f) g) Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Starch is in plants and made up of what?
Amylose
Amylopectin
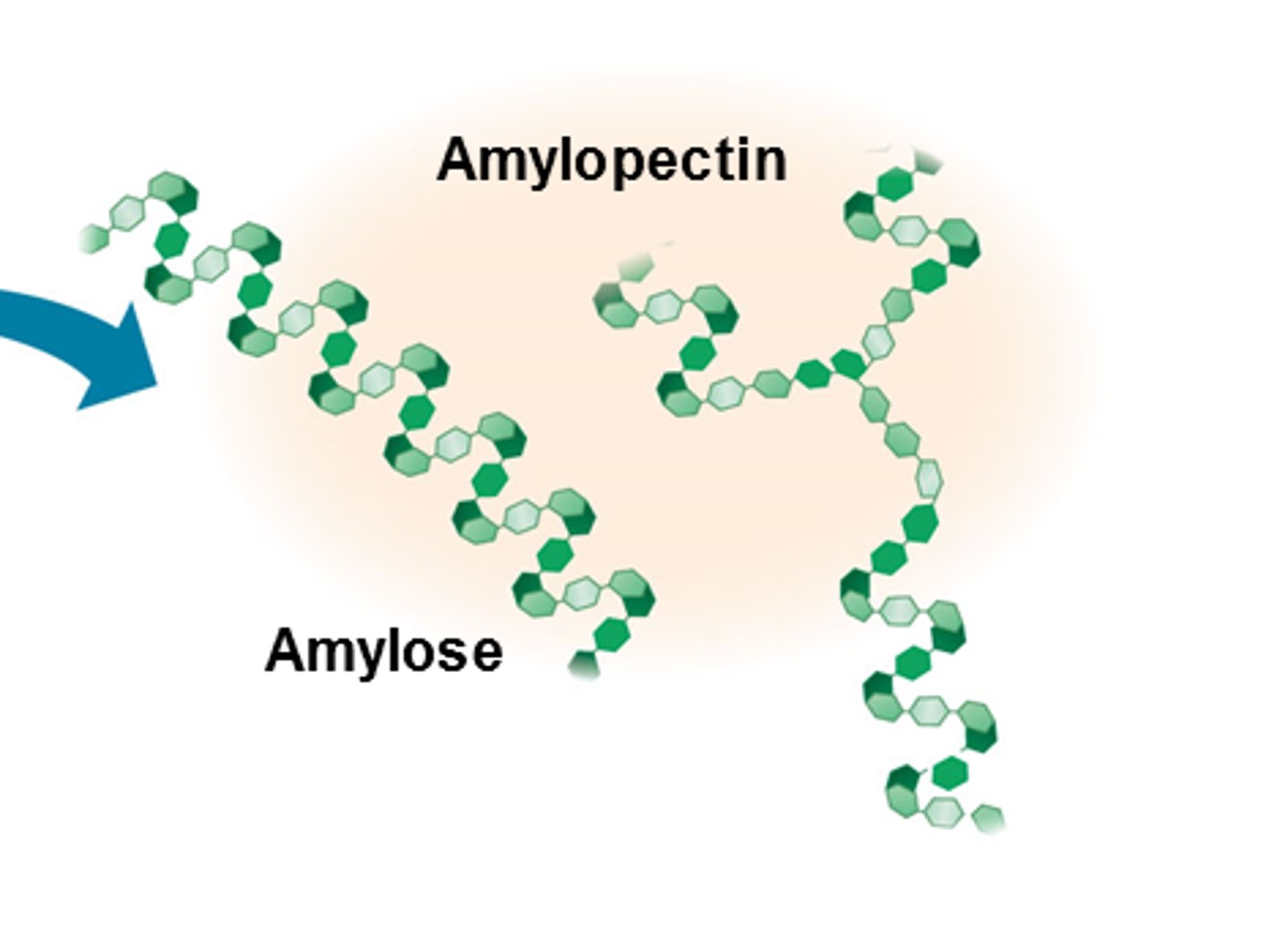
Amylose structure
