Comprehensive Review of Accounting Principles, Processes, and Business Types
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Analyzing
Transactions entered, documentary evidence.
Recording
The effect of the transaction.
Classifying
Sorting/grouping of similar transactions/events > account titles.
Summarizing
Accounts are grouped into assets, liabilities, owner's equity, revenue, cost and expenses.
Reporting
Financial statement (Income statement, balance sheet and cash flows statement).
Interpreting
Step that directs attention to the significance of various matters and relationships.
Merchandising/Trading
Buying of goods and selling the same without change in form.
Service
Doing work for others.
Business Entity
Business enterprise is separate from its owner/investor (exception in the case of paying for someone related to the company).
Monetary unit
Amounts should only be a single monetary unit (can't change from pesos to another currency, can make exception in case of foreign owner or investor).
Time period
Financial statements must have divided time periods (financial statements annually or expenses reported from only a specific time).
Objectivity
Financial statements must have supporting evidence.
Cost
Accounts should be recorded initially at cost (ex. buying a cash register, it must record its price when purchased).
Asset
Economic resources owned by the business for future gain, property and rights of value owned by the business.
Current Asset
Go away quickly; includes cash on hand/bank, accounts receivable, notes receivable, inventories/supplies, prepaid expenses, accrued income, short term investment, petty cash fund.
Non-Current Asset
Properties that don't just go away; includes property, plant, equipment, long term investment - ex. insurance, intangible assets.
Liabilities
Debts and obligations of the company to another entity.
Current Liabilities
Fall due within one year after year end date (short term).
Accounts Payable
Things to be paid on account.
Notes Payable
Promissory notes.
Accrued Expenses
Used up but not paid for yet.
Income Tax Payable
Paid at the end of the month once there is tax.
Non-Current Liabilities
Cannot be realized (long term); includes loans payable, notes payable, mortgage payable.
Equity
Residual interest of the owner from the business.
Capital
Money you will put into your business, value of cash and other assets invested in by the business by the owner.
Drawing
Money from the business, debited for assets withdrawn by the owner for personal use.
Income
Net increase in assets in a given accounting period.
Expenses
What you spend for your business costs of business during their operation, decreases in assets or increases in liabilities.
Branches of Accounting
Includes management accounting, tax accounting, and auditing.
Management Accounting
Analysis and communication of financial information to the managers of an organization to achieve internal goals and make well-informed decisions.
Tax Accounting
Focus on taxes rather than public financial statements.
Auditing
Formal examination of an organization or individual accounts or financial situation.
Father of Accounting
Luca Bartolomeo de Pacioli, first to publish about the double entry system of bookkeeping.
Sole Proprietorship
One owner (small business), easier decision making, limited budget, no definite life/term of existence.
Partnership
Two or more owners, less requirements, depends on degree, some exempted from income tax, unlimited liability/no control of partner.
Corporation
Five or more owners (amount of shares), unlimited life, limited liability, bigger capital, activities limited by articles of corporation.
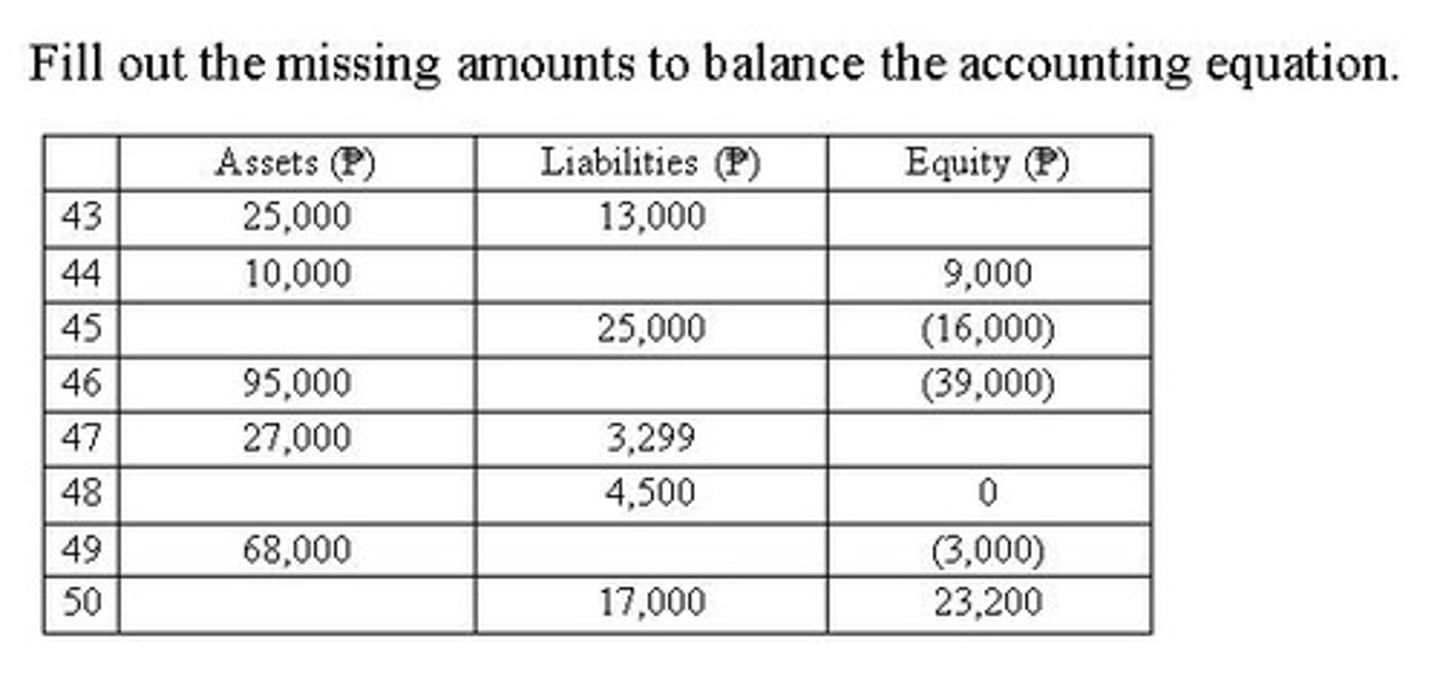
Accounting Equation
Financial worksheet/Analyze the effects.