GI E1- Intro
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
What is another name for indigestion?
dyspepsia
Persistent or recurrent pain/burning centered in the upper abdomen (epigastric region), early satiety, or postprandial fullness is known as _______
Dyspepsia
Dyspepsia can also be described as _______
bloating, N/V
What is heartburn?
retrosternal burning
Dyspepsia must be distinguished from _______
heartburn
What is almost aways present w/ heartburn?
GERD
What is the most common cause of chronic dyspepsia?
functional dyspepsia → sx mild & intermittent, no obvious organic cause
What are the GI ALARM symptoms that warrant further evaluation?
constant or severe pain
unintentional weight loss
persistent vomiting
dysphagia; odynophagia
hematemesis
melena
hematochezia
abd mass
unexplained IDA
Fhx of upper GI cancer
T/F: History and PE allows you to differentiate between ulcer related and non-ulcer dyspepsia.
false
Which kind of dyspepsia?
younger patients
variety of abdominal / GI symptoms
increased incidence of anxiety or depression or stress
non-ulcer
Which kind of dyspepsia?
older patients (> 55)
often smokers
pain is changed w/ food or meds
peptic ulcer
what must always be done for abdominal complaints?
rectal exams
What is the workup for dyspepsia?
abdominal + rectal exams, labs, upper endoscopy EGD (study of choice), noninvasive H. pylori testing (urea breath test, fecal antigen, IgG serology)
What should be done in ALL pts > 60 w/ dyspepsia or < 60 w/ alarm symptoms (wt loss, recurrent vomiting, evidence of bleeding, anemia)?
upper endoscopy EGD
What should be done for dyspepsia pts < 60 yrs without alarm symptoms and negative PE?
lifestyle modifications and noninvasive H, pylori testing (urea breath, fecal antigen, IgG serology)
What should be given to a patient with dyspepsia who is positive for H. pylori?
4-6 weeks of PPI’s + abx
At what age should you refer for endoscopy in dyspepsia patients who are born in areas w/ increased incidence of gastric cancer?
> 45
What lifestyle modifications should be made for dyspepsia patients?
D/C alcohol, caffeine, fatty foods, smoking
avoid lying down after meals; no food 3 hrs before HS
food diary → identify foods or drinks that exacerbates & WHEN pain/discomfort is worse
What are pharmacological treatment options for dyspepsia?
antacids, H2RAs, low dose antidepressants HS, PPIs, pro kinetic agents (metoclopramide, erythromycin), H. pylori triple drugs (prevpac, helidac)
What drug provides competitive inhibition of histamine at H2 receptors of gastric parietal cells, inhibiting gastric acid secretion?
H2RAs
What drug suppresses gastric acid secretion via inhibition of H+/K+ ATPase in the gastric parietal cell?
PPIs
What are SE of PPI therapy?
atrophic gastritis, fractures, osteoporosis, inc risk CV disease, CAP, c. diff infx
What should you always consider when prescribing PPIs?
shorter duration & lowest dose
What should be given along with PPis for those at risk of osteoporosis?
Ca, Vit D, and monitor bone status
What drug?
prokinetic agent to treat dyspepsia & an antiemetic
works to speed gastric emptying
SE- tardive dyskinesia (black box warning)
Metoclopramide (Reglan)
What are the drugs in Prevpac to treat H. pylori?
Lansoprazole, amoxicillin, clarithromycin
A vague, intensely disagreeable sensation of sickness or “queasiness” that is a subjective experience is known as _____
nausea
The forceful expulsion of gastric contents through a relaxed upper esophageal sphincter and open mouth is known as _____
vomiting
The effortless reflux of liquid or food stomach contents is known as ____
regurgitation
Vomiting is controlled by ________
brainstem / medulla & vagus nerves
What are possible complications of vomiting?
dehydration, hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis, pulm aspiration, boerhaave’s syndrome, mallory weiss tear, splenic /hepatic lacerations & intraabdominal bleeding (rare)
What is the non pharm management for acute mild and self limited vomiting?
clear oral fluids, broth, tea, soup, carbonated beverages, small feedings of toast or dry soda crackers
What antiemetics can be used to treat vomiting?
serotonin 5-HT3 antags: ondansetron
dopamine antags: promethazine, prochlorperazine
antihistamines/anticholinergics: diphenhydramine, meclizine, scopolamine patch
steroids: dexamethasone
sedatives: benzodiazepines
What drug?
antiemetic used for chemotherapy or post op nausea prophylaxis
ex: ondansetron (zofran) 4-8 mg x 12h IV or PO
serotonin 5-HT3 antagonists
What drug?