- Unbranched and helix shaped (coiled)
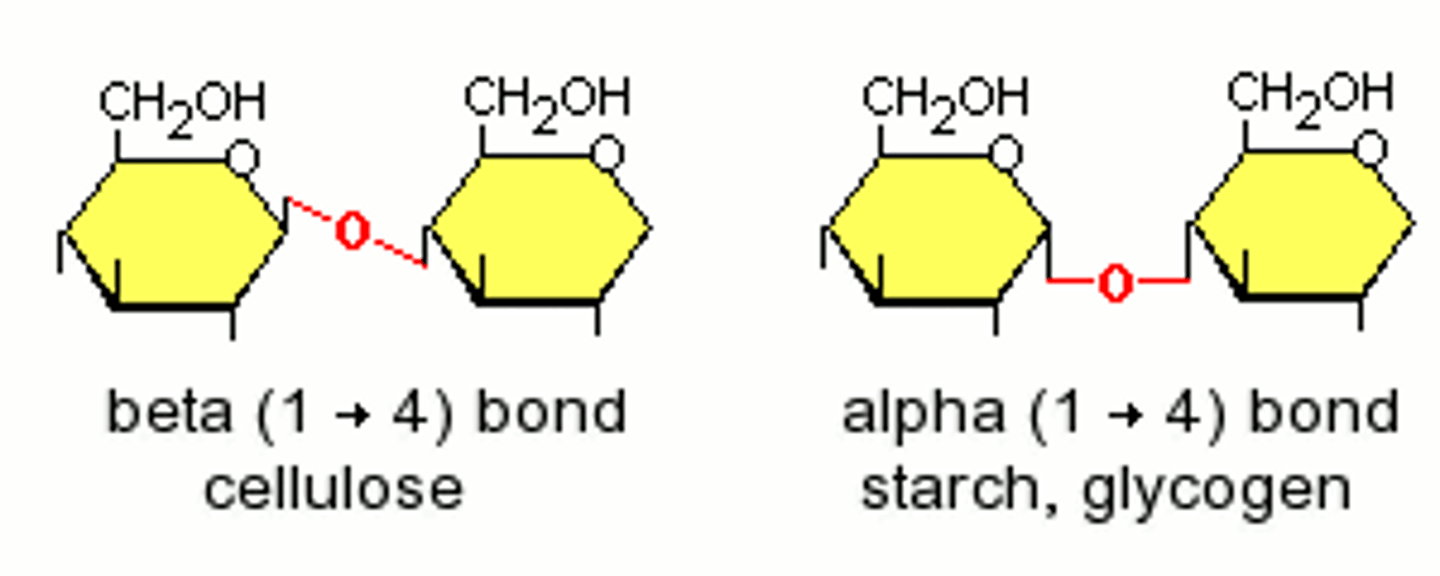
- Only 1,4 α-glycosidic bonds
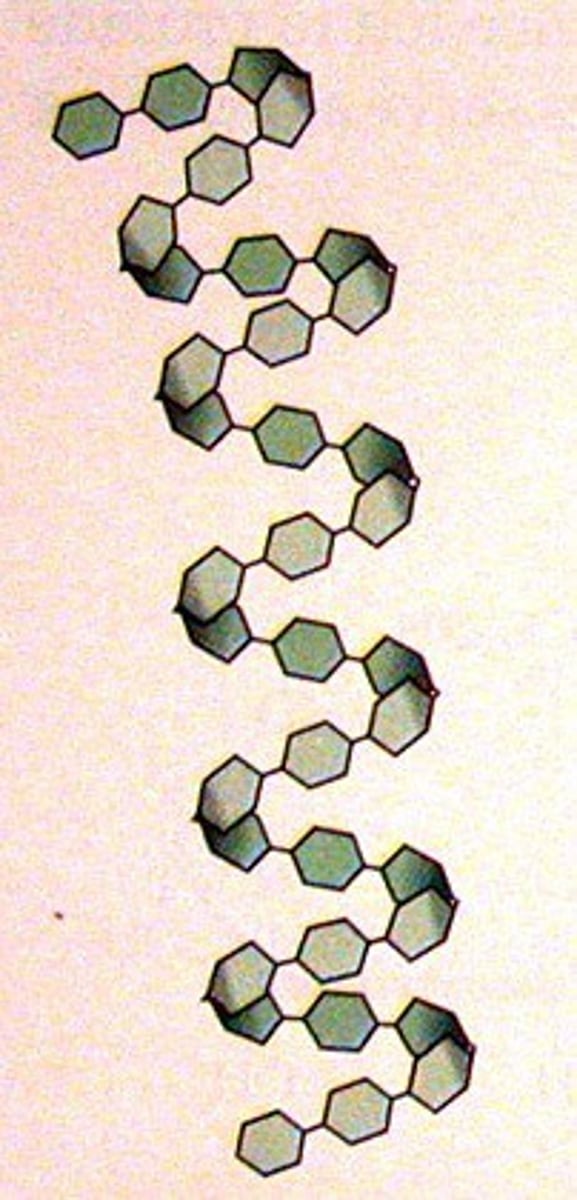
How does the coiled shape of amylose help?
