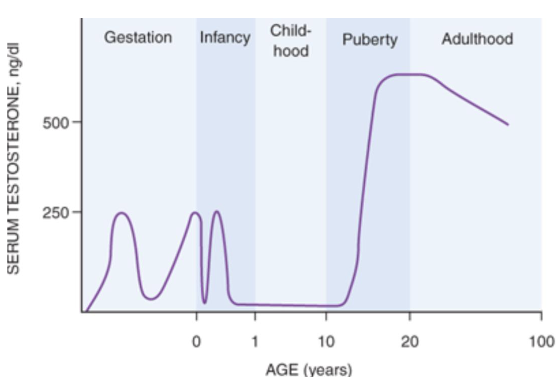
How often is LH released?
In pulses every 2 hours
When is the peak LH pulse?
In the morning
When are testosterone levels highest and lowest during the day?
Highest at 8 AM and lowest at 8 PM
What percentage of testosterone in plasma is bound to proteins?
98%
What percentage of testosterone is bound to gonadal steroid-binding globulin (GBG) or sex steroid-binding globulin?
65%
What is testosterone metabolized into by 5α-reductase?
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a more potent derivative
Where does the conversion of testosterone to DHT occur?
In the skin, prostate gland, hair follicles, and other tissues
What is testosterone converted to in bone and adipose tissue?
Estradiol by the enzyme aromatase (CYP19)
What are the inactive metabolites of testosterone in the liver?
Androsterone and etiocholanolone
To which receptor superfamily do androgen receptors belong?
The nuclear receptor superfamily
What protein are androgen receptors bound to in the cytosol?
Heat shock protein (HSP)
What happens when testosterone binds to androgen receptors?
HSP dissociates, and androgen receptors form dimers that translocate to the nucleus to affect gene expression
How does DHT compare to testosterone in terms of receptor affinity?
DHT has 5 times greater affinity for androgen receptors, making it more potent
What are causes of primary hypogonadism (defect in the testes)?
Klinefelter syndrome (XXY trisomy), undescended testicles (cryptorchidism), mumps orchitis, injury to testicles, chemotherapy or radiation, and certain drugs (ketoconazole, spironolactone, marijuana)
What drugs can lead to primary hypogonadism?
Ketoconazole, spironolactone, and marijuana
What is secondary hypogonadism?
Hypogonadism due to problems with the hypothalamus or pituitary
What are causes of secondary hypogonadism?
Kallmann syndrome, pituitary disorders, inflammatory diseases (sarcoidosis, histiocytosis, tuberculosis), hemochromatosis, HIV/AIDS, obesity, and andropause (age-related decline)
What syndrome is linked to abnormal hypothalamic development causing secondary hypogonadism?
Kallmann syndrome
What condition involving excessive iron can cause secondary hypogonadism?
Hemochromatosis
What is andropause?
Late-onset hypogonadism due to normal aging
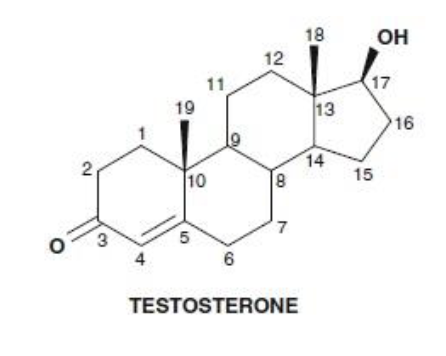
Testosteron has a ______ group at ______ and a _________ at _______ __.
ketone; carbon 3; hydroxyl; carbon 17
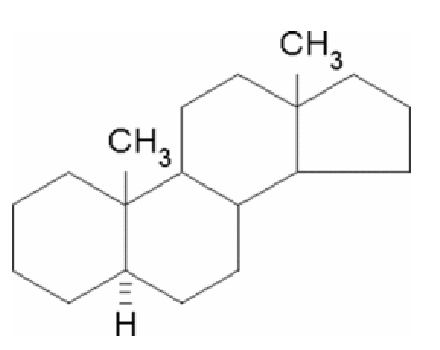
What is the minimum structure (pharmacophore) for binding to androgen receptors?
5α-androstane
Why is testosterone limited as an oral pharmacological agent?
It undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism, leading to very low levels in systemic circulation
What are two strategies to overcome testosterone's limitations as a drug?
A: 1) Development of testosterone derivatives with less hepatic metabolism, or 2) Use of administration routes that bypass first-pass metabolism.
How does the alpha methyl group affect 17α-methyl testosterone derivatives?
It makes them less susceptible to hepatic metabolism, increasing oral bioavailability
What is a major drawback of 17α-methyl testosterone derivatives?