antiemetic
avoid w/ CNS depressants such as alcohol
ex: promethazine (phenergan), prochlorperazine (compazine)
dopamine antagonists
What is another name for hiccups?
singultus
How do hiccups happen?
diaphragm goes into spasm, forcing air into lungs → epiglottis snaps shut making sound
What is the workup for persistent hiccups?
detailed neuro exam, serum creatinine, LFTs, CXR
if unclear cause → CT of head, chest, or abd
What is the treatment for benign cases of hiccups?
tongue traction, 1 tsp dry granulated sugar, hold breath for several resp cycles, valsalva, rebreathing into a bag
meds: chlorpromazine, benzodiazepines, anticonvulsants
A perception of abnormal bowel movements such as hard stools, straining, decreased frequency or feeling of incomplete evacuation is known as ______
constipation
What is a spasm of anal sphincter associated with cramping and ineffective straining at stool?
tenesmus
How does defecation normally work?
puborectalis muscle and external sphincter relax in response to increased rectal pressure → BM
How does abnormal defecation / constipation happen?
muscle or sphincter fails to relax
What is the normal frequency of BMs?
3-21 per week; approximately 35 hrs colonic transit time
what is the medical criteria for constipation?
< 3 BMs per week & excessive straining with defecation
If constipation pain is relieved by defecation, this suggests _____
IBS
What kind of constipation?
no structural abnormalities
may have slow colonic transit time or anorectal dysfunction
may be part of generalized dysmotility syndrome
primary
What kind of constipation?
due to systemic disorders, meds, or obstructing colonic lesions
secondary
what must be done for new onset constipation in pts >45 with or without alarm sx (hematochezia, anemia, wt loss, +fecal blood test) and a FHX colon cancer or IBD?
work up to r/o colorectal cancer
what is the most common cause of constipation?
diet → inadequate fiber, fluids, or exercise
What is the workup for constipation?
PE w/ rectal exam → sphincter tone & anal wink reflex
stool testing for occult blood
labs
if alarm sx → colonoscopy, flex sig, barium enema
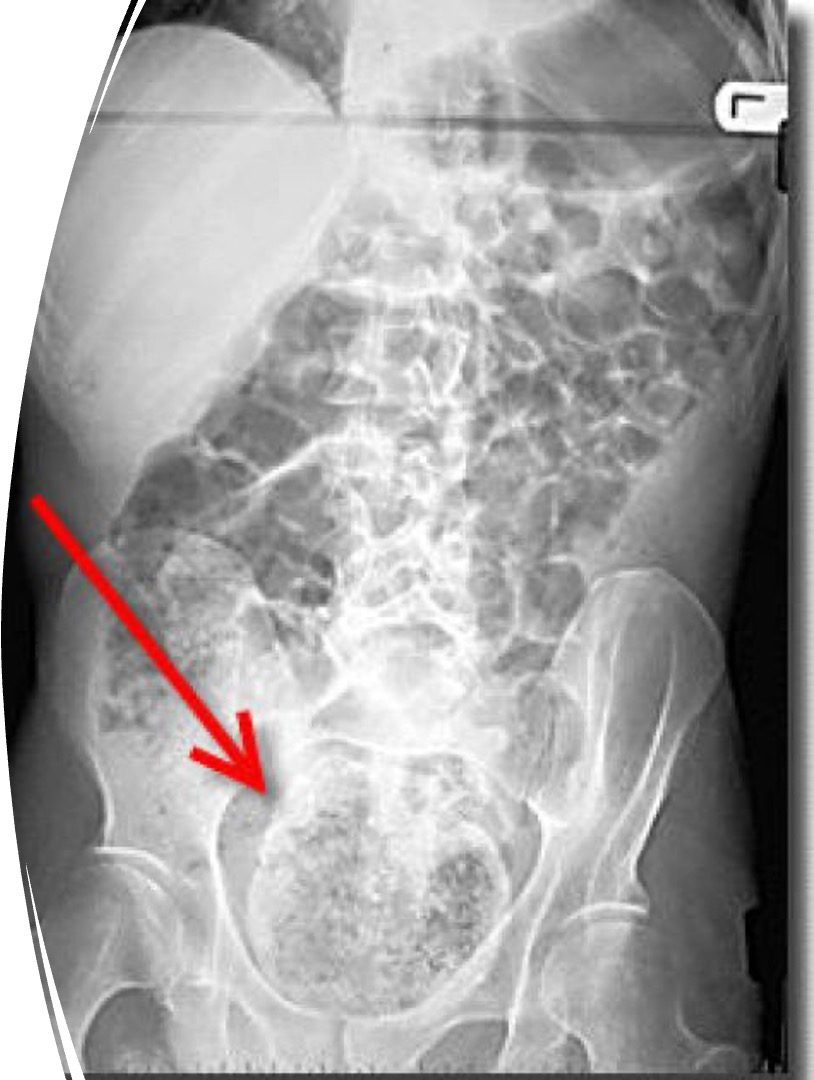
what is seen in this xray?
severe case of constipation showing a loaded colon
What are non pharmacological treatment options for constipation?