Enables it to be more compact
Amylopectin structure
- Branched and uncoiled
- Has 1,4 and 1,6 α-glycosidic bonds
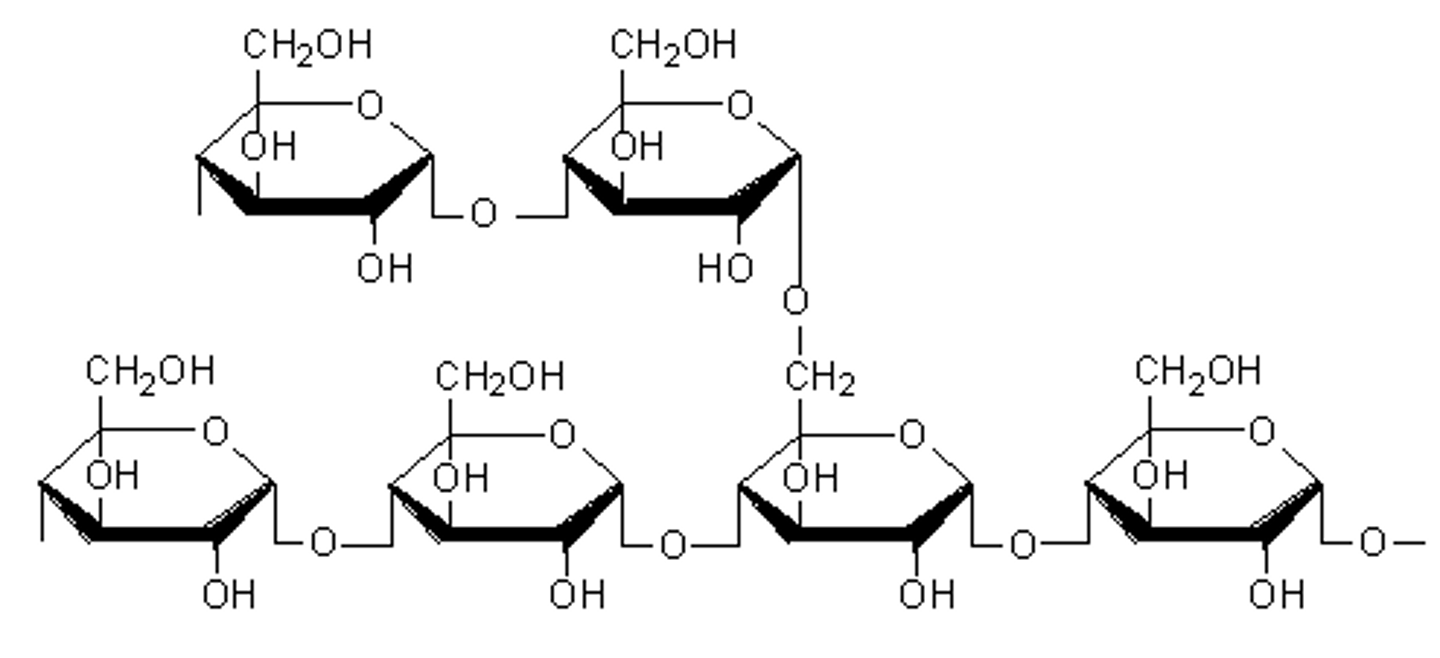
Why is the branched structure of amylopectin?
The branches mean many glucose molecules can be easily hydrolysed for use during cellular aerobic respiration
Glycogen is in animals and is made up of what?
Alpha glucose subunits
Glycogen structure
- Branched molecule
- Has 1,4 and 1,6 α-glycosidic bonds
Do starch and glycogen dissolve?
No, therefore they don't affect the water potential.
Cellulose structure
- Unbranched
- 1,4 β-glycosidic bonds, that must be rotated 180° to each other
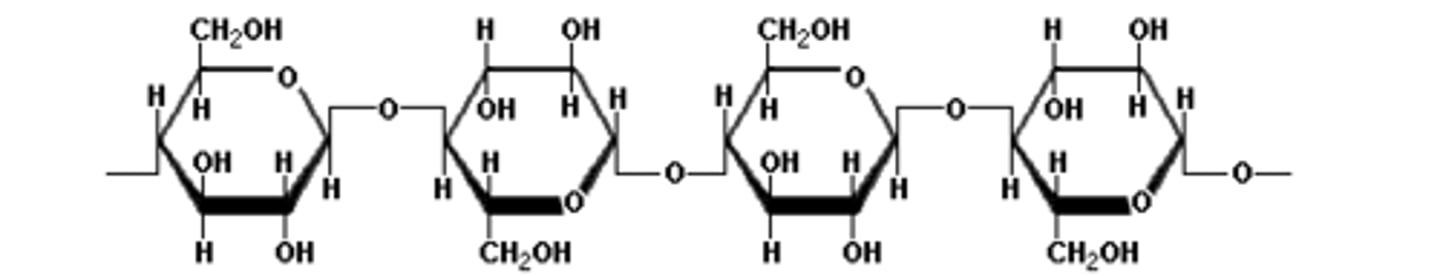
Beta glucose glycosidic bonds
They form beta pleated sheets between hydrogen bonds, which can form cross links to form bundles called microfibrils.
Larger microfibrils are called....
macrofibrils
Importance of cellulose structure:
Provides high tensile strength and make up plant cell walls.
Allows water to pass through, preventing the cell from bursting, determining shape.