They are hepatotoxic
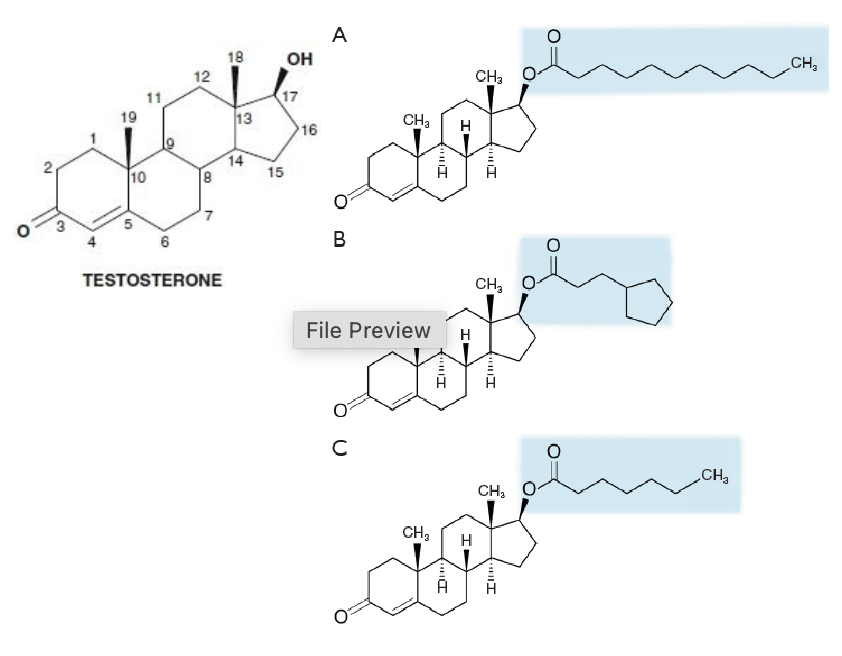
What are ester derivatives of testosterone used for?
Parenteral intramuscular administration
What is the purpose of esterification of testosterone at carbon 17?
To generate ester derivatives for intramuscular depot injections
Why are testosterone esters formulated in oils for intramuscular injections?
They are highly lipophilic and designed for long duration of action
Name the 3 testosterone esters used for intramuscular injections.
Testosterone undecanoate
Testosterone cypionate
Testosterone enanthate
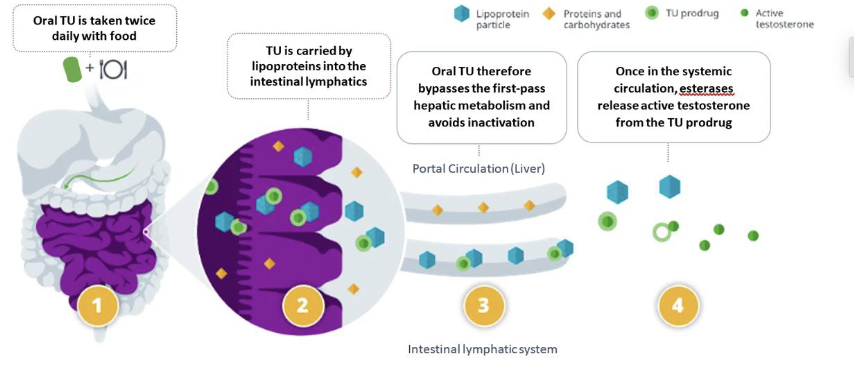
How does oral testosterone undecanoate (Jatenzo) bypass hepatic metabolism?
It uses a self-emulsifying lipoprotein particle formulation
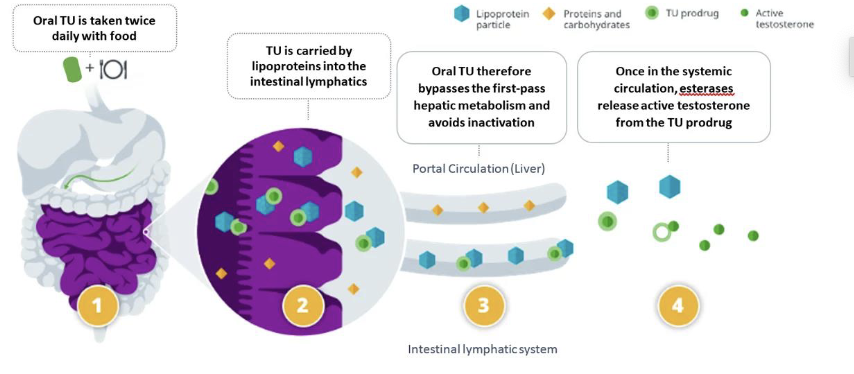
What is the role of the self-emulsifying lipoprotein particle formulation in oral testosterone undecanoate?
It facilitates absorption and helps bypass first-pass hepatic metabolism