Diet: bulking agents (fiber supps), high fiber diet (25 g/day), fluids & exercise
Psych referral if hx sexual abuse or depression
What medications can be used to treat constipation?
osmotic lax: MgOH, non digestible carbs (sorbitol, lactulose), polyethylene glycol (miralax)
stimulant lax(cathartics): bisacodyl, senokot, cascara, castor oil
opioid receptor antags: methylnaltrexone, lubiprotone, naloxegol
What osmotic laxative should be avoided in pts w/ chronic renal insufficiency?
magnesium hydroxide
What should be AVOIDED in pts > 55 with known kidney disease or on meds that affect kidney function (NSAIDs, ACEIs, ARBS, diuretics)?
Sodium Phosphate (Osmoprep, Fleets phosphor-soda)
What drug?
usually administered at HS to treat constipation
stimulates fluid secretion and colonic contraction
chronic use of these may result in loss of normal colonic muscular function
ex: bisacodyl, senokot, cascara, castor oil
stimulant laxatives (cathartics)
what drug?
block peripheral opioid receptors w/o affecting central analgesia
approved for use in opioid induced constipation
ex: methylnaltrexone, lubiprotone, naloxegol
opioid receptor antagonists
How do osmotic laxatives work to treat constipation?
increase water into intestinal lumen to soften stool
T/F: polyethylene glycol (miralax) does NOT cause fluid or electrolyte shifts
true
what are predisposing factors for fecal impactions?
meds (opioids), severe psychiatric dz, prolonged bed rest, neurogenic dz of colon/spine
what is the clinical presentation of a fecal impaction?
dec appetite, N/V
abd pain & distention
diarrhea- liquid stool seeps out around impaction
PE → firm feces are palpable
What studies can be done for fecal impactions?
DRE → diagnostic & therapeutic
Radiographs → megarectum, fecaloma
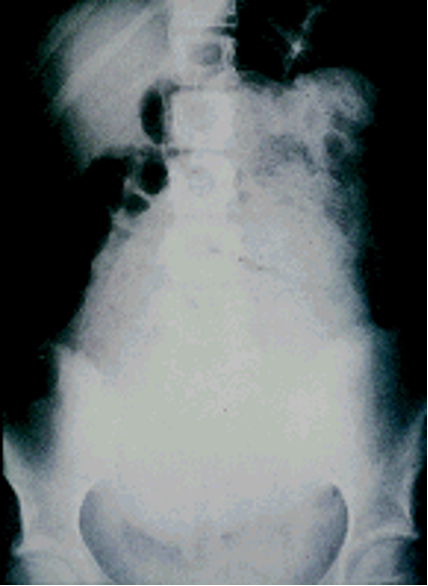
what is the treatment for fecal impactions?
impaction relief: DRE, enema (saline, mineral oil), disimpaction
prevention: maintain soft stools, avoid prolonged bathroom sessions, regular bowel schedule
An involuntary or voluntary release of gas from the stomach or esophagus is known as _____
belching / eructation
Passage of gas from the rectum caused by swallowed air or bacterial fermentation of undigested carbohydrates is known as _____
flatus
What is the treatment for GI gas?
lactose free diet, avoid gas producing foods, dec fatty food intake
probiotics & simethicone (gas-x, mylicon, beano, phazyme)
An increased liquidity / decreased consistency of stools is known as ____
diarrhea
A reduction as little as _____ in the water absorptive efficiency may lead to diarrhea.
1%
T/F: History can distinguish acute vs chronic diarrhea
true
What time frame classifies diarrhea as acute?
< 2 weeks
Which kind of acute diarrhea?
watery, non bloody
cramps, bloating, N/V, large volumes
e.coli, s. aureus, b. cereus, viruses, giardia
no tissue invasion (no fecal leukocytes)
comps: hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis from loss of HCO3
non-inflammatory
what kind of acute diarrhea?
fever + bloody (colonic tissue damage)
small volumes, LLQ cramps, urgency, tenesmus
shigella, salmonella, campylobacter, yersinia, c. diff, e. coli
fecal leukocytes
comp: HUS
inflammatory
What work up should be done for patients with diarrhea >7 days duration?
stool culture, O&P, fecal leukocytes
What is the treatment for acute noninflammatory diarrhea?
often self limiting
diet- bowel rest; avoid high fiber foods (BRAT diet), clear soups, crackers, no fats or milk products
rehydration- oral is best (pedialyte, gatorade), glucose, NaCl, K, bicarbonate or citrate, IV fluids if severe
What is the treatment for acute infectious diarrhea?
anti-diarrheal agents: kaopectate, peptobismol, ioperamide (immodium)
abx in select pts: rifaximin for traveler’s, cipro, azithro
What is the treatment for acute inflammatory diarrhea?
oral rehydration:, no high fiber/fatty foods, milk, caffeine, or alcohol
avoid antidiarrheal agents
abx usually not needed; can be used empirically while cultures pending or when specific organism found (*NOT w/ suspected STEC)
What time frame classifies diarrhea as chronic?
> 4 weeks
What kind of chronic diarrhea?
poorly absorbable, osmotically active solute ingested, drawing enough fluid into lumen to exceed the colon’s resorptive capacity
fecal water output increases in proportion to solute load
stool volume decreases w/ fasting
eti: meds (antacids, lactulose, sorbitol), lactose intolerance, factitious diarrhea (mg or na sulfate laxatives), carbohydrate malabsorption
osmotic
what kind of chronic diarrhea?
deranged fluid & elyte transport across enterocolonic mucosa
NO malabsorbed solute, so osmolality of stool w/in normal limits (no fecal osmotic gap)
large, watery volumes (> 1 L/day),
little change w/ fasting,
painless
eti: hormonal (carcinoid, zollinger-ellison, thyroid cancer), meds, factious (stimulant laxative abuse), bile salt malabsorption, chronic alcohol ingestion
secretory
what kind of chronic diarrhea?
fever, hematochezia, abd pain
eti: ulcerative colitis, crohns, microscopic colitis, malignancies, radiation enteritis
inflammatory
What kind of chronic diarrhea?
wt loss
stool analysis: fecal fat > 10 g/24 hrs
anemia
hypoalbuminemia
eti: small bowel mucosa dz, lymphatic obstruction, pancreatic dz
malabsorption
what kind of chronic diarrhea?
systemic dz or prior abdominal surgery
eti: vagotomy, partial gastrectomy/gastric bypass, systemic disorders (scleroderma, DM, hyperthyroidism), IBS
motility induced
what kind of chronic diarrhea?
immunosuppressed patients
eti: parasites (giardia lamblia, entamoeba histolytic, cyclospora), AIDS, viral (CMV, HIV), bacterial (c. diff, m. avium), protozoal (microsporidia, cryptosporidium)
chronic infection
What is the workup for chronic diarrhea?
Labs, stool studies, serologic tests, endoscopic evaluation, imaging
what is that treatment for chronic diarrhea?
narcotic analogues: loperamide, bismuth subsalicylate (pepto bismol), diphenoxylate w/ atropine (lomotil)
narcotics (generally avoided): codeine, paregoric (tincture of opium), morphine, cholestyramine (used in bile acid malabsorption)
In a patient w/ chronic diarrhea, what should always be r/o as a cause?
cancer
_____ peritoneum is innervated by the ANS, ______ peritoneum is inverted by spinal somatic nerves
visceral, parietal
Which kind of pain?
transmitted rapidly
very sharp and localized
a-delta neurons
somatic
what kind of pain?
from distention of an organ
poorly localized
dull, achy
C fibers transmit pain slowly
innervation is b/l → pain refers to midline
visceral
what kind of pain?
a vital, protective mechanism that permits us to live in our environment
acute
what kind of pain?
a disease state, not a symptom
pain that lasts beyond the normal duration of time that an injury or insult to the body needs to heal
usually 4-6 wks, up to 3 mos (if longer, may be an irreversible and intractable condition)
chronic
what is the major goal when evaluating abdominal pain?
determine presence of life threatening surgical dz (dissecting aortic aneurysm, perforated viscus, bowel obstruction)
What kind of pain may be perceived in the right shoulder or scapula?
gallbladder
what kind of pain is referred to the back?
retroperitoneal processes such as pancreatitis
what kind of pain may be localized to RLQ?
ileum (Crohn’s)
Episodic abdominal pain with pain free intervals is known as ____
colicky
what is the key to determining presence/severity of pain?
facial expressions
Bowel sounds are ____ in peritonitis
absent
Bowel sounds are ____ in early obstruction
high pitched & hyperactive